Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gravitation - Practice Sheet - Arjuna JEE 2024
Gravitation - Practice Sheet - Arjuna JEE 2024
Uploaded by
AkshitEditzCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Spotlight - CoE (XI) - (2022-23) - Day-4 - In-Class Assingement - Physics - (Only Que.)Document10 pagesSpotlight - CoE (XI) - (2022-23) - Day-4 - In-Class Assingement - Physics - (Only Que.)Anirudh S RaoNo ratings yet
- DPP12 - Gravitation - GenetryDocument10 pagesDPP12 - Gravitation - GenetryBrazil server passNo ratings yet
- Grav - CPP RDocument4 pagesGrav - CPP RHaina KumariNo ratings yet
- Gravitation: Single Answer Type QuestionsDocument22 pagesGravitation: Single Answer Type QuestionsRamesh BadamNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Sheet FinalDocument14 pagesGravitational Sheet FinalCalming MusicNo ratings yet
- Gravitational FieldDocument8 pagesGravitational FieldMalik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- P G L 1 O P: Hysics Ravitation Evel Bjective RoblemsDocument8 pagesP G L 1 O P: Hysics Ravitation Evel Bjective RoblemsGrag MeNo ratings yet
- GravitaionDocument15 pagesGravitaionJSM LiveNo ratings yet
- E-1 MergedDocument129 pagesE-1 Mergedkoushik molaNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: LPP - GravitationDocument5 pagesFiitjee: LPP - GravitationYash TandonNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument5 pagesGravitationdr.saidongargaonkaNo ratings yet
- NLM & Friction - DPP 06 (Extra) - NSEP Batch 2024Document4 pagesNLM & Friction - DPP 06 (Extra) - NSEP Batch 2024GAMING LAD YTNo ratings yet
- June PhysicsDocument5 pagesJune PhysicscbsencertNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Questions On Gravitation, Paper 2Document2 pagesGravitation Questions On Gravitation, Paper 2Trilok AkhaniNo ratings yet
- Gravitation PDFDocument11 pagesGravitation PDFsshree846No ratings yet
- Gate 2015Document16 pagesGate 2015RANGEQUITNo ratings yet
- FS-2 CPP 07 Physics Chemistry Mathematics 2020Document25 pagesFS-2 CPP 07 Physics Chemistry Mathematics 2020Durgesh SINGHNo ratings yet
- Final NSEP PYQs 2018 To 2023 All Chaper QuestionsDocument69 pagesFinal NSEP PYQs 2018 To 2023 All Chaper Questionspriya anbuNo ratings yet
- PHY GravationDocument10 pagesPHY GravationDaksh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- DPP No. 41: PhysicsDocument6 pagesDPP No. 41: PhysicsGajanan PurudNo ratings yet
- Quiz - GravitationDocument4 pagesQuiz - GravitationVIR MALHOTRA 12INo ratings yet
- Gravitation-04-Objective UnSolvedDocument6 pagesGravitation-04-Objective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Gravitation PDFDocument21 pagesGravitation PDFmohan730463No ratings yet
- GM L GM 2πL πGM 2L πGM LDocument4 pagesGM L GM 2πL πGM 2L πGM LAshish RajNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee Coimbatore Centre: 10 - Physics - PCMDocument3 pagesFiitjee Coimbatore Centre: 10 - Physics - PCMC.M.M GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Physics Chemistry Mathematics IITJEE TestDocument17 pagesPhysics Chemistry Mathematics IITJEE TestAbhay Kumar Nayak100% (5)
