Professional Documents
Culture Documents
III Exp@Dv Lab@21 Batch
III Exp@Dv Lab@21 Batch
Uploaded by
21x51a3249Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- List of Books 2023-24Document10 pagesList of Books 2023-24Moiz ahmedNo ratings yet
- Umoja - Job Aid - Intro To Ad-Hoc Reporting in BIDocument58 pagesUmoja - Job Aid - Intro To Ad-Hoc Reporting in BIagape82100% (1)
- DADM - Tools HelpDocument24 pagesDADM - Tools HelpvaskoreNo ratings yet
- LevelDocument12 pagesLevelAqilahJazuliNo ratings yet
- Hw2sol PDFDocument5 pagesHw2sol PDFelenaNo ratings yet
- Advertising PDFDocument34 pagesAdvertising PDFsofabod100% (1)
- Cognos 8 Analysis StudioDocument40 pagesCognos 8 Analysis StudioAthi SivasankariNo ratings yet
- Study Guide - Short PDFDocument13 pagesStudy Guide - Short PDFGeorge GeorgeNo ratings yet
- SAS Stat Studio v3.1Document69 pagesSAS Stat Studio v3.1Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument9 pagesLab ReportShruti DasNo ratings yet
- Query Wizard: Step 1 - Select FieldsDocument3 pagesQuery Wizard: Step 1 - Select FieldsClerenda McgradyNo ratings yet
- Analysis Plug-In User GuideDocument68 pagesAnalysis Plug-In User GuideIgor ProskurnyaNo ratings yet
- Akshat's Excel Assignment 2Document7 pagesAkshat's Excel Assignment 2rohitrajbhar1845No ratings yet
- Statdisk User ManualDocument20 pagesStatdisk User Manualmspandey20000% (1)
- Tableau Assignment - StephanDocument13 pagesTableau Assignment - StephanStephan ArepagNo ratings yet
- Mba Ii DviDocument43 pagesMba Ii DviArshad JamilNo ratings yet
- Web Intelligence AdvancedDocument96 pagesWeb Intelligence AdvancedSrikanth TatipakaNo ratings yet
- Tableau Ans.Document25 pagesTableau Ans.shubham chatterjeeNo ratings yet
- XLR XL Reporter SBO Training ManualDocument40 pagesXLR XL Reporter SBO Training Manualchanhuileng6613No ratings yet
- Tableau Cheat Sheet: Workbook ComponentsDocument5 pagesTableau Cheat Sheet: Workbook ComponentsIan KevinNo ratings yet
- Tableau Cheat Sheet: Workbook ComponentsDocument5 pagesTableau Cheat Sheet: Workbook ComponentsR TvNo ratings yet
- Tableau IntroductionDocument15 pagesTableau Introductionkaranjeet singhNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 2 - Reporting and DashboardsDocument22 pagesLab Exercise 2 - Reporting and DashboardsCuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- In Class Exercise ClusteringDocument46 pagesIn Class Exercise ClusteringMárcio NitãoNo ratings yet
- SAS VA Reports 7.5 Getting StartedDocument24 pagesSAS VA Reports 7.5 Getting StartedsachinNo ratings yet
- 2261 PDFDocument30 pages2261 PDFTessfaye Wolde GebretsadikNo ratings yet
- What Is A Selection?: Characteristics of SelectionsDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Selection?: Characteristics of SelectionsYaronBabaNo ratings yet
- Access 2007: Queries and Reports: Learning GuideDocument28 pagesAccess 2007: Queries and Reports: Learning GuideMegha JainNo ratings yet
- I Spss-Pasw: Ntroduction ToDocument37 pagesI Spss-Pasw: Ntroduction Tomoonlight345No ratings yet
- 7 Data Pre-Processing in ClementineDocument7 pages7 Data Pre-Processing in ClementineVũ Tuấn HưngNo ratings yet
- Dta102 - Bid102 - Day 2Document21 pagesDta102 - Bid102 - Day 2Adedamola AdegokeNo ratings yet
- Data Processing Using Advanced ToolsDocument58 pagesData Processing Using Advanced Toolsvishminu95No ratings yet
- Statistics II: Introduction To SPSSDocument10 pagesStatistics II: Introduction To SPSSkhadijaNo ratings yet
- Data TransformationDocument27 pagesData Transformationtdyy205No ratings yet
- DWH FAQS To YourDocument16 pagesDWH FAQS To YourKranti KumarNo ratings yet
- Analisis Dan Visualisasi Data - Chapter 4-1Document53 pagesAnalisis Dan Visualisasi Data - Chapter 4-1Delvin LeonardNo ratings yet
- r20 DWDM Unit 2 PART 2Document15 pagesr20 DWDM Unit 2 PART 2Chandhu ChodisettyNo ratings yet
