Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FAQID x264
FAQID x264
Uploaded by
napoleonmOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FAQID x264
FAQID x264
Uploaded by
napoleonmCopyright:
Available Formats
Article ID: x264 - Bonded contact using constraint equations
Bonded contact using constraint equations
Article ID: x264
Solution ID: S-018871
Applies to: SOLIDWORKS Simulation, COSMOSM
Version: 2006 and up
Category: Contact
Created: 09/05/2005
Last Revised: 11/23/2016
Discussion
For SOLIDWORKS Simulation
Starting with version 2006, bonded contact can be defined between geometric entities having an
incompatible or compatible mesh.
The way it works in static studies is summarized in the table below:
Selected source and target touch each Selected source and target are separated by a gap
other
Target is face of Target is face of Target is face of Target is face Target is edge
solid body shell solid body of shell of shell
Source is Up to 2011: Mesh is incompatible and 6 constraint equations are
Beam joint created per beam joint (for each 3 translational DOF and 3 rotational
DOF of the single source node on the beam joint). The program
projects the Beam joint onto the face (normal projection if the face is
planar, more sophisticated way if not). The beam joint is only
connected to the face of the element on which the projection happens
to lie.
2012 and up: Beam cross section is imprinted onto the shell/solid face.
Constraint equations are created between the Beam end nodes and all
the nodes on the imprint. If the imprint fails, then the 2011 method is
used.
Source is Mesh is incompatible and 6 constraint equations are created per node Mesh is
whole on the beam (for each 3 translational DOF and 3 rotational DOF of the incompatible.
beam each source node on the beam). Currently, the program projects each The program
beam node onto the face (normal projection if the face is planar, more projects all the
sophisticated way if not). Then each beam node is only connected to nodes of the
the face of the element on which the projection happens to lie. shell edge
radially onto
the beam.
file:///D|/Product%20Management/KnowledgeBase/FAQID__x264.htm (1 of 4) [3/10/2017 11:07:39 AM]
Article ID: x264 - Bonded contact using constraint equations
Source is If possible, nodes If vertices are Mesh is incompatible and 6 2015 and up:
vertex of are coincident, but coincident, then constraint equations are created possible in 2D
shell never merged. 6 the program tries per node of the source entity simplification
constraint to merge nodes. (for each 3 translational DOF analysis
equations are Everywhere else, and 3 rotational DOF of the
created per node of mesh is source node)
the source entity incompatible and
(for each 3 6 constraint
translational DOF equations are
Source is and 3 rotational created per node
of face DOF of the source of the source
shell node) entity (for each 3
translational DOF
and 3 rotational
DOF of the
source node)
Source is 2012 and up: If possible, 2012 and up: 6 constraint 2015 and up: 6
edge of When More nodes are When More equations are constraint
shell Accurate method coincident, but Accurate created per equations are
is used, shell end never merged. method is used, node of the generated
face (with thickness 6 constraint shell end face source entity When More
and offset) is equations are (with thickness (for each 3 Accurate
virtually imprinted created per and offset) is translational method is used,
onto the face and node of the virtually DOF and 3 element edges
constraint source entity imprinted onto rotational DOF on the source
equations are (for each 3 the face and of the source edge are
created between translational constraint node) bonded to
the nodes of the DOF and 3 equations are element edges
shell edge and the rotational DOF created between on the target.
nodes on the of the source the nodes of the
node) When
imprint zone. shell edge and Simplified
When Simplified the nodes on bonding
bonding method is the imprint zone. method is used,
used, offset and When nodes on the
shell thickness are Simplified source edge are
ignored. 6 bonding method bonded to
constraint is used, offset element edges
equations are and shell on the target.
created per node of thickness are
the source entity ignored. 6
(for each 3 constraint
translational DOF equations are
and 3 rotational created per
DOF of the source node of the
node) source entity
(for each 3
translational
DOF and 3
rotational DOF
of the source
node)
file:///D|/Product%20Management/KnowledgeBase/FAQID__x264.htm (2 of 4) [3/10/2017 11:07:39 AM]
Article ID: x264 - Bonded contact using constraint equations
Source is Mesh is Mesh is incompatible and 3 constraint equations
vertex of incompatible and 3 are created per node of the source entity (for each
solid body constraint 3 translational DOF of the source node - there is no
equations are rotational DOF )
created per node of
the source entity
Source is (for each 3
edge of translational DOF of
solid body the source node -
there is no
rotational DOF )
Source Mesh is compatible
face of and nodes are
solid body merged
Note:
● For more information, please refer to See Article ID: x428 - Bonded contact between non-
touching entities (Solution ID: S-034488).
