Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sources of Electricity
Sources of Electricity
Uploaded by
raghg2005Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sources of Electricity
Sources of Electricity
Uploaded by
raghg2005Copyright:
Available Formats
Electricity
Electrical energy is the most popular form of energy, used in day to day life for Heating, Mechanical , Lighting and Transportation
purposes.
Following are the main reasons for its popularity.
1. Cleaner environments for user
2. Higher efficiency
3. Better controllability
4. Easier bulk-power, long-distance transportation of power using overhead transmission / underground cables
5. Most versatile devices of energy conversions from Electrical to other forms such as thermal, illumination,
mechanical, sound, chemical, videos etc.
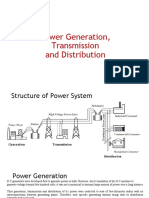
Sources for Generation of Electricity
The different sources of electrical energy are as follows:
Conventional methods Non conventional methods
a) Thermal power stations a) Solar power plants
b) Neuclear Power stations b) Wind power plants
c) Hydal power stations c) Tidal power plants
d) Biomass power plants
Conventional methods
Thermal Power Stations (Coal-fired)
India has rich stocks of coal as a natural
resource. Chemical energy stored within the
coal is converted into Electrical energy in these
power plants. Heat released by the combustion
of coal produces steam in a boiler. It is then
passed through steam turbines, which drive the
alternator. The alternator delivers electrical
energy, at its rated voltage (which may be between
11kv to 30 kV).
And this voltage is stepped up to 220kv or
400kv by the power transformers and
transmitted over long distances.
Figure shows a simple diagram of a modern
coal-fired thermal station.
RTPS : Raichur Thermal Power Plant.
Nuclear Power Stations
Nuclear energy is available as a result of fission
reaction. In a typical system, Uranium 235 is
bombarded with neutrons and Heat energy is
released. This Heat released produces steam in a
boiler. It is then passed through steam turbines,
which drive the alternator. The alternator delivers
electrical energy, at its rated voltage (which may be
between 11 to 30 kV).
And this voltage is stepped up to 220kv or 400kv
by the power transformers and transmitted over
long distances.
Fig. shows a basic diagram of a Nuclear power-
station.
Hydroelectric Power Stations
In this method of generation, water from higher height
is passed through penstock and into the water turbine.
Thus, potential energy of water stored at higher
altitudes is first converted into Kinetic energy. As
the water reaches the turbine, it gains speed after
losing the Potential energy. Kinetic energy of this
speedy water drives the water turbine, which
coupled to a generator, which gives Electrical energy
output.
A schematic diagram of such a system is shown in
fig.
Non-Conventional Energy Sources
Solar power plant (P.V. Cells or SOLAR Cells)
The solar power plant is also known as the
Photovoltaic (PV) power plant. It is a large-scale PV
plant designed to produce bulk electrical power from
solar radiation. The solar power plant uses solar energy
to produce electrical power.
Hence, to produce electrical power on a large scale,
solar PV panels are used. Below is the layout plan of
photovoltaic power plant.
Individual stations using solar cells are in operation
with ratings of the order of 250-1000 kW.
Wind Power
A wind power plant is also known as a wind farm or
wind turbine. A wind power plant is a renewable source
of electrical energy. The wind turbine is designed to use
the speed and power of wind and convert it into electrical
energy.
The wind turbine can be operating between a wind speed
of 14 km/hr to 90 km/hr.
The electric power generated from the wind power plant
varies with variations in wind velocity. But the advantage
of a wind power plant is that the operating cost of this
plant is less and it is a non-polluting source of electrical
energy.
One single wind turbine is not sufficient to produce
electrical energy in bulk amounts. Therefore, more than
one wind turbine is placed at the location at which the
wind is continually available. And that place is known as
a wind farm. Generally, wind farms are located near the
sea/hilly areas.
Tidal Power plant:
Tide or wave is periodic rise and fall of water level of the
sea. Tides occur due to the attraction of sea water by the
moon. Tides contain large amount of potential energy
which is used for power generation. When the water is
above the mean sea level, it is called flood tide. When the
water level is below the mean level it is called ebb tide.
Biomass power plant
A biomass power plant produces electricity from the steam that is released during the combustion of plant or animal
matter in a combustion chamber. This process is done in several steps:
1. Combustion: The biomass is burned in a
combustion chamber.