- LSS LabDocument45 pagesLSS LabMian Umer AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Changing Data Types: Converting Dimensions To MeasuresDocument10 pagesChanging Data Types: Converting Dimensions To Measuresksanthosh7579100% (1)
- Advanced Engineering Statistics: Lectures For M.SCDocument77 pagesAdvanced Engineering Statistics: Lectures For M.SCBest PracticeNo ratings yet
- Searches and Ad-Hoc ReportingDocument10 pagesSearches and Ad-Hoc ReportingVivek ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- TABLEAUDocument3 pagesTABLEAUShweta SainiNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Kashyap DAET Lab FileDocument28 pagesAbhishek Kashyap DAET Lab FileAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Aindump.70 452.v2010!11!12.byDocument71 pagesAindump.70 452.v2010!11!12.byvikas4cat09No ratings yet
- Orange Machine LearningDocument8 pagesOrange Machine LearningTarekHemdanNo ratings yet
- Cluster AnalysisDocument43 pagesCluster AnalysisArpan KumarNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper Advanced Analytics With Tableau EngDocument21 pagesWhitepaper Advanced Analytics With Tableau EngAshhar AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Tablue Et GoDocument16 pagesTablue Et GoKranti KumarNo ratings yet
- Tableau Study GuideDocument37 pagesTableau Study GuideBalachandar Ganesan67% (3)
- IT SkillsDocument5 pagesIT SkillsMohd. RaziNo ratings yet
- Fixturlaser Documenter User ManualDocument58 pagesFixturlaser Documenter User ManualMicroficheNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Tableau Interview QuestionsDocument21 pagesTop 10 Tableau Interview QuestionsPata nahiNo ratings yet
- Sap Bo Universe Designer GuideDocument76 pagesSap Bo Universe Designer GuideRam Krishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- Access Session 4: Using Queries To Select DataDocument19 pagesAccess Session 4: Using Queries To Select DataShaira Sarip Mamantar-BalindongNo ratings yet
- Dan Dillon Homework Problem #7 - Part 2 STAT 582, Statistical Consulting and Collaboration Dr. JenningsDocument12 pagesDan Dillon Homework Problem #7 - Part 2 STAT 582, Statistical Consulting and Collaboration Dr. JenningspamfrrNo ratings yet
- AXXXDocument20 pagesAXXXChristianAlessiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SPSS TO MOANRDocument77 pagesIntroduction To SPSS TO MOANRshimelisNo ratings yet
- Mod10 Control ChartDocument70 pagesMod10 Control ChartArnela Hodzic100% (1)
- Optima PresentationDocument50 pagesOptima PresentationNaveedAhsanJafriNo ratings yet
- SDC PagesDocument11 pagesSDC Pagessohailmohammad211No ratings yet
- ML Unit 2Document41 pagesML Unit 2abhijit kateNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations in Note TakingDocument6 pagesAbbreviations in Note TakingdmuitranNo ratings yet
- USC Handbook Handbook: University Student Council 2010-2011 University Student CouncilDocument22 pagesUSC Handbook Handbook: University Student Council 2010-2011 University Student Counciltin_borja100% (1)
- ReDocument48 pagesReGnaneswari KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Finding Nemo Critical AnalysisDocument9 pagesFinding Nemo Critical Analysisapi-429970061No ratings yet
- What Is A Parent?Document3 pagesWhat Is A Parent?gadgetgyrlNo ratings yet
- Presentation SkillsDocument23 pagesPresentation SkillsAditya RautNo ratings yet
- 550 550 550 Dalam 1850 548 548 548 548 548 548 4000 1850 1969Document1 page550 550 550 Dalam 1850 548 548 548 548 548 548 4000 1850 1969Kevin Raven D'aNo ratings yet
- Seven Steps: To Effective Problem-Solving and Strategies For Personal SuccessDocument72 pagesSeven Steps: To Effective Problem-Solving and Strategies For Personal SuccessOscar Osorio100% (1)
- 4 DiDocument37 pages4 Diapi-301619324No ratings yet
- PLS 308 Lecture Notes Decision MakingDocument13 pagesPLS 308 Lecture Notes Decision MakingMahalecumy NarayananSamyNo ratings yet
