Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F5 Phy Final 1A 22-23
F5 Phy Final 1A 22-23
Uploaded by
s20139Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 1-Relative Velocity in Special Relativity: Page898 CollegeDocument26 pages1-Relative Velocity in Special Relativity: Page898 CollegeAbdulrhman fNo ratings yet
- Complete Notes On 9th Physics by Asif RasheedDocument82 pagesComplete Notes On 9th Physics by Asif RasheedAsif Rasheed Rajput75% (28)
- Physical Science Midterm Study GuideDocument11 pagesPhysical Science Midterm Study GuideeherrerahghsNo ratings yet
- F5 - Phy - Final - 1A - 21-22 2Document15 pagesF5 - Phy - Final - 1A - 21-22 2s20139No ratings yet
- F4 PhMid 1A 19Document11 pagesF4 PhMid 1A 19pg7rrnqw9fNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper 1 - AnskeyDocument8 pagesPractice Paper 1 - Anskeykim loveNo ratings yet
- F.4 Phy Mock Paper (Paper 1A)Document13 pagesF.4 Phy Mock Paper (Paper 1A)Silly Ben bbNo ratings yet
- Kovai Sahodaya Schools Complex: Preboard Examination - I D 2023 Grade Xii - Physics 15.12.2023Document10 pagesKovai Sahodaya Schools Complex: Preboard Examination - I D 2023 Grade Xii - Physics 15.12.2023Dharani MNo ratings yet
- F5 Phy Final 1B 21-22Document17 pagesF5 Phy Final 1B 21-22s20139No ratings yet
- 1920 F4 Physics Final ExamDocument23 pages1920 F4 Physics Final ExamEvelyn ChongNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Final Examination 2007-2008 17th June 2008 8:25 Am Question-Answer BookDocument15 pagesForm 3 Final Examination 2007-2008 17th June 2008 8:25 Am Question-Answer Bookjonas hoNo ratings yet
- 2017 Sem 1 - Physics 1 Test 3 & MemoDocument7 pages2017 Sem 1 - Physics 1 Test 3 & MemomphoNo ratings yet
- Class 12 National Genius Search Examination: Advanced: Test CodeDocument8 pagesClass 12 National Genius Search Examination: Advanced: Test CodePPNo ratings yet
- Physics: Question-Answer BookDocument16 pagesPhysics: Question-Answer Bookjonas hoNo ratings yet
- 08 F3 Final Exam With AnswerDocument20 pages08 F3 Final Exam With Answerjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper 2022-23 Class Xii PhysicsDocument8 pagesModel Question Paper 2022-23 Class Xii PhysicsyuvanithanrNo ratings yet
- No. 1 UCE-Physics - Paper-1Document10 pagesNo. 1 UCE-Physics - Paper-1BashirNo ratings yet
- PHYS1001 Test 1 2017 SEM-1Document14 pagesPHYS1001 Test 1 2017 SEM-1Angad MangatNo ratings yet
- Physics Tes2Document4 pagesPhysics Tes2Krishna AgarwalNo ratings yet
- B-1111-Final ExamPhysics1 - HK222 - DethiDocument3 pagesB-1111-Final ExamPhysics1 - HK222 - DethiNhật Thanh TôNo ratings yet
- 2020 Sec 3 Physics Term 3 WA 3Document10 pages2020 Sec 3 Physics Term 3 WA 3VinidraNo ratings yet
- S2 Holiday Homework 2Document14 pagesS2 Holiday Homework 24A10 FUNG CHAK FAINo ratings yet
- Aea Physics Prelims 2Document8 pagesAea Physics Prelims 2Rudraksh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class - Xi - Nipl & Nelite - Physics Desc Q.P.25.11.2023Document3 pagesClass - Xi - Nipl & Nelite - Physics Desc Q.P.25.11.2023squadralsupremeNo ratings yet
- XII - Physics - Preboard 1 - Set A 2023Document6 pagesXII - Physics - Preboard 1 - Set A 2023Anuradha MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- MT AprilDocument2 pagesMT AprilAnkit SinghNo ratings yet
- S4 Physics Paper 1-Resourceful Mock Examinations 2019ADocument11 pagesS4 Physics Paper 1-Resourceful Mock Examinations 2019ATwinomujuniNo ratings yet
- Sing Yin Secondary School First Term Test, 2019 - 2020 PhysicsDocument4 pagesSing Yin Secondary School First Term Test, 2019 - 2020 PhysicstestNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Physics Paper 1Document69 pagesPractice Paper Physics Paper 1hNo ratings yet
- 2022-JEE Main-7 Question PaperDocument11 pages2022-JEE Main-7 Question PaperAchint Kumar Mishra50% (2)
- Physics 1Document161 pagesPhysics 1Muskan PooniaNo ratings yet
- Media Communications: Test Booklet Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Paper - IDocument27 pagesMedia Communications: Test Booklet Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Paper - IRaghuNo ratings yet
- 2022-Mock JEE Main-19 - PaperDocument16 pages2022-Mock JEE Main-19 - PaperHalfborn GundersonNo ratings yet
- 2023 Unit 1 Semester 1 Physics Exam Question and Extended Answer Booklet Teams (AutoRecovered)Document19 pages2023 Unit 1 Semester 1 Physics Exam Question and Extended Answer Booklet Teams (AutoRecovered)WillsollyNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 9Document14 pagesPractice Test 9TEJASSINGH ARORANo ratings yet
- 19-08-2023_ITPL_NEET_XII_OFFLINDocument40 pages19-08-2023_ITPL_NEET_XII_OFFLINDheeraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: Solutions To JEE (Main) - 2020Document33 pagesFiitjee: Solutions To JEE (Main) - 2020srijan jhaNo ratings yet
