Professional Documents
Culture Documents
S2 P - I Introduction To FSA - Extra - H&M
S2 P - I Introduction To FSA - Extra - H&M
Uploaded by
Benedikt BrandesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
S2 P - I Introduction To FSA - Extra - H&M
S2 P - I Introduction To FSA - Extra - H&M
Uploaded by
Benedikt BrandesCopyright:
Available Formats
Business analysis
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS & FORECASTING| Joana Cardoso Fontes
H&M business analysis
• Quick look on MARKETLINE: https://advantage.marketline.com/HomePage
Companies: H & M Hennes & Mauritz AB
• Firm:
– Designing and retailing of fashion apparel and accessories, under brands names such as H&M,
COS, Monki
– listed in Stockholm stock exchange
– 2019: 5.000 + stores in 50+ countries and internet sales in 50 + countries
– Europe and Africa represents more than 2/3 of revenues
– End of 2017: plan is to open 220 new stores worldwide (2014: 400 and start internet sales in 9
more countries)
• Competitor and peers:
– Largest international peer: Inditex, a Spain based firm listed on the Spanish exchange but
closely held by Ortega, with 7,475 stores in 96 countries and internet sales also in 49 countries;
Europe represents 65% of revenues
– European peers: French Connection (UK), Next (UK), Etam (France) and Charles Voegele
(Switzerland);
• much smaller with revenues between €0.25 and €5.32 billion;
• H&M and Inditex follow a fast fashion strategy whereas the others not;
• H&M and Inditex operate on global scale, whereas the peers focus in smaller group of countries
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS & FORECASTING| Joana Cardoso Fontes
H&M business analysis
• H&M’s strategy: fast fashion retailing characterized by:
(i) trendy and affordable products;
(ii) quick response to changing trends using digital analytics to follow customers tastes and with short
production and lead times; high inventory turnover;
H&M’s and Inditex core competencies and advantages
– In-house design: allows for continuous monitoring of customers’ preferences and anticipate new
fashion trends very quickly
– Competitive pricing: low price with cost efficiency;
• H&M: outsourcing production with self-operated production offices around the world;
• Inditex: less outsourcing and manages own production facilities; makes use of local suppliers and has one central
logistics center from where it ships products across world and has sophisticated inventory management system
– Brand identity: high customer awareness and customer loyalty
• H&M: high profile advertising campaigns and collaborations with star designers and celebrities; sustainable brand
being committed to social development in production countries and reducing environmental impact
• Inditex: does not advertise; brand awareness through presence and appeal of its stores
– Size and growth: growth strategy, expanding store network by 8-12% every year (H&M and Zara);
allows economies of scale in design, production/sourcing and advertising. Expansion to emerging
markets allows less dependency on saturated markets
• Low dependence on debt financing and high profitability provides financial flexibility to realize growth plans
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS & FORECASTING| Joana Cardoso Fontes
H&M business analysis
Source: Marketline
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS & FORECASTING| Joana Cardoso Fontes
H&M business analysis
Risks: foreign exchange rate fluctuations, inflation in cotton prices, dependency on suppliers (H&M:
900) and competition from discount apparel retailers (Primark)
• to address this, H&M has introduced new brands and store concepts (eg: &OtherStories) and
sells its apparels under 8 different brands and varying price segments
Source: Marketline