- 3i's Module 2Document30 pages3i's Module 2Aiza Abanto100% (2)
- User Hook - White PaperDocument13 pagesUser Hook - White PaperRajeev MundraNo ratings yet
- Wheelen Smbp12 PPT 06Document33 pagesWheelen Smbp12 PPT 06syed_murshedNo ratings yet
- Static & Couple BalancingDocument11 pagesStatic & Couple BalancingYeshwanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire Employee MotivationDocument6 pagesQuestionnaire Employee MotivationMeena Sivasubramanian100% (1)
- The Language and Communication of Helen KelerDocument16 pagesThe Language and Communication of Helen KelerAdam DamanhuriNo ratings yet
- Humidification and Air Conditioning: Lecture No. 3Document5 pagesHumidification and Air Conditioning: Lecture No. 3sherilyn pagarintanNo ratings yet
- EzvizDocument71 pagesEzvizHenry CruzNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Supply Chain ManagementDocument16 pagesFundamentals of Supply Chain Managementamirq450% (4)
- Math Monthly Test Y3Document7 pagesMath Monthly Test Y3tompiangNo ratings yet
- Modernism: An OverviewDocument7 pagesModernism: An OverviewJoana JacobsNo ratings yet
- КТП - Английский язык - 7 классDocument14 pagesКТП - Английский язык - 7 классshakhrukhkhan shamuratovNo ratings yet
- InCoBAN Bootcamp Brochure 290423Document6 pagesInCoBAN Bootcamp Brochure 290423Rohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Town Planning Practice and Process in IndiaDocument9 pagesEvolution of Town Planning Practice and Process in IndiaSahil Pruthi100% (1)
- Medical Cartoon and The AwesomeDocument2 pagesMedical Cartoon and The Awesomekrrishshrish140% (1)
- 4b Soal Distribusi Diskrit - PoissonDocument10 pages4b Soal Distribusi Diskrit - PoissonMtaufikalfanNo ratings yet
III Exp@Dv Lab@21 Batch
III Exp@Dv Lab@21 Batch
Uploaded by
21x51a3249Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
III Exp@Dv Lab@21 Batch
III Exp@Dv Lab@21 Batch
Uploaded by
21x51a3249Copyright:
Available Formats
EXP-3 15.02.
24 21X51A3246 III-II CSD
EXP3: Creating worksheets, navigating the sheets, applying filters,
aggregating the data
Aim: Creating worksheets, navigating the sheets, applying filters,
aggregating the data.
Description:
Filtering is an essential part of analyzing data. This article describes the many ways you can
filter data from your view. It also describes how you can display interactive filters in the view,
and format filters in the view.
Filtering:
It is the process of removing certain values or range of values from a result set.
Tableau filtering feature allows both simple scenarios using field values as well as
advanced calculation or context-based filters.
There are three types of basic filters available in Tableau. They are as follows −
Filter Dimensions are the filters applied on the dimension fields.
Filter Measures are the filters applied on the measure fields.
Filter Dates are the filters applied on the date fields.
Filtering Order of Operations:
Before you begin filtering data in Tableau, it's important to understand the order in
which
Tableau executes filters in your workbook.
Tableau performs actions on your view in a very specific order; this is called the Order of
Operations. Filters are executed in the following order:
1. Extract filters
2. Data source filters
3. Context filters
4. Filters on dimensions (whether on the Filters shelf or in filter cards in the view)
5. Filters on measures (whether on the Filters shelf or in filter cards in the view)
(20A32601P) DATA VISUALIZATION LAB@CSD 1
EXP-3 15.02.24 21X51A3246 III-II CSD
Select to keep or exclude data points in your view
You can filter individual data points (marks), or a selection of data points from your view.
For example, if you have a scatter plot with outliers, you can exclude them from the view
so you can better focus on the rest of the data.