- Mock Examination 2007 Physics Paper 2Document20 pagesMock Examination 2007 Physics Paper 2api-19650882No ratings yet
- f3 Nov 2022 Exam PaperDocument14 pagesf3 Nov 2022 Exam Paperrileydebeer21No ratings yet
- Quiz - Enthuse - Independence DayDocument6 pagesQuiz - Enthuse - Independence Dayyashwant bhaduNo ratings yet
- UCE Physics 2009 Paper 1 GuideDocument15 pagesUCE Physics 2009 Paper 1 GuideAinebyoona ChriscentNo ratings yet
- Cusat 2016Document37 pagesCusat 2016sreejitha KNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jan 10, 2024Document7 pagesAdobe Scan Jan 10, 2024rishirajkaran2006No ratings yet
- 2023 - 05 - 14 12 - 33 Office LensDocument4 pages2023 - 05 - 14 12 - 33 Office LensShyam Shankar DasNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee - Jee (Main) : Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics Phase-4Document13 pagesFiitjee - Jee (Main) : Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics Phase-4Abhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Form IvDocument6 pagesMid Term Form IvTitus KaselaNo ratings yet
- Cblephpl 04Document9 pagesCblephpl 04Srikanth G.RNo ratings yet
- 2022 JEE Main Home Practice Test - 1 - Paper (@vmclectures On Telegram)Document15 pages2022 JEE Main Home Practice Test - 1 - Paper (@vmclectures On Telegram)muktibakshiNo ratings yet
- Chem SSC 2 2nd Half BookDocument4 pagesChem SSC 2 2nd Half BookAsif AyazNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Sample Test 2 With Ans KeyDocument15 pagesJee Main Sample Test 2 With Ans KeyrahulNo ratings yet
- F2 Midyear Sample Paper MCDocument5 pagesF2 Midyear Sample Paper MCnatalie161131No ratings yet
- Questions - Physics - Electrodynamics & ElectrostaticsDocument6 pagesQuestions - Physics - Electrodynamics & Electrostaticsboorsudithi0No ratings yet
- Jss International School DubaiDocument7 pagesJss International School DubairakshitrewardsNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Science - Ut1 QP - 2021-22Document4 pagesClass 10 - Science - Ut1 QP - 2021-22MugdhaNo ratings yet
- Physics SQP - 04 Latest (2023) Class 12 CBSEDocument28 pagesPhysics SQP - 04 Latest (2023) Class 12 CBSEmr mindNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering and Technology: Term Test Question Paper - B. TechDocument3 pagesFaculty of Engineering and Technology: Term Test Question Paper - B. TechYash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- F5 Phy Final 1B 22-23Document21 pagesF5 Phy Final 1B 22-23s20139No ratings yet
- Xii PhysicsDocument9 pagesXii PhysicsLalu kuttyNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument9 pagesPhysicsAnsh MishraNo ratings yet
- 2MT Revision Practice 5Document25 pages2MT Revision Practice 5Sara -No ratings yet
- NS Grade 9 Sept 2019Document9 pagesNS Grade 9 Sept 2019Hlayiseko RikhotsoNo ratings yet
- Phy SQP3Document11 pagesPhy SQP3Kanhaiya LalNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument3 pagesForces and MotionJulia Geonzon LabajoNo ratings yet
- 02 Newtonian Mechanics AdvancedDocument37 pages02 Newtonian Mechanics AdvancedRithish BarathNo ratings yet
- PHY101 MIDTERM SOLVED MCQS by JUNAIDDocument19 pagesPHY101 MIDTERM SOLVED MCQS by JUNAIDhs6077074No ratings yet
- 3 Forces and MotionDocument34 pages3 Forces and MotionIoryNo ratings yet
- Myp 4 Summ Unit 5 Free To MoveDocument7 pagesMyp 4 Summ Unit 5 Free To MoveMiley MutolaNo ratings yet
- Part A - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesPart A - Multiple Choice QuestionsBryan SutantoNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 Syllabus 2015-16Document8 pagesPhysics 1 Syllabus 2015-16api-301989803No ratings yet
- Introduction To Particle Tracing ModuleDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Particle Tracing ModulePaulo FidelisNo ratings yet
- MBX ExplosivesDocument10 pagesMBX ExplosivesrdugasNo ratings yet
- Tabib2008 PDFDocument26 pagesTabib2008 PDFlrodriguez_892566No ratings yet
- 5 - Unsteady Flow in Rivers Pp. 122-157Document37 pages5 - Unsteady Flow in Rivers Pp. 122-157Anonymous 87xpkIJ6CFNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Second Quarter ExamDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Second Quarter ExamMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4&5 Review and Chapter 7 IntroductionDocument22 pagesChapter 4&5 Review and Chapter 7 IntroductionJunyi JiNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 HomeworkDocument10 pagesChem 1 HomeworkkwilsonNo ratings yet
- PBL Report From The Best GroupDocument8 pagesPBL Report From The Best GroupZaid ZulNo ratings yet
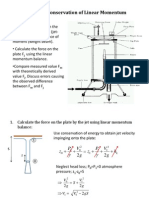