- DPP+2++Gravitation+07 01 2021Document7 pagesDPP+2++Gravitation+07 01 2021Shivam RoyNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Ad2Document31 pagesMechanics Ad2kamlesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Ex. Module-2Document21 pagesGravitation Ex. Module-2Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- LOM Adv 2122 ARC ObjDocument4 pagesLOM Adv 2122 ARC ObjShahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Gravitation TestDocument2 pagesGravitation TesthinjalapraveshNo ratings yet
- Gravitation-02-Objective SolvedDocument5 pagesGravitation-02-Objective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- TestDocument17 pagesTestPhantom1699No ratings yet
- Model Test Paper 1 PDFDocument5 pagesModel Test Paper 1 PDFShaunak ThakarNo ratings yet
- GATE Geology Paper 2015Document11 pagesGATE Geology Paper 2015Debanga BoruahNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - DPP 01 (Of Lec 03) - Lakshya JEE AIR Recorded 2025Document4 pagesElectrostatics - DPP 01 (Of Lec 03) - Lakshya JEE AIR Recorded 2025udayshirsat1708No ratings yet
- Gravitation PDFDocument24 pagesGravitation PDFsriNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion (S.C.Q.) EDocument47 pagesCircular Motion (S.C.Q.) Earya yadaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main DPYQ Full Syllabus PAPER-1Document5 pagesJEE Main DPYQ Full Syllabus PAPER-1Saravanan BNo ratings yet
- Gravitation 2Document2 pagesGravitation 2Ajuba AbujaNo ratings yet
- 9-Chapter Test (Gravitation) - SolutionsDocument2 pages9-Chapter Test (Gravitation) - Solutionsਸ. ਇੰਦਰਦੀਪ ਸਿੰਘNo ratings yet
- Rotational MotionDocument9 pagesRotational MotionAditya ChudasamaNo ratings yet
- Test Phase II P3 05 11 2021Document15 pagesTest Phase II P3 05 11 2021ik62299No ratings yet
- Jee Main PaperDocument14 pagesJee Main PapervjaNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument5 pagesGravitationManan JainNo ratings yet
- Gravitation TESTDocument3 pagesGravitation TESTUJJVAL GAHOINo ratings yet
- FS-2 CPP 12 Physics Chemistry 2020Document23 pagesFS-2 CPP 12 Physics Chemistry 2020Durgesh SINGHNo ratings yet
- Gravitation 1b520cfa 17cf 4af0 b58c 14d72fccc668Document17 pagesGravitation 1b520cfa 17cf 4af0 b58c 14d72fccc668ajmerapavan2024No ratings yet
- Gra 15 02 2024Document14 pagesGra 15 02 2024aquib.aquil40036No ratings yet
- Motion in A PlaneDocument2 pagesMotion in A PlaneSowmiya BoobNo ratings yet
- Laws of GravitationDocument3 pagesLaws of GravitationJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument16 pagesGravitationAmal AugustineNo ratings yet
- APA-1A (124Q+A) (Mechanics)Document18 pagesAPA-1A (124Q+A) (Mechanics)Vedant TodiNo ratings yet
- Mock Test # 11 (P-1) Ans - Key & Solution - DT. 05-07-2020 PDFDocument23 pagesMock Test # 11 (P-1) Ans - Key & Solution - DT. 05-07-2020 PDFSaumya MundraNo ratings yet
- SHM & Elasticity: Ba C BC A Ba CDocument13 pagesSHM & Elasticity: Ba C BC A Ba CKrithikaNo ratings yet
- Rank Improvement Program: - Laws of Motion - Work, Energy & PowerDocument24 pagesRank Improvement Program: - Laws of Motion - Work, Energy & PowerVISHNU PRIYA BUDDANINo ratings yet
- Class XI Math Moving To Class XII Math Test Paper With Detailed SolutionDocument20 pagesClass XI Math Moving To Class XII Math Test Paper With Detailed Solutionghostrider828837No ratings yet
- GravitationDocument32 pagesGravitationMusic BanglaNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Class 11Document8 pagesGravitation Class 11mission.iist.1No ratings yet