● Only Static, frequency, buckling, thermal, and linear dynamic studies let users choose
between the More Accurate and Simplified bonding methods. In nonlinear studies, the
Simplified method is used.
● The More Accurate and Simplified bonding methods are compatible with High quality
and Draft quality elements.
● Because the constraint equations are created for the nodes on the Source entity, 6
equations per nodes are created if the source entity belongs to shell elements, while only
3 constraint equations are created if the source entity belongs to solid elements.
Therefore, when a vertex or a straight edge from a solid is selected as source, a spherical
or hinge joint is created instead of a rigid joint.
● More accurate results will be obtained if the created mesh is such that nodes on Source
and Target entity are coincident. To achieve this, you may have to create Split lines.
For COSMOSM only
The following points should be considered in the application of this command:
1. Bonding internally uses constraint equations to match the displacements and rotations of the
two parts. The quality assurance tests have shown that for parts with reasonable stiffness
properties and mesh densities, the maximum displacement and stress values obtained from
the bond command are within ten percent of those values obtained from a merged model
with compatible elements.
2. This command is currently applicable to linear static and nonlinear structural analysis,
frequency and buckling analysis as well as heat transfer analysis.
3. When bonding solids and shells, it is advisable to use shells as the source and solids as the
target irrespective of the element order.
4. When shell elements are connected to solid elements, the common nodes at the boundary
file:///D|/Product%20Management/KnowledgeBase/FAQID__x264.htm (3 of 4) [3/10/2017 11:07:39 AM]
Article ID: x264 - Bonded contact using constraint equations
should not be merged as this will free the rotational degrees of shell at that node. Actually, it
is advantageous not to have coincident nodes at all in such problems. In shell-to-shell, or,
solid-to-solid connections, merging of the coincident nodes at the boundary is allowed.
5. In problems where the stress concentration at the bonded intersection is critical, both parts
should have a fine mesh in this region.
6. The results obtained may deteriorate in problems where a rigid part is connected to a
relatively flexible part. The bonded area in the flexible part undergoes warping or has high
displacement gradients. The results will improve if the mesh density for the flexible part is
increased in the bonded area.
7. The actual constraint relations between the nodes of source and target geometric entities are
formed and computed in the analysis stage.
Note:
● The above recommendations come from the COSMOSM Basic FEA System manual's
chapter 8: Modeling and Analysis Guidelines (pages 8-1 to 8-7).