- Impact of A Jet - Conservation of Linear MomentumDocument6 pagesImpact of A Jet - Conservation of Linear MomentumRufus ChengNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter & Uncertainity PrincipleDocument2 pagesDual Nature of Matter & Uncertainity PrincipleParthNo ratings yet
- Group No. Course Code Course Title Unique CodeDocument74 pagesGroup No. Course Code Course Title Unique CodeMVJCE IDCARDNo ratings yet
- Analysis Method For Inertial Particle SeparatorDocument9 pagesAnalysis Method For Inertial Particle SeparatorD ARUL KUMARESANNo ratings yet
- 31bbd483 E8d3 4376 Abcc Cde0e74e950a o Level Quick Physics QN BankDocument138 pages31bbd483 E8d3 4376 Abcc Cde0e74e950a o Level Quick Physics QN BankMaama PhionaNo ratings yet
- The Specialist Committee On Validation of Waterjet Test ProceduresDocument38 pagesThe Specialist Committee On Validation of Waterjet Test Proceduresdushan diasNo ratings yet
- JR InterDocument4 pagesJR InterAswani Kumar67% (3)
- Chapter 8: Conservation Laws The Continuity EquationDocument7 pagesChapter 8: Conservation Laws The Continuity EquationMadhumika ThammaliNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Physics: Chapter-4 Momentum Study QuestionDocument2 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Physics: Chapter-4 Momentum Study QuestionMahbub KhanNo ratings yet
- ES 2 Impulse and MomentumDocument18 pagesES 2 Impulse and MomentumAbor ShawnNo ratings yet
F5 Phy Final 1A 22-23
F5 Phy Final 1A 22-23
Uploaded by
s20139Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F5 Phy Final 1A 22-23
F5 Phy Final 1A 22-23
Uploaded by
s20139Copyright:
Available Formats
PHY
SECTION A ST. PAUL’S COLLEGE
F.5 Final Examination 2022 – 2023
PHYSICS
(2 hours 30 minutes)
This paper must be answered in English
Name
Class & Class No. ( )
Subject Teacher Mr Kwok / Miss Ma
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
1. You should write your Name, Class and Class Number in the spaces provided on this
cover. Circle your Subject Teacher.
2. There are TWO sections, A and B, in this Paper. Section A and B carry 35% and 65 %
respectively. You are advised to finish Section A in about 60 minutes.
3. Section A consists of multiple-choice questions in this question paper, while Section B
contains conventional questions printed separately in Question-Answer Book B.
4. Answers to Section A should be marked on the Multiple-choice Answer Sheet while
answers to Section B should be written in the spaces provided in Question-Answer Book
B. The Answer Sheet for Section A and the Question-Answer Book for Section B
will be collected separately at the end of the examination.
5. The diagrams in this paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
6. The last pages of this question paper contain a list of data, formulae and relationships
which you may find useful.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR SECTION A (MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS)
1. Read carefully the instructions on the Answer Sheet. After the announcement of the
start of the examination, you should first insert the information required in the spaces
provided.
2. When told to open this book, you should check that all the questions are there. Look for
the words ‘END OF SECTION A’ after the last question.
3. All questions carry equal marks.
4. ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS. You are advised to use an HB pencil to mark all the
answers on the Answer Sheet, so that wrong marks can be completely erased with a
clean rubber. You must mark the answers clearly; otherwise you will lose marks if the
answers cannot be captured.
5. You should mark only ONE answer for each question. If you mark more than one
answer, you will receive NO MARKS for that question.
6. No marks will be deducted for wrong answers.
F.5 Physics Sect A Final Exam 22-23 Page - 1
Section A (35 %)
There are 33 questions.
1. In North Pole, lake surfaces are always covered in a thick layer of ice in winter. This helps the
aquatic life in the lakes to survive. The aquatic life survives because
A. The thick layer of ice acts as good heat insulator.
B. The thick layer of ice melts slowly and releases heat to the water.
C. The thick layer of ice reflects heat from the sun.
D. The thick layer of ice has lower density than water.
2. 600 g of boiling water is added to 150 g of instant noodles originally at 20C. The final
temperature of the mixture is 85C. What is the ratio of the specific heat capacity of the
noodles to that of the specific heat capacity of water ?
A. 0.85 B. 0.92
C. 1.08 D. 1.18
3. When a gas is heated,
(1) its average internal energy always increases.
(2) its temperature always increases.
(3) it always expands.