2. Steam production: The biomass releases
heat that heats water in a boiler. The water is
transformed into steam, which is sent under
pressure to turbines.
3. Electricity production: The steam turns a
turbine which in turn drives an alternator.
Thanks to the energy supplied by the
turbine, the alternator produces an
alternating electric current. A transformer
raises the voltage of the electric current
produced by the alternator so that it can be
more easily transported in medium and high
voltage lines.
4. Recycling: At the exit of the turbine, part of the steam is recovered to be used for heating. This is called cogeneration.
You might also like
- Caravan and Motorhome Electrics: the complete guideFrom EverandCaravan and Motorhome Electrics: the complete guideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Trilogy of Wireless Power: Basic principles, WPT Systems and ApplicationsFrom EverandTrilogy of Wireless Power: Basic principles, WPT Systems and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- SLM Science 9Document10 pagesSLM Science 9Rycel BueronNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 GENERATION Edited Sesi1 (Autosaved)Document92 pagesCHAPTER 2 GENERATION Edited Sesi1 (Autosaved)Danieal HakimNo ratings yet
- Understanding Transmission of ElectricityDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Transmission of ElectricityismailNo ratings yet
- Ngrid - Be The Source - How Electricity Made TransmittedDocument4 pagesNgrid - Be The Source - How Electricity Made TransmittedMark WoodNo ratings yet
- Introduction: Structure of Power SystemDocument3 pagesIntroduction: Structure of Power SystemAasif SubhaniNo ratings yet
- Q4 M7 Electrcity and Magnetism 1Document30 pagesQ4 M7 Electrcity and Magnetism 1kliz TanNo ratings yet
- Geothermal PlantDocument4 pagesGeothermal PlantJamandre, Joseph M.No ratings yet
- Bu 2 - ElectricalDocument6 pagesBu 2 - ElectricalSharmaine Danica MarceloNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Electrical EngineeringDocument28 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Electrical EngineeringC SelvenNo ratings yet
- LEC-1 Electric Supply SystemDocument30 pagesLEC-1 Electric Supply SystemRafia AsifNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 6 Electricity and MagnetismDocument24 pagesF3 Chapter 6 Electricity and MagnetismJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- What Is Renewable Energy ?Document38 pagesWhat Is Renewable Energy ?ASR REDDYNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 1.0 Introduction To Electrical Power SystemDocument15 pagesCHAPTER 1 1.0 Introduction To Electrical Power SystemMUHAMMAD ALIFF DANIAL RAZMINo ratings yet
- Electrical Installation System in The BuildingDocument44 pagesElectrical Installation System in The BuildingNKWENTI FLAVIOUS TANUENo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL THEORY - Group 2 - 085619Document51 pagesELECTRICAL THEORY - Group 2 - 085619BASITO, CHRISTIAN PAUL B.No ratings yet
- 2&3 Sistem Pembangkit TenagaDocument62 pages2&3 Sistem Pembangkit TenagaGalihNo ratings yet
- أساسيات هندسة القوى الكهربائية-1Document53 pagesأساسيات هندسة القوى الكهربائية-1Salim AlabriNo ratings yet
- EEE 210 - Introduction To Power SystemsDocument5 pagesEEE 210 - Introduction To Power SystemsAgbolade OluwaseyiNo ratings yet
- Power PlantsDocument7 pagesPower Plantsjoshuapagay.abmNo ratings yet
- Forms of EnergyDocument18 pagesForms of EnergyJAYESHNo ratings yet
- Electrical Supply SystemDocument52 pagesElectrical Supply SystemfarahNo ratings yet
- Unit1 - Introduction To Electrical Power NotesDocument14 pagesUnit1 - Introduction To Electrical Power Notes1ms20ei002No ratings yet
- Grade 6 Renewable Energy SourcesDocument60 pagesGrade 6 Renewable Energy SourcesMohammad Hazaa El-SherifNo ratings yet
- Battery DC Generator Electric Power Voltage: NextDocument13 pagesBattery DC Generator Electric Power Voltage: NextHussam GujjarNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document3 pagesExp 3HR HabibNo ratings yet