file:///D|/Product%20Management/KnowledgeBase/FAQID__x264.htm (4 of 4) [3/10/2017 11:07:39 AM]
You might also like
- As 1228-2006 Pressure Equipment - BoilersDocument9 pagesAs 1228-2006 Pressure Equipment - BoilersSAI Global - APAC20% (5)
- HLCL Container Inspection ManualDocument36 pagesHLCL Container Inspection ManualAlexis Antonio Francois Reyes100% (4)
- Sti07 - Cerig Rbe3 Rigid184 PDFDocument6 pagesSti07 - Cerig Rbe3 Rigid184 PDFtriboniNo ratings yet
- 6522ENG Lecture6Document32 pages6522ENG Lecture6Junaid AshrafNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument10 pagesCase Studytran hungNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FEA: Won Hyun ParkDocument25 pagesIntroduction To FEA: Won Hyun Park04935No ratings yet
- Modelling TechniqueDocument13 pagesModelling TechniqueیاسرانسNo ratings yet
- Part 2 JointsDocument15 pagesPart 2 JointsManny CheungNo ratings yet
- GraphDocument14 pagesGraphsdsourav713No ratings yet
- Tie BreakDocument33 pagesTie Breaksuribala100% (3)
- Graph IsoDocument26 pagesGraph IsoJim WangNo ratings yet
- FEA Basic Theory IntroductionDocument33 pagesFEA Basic Theory IntroductionAshokNo ratings yet
- Cerig Rbe3 Rigid184Document6 pagesCerig Rbe3 Rigid184Balaji ModepalliNo ratings yet
- Devdept - Eyeshot.entities ClassesDocument10 pagesDevdept - Eyeshot.entities Classesnirmal sutharNo ratings yet
- Handout7 DynamicsDocument12 pagesHandout7 DynamicsRituraj KaushikNo ratings yet
- CPES Networked Control System IDocument43 pagesCPES Networked Control System IJhonNo ratings yet
- 7231 Protein Interface Prediction Using Graph Convolutional NetworksDocument10 pages7231 Protein Interface Prediction Using Graph Convolutional NetworksVishal D MishraNo ratings yet
- CH3 - Stiffness Method - Beams FramesDocument58 pagesCH3 - Stiffness Method - Beams Frames2499361939wNo ratings yet
- Shell Elements in AbaqusDocument26 pagesShell Elements in Abaqusnaghdi.mnnNo ratings yet
- Vol.1 - 37 - What Is The Difference Between Rigid Link and Rigid Type Elastic LinkDocument3 pagesVol.1 - 37 - What Is The Difference Between Rigid Link and Rigid Type Elastic Linklim kang haiNo ratings yet
- Number Synthesis Isomers Linkage TransformationDocument14 pagesNumber Synthesis Isomers Linkage TransformationSaleem KhanNo ratings yet
- FEA Element TypesDocument30 pagesFEA Element TypesGoutam AcharjeeNo ratings yet
- Glue ModellingDocument3 pagesGlue ModellinggeppolaNo ratings yet
- Overcoming Model Singularities in Nastran (Or Any Other Finite Element System)Document7 pagesOvercoming Model Singularities in Nastran (Or Any Other Finite Element System)flcwkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: CROSSOVERDocument15 pagesChapter 9: CROSSOVERMorteza SharafiNo ratings yet
- FEA Element Types: Truss Element (2D Line)Document4 pagesFEA Element Types: Truss Element (2D Line)imranNo ratings yet
- DEM Application: WARNING: This Page Is Still Under Construction. The DEM Kratos TeamDocument35 pagesDEM Application: WARNING: This Page Is Still Under Construction. The DEM Kratos TeamRuben PurcaNo ratings yet
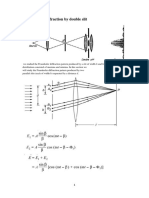
- Fraunhofer Diffraction by Double SlitDocument8 pagesFraunhofer Diffraction by Double SlitMuhîbNo ratings yet
- RefmanDocument19 pagesRefmanerva.kutluNo ratings yet
- 27-04-2021-1619511864-6-Ijme-1. Ijme - A Cooperative Augmented Reality - Ar - Framework Based On Distributive Visual SlamDocument12 pages27-04-2021-1619511864-6-Ijme-1. Ijme - A Cooperative Augmented Reality - Ar - Framework Based On Distributive Visual Slamiaset123No ratings yet
- INF574 - Lecture 5 - ReconstructionDocument28 pagesINF574 - Lecture 5 - ReconstructionJackson SunnyNo ratings yet
- Contatto in ANSYSDocument20 pagesContatto in ANSYSmatteo.daccNo ratings yet
- Representing Things With Neurons: CSC2535: Computation in Neural NetworksDocument23 pagesRepresenting Things With Neurons: CSC2535: Computation in Neural NetworksE6330 HALNo ratings yet
- Femap - Rbe2 & Rbe3Document6 pagesFemap - Rbe2 & Rbe3Hesham Abd El-azizNo ratings yet