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS & FORECASTING| Joana Cardoso Fontes
H&M business analysis
• Industry:
– Apparel retail is a cyclical industry, function of consumer’s discretionary spending and varies with
economic cycles;
• industry growth rates were negatively affected by 2008’s credit crisis and European
sovereign debt crisis and picked up around 2015
– Factors contributing to industry’s profit potential :
• Moderate growth: expected future growth rate 4-5%; growth opportunities in emerging
markets and online sales segment:
• Pricing and supply chain management: price sensitive customers and increasing
competition from low-cost retailers increase importance of inventory and supply chain
management to preserve margins
• Perishable nature of fashion: consumers’ fast changing tastes production cycles need to
be efficient and short to avoid inventory markdowns or write offs
• Sourcing of production: outsourcing to low-cost labor markets to be price competitive
quality control is key and more challenging, supply chain management is complicated and
reputational costs
• Private labels and specialty retailing: differentiation via branding (private label sales)
• Input prices: 2010-2011 cotton prices reached historical levels, but have reverted to normal
levels by end of 2014
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS & FORECASTING| Joana Cardoso Fontes
You might also like
- Business Model of H&MDocument14 pagesBusiness Model of H&Mankitkumar835204No ratings yet
- HAIER: How To Turn A Chinese Household Name Into A Global BrandDocument24 pagesHAIER: How To Turn A Chinese Household Name Into A Global BrandAshwin VigneshNo ratings yet
- HM PresentationDocument28 pagesHM Presentationsaritha100% (5)
- Case Study On: Metro Cash & Carry: Group: 11 Subhabrata Saha Suproteek Sinha Harshda Gaur Udit Bansal Sarin PDocument20 pagesCase Study On: Metro Cash & Carry: Group: 11 Subhabrata Saha Suproteek Sinha Harshda Gaur Udit Bansal Sarin PSuproteek sinhaNo ratings yet
- BudgetingDocument28 pagesBudgetingJade Gomez67% (3)
- Oracle Warehouse Management: Mark MandevilleDocument42 pagesOracle Warehouse Management: Mark MandevilleRavikumar Lam100% (3)
- Background Information On H&MDocument4 pagesBackground Information On H&MSakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- H&M MatricaDocument3 pagesH&M MatricaIvan NikolicNo ratings yet
- Understanding Brand H&MDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Brand H&MsheetiNo ratings yet
- H&MDocument29 pagesH&MLuciene Antunes100% (3)
- HRM - Henkel Case StudyDocument6 pagesHRM - Henkel Case StudySohel MallickNo ratings yet
- Final Marketing Plan: Kevinduong Christenfurniss Tatianakorman Chelsilopez Paytono'NealDocument14 pagesFinal Marketing Plan: Kevinduong Christenfurniss Tatianakorman Chelsilopez Paytono'NealGeorgeBlanaruNo ratings yet
- Best Buy Co.Document7 pagesBest Buy Co.Hanan AbazaNo ratings yet
- Anna Taktikou Apostolos Koumpotis Léa Meunier: Business ReportDocument30 pagesAnna Taktikou Apostolos Koumpotis Léa Meunier: Business ReportBlog Comment DạoNo ratings yet
- RTM Assignment - 2 (H&M)Document17 pagesRTM Assignment - 2 (H&M)Amitha MariaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 IM PDFDocument121 pagesUnit-1 IM PDFnitesh kumarNo ratings yet
- IB Group08Document9 pagesIB Group08Army2No ratings yet
- Marketing Plan Template 22-23 Besma K.TDocument9 pagesMarketing Plan Template 22-23 Besma K.TBesma Kinidi TariafNo ratings yet
- Carrera: Management and International Business: IntegrantesDocument7 pagesCarrera: Management and International Business: IntegrantesFred FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter I (MM - 3)Document20 pagesChapter I (MM - 3)Vikram AdityaNo ratings yet
- HAIERDocument27 pagesHAIERAnshul AnandNo ratings yet