A. (1) only B. (3) only
C. (1) and (2) only D. (1), (2) and (3)
4. An ideal gas is enclosed in a container at absolute temperature 100 K. The absolute
temperature is now raised to 200 K, whilst the volume is kept constant. Which of the
following statements is/are correct ?
(1) The frequency of collisions between the molecules and the wall of the container
increases.
(2) The root-mean-square speed of the molecules is doubled.
(3) The average kinetic energy of the molecules is doubled.
A. (1) only B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only D. (2) and (3) only
5. Steam of mass m1 at 100 C is injected into a melting ice block of mass m2. Assume that no
m
energy is lost to the surroundings. If the final temperature of the mixture is 50 C, find 1 .
m2
–1 –1
Given: Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg °C
Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.34 105 J kg–1
Specific latent heat of vaporization of water = 2.26 106 J kg–1
A. 0.15 B. 0.22
C. 4.54 D. 6.77
F.5 Physics Sect A Final Exam 22-23 Page - 2
6.
A heating unit as used on the rear window of a car consists of five strips of resistive material
joined at either end by strips of copper of negligible resistance, shown in the diagram. Heat is
generated at a rate of 45 W when the unit is connected to a 12 V car battery. If each resistive
strip is 2.5 mm wide and of length 0.80 m, determine the thickness of each strip.
Given that the resistivity of the resistive material is 5.0 x 10–5 Ω m.
A. 0.20 mm B. 0.30 mm
C. 0.60 mm D. 1.00 mm
7.
In the fiagram, a coil, mounted on an axle, has its plane parallel to the flux lines of a uniform
magnetic field B. When a current I is switched on, and before the coil is allowed to move,
A. there are no forces due to B on the sides PQ and RS.
B. there are no forces due to B on the sides SP and QR.
C. sides SP and QR attract each other.
D. sides PQ and RS attract each other.
8.
In the circuit, the battery has an emf of 12 V and an internal resistance of 2.0 Ω. The resistors
A and B each have resistance of 30 Ω. Find the energy dissipated by resistor A in 20 s.
A. 10 J B. 18 J
C. 22 J D. 24 J
F.5 Physics Sect A Final Exam 22-23 Page - 3
9.
An elastic circular wire frame of radius 1 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.6 mT
into the paper. If the radius is doubled in 0.2 ms find the average induced e.m.f. and the
direction of the induced current in the frame in this period.
average induced e.m.f. / mV direction of the induced current
A. 0.95 clockwise
B. 0.95 anticlockwise
C. 2.8 clockwise
D. 2.8 anticlockwise
10.
The figure shows the situation with two stationary charges. There is a neutral point N where
its distance from Q1 equals to the distance between the two charges Q1 and Q2. What can be
deduced from the information ?
(1) Q1 and Q2 are of opposite signs.
(2) The magnitude of charge of Q2 doubles that of Q1.
(3) If the sign of two charges are interchanged, the neutral point will not be changed.
A. (1) only B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only D. (2) and (3) only
11. Which of the following concerning the household circuit is/are correct ?
(1) Fuse should be installed in the live wire of an electrical appliance.
(2) Switch should be installed in the neutral wire of an electrical appliance.
(3) Current always flows from the live wire through the appliance to the neutral wire.
A. (1) only B. (3) only
C. (1) and (2) only D. (2) and (3) only
F.5 Physics Sect A Final Exam 22-23 Page - 4
12.
A positively charged metal sphere X is brought near an uncharged metal sphere Y as shown.
Y is then touched momentarily with a finger. X is then taken away. Y is now
A. positively charged.
B. negatively charged.
C. negatively charged on the left side and positively charged on the right side.
D. positively charged on the left side and negatively charged on the right side.
13. Which of the following statements about the coulomb is/are correct ?
(1) When one coulomb of charge flows across a potential difference of one volt, one joule
of energy is released.
(2) The force exerted on a charge of 1 coulomb in an electric field of 1 volt/metre is 1
newton.
(3) 1 coulomb is the charge of one mole of electrons.
A. (1) only B. (3) only
C. (1) and (2) only D. (2) and (3) only
14.
A student sets up the above circuit to study the effect of the length of a resistance wire on its
resistance. As the crocodile clip is moved from A to B along the resistance wire, which of the
following statements is/are correct ?
(1) The reading of the ammeter increases.
(2) The reading of the voltmeter increases.
(3) The voltmeter reading is directly proportional to the reading of the ammeter.
A. (1) only B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only D. (2) and (3) only
F.5 Physics Sect A Final Exam 22-23 Page - 5
15. The electric kettle is rated at ‘220 V, 2400 W’. When it works at its rated value, it takes time T
to boil a certain amount of water. How long does it take to boil the same amount of water
when the kettle works at 110 V ?
1 1
A. T B. T
4 2
C. 2T D. 4T
16.
N S N S
A B
The following shows the magnets and coils of two d.c. motors A and B. What is the advantage
of the curved magnets in B over the ones in A ?
A. Curved magnets provide a stronger magnetic field than rectangular ones.
B. Magnets of this shape can provide a larger average torque on the coil.
C. Magnets of this shape allow the coil to rotate more freely.
D. Curved magnets are easier to produce and are more economical.
17.