- I. Electrical Systems: Ar. Harvin Julius Lasquero, Uap Ar. Earl Quinn Varilla, UapDocument70 pagesI. Electrical Systems: Ar. Harvin Julius Lasquero, Uap Ar. Earl Quinn Varilla, Uapjomarie apolinarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Generation of Electricity (Penjanaan Elektrik)Document29 pagesChapter 8: Generation of Electricity (Penjanaan Elektrik)Mohd AzlanNo ratings yet
- Power Generation & Distribution: Group MembersDocument19 pagesPower Generation & Distribution: Group MembersCS-57 Ritesh ShingoteNo ratings yet
- BEE Unit-5Document26 pagesBEE Unit-5gunasundar choppaNo ratings yet
- L5 & L6-ElectricityDocument24 pagesL5 & L6-ElectricityZwile MsibiNo ratings yet
- IntroMechEng Lecture3Document7 pagesIntroMechEng Lecture3metehanf764No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Unit - 1Document16 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Unit - 1S085 Pranav HNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 37Document1 pageTHBHDK 37RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- CHAP 1, Lecture 1-A Fundamental's of Power SystemDocument54 pagesCHAP 1, Lecture 1-A Fundamental's of Power SystemBiruk DawitNo ratings yet
- Practical ElectricityDocument70 pagesPractical ElectricityBjorn Low100% (1)
- BNB 31403 Electrical & Energy SupplyDocument18 pagesBNB 31403 Electrical & Energy SupplyAidi RedzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Solar EnergyDocument33 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Solar EnergyNathan EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- M4 Ch2 Electric Power Generation PDFDocument5 pagesM4 Ch2 Electric Power Generation PDFMujeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Solar Based Induction CooktopDocument5 pagesSolar Based Induction CooktopSunil MåüřÿäNo ratings yet
- Uty 2Document3 pagesUty 2Lei Yunice NorberteNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Figure 1. Geothermal Power PlantDocument2 pagesElectricity and Magnetism: Figure 1. Geothermal Power PlantRicky Peñaroyo VentozaNo ratings yet
- Sources of Electrical Power Supply.Document10 pagesSources of Electrical Power Supply.Lawrence Wahome ngariNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Basics of Energy and Its Various FormsDocument19 pages1.2 Basics of Energy and Its Various FormsKali DasNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument121 pagesElectricityKhairul Hazwan100% (3)
- KS3 LeaP Q4 W8 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISMDocument6 pagesKS3 LeaP Q4 W8 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISMtolisNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit&MechineDocument96 pagesElectrical Circuit&MechineDipendra Bahadur SinghNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Grade 9Document20 pagesScience 9 Grade 9c50799454No ratings yet
- 14.9 The Power Station: Thermal Power Stations All Start by Making HeatDocument1 page14.9 The Power Station: Thermal Power Stations All Start by Making HeatSuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Elrctrical Power Engineering SyllabusDocument75 pagesElrctrical Power Engineering Syllabusgishi_sjdc6983No ratings yet
- COURS D'INSTALL. TLe F3 enDocument69 pagesCOURS D'INSTALL. TLe F3 eneugeni madaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Part 2 - EE 421Document5 pagesModule 1 - Part 2 - EE 421Mirasol JavierNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document24 pagesModule 1Ramiksha ShettyNo ratings yet
- BBC - GCSE Bitesize - Generating ElectricityDocument5 pagesBBC - GCSE Bitesize - Generating ElectricityinejattNo ratings yet
- q4 Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesq4 Electricity and MagnetismBishIn aMillionNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Electricity Supply and Regulation in IndiaFrom EverandIntroduction to Electricity Supply and Regulation in IndiaNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- The Shocking World of Electricity with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Shocking World of Electricity with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Engineering: 6 Aug 18 Oct 16 Nov Engineering I T F Engineering S R R S in T Are S e TDocument1 pageSteam Power Engineering: 6 Aug 18 Oct 16 Nov Engineering I T F Engineering S R R S in T Are S e TaftabNo ratings yet