- Assessment 02 (H&M)Document13 pagesAssessment 02 (H&M)Tashi DhendrupNo ratings yet
- International ManagementDocument17 pagesInternational ManagementMartina Clarke GarciaNo ratings yet
- WhirlpoolDocument31 pagesWhirlpoolNeha Nair100% (5)
- Retail and Supply Chain SolutionsDocument16 pagesRetail and Supply Chain Solutionsutkarshrajput64No ratings yet
- Module 5A International Business Strategy - International Marketing Strategies in APACDocument19 pagesModule 5A International Business Strategy - International Marketing Strategies in APACĐỗ Thị QuyênNo ratings yet
- MK AssingmentDocument4 pagesMK Assingmentras dawitNo ratings yet
- Philips MarketingDocument24 pagesPhilips MarketingTANGI85No ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document34 pagesChapter 8JP ONo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing Technique For Growth-ZaraDocument9 pagesStrategic Marketing Technique For Growth-Zaraprayash_07No ratings yet
- Introduction To Global BusinessDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Global BusinessAkhil VighNo ratings yet
- Rocky Mountain Chocolate Case - Syndicate 10 DRAFTDocument18 pagesRocky Mountain Chocolate Case - Syndicate 10 DRAFTR. Rizki MuttaqienNo ratings yet
- Strategic PositioningDocument31 pagesStrategic PositioningRavindra Pratap Gupta100% (1)
- Marketing Project On Magnum and CornettoDocument37 pagesMarketing Project On Magnum and CornettoMalik Muhammad Bilal50% (2)
- International Marketing Unit 1-1Document149 pagesInternational Marketing Unit 1-1shaikh hamidNo ratings yet
- H&M SWOT AnalysisDocument10 pagesH&M SWOT AnalysisMayumi KeviniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter I (MM - 3)Document19 pagesChapter I (MM - 3)Abhigyat ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Review International BusinessDocument25 pagesReview International BusinessDas PoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Marketing Strategy NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 22 Marketing Strategy NotesHassaan UmerNo ratings yet
- Case AnalysisDocument6 pagesCase AnalysisDipu1547No ratings yet
- H&M - Case AnalysisDocument17 pagesH&M - Case Analysiskirt diazNo ratings yet
- L'orealDocument2 pagesL'orealRipunjoy SonowalNo ratings yet
- International Business - Haier Taking A Chinese Company GlobalDocument22 pagesInternational Business - Haier Taking A Chinese Company GlobalArnab Guha Mallik100% (10)
- METRO Cash & CarryDocument17 pagesMETRO Cash & CarryFatima RazaNo ratings yet
- Metro Cash and Carry PakistanDocument31 pagesMetro Cash and Carry PakistanRaja KhurramNo ratings yet
- Ahmad 84 Business IdeaDocument26 pagesAhmad 84 Business IdeaAhmad TariqNo ratings yet
- Spencer'S Retail Limited: Repositioning in A Changing Retail EnvironmentDocument11 pagesSpencer'S Retail Limited: Repositioning in A Changing Retail EnvironmentSaurabh NaikNo ratings yet
- 4.sourcing StrategyDocument29 pages4.sourcing StrategyShamim HossainNo ratings yet
- The History of Marketing and Distribution SystemsDocument7 pagesThe History of Marketing and Distribution SystemsArmie LandritoNo ratings yet
- Carrefour PrezentareDocument25 pagesCarrefour PrezentareTuță Cristi FlorinNo ratings yet
- Pestel Analysis NimraDocument23 pagesPestel Analysis NimraDaraz WorldNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Global Marketing in A FirmDocument7 pagesCH 1 Global Marketing in A FirmBrigitta VianneyNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Lululemon Case StudyDocument18 pagesGroup 3 - Lululemon Case StudySheikh Towhidul Islam TanimNo ratings yet
- RM - Pre MidsDocument239 pagesRM - Pre MidsasniNo ratings yet
- Retail MGMT 1 - MergedDocument188 pagesRetail MGMT 1 - MergedasniNo ratings yet
- Case-Study - "H&M in Fast Fashion: Continued Success?"Document7 pagesCase-Study - "H&M in Fast Fashion: Continued Success?"Harumaru Japanese Ladies WearNo ratings yet