To filter marks from the view, select a single mark (data point) or click and drag in the
view to select several marks. On the tooltip that appears, you can:
• Select Keep only to keep only the selected marks in the view. Or Open Workbooks
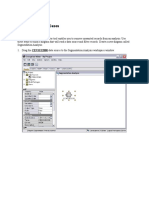
Filter quantitative data (measures)
Measures contain quantitative data, so filtering this type of field generally involves selecting a
range of values that you want to include. When you drag a measure from the Data pane to
the Filters shelf in Tableau Desktop, the following dialog box appears:
(20A32601P) DATA VISUALIZATION LAB@CSD 2
EXP-3 15.02.24 21X51A3246 III-II CSD
Select how you want to aggregate the field, and then click Next.
In the subsequent dialog box, you're given the option to create four types of
quantitative filters:
Range of Values: Select the Range of Values option to specify the minimum and maximum
values of the range to include in the view. The values you specify are included in the range.
At Least: Select the At Least option to include all values that are greater than or equal to a
specified minimum value. This type of filter is useful when the data changes often so
specifying an upper limit may not be possible.
At Most: Select the At Most option to include all values that are less than or equal
to a specified maximum value. This type of filter is useful when the data changes
often so
specifying a lower limit may not be possible.
Special: Select the Special option to filter on Null values. Include only Null values, Non-null
values, or All Values.
Data Aggregation in Tableau:
In Tableau, you can aggregate measures or dimensions, though it’s more common to
aggregate measures. Whenever you add a measure to your view, an aggregation is applied to
that measure by default. The type of aggregation applied varies depending on the context of
the view.
You can aggregate measures using Tableau only for relational data sources. Multidimensional
data sources contain data that is already aggregated. In Tableau, multidimensional data
sources are supported only in Windows.
You can change the aggregation for a measure in the view from its context menu:
(20A32601P) DATA VISUALIZATION LAB@CSD 3
EXP-3 15.02.24 21X51A3246 III-II CSD
Aggregating Dimensions
You can aggregate a dimension in the view as Minimum, Maximum, Count, or Count
(Distinct). When you aggregate a dimension, you create a new temporary measure column, so
the dimension actually takes on the characteristics of a measure.
Output:
(20A32601P) DATA VISUALIZATION LAB@CSD 4
EXP-3 15.02.24 21X51A3246 III-II CSD
Result: Creating worksheets, navigating the sheets, applying filters,
aggregating the data. Completed successfully.
(20A32601P) DATA VISUALIZATION LAB@CSD 5
You might also like
- List of Books 2023-24Document10 pagesList of Books 2023-24Moiz ahmedNo ratings yet
- Umoja - Job Aid - Intro To Ad-Hoc Reporting in BIDocument58 pagesUmoja - Job Aid - Intro To Ad-Hoc Reporting in BIagape82100% (1)
- DADM - Tools HelpDocument24 pagesDADM - Tools HelpvaskoreNo ratings yet
- LevelDocument12 pagesLevelAqilahJazuliNo ratings yet
- Hw2sol PDFDocument5 pagesHw2sol PDFelenaNo ratings yet
- Advertising PDFDocument34 pagesAdvertising PDFsofabod100% (1)
- Cognos 8 Analysis StudioDocument40 pagesCognos 8 Analysis StudioAthi SivasankariNo ratings yet
- Study Guide - Short PDFDocument13 pagesStudy Guide - Short PDFGeorge GeorgeNo ratings yet
- SAS Stat Studio v3.1Document69 pagesSAS Stat Studio v3.1Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument9 pagesLab ReportShruti DasNo ratings yet
- Query Wizard: Step 1 - Select FieldsDocument3 pagesQuery Wizard: Step 1 - Select FieldsClerenda McgradyNo ratings yet
- Analysis Plug-In User GuideDocument68 pagesAnalysis Plug-In User GuideIgor ProskurnyaNo ratings yet
- Akshat's Excel Assignment 2Document7 pagesAkshat's Excel Assignment 2rohitrajbhar1845No ratings yet
- Statdisk User ManualDocument20 pagesStatdisk User Manualmspandey20000% (1)