- Classifying Spaces for Surgery and Corbordism of Manifolds. (AM-92), Volume 92From EverandClassifying Spaces for Surgery and Corbordism of Manifolds. (AM-92), Volume 92No ratings yet
- Phy CH 10 Final 10thDocument21 pagesPhy CH 10 Final 10thHaroon Khan0% (1)
- Mce30Tl Mce30Tc MCA-26G MCA-30ADocument1 pageMce30Tl Mce30Tc MCA-26G MCA-30AFarzad SagharchiNo ratings yet
- 1 Ncert Ge1Document9 pages1 Ncert Ge1KV MADHUPURNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Education: Test Blueprint For Ethiopian Higher Education Institutions' Exit Examination Band-1 ProgramDocument15 pagesMinistry of Education: Test Blueprint For Ethiopian Higher Education Institutions' Exit Examination Band-1 ProgramŤêk Mãñ JôśÿNo ratings yet
- Environmental SciencesDocument11 pagesEnvironmental SciencesArif SetyaNo ratings yet
- Reading ComprehensionDocument18 pagesReading ComprehensionZunaira KamranNo ratings yet
- CV Hadj Yahia Seba 2023Document5 pagesCV Hadj Yahia Seba 2023Yahia SebaNo ratings yet
- Improvement in The Surface Quality of Ball Bearing Steel Rounds at Bar MillDocument5 pagesImprovement in The Surface Quality of Ball Bearing Steel Rounds at Bar MillEvren ÇaprazNo ratings yet
- Baro Mano WorksheetDocument12 pagesBaro Mano WorksheetashokNo ratings yet
- AstronomyformulaDocument30 pagesAstronomyformulapalharjeetNo ratings yet
- Iocl Haldia ReportDocument99 pagesIocl Haldia ReportArkadev GhoshNo ratings yet
- Case Studies - Control of Boiler and Distillation ColumnDocument9 pagesCase Studies - Control of Boiler and Distillation Columnlaluseban100% (1)
- ISBM PET Part 1 - IM Troubleshooting & BM BasicsDocument45 pagesISBM PET Part 1 - IM Troubleshooting & BM BasicsCarlos AgianiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Rapidity and PseudorapidityDocument8 pagesLecture 7 - Rapidity and PseudorapidityDEEPARNA BHATTACHARYYANo ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis BrochureDocument2 pagesChemical Analysis BrochurePSIBSNo ratings yet
- FICCA COOL ProjectDocument1 pageFICCA COOL ProjectJim Lee ClimateViewerNo ratings yet
- Topographic SurveyDocument12 pagesTopographic SurveyVerlyn Kate Pang-ayNo ratings yet
- Microreview: Oleg KulinkovichDocument13 pagesMicroreview: Oleg KulinkovichSangvenkatNo ratings yet
- Articulo Sobre La Determinación Experimental Del Ácido Fosfórico en La Coca ColaDocument5 pagesArticulo Sobre La Determinación Experimental Del Ácido Fosfórico en La Coca ColaDiego Isac Cruz LopezNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Work Permit SystemDocument14 pages5.4 Work Permit Systembilo1984100% (1)
- MSDS-HCFC-R141b (1) - 220819 - 124426Document5 pagesMSDS-HCFC-R141b (1) - 220819 - 124426mursalina mulyasariNo ratings yet
- Percent Yield - WKSTDocument4 pagesPercent Yield - WKSTJunghoon LeeNo ratings yet
- CH 20 ThermodynamicsDocument11 pagesCH 20 ThermodynamicsElle QuizonNo ratings yet
- 02 Electrochemistry Ques. Final E PDFDocument21 pages02 Electrochemistry Ques. Final E PDFAri GamakiNo ratings yet
- Solar Panel InstallationDocument10 pagesSolar Panel Installationpeculiarchild2020No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher' GuideDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher' GuideAhmad Zaidi100% (1)