A thin metal plate is suspended in a uniform magnetic field B pointing upwards. The plate is
pulled to one side and then released. Which of the following statements is/are correct ?
(1) When the plate swings, eddy currents flow clockwise in it.
(2) The plate takes the same amount of time to stop as if there is no magnetic field.
(3) When the plate swings, its temperature remains unchanged.
A. (1) only B. (3) only
C. (1) and (2) only D. (2) and (3) only
18. Two identical satellites X and Y are moving in two circular orbits around the Earth as shown.
Which of the following statement is correct?
A. The period of X is smaller than that of Y.
B. The speed of X is greater than that of Y.
C. The gravitational force on X is greater than that of Y.
D. The gravitational potential energy of X is greater than that of Y.
F.5 Physics Sect A Final Exam 22-23 Page - 6
19. Particles P and Q are fixed at distances r and r/2 respectively from the centre O of a horizontal
circular platform which is rotating uniformly as shown.
The ratio of the acceleration of P to that of Q is
A. 1 : 2.
B. 2 : 1.
C. 1 : 4.
D. 4 : 1.
20. Two identical coins P and Q are placed at the edge of a table. At the same instant, P is pushed
slightly and falls vertically to the ground while Q is projected horizontally and reaches the
ground through a parabolic path as shown.
Which of the following statements are correct? (Neglect air resistance)
(1) P and Q reach the ground at the same time.
(2) P and Q have the same acceleration.
(3) P and Q have the same vertical speed on reaching the ground.
A. (1) and (2) only B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only D. (1), (2) and (3)
21. A particle of mass m is thrown vertically upwards with initial speed v. When the particle
returns to its starting point, what are the changes in momentum and kinetic energy of the
particle?
Change in momentum Change in kinetic energy
A. 2mv 0
1 2
B. 0 mv
2
C. 2mv mv 2
D. 0 0
F.5 Physics Sect A Final Exam 22-23 Page - 7
22. A uniform plank AB of weight 200 N rests on two trestles as shown. A boy stands at the end B
of the plank.
What can the maximum weight of the boy be without tilting the plank? (Assume the weight of
the plank acts through its centre.)
A. 300 N B. 200 N
C. 100 N D. 75 N
23. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown. A constant
force F is applied to block A so that the three blocks move towards the right with the same
acceleration.
The net force acting on the block B is
1
A. 0 F. B. F.
3
2
C. F. D. 1F .
3
24. Which of the following descriptions about kinetic energy is NOT correct?
A. A body possesses kinetic energy when it is moving.
B. The work done on an object moving along a horizontal surface by a force is
1
equal to the increase in kinetic energy of the object, i.e., KE = mv 2 .
2
C. The work done on an object which decelerates to the rest from initial speed v is
1
equal to the decrease in kinetic energy of the object, i.e., mv 2 .
2
D. The object does not possess kinetic energy when the net force acted on it is
zero.
25. Blocks P and Q are placed on a smooth horizontal surface and the mass of Q is n times that of
P. A light spring is compressed by the two blocks which are held stationary as shown. The
blocks are then released from rest.
Find the ratio of the magnitude of momentum P to that of Q.
A. 1:1 B. 1:n
C. n:1 D. n2 : 1
F.5 Physics Sect A Final Exam 22-23 Page - 8
26. Which of the following graphs show(s) there is a constant force exerted on the object?
(1) s (2)
(3)
A. (1) only B. (1) and (2) only
C. (2) and (3) only D. (1), (2) and (3)
27.
In the figure, a uniform plank of weight W is hinged to a vertical wall and supported by a strut,
which makes an angle of 50° with the wall. The force F exerted by the strut on the plank acts
along the length of the strut. Which of the following about the force F and the contact force at
the hinge is correct?
force F exerted by the strut contact force at the hinge
A. 0.50W horizontal component points towards the left
B. 0.78W horizontal component points towards the left
C. 0.50W horizontal component points towards the right
D. 0.78W horizontal component points towards the right
28. A ray of light enters a glass prism and travels along the path as shown.
Find the refractive index of the glass.
A. 0.68 B. 1.37
C. 1.47 D. 1.50
F.5 Physics Sect A Final Exam 22-23 Page - 9
29. A slide illuminated by a light source is placed in front of a convex lens of focal length f as
shown in the figure.
The image seen on the translucent screen is probably
A. B. C. D.
30. A student prepares a double-slit set-up as shown. However, no interference fringe can be
observed on the screen.
Your suggestion for the improvement may be
A. reducing d B. reducing x
C. reducing D D. increasing a
31. When a monochromatic light beam is incident normally on a diffraction grating with 450 lines
per mm, a pattern of bright fringes is formed. The angle between the two second-order bright
fringes is 40°.
Find the frequency of the light.
A. 1.4 1014 Hz
B. 4.0 1014 Hz
C. 6.6 1014 Hz
D. 7.9 1014 Hz
F.5 Physics Sect A Final Exam 22-23 Page - 10
32. A vibrator generates a stationary wave on a string.
The above diagram shows the shape of the string at a certain instant. Which of the following
shows the shape of the string between PQ after a quarter of a period?
