Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Human Nervous System
The Human Nervous System
Uploaded by
jemijemthegem0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesOriginal Title
The human nervous system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesThe Human Nervous System
The Human Nervous System
Uploaded by
jemijemthegemCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
The human nervous system
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is what allows you to respond
to changes in your environment. It is made up of
all the neurons (nerve cells) in your body.
Stimuli and receptors
A change in environment that you might need to
respond to is called a stimulus e.g. light, sounds,
touch, pressure, pain.
Stimuli are detected by a group of cells called
receptors.
Eyes – contain light receptors
Ears – contain sound receptors also contain
‘balance’ receptors
Nose – contains smell receptors
Tongue – contains taste receptors
Skin – contains receptors sensitive to touch
Central Nervous System
The CNS is where all the information from the
receptors is sent and where reflexes and actions
are coordinated.
The CNS only consist of the spinal cord and brain.
Effectors
Instructions from the CNS are sent along neurons
to effectors. Which are muscles or gland which
respond to nervous impulses and react in different
ways:
- Muscles contract
- Glands secrete chemical substances called
hormones
Different types of neurones
Sensory Neurones = Carry signals from receptors
in the sense organs to the CNS.
Relay Neurones = nerve cells carry signals from
sensory neurones to motor neurones. They are
found in the CNS.
Motor Neurons = nerve cell that carries a signal
from the CNS to the receptors.
Synapses
The connection between two neurones is called a
synapse. The nerve signal is transferred across a
chemical which is diffuse across the gap.
Reflexes
Reflexes are fast, automatic responses to stimuli.
Reflexes can reduce your chance of being injured.
Examples of uses for reflexes:
- If someone shines a bright light in your eyes
your pupils automatically get smaller so less
light gets in your eyes stopping damage.
- Adrenaline is a hormone that gets your body
ready for action if you get a shock your body
releases it automatically.
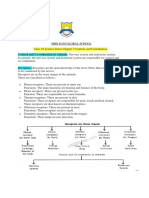
Stimuli – receptor – sensory neurone – relay
neuron – motor neurone – effector – response.
You might also like
- Year 10 Science NotesDocument45 pagesYear 10 Science NotesAmal VivekNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous Systemkrista2007xxNo ratings yet
- NERVOUS - SYSTEM (Auto-Saved)Document52 pagesNERVOUS - SYSTEM (Auto-Saved)nadeemyakubu47No ratings yet
- Irritability, Sensitivity and Co-Ordination - AnimalsDocument6 pagesIrritability, Sensitivity and Co-Ordination - AnimalsJada MillerNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument7 pagesCoordination and ResponseMemona KhalidNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Nervous Systemzainab umerNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous Systemvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous Systemkmakabe78No ratings yet
- Notes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesDocument6 pagesNotes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesamberNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Neurologists: Dr. Cindy, Dr. Kevin, DR - SherlaDocument8 pagesNervous System: Neurologists: Dr. Cindy, Dr. Kevin, DR - Sherlamsacosta7No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument36 pagesThe Nervous SystemespirituronnierickNo ratings yet
- Stimuli AND ResponseDocument57 pagesStimuli AND Responseaniszainuddin77No ratings yet
- Types and Functions of Sensory ReceptorsDocument20 pagesTypes and Functions of Sensory ReceptorspashaNo ratings yet
- Form 3 History BookDocument21 pagesForm 3 History BookDISHONNo ratings yet
- Control & Coordination Part - 1Document35 pagesControl & Coordination Part - 1Dance is LifeNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument4 pagesControl and CoordinationdeveshigiricontactNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemDeejay BeekayNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Nervous SystemAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument69 pagesCoordination and ResponseRegis WachenukaNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument5 pagesCoordination and ResponseChal WijeNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychology Summary BookletDocument12 pagesNeuropsychology Summary Bookletapi-642709499No ratings yet