- BAUL ReportDocument24 pagesBAUL ReportArnold ApostolNo ratings yet
- Earth Works Volume Conversion and Swell FactorsDocument4 pagesEarth Works Volume Conversion and Swell FactorsJj BarakaNo ratings yet
- INFLUENCE CHITOSAN AND CARBON NANODOTS (CNDS) OF THE CONTACT OILDocument14 pagesINFLUENCE CHITOSAN AND CARBON NANODOTS (CNDS) OF THE CONTACT OILindex PubNo ratings yet
- CHM 229 Slides PDFDocument13 pagesCHM 229 Slides PDFGlory UsoroNo ratings yet
Gravitation - Practice Sheet - Arjuna JEE 2024
Gravitation - Practice Sheet - Arjuna JEE 2024
Uploaded by
AkshitEditzOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gravitation - Practice Sheet - Arjuna JEE 2024
Gravitation - Practice Sheet - Arjuna JEE 2024
Uploaded by
AkshitEditzCopyright:
Available Formats
JEE
ARJUNA JEE 2024
PHYSICS
GRAVITATION
Q1 The mass of moon is about 1.5% of the mass of (B) g (1 − 2h
R
)
the Earth. If the gravitational pull that the Earth (C)
g
2
h
exerts on the moon is F , then the pull exerted (1−
R
)
by moon on the Earth (D) g (1 − h
R
)
(A) > F
Q5 Let g be the acceleration due to gravity at
(B) = F
earth's surface and K be the rotational kinetic
(C) < F
energy of the earth. Suppose the earths radius
(D) Information is insufficient to predict
decreases by 2% keeping all other quantities
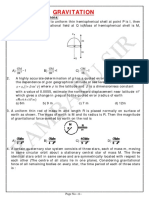
Q2 Four particles of equal mass m are placed at same, then
the four corners of a square ABC D as shown (A) g decreases by 2% and K decreases by 4%
in the figure. Gravitational force on C is along (B) g decreased by 4% and K increases by 2%
(C) g increase by 4% and K increases by 4%
(D) g decrease by 4% and K increases by 4%
Q6 At what height from the ground will the value of
g be the same as that in 10 km deep mine
below the surface of earth
(A) 20 km
(B) 10 km
(C) 15 km
(A) C B (B) C D (D) 5 km
(C) C A (D) AB
Q7 A thin rod of length L is bent to form a semi
Q3 Two bodies of mass M and 4M are kept at a circle. The mass of the rod is M . What will be
distance y apart. Where should a small particle the gravitational potential at the centre of the
of mass m be placed from M so that the net circle?
gravitational force on it is zero (A) −GM
L
y
(A) 5 (B) −GM
y 2πL
(B) 2 (C) −πGM
y 2L
(C) 4 (D) −πGM
y L
(D) 3
Q8 If mass of earth is M , radius is R , and
Q4 What will be the acceleration due to gravity at gravitational constant is G , then work done to
height h if h ≫ R . Where R is radius of earth take 1Kg mass from earth surface to infinity will
and g is acceleration due to gravity on the be
surface of earth (A) √ GM
−−−
g
(A) 2
2R
(1+
h
R
) (B) GM
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
JEE
−−−−
(C) √ 2GM (C) R
R
(D) R
(D) GM
2R
4
Q14 A particle is dropped from a height h = 3R
Q9 If mass of earth is M , radius is R , and
above earth surface, where R is the radius of
gravitational constant is G , then work done to
earth. If g is the acceleration due to gravity on
take 1Kg mass from earth surface to infinity will
earth surface, then speed with which the
be
−−− particle strikes the earth surface is
(A) √ GM −
− −
−
2R (A) √3gR
(B) GM
R (B) √2gR
−
− −
−
−−−−
(C) √ 2GM (C) √1.5gR
−−−−−
R
−−
−
(D) GM (D) √gR
2R
Q10 If the gravitational potential energy of a body Q15 For a satellite escape velocity is 11 km/s . If the
at a distance r from the centre of the earth is satellite is launched at an angle of 60∘ with the