- 33.regulation On The Scope and Method For The Performance of Safety Analyses and The Scope of The Preliminary Safety Report For A Nuclear FacilityDocument39 pages33.regulation On The Scope and Method For The Performance of Safety Analyses and The Scope of The Preliminary Safety Report For A Nuclear FacilityFernando A.No ratings yet
- Wang 2016Document9 pagesWang 2016Amore SNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Corporation of India - WikipediaDocument9 pagesNuclear Power Corporation of India - WikipediaChethan HalkurNo ratings yet
- Role of NDT in Mega Projects - Md. Faruque Hossain ChowdhuryDocument28 pagesRole of NDT in Mega Projects - Md. Faruque Hossain ChowdhuryFatin IshraqueNo ratings yet
- Consolis Presentation - Bonna RCCP PDFDocument61 pagesConsolis Presentation - Bonna RCCP PDFiabdillahNo ratings yet
- Contoh Discussion TextDocument19 pagesContoh Discussion TextAmalia MeisyaNo ratings yet
- Hyo Sung EbaraDocument33 pagesHyo Sung Ebaraduongbk24 luu quang duongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1M.Hassan AliNo ratings yet
- 012 NAPS UFSAR Chapter 12Document94 pages012 NAPS UFSAR Chapter 12Russell ShacklefordNo ratings yet
- Central Electricity Authority Go&Dwing Operation Performance Monitoring DivisionDocument4 pagesCentral Electricity Authority Go&Dwing Operation Performance Monitoring DivisionData CentrumNo ratings yet
- Estudio de ViabilidadDocument288 pagesEstudio de ViabilidadEl Nuevo DíaNo ratings yet
- Revised Syllabus: M. Tech. (Energy Sciences)Document39 pagesRevised Syllabus: M. Tech. (Energy Sciences)TalibNo ratings yet
- CVE471 Lecture Notes 9 - Hydroelectric PowerDocument28 pagesCVE471 Lecture Notes 9 - Hydroelectric PowermohammedNo ratings yet
- Shizen EnergyShizen Energy Group and Alam Nix Renewables Complete 1MW Solar Power Plant in IndonesiaDocument3 pagesShizen EnergyShizen Energy Group and Alam Nix Renewables Complete 1MW Solar Power Plant in IndonesiaAzzahra PrabudiNo ratings yet
- Physics Nat ReviewDocument134 pagesPhysics Nat ReviewGon FrecssNo ratings yet
- 2 Soal Bahasa InggrisDocument16 pages2 Soal Bahasa InggrisAnanta Qawama FikriNo ratings yet
- Solar Power For Beginners Basics Design and Installation of A Solar Panel System The Complete Guide For Your Off Grid HomeDocument96 pagesSolar Power For Beginners Basics Design and Installation of A Solar Panel System The Complete Guide For Your Off Grid HomeTek_nikkosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Non-Conventional Sources of Energy - SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 13 - Non-Conventional Sources of Energy - SummaryMayank SahuNo ratings yet
- Power Generation, Transmission and DistributionDocument15 pagesPower Generation, Transmission and DistributionSaiei ei100% (1)
- ME8792 Power Plant Engineering SyllabusDocument2 pagesME8792 Power Plant Engineering SyllabusThangamKumarNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Electrical AppliancesDocument38 pagesUnit3 Electrical Appliances21MEB358 Kunal AryaNo ratings yet
- Commercial ApplicationsDocument6 pagesCommercial ApplicationsAaryaman Rathi (Yr. 21-23)No ratings yet
- AP1000 Design Control Document: Tier 2 Master Table of Contents Section TitleDocument32 pagesAP1000 Design Control Document: Tier 2 Master Table of Contents Section TitleBob HavrNo ratings yet
- Clauses of PurposeDocument1 pageClauses of PurposeAydın YaşarNo ratings yet
- Developing Arguments: Test Section - Writing Task 2Document13 pagesDeveloping Arguments: Test Section - Writing Task 2Cengizhan AkdağNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Reading Practice (Oct 4Th, 2021) Reading Passage IDocument5 pagesLesson 4 Reading Practice (Oct 4Th, 2021) Reading Passage INguyễn Phương NgọcNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Fusion1Document12 pagesNuclear Fusion1Rajesh MeppayilNo ratings yet
- 1258GH785Document31 pages1258GH785Ali ANo ratings yet
- Isotopes: Characteristics and Properties of IsotopeDocument2 pagesIsotopes: Characteristics and Properties of IsotopeAnara HannahNo ratings yet