A. B.
C. D.
33. The following data show the frequency and sound intensity levels of some musical notes
produced by a piano.
Note Frequency / Hz Intensity level / dB
C 256 64
D 288 68
E 320 65
F 341 63
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(1) The note F has the lowest pitch.
(2) The note D has the greatest loudness.
(3) The note C played on a guitar will sound differently from the same note produced by
the piano.
A. (1) only B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only D. (2) and (3) only
END OF SECTION A
F.5 Physics Sect A Final Exam 22-23 Page - 11
List of data, formulae and relationships
Data
molar gas constant R = 8.31 J K-1 mol-1
Avogadro constant NA = 6.02 x1023 mol−1
acceleration due to gravity g = 9.81 m s-2 (Close to the Earth)
universal gravitational constant G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2 kg-2
speed of light in vacuum c = 3.00 x 108 m s-1
charge of electron e = 1.60 x 10-19 C
electron rest mass me = 9.11 x 10-31 kg
permittivity of free space 0 = 8.85 x 10-12 C2 N-1 m-2
permeability of free space 0 = 4 10−7 H m-1
Rectilinear motion Mathematics
For uniformly accelerated motion : Equation of a straight line y = mx + c
v = u + at Arc length = r
1
s = ut + at 2 Surface area of cylinder = 2 r h + 2 r 2
2
v 2 = u 2 + 2as Volume of cylinder = r2h
Surface area of sphere = 4 r 2
4
Volume of sphere = r3
3
For small angles, sin tan (in radians)
F.5 Physics Sect A Final Exam 22-23 Page - 12
energy transfer during Q1Q2
A1. E = mc T D1. F= Coulomb’s law
heating and cooling 4 0 r 2
energy transfer during Q electric field strength due to a
A2. E = m D2. E=
change of state 4 0 r 2
point charge
equation of state for an V electric field between parallel
A3. pV = nRT D3. E=
ideal gas d plates (numerically)
1 l
A4. pV = Nmc 2 kinetic theory equation D4. R= resistance and resistivity
3 A
3RT
A5. Ek = molecular kinetic energy D5. R = R1 + R2 resistors in series
2N A
1 1 1
D6. = + resistors in parallel
R R1 R2
v p
B1. F =m = Force D7. P = IV = I 2 R power in a circuit
t t
force on a moving charge in a
B2. moment = F d moment of a force D8. F = BQ sin
magnetic field
gravitational potential force on a current-carrying
B3. EP = mgh D9. F = BIl sin
energy conductor in a magnetic field
1 0 I magnetic field due to a long
B4. E k = mv 2 kinetic energy D10. B=
2 2 r straight wire
W 0 NI magnetic field inside a long
B5. P = Fv = mechanical power D11. B=
t l solenoid
v2
B6. a = = 2r centripetal acceleration D12. =N induced e.m.f.
r t
Gm1m2 Newton’s law of
B7. F=
r2 gravitation
D fringe width in double-
C1. y =
a slit interference
diffraction grating
C2. d sin = n
equation
1 1 1 equation for a single
C3. + =
u v f lens
F.5 Physics Sect A Final Exam 22-23 Page - 13
You might also like
- 1-Relative Velocity in Special Relativity: Page898 CollegeDocument26 pages1-Relative Velocity in Special Relativity: Page898 CollegeAbdulrhman fNo ratings yet
- Complete Notes On 9th Physics by Asif RasheedDocument82 pagesComplete Notes On 9th Physics by Asif RasheedAsif Rasheed Rajput75% (28)
- Physical Science Midterm Study GuideDocument11 pagesPhysical Science Midterm Study GuideeherrerahghsNo ratings yet
- F5 - Phy - Final - 1A - 21-22 2Document15 pagesF5 - Phy - Final - 1A - 21-22 2s20139No ratings yet
- F4 PhMid 1A 19Document11 pagesF4 PhMid 1A 19pg7rrnqw9fNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper 1 - AnskeyDocument8 pagesPractice Paper 1 - Anskeykim loveNo ratings yet
- F.4 Phy Mock Paper (Paper 1A)Document13 pagesF.4 Phy Mock Paper (Paper 1A)Silly Ben bbNo ratings yet
- Kovai Sahodaya Schools Complex: Preboard Examination - I D 2023 Grade Xii - Physics 15.12.2023Document10 pagesKovai Sahodaya Schools Complex: Preboard Examination - I D 2023 Grade Xii - Physics 15.12.2023Dharani MNo ratings yet
- F5 Phy Final 1B 21-22Document17 pagesF5 Phy Final 1B 21-22s20139No ratings yet
- 1920 F4 Physics Final ExamDocument23 pages1920 F4 Physics Final ExamEvelyn ChongNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Final Examination 2007-2008 17th June 2008 8:25 Am Question-Answer BookDocument15 pagesForm 3 Final Examination 2007-2008 17th June 2008 8:25 Am Question-Answer Bookjonas hoNo ratings yet
- 2017 Sem 1 - Physics 1 Test 3 & MemoDocument7 pages2017 Sem 1 - Physics 1 Test 3 & MemomphoNo ratings yet
- Class 12 National Genius Search Examination: Advanced: Test CodeDocument8 pagesClass 12 National Genius Search Examination: Advanced: Test CodePPNo ratings yet