U , then its weight at that point is vertical, then escape velocity will be
(A) U (A) 11 km/s
–
(B) U
2
(B) 11√3 km/s
r
(C) 11
km/s
(C) U 2 r √3
(D) U (D) 33 km/s
r
Q11 If the gravitational field intensity at a point is Q16 Two spherical planets P and Q have the same
GM
, then potential at a distance r is uniform density ρ , masses MP and MQ and
1.5
3r
(A) 2GM surface areas A and 4A respectively. A
0.5
3r
spherical planet R also has uniform density ρ
(B) −GM
r
1.5
and its mass is (MP + MQ ) . The escape
(C) − 2GM
3r
0.5
velocities from the planets P , Q and R are
(D) GM
1.5 VP , VQ and VR , respectively. Then
r
(A) VQ > VR > VP
Q12 Three identical particles each of mass M are
(B) VR > VQ > VP
located at the vertices of an equilateral
(C) VR /VP = 3
triangle of side a . The escape speed of one
(D) VP /VQ =
1
particle will be 2
−−−−
(A) √ 4GM Q17 The magnitudes of the gravitational field at
a
−−−−
(B) √ 3GM distance r1 and r2 from the centre of a uniform
a
−−−− sphere of radius R and mass m are F1 and F2
(C) √ 2GM
a respectively. Then:
−−−
(D) √ GM (A) F1
=
r1
if r1 < R and r2 < R
a F2 r2
2
(B) F1
=
r
2
if r1 > R and r2 > R
2
Q13 A body thrown vertically upward with initial F2 r
1
speed
−−
−
, where is the radius of earth. (C) F1
=
r1
if r1 > R and r2 > R
√ gR R F2 r2
2
Then maximum height reached by the body (D) F1
=
r
1
if r1 < R and r2 < R
2
F2 r
2
from the surface of earth is
(A) R
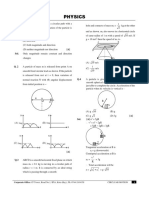
Q18 A satellite S is moving in an elliptical orbit
2
(B) 3R
around the earth. The mass of the satellite is
2
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
JEE
very small compared to the mass of the earth.
(A) The acceleration of S is always directed
towards the centre of the earth
(B) The angular momentum of S about the
centre of the earth changes in direction, but
its magnitude remains constant
(C) The total mechanical energy of S varies
periodically with time
(D) The linear momentum of S remains constant (A) A → r; B → t; D → s; D → q
in magnitude. (B) A → q, r; B → s; C → p; D → q
(C) A → q; B → s; C → p; D → r
Directions (19) Read the following passage and (D) None of these
answer the given questions.
The maximum and minimum distances of a Q22 Considering earth to be a homogeneous
planet from the centre of the sun are 2R and sphere but keeping in mind its spin.
4R respectively, where R is radius of sun. Let M
be the mass of sun.
Q19 What is the ratio of maximum speed to
minimum speed of the planet?
(A) 1 : 2 (B) 2 : 1
(C) 1 : 1 (D) Not determine
Directions (20) Read the following passage and
answer the given questions.
The maximum and minimum distances of a
planet from the centre of the sun are 2R and
(A) A → s; B → q; C → q; D → p
4R respectively, where R is radius of sun. Let M
(B) A → r; B → q; C → p; D → s
be the mass of sun.
(C) A → p, q; B → r; C → p; D → r
Q20 The maximum speed of planet is (D) None of these
−−−
(A) √ GM
6R Q23 A point mass when enters d depth below the
−−−−
(B) √ 2GM
earths surface such that the g reduces by 1%
3R
(C) √ GM
−−−
then find the value of d (in km ) [Take
−−−
R
Re = 6400 km ]
(D) √ GM
2R
Q24 Two planets of radii in the ratio 2 : 3 are made
Q21 The gravitational potential energy at from the materials of density in the ratio 3 : 2 .