- Coordination, Response and HomeostasisDocument31 pagesCoordination, Response and HomeostasisVenusCrazy 550No ratings yet
- Class:10 Subject:biology Chapter:control and CoordinationDocument16 pagesClass:10 Subject:biology Chapter:control and Coordinationkhushi guptaNo ratings yet
- Notes in Psych101 (Unit 2)Document2 pagesNotes in Psych101 (Unit 2)Poppy MargoNo ratings yet
- Nervous Sys BiologyDocument6 pagesNervous Sys Biologyalviayaan807No ratings yet
- Nervous System - Cabil (G6)Document96 pagesNervous System - Cabil (G6)Lady Ann CabilNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of Behavior: Presented By: Dr. Saima ShaheenDocument31 pagesBiological Basis of Behavior: Presented By: Dr. Saima ShaheenSana FatimaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Report, Langam, Aclao, Aguipo, DapacDocument21 pagesNervous System Report, Langam, Aclao, Aguipo, Dapachenrylangam100% (1)
- The Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesThe Nervous SystemAkheyla GarciaNo ratings yet
- Physiological Basis of Psychology: Neurons Serve To Receive and Transmit Impulses FromDocument4 pagesPhysiological Basis of Psychology: Neurons Serve To Receive and Transmit Impulses FromPatrick RilleraNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesThe Nervous System868.CapalotNo ratings yet
- Nevous System NotesDocument7 pagesNevous System NotesSchool ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Nervous System-Animal ScienceDocument16 pagesNervous System-Animal ScienceBeatrize BernardoNo ratings yet
- Physiological Basis of Behaviour: Neurons: Structure and Function, Synapse and NeurotransmittersDocument12 pagesPhysiological Basis of Behaviour: Neurons: Structure and Function, Synapse and NeurotransmittersKiran TradeNo ratings yet
- Nerve CellDocument17 pagesNerve CellCathy C DNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemDocument32 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemLouise Murphy100% (1)
- General Psychology - Biological FoundationDocument55 pagesGeneral Psychology - Biological FoundationKomala PodapatiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Nervous SystemSittie Asleah SandiganNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument3 pagesCoordination and ResponseclintonbogololephojaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document35 pagesChapter 2Amiey SehokNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesCentral Nervous SystemAnne Dominique VenturaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesThe Nervous SystemAyan AtifNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemBryan Bries100% (2)
- Nerve System and Sensing DeviceDocument16 pagesNerve System and Sensing DeviceFikrah Hafiz SuniNo ratings yet
- Control Coordination FinalDocument27 pagesControl Coordination Finalabiarju0208No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument1 pageNervous SystemErica CulturaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Body Coordination. Koordinasi BadanDocument20 pages2.1 Body Coordination. Koordinasi BadanElly EllynaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesEndocrine SystemAnanya MishraNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument12 pagesCoordination and ResponsemandonaldboikanyoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Notes #2Document7 pagesNervous System Notes #2LeoNo ratings yet
- Topic 14 Coordination and Response: 14.1.1 Nervous Control in Humans The Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesTopic 14 Coordination and Response: 14.1.1 Nervous Control in Humans The Nervous SystemHassanNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ControlDocument7 pagesCoordination and ControlanonymousNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Control and CoordinationDocument8 pagesChapter 7 Control and CoordinationS. KishoreNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument6 pagesControl and CoordinationNabeel KhanNo ratings yet
- CAMBRIDGE IGCSE BIOLOGY Chapter 14 Coordination and ResponseDocument203 pagesCAMBRIDGE IGCSE BIOLOGY Chapter 14 Coordination and ResponseVentus Tan100% (2)
- Control and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesDocument45 pagesControl and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesPriyanshu ManwaniNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesNervous Systemhailee blackieNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument11 pagesControl and CoordinationADITYA MISHRANo ratings yet
- HSB NotesDocument14 pagesHSB NotesedhanassarNo ratings yet