- Physics: Question-Answer BookDocument16 pagesPhysics: Question-Answer Bookjonas hoNo ratings yet
- 08 F3 Final Exam With AnswerDocument20 pages08 F3 Final Exam With Answerjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper 2022-23 Class Xii PhysicsDocument8 pagesModel Question Paper 2022-23 Class Xii PhysicsyuvanithanrNo ratings yet
- No. 1 UCE-Physics - Paper-1Document10 pagesNo. 1 UCE-Physics - Paper-1BashirNo ratings yet
- PHYS1001 Test 1 2017 SEM-1Document14 pagesPHYS1001 Test 1 2017 SEM-1Angad MangatNo ratings yet
- Physics Tes2Document4 pagesPhysics Tes2Krishna AgarwalNo ratings yet
- B-1111-Final ExamPhysics1 - HK222 - DethiDocument3 pagesB-1111-Final ExamPhysics1 - HK222 - DethiNhật Thanh TôNo ratings yet
- 2020 Sec 3 Physics Term 3 WA 3Document10 pages2020 Sec 3 Physics Term 3 WA 3VinidraNo ratings yet
- S2 Holiday Homework 2Document14 pagesS2 Holiday Homework 24A10 FUNG CHAK FAINo ratings yet
- Aea Physics Prelims 2Document8 pagesAea Physics Prelims 2Rudraksh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class - Xi - Nipl & Nelite - Physics Desc Q.P.25.11.2023Document3 pagesClass - Xi - Nipl & Nelite - Physics Desc Q.P.25.11.2023squadralsupremeNo ratings yet
- XII - Physics - Preboard 1 - Set A 2023Document6 pagesXII - Physics - Preboard 1 - Set A 2023Anuradha MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- MT AprilDocument2 pagesMT AprilAnkit SinghNo ratings yet
- S4 Physics Paper 1-Resourceful Mock Examinations 2019ADocument11 pagesS4 Physics Paper 1-Resourceful Mock Examinations 2019ATwinomujuniNo ratings yet
- Sing Yin Secondary School First Term Test, 2019 - 2020 PhysicsDocument4 pagesSing Yin Secondary School First Term Test, 2019 - 2020 PhysicstestNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Physics Paper 1Document69 pagesPractice Paper Physics Paper 1hNo ratings yet
- 2022-JEE Main-7 Question PaperDocument11 pages2022-JEE Main-7 Question PaperAchint Kumar Mishra50% (2)
- Physics 1Document161 pagesPhysics 1Muskan PooniaNo ratings yet
- Media Communications: Test Booklet Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Paper - IDocument27 pagesMedia Communications: Test Booklet Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Paper - IRaghuNo ratings yet
- 2022-Mock JEE Main-19 - PaperDocument16 pages2022-Mock JEE Main-19 - PaperHalfborn GundersonNo ratings yet
- 2023 Unit 1 Semester 1 Physics Exam Question and Extended Answer Booklet Teams (AutoRecovered)Document19 pages2023 Unit 1 Semester 1 Physics Exam Question and Extended Answer Booklet Teams (AutoRecovered)WillsollyNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 9Document14 pagesPractice Test 9TEJASSINGH ARORANo ratings yet
- 19-08-2023_ITPL_NEET_XII_OFFLINDocument40 pages19-08-2023_ITPL_NEET_XII_OFFLINDheeraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: Solutions To JEE (Main) - 2020Document33 pagesFiitjee: Solutions To JEE (Main) - 2020srijan jhaNo ratings yet
- Mock Examination 2007 Physics Paper 2Document20 pagesMock Examination 2007 Physics Paper 2api-19650882No ratings yet
- f3 Nov 2022 Exam PaperDocument14 pagesf3 Nov 2022 Exam Paperrileydebeer21No ratings yet
- Quiz - Enthuse - Independence DayDocument6 pagesQuiz - Enthuse - Independence Dayyashwant bhaduNo ratings yet
- UCE Physics 2009 Paper 1 GuideDocument15 pagesUCE Physics 2009 Paper 1 GuideAinebyoona ChriscentNo ratings yet
- Cusat 2016Document37 pagesCusat 2016sreejitha KNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jan 10, 2024Document7 pagesAdobe Scan Jan 10, 2024rishirajkaran2006No ratings yet
- 2023 - 05 - 14 12 - 33 Office LensDocument4 pages2023 - 05 - 14 12 - 33 Office LensShyam Shankar DasNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee - Jee (Main) : Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics Phase-4Document13 pagesFiitjee - Jee (Main) : Physics, Chemistry & Mathematics Phase-4Abhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Form IvDocument6 pagesMid Term Form IvTitus KaselaNo ratings yet
- Cblephpl 04Document9 pagesCblephpl 04Srikanth G.RNo ratings yet
- 2022 JEE Main Home Practice Test - 1 - Paper (@vmclectures On Telegram)Document15 pages2022 JEE Main Home Practice Test - 1 - Paper (@vmclectures On Telegram)muktibakshiNo ratings yet
- Chem SSC 2 2nd Half BookDocument4 pagesChem SSC 2 2nd Half BookAsif AyazNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Sample Test 2 With Ans KeyDocument15 pagesJee Main Sample Test 2 With Ans KeyrahulNo ratings yet