Then the ratio of acceleration due to gravity
g1 /g2 at the surface of two planets will be:
Q25 The weight of an object on the surface of the
earth is 40 N . Its weight (in N ) at a height
equal to the radius of the Earth is
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
JEE
Answer Key
Q1 (B) Q14 (C)
Q2 (C) Q15 (A)
Q3 (D) Q16 (B, D)
Q4 (A) Q17 (A, B)
Q5 (C) Q18 (A)
Q6 (D) Q19 (B)
Q7 (D) Q20 (B)
Q8 (B) Q21 (C)
Q9 (B) Q22 (C)
Q10 (D) Q23 64
Q11 (A) Q24 1
Q12 (A) Q25 10
Q13 (C)
Android App | iOS App | PW Website
You might also like
- Spotlight - CoE (XI) - (2022-23) - Day-4 - In-Class Assingement - Physics - (Only Que.)Document10 pagesSpotlight - CoE (XI) - (2022-23) - Day-4 - In-Class Assingement - Physics - (Only Que.)Anirudh S RaoNo ratings yet
- DPP12 - Gravitation - GenetryDocument10 pagesDPP12 - Gravitation - GenetryBrazil server passNo ratings yet
- Grav - CPP RDocument4 pagesGrav - CPP RHaina KumariNo ratings yet
- Gravitation: Single Answer Type QuestionsDocument22 pagesGravitation: Single Answer Type QuestionsRamesh BadamNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Sheet FinalDocument14 pagesGravitational Sheet FinalCalming MusicNo ratings yet
- Gravitational FieldDocument8 pagesGravitational FieldMalik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- P G L 1 O P: Hysics Ravitation Evel Bjective RoblemsDocument8 pagesP G L 1 O P: Hysics Ravitation Evel Bjective RoblemsGrag MeNo ratings yet
- GravitaionDocument15 pagesGravitaionJSM LiveNo ratings yet
- E-1 MergedDocument129 pagesE-1 Mergedkoushik molaNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: LPP - GravitationDocument5 pagesFiitjee: LPP - GravitationYash TandonNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument5 pagesGravitationdr.saidongargaonkaNo ratings yet
- NLM & Friction - DPP 06 (Extra) - NSEP Batch 2024Document4 pagesNLM & Friction - DPP 06 (Extra) - NSEP Batch 2024GAMING LAD YTNo ratings yet
- June PhysicsDocument5 pagesJune PhysicscbsencertNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Questions On Gravitation, Paper 2Document2 pagesGravitation Questions On Gravitation, Paper 2Trilok AkhaniNo ratings yet
- Gravitation PDFDocument11 pagesGravitation PDFsshree846No ratings yet
- Gate 2015Document16 pagesGate 2015RANGEQUITNo ratings yet
- FS-2 CPP 07 Physics Chemistry Mathematics 2020Document25 pagesFS-2 CPP 07 Physics Chemistry Mathematics 2020Durgesh SINGHNo ratings yet
- Final NSEP PYQs 2018 To 2023 All Chaper QuestionsDocument69 pagesFinal NSEP PYQs 2018 To 2023 All Chaper Questionspriya anbuNo ratings yet
- PHY GravationDocument10 pagesPHY GravationDaksh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- DPP No. 41: PhysicsDocument6 pagesDPP No. 41: PhysicsGajanan PurudNo ratings yet
- Quiz - GravitationDocument4 pagesQuiz - GravitationVIR MALHOTRA 12INo ratings yet
- Gravitation-04-Objective UnSolvedDocument6 pagesGravitation-04-Objective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Gravitation PDFDocument21 pagesGravitation PDFmohan730463No ratings yet
- GM L GM 2πL πGM 2L πGM LDocument4 pagesGM L GM 2πL πGM 2L πGM LAshish RajNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee Coimbatore Centre: 10 - Physics - PCMDocument3 pagesFiitjee Coimbatore Centre: 10 - Physics - PCMC.M.M GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Physics Chemistry Mathematics IITJEE TestDocument17 pagesPhysics Chemistry Mathematics IITJEE TestAbhay Kumar Nayak100% (5)