- Tableau Assignment - StephanDocument13 pagesTableau Assignment - StephanStephan ArepagNo ratings yet
- Mba Ii DviDocument43 pagesMba Ii DviArshad JamilNo ratings yet
- Web Intelligence AdvancedDocument96 pagesWeb Intelligence AdvancedSrikanth TatipakaNo ratings yet
- Tableau Ans.Document25 pagesTableau Ans.shubham chatterjeeNo ratings yet
- XLR XL Reporter SBO Training ManualDocument40 pagesXLR XL Reporter SBO Training Manualchanhuileng6613No ratings yet
- Tableau Cheat Sheet: Workbook ComponentsDocument5 pagesTableau Cheat Sheet: Workbook ComponentsIan KevinNo ratings yet
- Tableau Cheat Sheet: Workbook ComponentsDocument5 pagesTableau Cheat Sheet: Workbook ComponentsR TvNo ratings yet
- Tableau IntroductionDocument15 pagesTableau Introductionkaranjeet singhNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 2 - Reporting and DashboardsDocument22 pagesLab Exercise 2 - Reporting and DashboardsCuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- In Class Exercise ClusteringDocument46 pagesIn Class Exercise ClusteringMárcio NitãoNo ratings yet
- SAS VA Reports 7.5 Getting StartedDocument24 pagesSAS VA Reports 7.5 Getting StartedsachinNo ratings yet
- 2261 PDFDocument30 pages2261 PDFTessfaye Wolde GebretsadikNo ratings yet
- What Is A Selection?: Characteristics of SelectionsDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Selection?: Characteristics of SelectionsYaronBabaNo ratings yet
- Access 2007: Queries and Reports: Learning GuideDocument28 pagesAccess 2007: Queries and Reports: Learning GuideMegha JainNo ratings yet
- I Spss-Pasw: Ntroduction ToDocument37 pagesI Spss-Pasw: Ntroduction Tomoonlight345No ratings yet
- 7 Data Pre-Processing in ClementineDocument7 pages7 Data Pre-Processing in ClementineVũ Tuấn HưngNo ratings yet
- Dta102 - Bid102 - Day 2Document21 pagesDta102 - Bid102 - Day 2Adedamola AdegokeNo ratings yet
- Data Processing Using Advanced ToolsDocument58 pagesData Processing Using Advanced Toolsvishminu95No ratings yet
- Statistics II: Introduction To SPSSDocument10 pagesStatistics II: Introduction To SPSSkhadijaNo ratings yet
- Data TransformationDocument27 pagesData Transformationtdyy205No ratings yet
- DWH FAQS To YourDocument16 pagesDWH FAQS To YourKranti KumarNo ratings yet
- Analisis Dan Visualisasi Data - Chapter 4-1Document53 pagesAnalisis Dan Visualisasi Data - Chapter 4-1Delvin LeonardNo ratings yet
- r20 DWDM Unit 2 PART 2Document15 pagesr20 DWDM Unit 2 PART 2Chandhu ChodisettyNo ratings yet
- LSS LabDocument45 pagesLSS LabMian Umer AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Changing Data Types: Converting Dimensions To MeasuresDocument10 pagesChanging Data Types: Converting Dimensions To Measuresksanthosh7579100% (1)
- Advanced Engineering Statistics: Lectures For M.SCDocument77 pagesAdvanced Engineering Statistics: Lectures For M.SCBest PracticeNo ratings yet
- Searches and Ad-Hoc ReportingDocument10 pagesSearches and Ad-Hoc ReportingVivek ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- TABLEAUDocument3 pagesTABLEAUShweta SainiNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Kashyap DAET Lab FileDocument28 pagesAbhishek Kashyap DAET Lab FileAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Aindump.70 452.v2010!11!12.byDocument71 pagesAindump.70 452.v2010!11!12.byvikas4cat09No ratings yet
- Orange Machine LearningDocument8 pagesOrange Machine LearningTarekHemdanNo ratings yet
- Cluster AnalysisDocument43 pagesCluster AnalysisArpan KumarNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper Advanced Analytics With Tableau EngDocument21 pagesWhitepaper Advanced Analytics With Tableau EngAshhar AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Tablue Et GoDocument16 pagesTablue Et GoKranti KumarNo ratings yet
- Tableau Study GuideDocument37 pagesTableau Study GuideBalachandar Ganesan67% (3)
- IT SkillsDocument5 pagesIT SkillsMohd. RaziNo ratings yet
- Fixturlaser Documenter User ManualDocument58 pagesFixturlaser Documenter User ManualMicroficheNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Tableau Interview QuestionsDocument21 pagesTop 10 Tableau Interview QuestionsPata nahiNo ratings yet