- F2 Midyear Sample Paper MCDocument5 pagesF2 Midyear Sample Paper MCnatalie161131No ratings yet
- Questions - Physics - Electrodynamics & ElectrostaticsDocument6 pagesQuestions - Physics - Electrodynamics & Electrostaticsboorsudithi0No ratings yet
- Jss International School DubaiDocument7 pagesJss International School DubairakshitrewardsNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Science - Ut1 QP - 2021-22Document4 pagesClass 10 - Science - Ut1 QP - 2021-22MugdhaNo ratings yet
- Physics SQP - 04 Latest (2023) Class 12 CBSEDocument28 pagesPhysics SQP - 04 Latest (2023) Class 12 CBSEmr mindNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering and Technology: Term Test Question Paper - B. TechDocument3 pagesFaculty of Engineering and Technology: Term Test Question Paper - B. TechYash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- F5 Phy Final 1B 22-23Document21 pagesF5 Phy Final 1B 22-23s20139No ratings yet
- Xii PhysicsDocument9 pagesXii PhysicsLalu kuttyNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument9 pagesPhysicsAnsh MishraNo ratings yet
- 2MT Revision Practice 5Document25 pages2MT Revision Practice 5Sara -No ratings yet
- NS Grade 9 Sept 2019Document9 pagesNS Grade 9 Sept 2019Hlayiseko RikhotsoNo ratings yet
- Phy SQP3Document11 pagesPhy SQP3Kanhaiya LalNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument3 pagesForces and MotionJulia Geonzon LabajoNo ratings yet
- 02 Newtonian Mechanics AdvancedDocument37 pages02 Newtonian Mechanics AdvancedRithish BarathNo ratings yet
- PHY101 MIDTERM SOLVED MCQS by JUNAIDDocument19 pagesPHY101 MIDTERM SOLVED MCQS by JUNAIDhs6077074No ratings yet
- 3 Forces and MotionDocument34 pages3 Forces and MotionIoryNo ratings yet
- Myp 4 Summ Unit 5 Free To MoveDocument7 pagesMyp 4 Summ Unit 5 Free To MoveMiley MutolaNo ratings yet
- Part A - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesPart A - Multiple Choice QuestionsBryan SutantoNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 Syllabus 2015-16Document8 pagesPhysics 1 Syllabus 2015-16api-301989803No ratings yet
- Introduction To Particle Tracing ModuleDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Particle Tracing ModulePaulo FidelisNo ratings yet
- MBX ExplosivesDocument10 pagesMBX ExplosivesrdugasNo ratings yet
- Tabib2008 PDFDocument26 pagesTabib2008 PDFlrodriguez_892566No ratings yet
- 5 - Unsteady Flow in Rivers Pp. 122-157Document37 pages5 - Unsteady Flow in Rivers Pp. 122-157Anonymous 87xpkIJ6CFNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Second Quarter ExamDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Second Quarter ExamMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4&5 Review and Chapter 7 IntroductionDocument22 pagesChapter 4&5 Review and Chapter 7 IntroductionJunyi JiNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 HomeworkDocument10 pagesChem 1 HomeworkkwilsonNo ratings yet
- PBL Report From The Best GroupDocument8 pagesPBL Report From The Best GroupZaid ZulNo ratings yet
- Impact of A Jet - Conservation of Linear MomentumDocument6 pagesImpact of A Jet - Conservation of Linear MomentumRufus ChengNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter & Uncertainity PrincipleDocument2 pagesDual Nature of Matter & Uncertainity PrincipleParthNo ratings yet
- Group No. Course Code Course Title Unique CodeDocument74 pagesGroup No. Course Code Course Title Unique CodeMVJCE IDCARDNo ratings yet
- Analysis Method For Inertial Particle SeparatorDocument9 pagesAnalysis Method For Inertial Particle SeparatorD ARUL KUMARESANNo ratings yet
- 31bbd483 E8d3 4376 Abcc Cde0e74e950a o Level Quick Physics QN BankDocument138 pages31bbd483 E8d3 4376 Abcc Cde0e74e950a o Level Quick Physics QN BankMaama PhionaNo ratings yet
- The Specialist Committee On Validation of Waterjet Test ProceduresDocument38 pagesThe Specialist Committee On Validation of Waterjet Test Proceduresdushan diasNo ratings yet
- JR InterDocument4 pagesJR InterAswani Kumar67% (3)
- Chapter 8: Conservation Laws The Continuity EquationDocument7 pagesChapter 8: Conservation Laws The Continuity EquationMadhumika ThammaliNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Physics: Chapter-4 Momentum Study QuestionDocument2 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Physics: Chapter-4 Momentum Study QuestionMahbub KhanNo ratings yet
- ES 2 Impulse and MomentumDocument18 pagesES 2 Impulse and MomentumAbor ShawnNo ratings yet