- DPP+2++Gravitation+07 01 2021Document7 pagesDPP+2++Gravitation+07 01 2021Shivam RoyNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Ad2Document31 pagesMechanics Ad2kamlesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Ex. Module-2Document21 pagesGravitation Ex. Module-2Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- LOM Adv 2122 ARC ObjDocument4 pagesLOM Adv 2122 ARC ObjShahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Gravitation TestDocument2 pagesGravitation TesthinjalapraveshNo ratings yet
- Gravitation-02-Objective SolvedDocument5 pagesGravitation-02-Objective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- TestDocument17 pagesTestPhantom1699No ratings yet
- Model Test Paper 1 PDFDocument5 pagesModel Test Paper 1 PDFShaunak ThakarNo ratings yet
- GATE Geology Paper 2015Document11 pagesGATE Geology Paper 2015Debanga BoruahNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - DPP 01 (Of Lec 03) - Lakshya JEE AIR Recorded 2025Document4 pagesElectrostatics - DPP 01 (Of Lec 03) - Lakshya JEE AIR Recorded 2025udayshirsat1708No ratings yet
- Gravitation PDFDocument24 pagesGravitation PDFsriNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion (S.C.Q.) EDocument47 pagesCircular Motion (S.C.Q.) Earya yadaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main DPYQ Full Syllabus PAPER-1Document5 pagesJEE Main DPYQ Full Syllabus PAPER-1Saravanan BNo ratings yet
- Gravitation 2Document2 pagesGravitation 2Ajuba AbujaNo ratings yet
- 9-Chapter Test (Gravitation) - SolutionsDocument2 pages9-Chapter Test (Gravitation) - Solutionsਸ. ਇੰਦਰਦੀਪ ਸਿੰਘNo ratings yet
- Rotational MotionDocument9 pagesRotational MotionAditya ChudasamaNo ratings yet
- Test Phase II P3 05 11 2021Document15 pagesTest Phase II P3 05 11 2021ik62299No ratings yet
- Jee Main PaperDocument14 pagesJee Main PapervjaNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument5 pagesGravitationManan JainNo ratings yet
- Gravitation TESTDocument3 pagesGravitation TESTUJJVAL GAHOINo ratings yet
- FS-2 CPP 12 Physics Chemistry 2020Document23 pagesFS-2 CPP 12 Physics Chemistry 2020Durgesh SINGHNo ratings yet
- Gravitation 1b520cfa 17cf 4af0 b58c 14d72fccc668Document17 pagesGravitation 1b520cfa 17cf 4af0 b58c 14d72fccc668ajmerapavan2024No ratings yet
- Gra 15 02 2024Document14 pagesGra 15 02 2024aquib.aquil40036No ratings yet
- Motion in A PlaneDocument2 pagesMotion in A PlaneSowmiya BoobNo ratings yet
- Laws of GravitationDocument3 pagesLaws of GravitationJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument16 pagesGravitationAmal AugustineNo ratings yet
- APA-1A (124Q+A) (Mechanics)Document18 pagesAPA-1A (124Q+A) (Mechanics)Vedant TodiNo ratings yet
- Mock Test # 11 (P-1) Ans - Key & Solution - DT. 05-07-2020 PDFDocument23 pagesMock Test # 11 (P-1) Ans - Key & Solution - DT. 05-07-2020 PDFSaumya MundraNo ratings yet
- SHM & Elasticity: Ba C BC A Ba CDocument13 pagesSHM & Elasticity: Ba C BC A Ba CKrithikaNo ratings yet
- Rank Improvement Program: - Laws of Motion - Work, Energy & PowerDocument24 pagesRank Improvement Program: - Laws of Motion - Work, Energy & PowerVISHNU PRIYA BUDDANINo ratings yet
- Class XI Math Moving To Class XII Math Test Paper With Detailed SolutionDocument20 pagesClass XI Math Moving To Class XII Math Test Paper With Detailed Solutionghostrider828837No ratings yet
- GravitationDocument32 pagesGravitationMusic BanglaNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Class 11Document8 pagesGravitation Class 11mission.iist.1No ratings yet
- Classifying Spaces for Surgery and Corbordism of Manifolds. (AM-92), Volume 92From EverandClassifying Spaces for Surgery and Corbordism of Manifolds. (AM-92), Volume 92No ratings yet