- FUTURE TECH GLOBAL SOLUTION Corporate DeckDocument12 pagesFUTURE TECH GLOBAL SOLUTION Corporate DeckAkshayNo ratings yet
- Emerging Market Brands Will Go GlobalDocument28 pagesEmerging Market Brands Will Go GlobalReza TiantoNo ratings yet
- Unlock Multi-Channel Profits: Proven Strategies for Business GrowthFrom EverandUnlock Multi-Channel Profits: Proven Strategies for Business GrowthNo ratings yet
- Jawaban - Jurnal Prepetual PeriodikDocument8 pagesJawaban - Jurnal Prepetual PeriodikWini WachidahNo ratings yet
- CAPE Accounting 2010 U2 P1Document11 pagesCAPE Accounting 2010 U2 P1jsjkdnckdfcNo ratings yet
- Logistical Information System (LIS)Document35 pagesLogistical Information System (LIS)Menaaz AlekarNo ratings yet
- Inventories 2Document1 pageInventories 2Vel JuneNo ratings yet
- Restructing P GDocument17 pagesRestructing P GAsif AliNo ratings yet
- Quantitative TechniquesDocument18 pagesQuantitative TechniquesPing PingNo ratings yet
- Process Costing: © 2012 Pearson Prentice Hall. All Rights ReservedDocument26 pagesProcess Costing: © 2012 Pearson Prentice Hall. All Rights ReservedayyazmNo ratings yet
- 2 - Home Office and Branch, Joint VentureDocument6 pages2 - Home Office and Branch, Joint VentureJason BautistaNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument7 pagesCost AccountingCarl AngeloNo ratings yet
- 2391 6920 2 PBDocument17 pages2391 6920 2 PBMary MendezNo ratings yet
- Guidance ManualDocument39 pagesGuidance ManualAnthony AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Working Capital Management in India PDFDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Working Capital Management in India PDFgz8reqdcNo ratings yet
- I General: Internal Audit ChecklistDocument33 pagesI General: Internal Audit ChecklistHimanshu GaurNo ratings yet
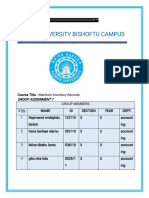
- Admas University Bishoftu Campus: Group Assignment 1Document3 pagesAdmas University Bishoftu Campus: Group Assignment 1Tilahun GirmaNo ratings yet
- Resume - Rehema Adballah UpdatedDocument3 pagesResume - Rehema Adballah UpdatedJose mainaNo ratings yet
- A) Finished Inventories Budget Showing Just Physical QuantitiesDocument3 pagesA) Finished Inventories Budget Showing Just Physical QuantitiesdoriaNo ratings yet
- GF&AR Part-IIDocument131 pagesGF&AR Part-IIAbdul Rashid QureshiNo ratings yet
- Marginal and Absorption Costing 7: This Chapter Covers..Document20 pagesMarginal and Absorption Costing 7: This Chapter Covers..PontuChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Full Test 3 CO Management AccountingDocument7 pagesFull Test 3 CO Management AccountingDiana Dobrescu0% (1)
- Illumina StrategicplanDocument14 pagesIllumina Strategicplanapi-488063825No ratings yet
- How To Read Metals Numbers in LME PDFDocument5 pagesHow To Read Metals Numbers in LME PDFrubencito1No ratings yet
- New Retail FormatDocument3 pagesNew Retail FormatpodderNo ratings yet
- Questions Supplychain RegalDocument2 pagesQuestions Supplychain RegalArikuntoPadmadewaNo ratings yet
- Imapct of Working Capital Management On Profitability of The Select Commercial Vehicle Manufacturers in IndiaDocument11 pagesImapct of Working Capital Management On Profitability of The Select Commercial Vehicle Manufacturers in IndiaHakimi AssadNo ratings yet
- 4 ResumeDocument3 pages4 Resumeapi-552941752No ratings yet
- A Detailed Study On Logistics Management With Regard To GatiDocument48 pagesA Detailed Study On Logistics Management With Regard To GatiSona Pokarna100% (2)
- Service Operation Management: Session 8Document59 pagesService Operation Management: Session 8mukul3087_305865623No ratings yet
- Inventory Management Session 1 - StudentDocument58 pagesInventory Management Session 1 - StudentShivam TripathiNo ratings yet