- Sap Bo Universe Designer GuideDocument76 pagesSap Bo Universe Designer GuideRam Krishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- Access Session 4: Using Queries To Select DataDocument19 pagesAccess Session 4: Using Queries To Select DataShaira Sarip Mamantar-BalindongNo ratings yet
- Dan Dillon Homework Problem #7 - Part 2 STAT 582, Statistical Consulting and Collaboration Dr. JenningsDocument12 pagesDan Dillon Homework Problem #7 - Part 2 STAT 582, Statistical Consulting and Collaboration Dr. JenningspamfrrNo ratings yet
- AXXXDocument20 pagesAXXXChristianAlessiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SPSS TO MOANRDocument77 pagesIntroduction To SPSS TO MOANRshimelisNo ratings yet
- Mod10 Control ChartDocument70 pagesMod10 Control ChartArnela Hodzic100% (1)
- Optima PresentationDocument50 pagesOptima PresentationNaveedAhsanJafriNo ratings yet
- SDC PagesDocument11 pagesSDC Pagessohailmohammad211No ratings yet
- ML Unit 2Document41 pagesML Unit 2abhijit kateNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations in Note TakingDocument6 pagesAbbreviations in Note TakingdmuitranNo ratings yet
- USC Handbook Handbook: University Student Council 2010-2011 University Student CouncilDocument22 pagesUSC Handbook Handbook: University Student Council 2010-2011 University Student Counciltin_borja100% (1)
- ReDocument48 pagesReGnaneswari KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Finding Nemo Critical AnalysisDocument9 pagesFinding Nemo Critical Analysisapi-429970061No ratings yet
- What Is A Parent?Document3 pagesWhat Is A Parent?gadgetgyrlNo ratings yet
- Presentation SkillsDocument23 pagesPresentation SkillsAditya RautNo ratings yet
- 550 550 550 Dalam 1850 548 548 548 548 548 548 4000 1850 1969Document1 page550 550 550 Dalam 1850 548 548 548 548 548 548 4000 1850 1969Kevin Raven D'aNo ratings yet
- Seven Steps: To Effective Problem-Solving and Strategies For Personal SuccessDocument72 pagesSeven Steps: To Effective Problem-Solving and Strategies For Personal SuccessOscar Osorio100% (1)
- 4 DiDocument37 pages4 Diapi-301619324No ratings yet
- PLS 308 Lecture Notes Decision MakingDocument13 pagesPLS 308 Lecture Notes Decision MakingMahalecumy NarayananSamyNo ratings yet
- 3i's Module 2Document30 pages3i's Module 2Aiza Abanto100% (2)
- User Hook - White PaperDocument13 pagesUser Hook - White PaperRajeev MundraNo ratings yet
- Wheelen Smbp12 PPT 06Document33 pagesWheelen Smbp12 PPT 06syed_murshedNo ratings yet
- Static & Couple BalancingDocument11 pagesStatic & Couple BalancingYeshwanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire Employee MotivationDocument6 pagesQuestionnaire Employee MotivationMeena Sivasubramanian100% (1)
- The Language and Communication of Helen KelerDocument16 pagesThe Language and Communication of Helen KelerAdam DamanhuriNo ratings yet
- Humidification and Air Conditioning: Lecture No. 3Document5 pagesHumidification and Air Conditioning: Lecture No. 3sherilyn pagarintanNo ratings yet
- EzvizDocument71 pagesEzvizHenry CruzNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Supply Chain ManagementDocument16 pagesFundamentals of Supply Chain Managementamirq450% (4)
- Math Monthly Test Y3Document7 pagesMath Monthly Test Y3tompiangNo ratings yet
- Modernism: An OverviewDocument7 pagesModernism: An OverviewJoana JacobsNo ratings yet
- КТП - Английский язык - 7 классDocument14 pagesКТП - Английский язык - 7 классshakhrukhkhan shamuratovNo ratings yet
- InCoBAN Bootcamp Brochure 290423Document6 pagesInCoBAN Bootcamp Brochure 290423Rohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Town Planning Practice and Process in IndiaDocument9 pagesEvolution of Town Planning Practice and Process in IndiaSahil Pruthi100% (1)
- Medical Cartoon and The AwesomeDocument2 pagesMedical Cartoon and The Awesomekrrishshrish140% (1)
- 4b Soal Distribusi Diskrit - PoissonDocument10 pages4b Soal Distribusi Diskrit - PoissonMtaufikalfanNo ratings yet