- Phy CH 10 Final 10thDocument21 pagesPhy CH 10 Final 10thHaroon Khan0% (1)
- Mce30Tl Mce30Tc MCA-26G MCA-30ADocument1 pageMce30Tl Mce30Tc MCA-26G MCA-30AFarzad SagharchiNo ratings yet
- 1 Ncert Ge1Document9 pages1 Ncert Ge1KV MADHUPURNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Education: Test Blueprint For Ethiopian Higher Education Institutions' Exit Examination Band-1 ProgramDocument15 pagesMinistry of Education: Test Blueprint For Ethiopian Higher Education Institutions' Exit Examination Band-1 ProgramŤêk Mãñ JôśÿNo ratings yet
- Environmental SciencesDocument11 pagesEnvironmental SciencesArif SetyaNo ratings yet
- Reading ComprehensionDocument18 pagesReading ComprehensionZunaira KamranNo ratings yet
- CV Hadj Yahia Seba 2023Document5 pagesCV Hadj Yahia Seba 2023Yahia SebaNo ratings yet
- Improvement in The Surface Quality of Ball Bearing Steel Rounds at Bar MillDocument5 pagesImprovement in The Surface Quality of Ball Bearing Steel Rounds at Bar MillEvren ÇaprazNo ratings yet
- Baro Mano WorksheetDocument12 pagesBaro Mano WorksheetashokNo ratings yet
- AstronomyformulaDocument30 pagesAstronomyformulapalharjeetNo ratings yet
- Iocl Haldia ReportDocument99 pagesIocl Haldia ReportArkadev GhoshNo ratings yet
- Case Studies - Control of Boiler and Distillation ColumnDocument9 pagesCase Studies - Control of Boiler and Distillation Columnlaluseban100% (1)
- ISBM PET Part 1 - IM Troubleshooting & BM BasicsDocument45 pagesISBM PET Part 1 - IM Troubleshooting & BM BasicsCarlos AgianiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Rapidity and PseudorapidityDocument8 pagesLecture 7 - Rapidity and PseudorapidityDEEPARNA BHATTACHARYYANo ratings yet
- Chemical Analysis BrochureDocument2 pagesChemical Analysis BrochurePSIBSNo ratings yet
- FICCA COOL ProjectDocument1 pageFICCA COOL ProjectJim Lee ClimateViewerNo ratings yet
- Topographic SurveyDocument12 pagesTopographic SurveyVerlyn Kate Pang-ayNo ratings yet
- Microreview: Oleg KulinkovichDocument13 pagesMicroreview: Oleg KulinkovichSangvenkatNo ratings yet
- Articulo Sobre La Determinación Experimental Del Ácido Fosfórico en La Coca ColaDocument5 pagesArticulo Sobre La Determinación Experimental Del Ácido Fosfórico en La Coca ColaDiego Isac Cruz LopezNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Work Permit SystemDocument14 pages5.4 Work Permit Systembilo1984100% (1)
- MSDS-HCFC-R141b (1) - 220819 - 124426Document5 pagesMSDS-HCFC-R141b (1) - 220819 - 124426mursalina mulyasariNo ratings yet
- Percent Yield - WKSTDocument4 pagesPercent Yield - WKSTJunghoon LeeNo ratings yet
- CH 20 ThermodynamicsDocument11 pagesCH 20 ThermodynamicsElle QuizonNo ratings yet
- 02 Electrochemistry Ques. Final E PDFDocument21 pages02 Electrochemistry Ques. Final E PDFAri GamakiNo ratings yet
- Solar Panel InstallationDocument10 pagesSolar Panel Installationpeculiarchild2020No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher' GuideDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher' GuideAhmad Zaidi100% (1)
- BAUL ReportDocument24 pagesBAUL ReportArnold ApostolNo ratings yet
- Earth Works Volume Conversion and Swell FactorsDocument4 pagesEarth Works Volume Conversion and Swell FactorsJj BarakaNo ratings yet
- INFLUENCE CHITOSAN AND CARBON NANODOTS (CNDS) OF THE CONTACT OILDocument14 pagesINFLUENCE CHITOSAN AND CARBON NANODOTS (CNDS) OF THE CONTACT OILindex PubNo ratings yet
- CHM 229 Slides PDFDocument13 pagesCHM 229 Slides PDFGlory UsoroNo ratings yet