- Flac InterfaceDocument34 pagesFlac InterfaceLuca Brandi100% (1)
- Re-Examination of JRC - DR Wong - HKRG-20160223Document20 pagesRe-Examination of JRC - DR Wong - HKRG-20160223Nguyen Viet HaNo ratings yet
- Community v4Document31 pagesCommunity v4E JagadeeshNo ratings yet
- Tinning PDFDocument5 pagesTinning PDFMoise SoaresNo ratings yet
- Book 279Document1 pageBook 279as dds aaadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - 1 Kinematics - Forward (00-11-17)Document53 pagesLecture 3 - 1 Kinematics - Forward (00-11-17)MahdiNo ratings yet
- Shell ElementsDocument5 pagesShell ElementsmohgscribdNo ratings yet
- Progressive Image Compression With Ridgelets and Vector QuantizationDocument7 pagesProgressive Image Compression With Ridgelets and Vector Quantizationvol1no3No ratings yet
- Steel Design: Stability of BeamsDocument7 pagesSteel Design: Stability of BeamsYousif alhassankoNo ratings yet
- Mesh-Intro 19R2 M05 Lecture Slides Mesh Quality and Advanced TopicsDocument60 pagesMesh-Intro 19R2 M05 Lecture Slides Mesh Quality and Advanced TopicsSahil Jawa100% (1)
- 5 Interfaces: 5.1 General CommentsDocument36 pages5 Interfaces: 5.1 General CommentsGuido AndreottiNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Project Report: Usama Mehmood - 110614650 Stony Brook UniversityDocument6 pagesComputer Graphics Project Report: Usama Mehmood - 110614650 Stony Brook UniversityUsama MehmoodNo ratings yet
- The Fracpole Suite: The Designer's Guide CommunityDocument12 pagesThe Fracpole Suite: The Designer's Guide CommunityalirezadNo ratings yet
- Finite Difference MethodsDocument3 pagesFinite Difference MethodsFelipe LucenaNo ratings yet
- Submarine HybridDocument6 pagesSubmarine Hybridali.kalairNo ratings yet
- Question 2Document2 pagesQuestion 2ejaknonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1b MobilityDocument85 pagesChapter 1b Mobility劉德信No ratings yet
- SM - Ug 21 54Document34 pagesSM - Ug 21 54Quốc Thanh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Optical FibreDocument2 pagesOptical Fibrelovelyboy.yashNo ratings yet
- DEMEA - Deep Mesh Autoencoders For Non-Rigidly Deforming ObjectsDocument27 pagesDEMEA - Deep Mesh Autoencoders For Non-Rigidly Deforming ObjectsLakshika RathiNo ratings yet
- Saliency Detection Via Absorbing Markov ChainDocument8 pagesSaliency Detection Via Absorbing Markov ChainHania NoorNo ratings yet
- Physical Metallurgy II - 03 Crystal InterfacesDocument32 pagesPhysical Metallurgy II - 03 Crystal Interfacesmehrnoosh seifalianNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Surface Extraction From Anisotropic Volumetric Data - Contouring On Generalized OctreesDocument13 pagesAdaptive Surface Extraction From Anisotropic Volumetric Data - Contouring On Generalized OctreesthekiwisenseiNo ratings yet
- VEX Attribute GlossaryDocument10 pagesVEX Attribute GlossaryKartikeye SisodiyaNo ratings yet
- Measurement of RiDocument6 pagesMeasurement of Risaikat mitraNo ratings yet
- A Computationally Efficient Framework For Modeling Soft Body ImpactDocument10 pagesA Computationally Efficient Framework For Modeling Soft Body ImpactsasidharNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Finite Element Method TheoryDocument32 pagesLecture - Finite Element Method TheoryJumaane ShakespeareNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural Networks: Fundamentals and Applications for Analyzing Visual ImageryFrom EverandConvolutional Neural Networks: Fundamentals and Applications for Analyzing Visual ImageryNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Snap ThroughDocument4 pagesDynamic Snap ThroughnapoleonmNo ratings yet
- On Snap-Through BucklingDocument9 pagesOn Snap-Through BucklingnapoleonmNo ratings yet
- ALE and Fluid-Structure Interaction Capabilities in LS-DynaDocument10 pagesALE and Fluid-Structure Interaction Capabilities in LS-DynanapoleonmNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Technologies Part 2Document100 pagesFundamentals of Vacuum Technologies Part 2napoleonmNo ratings yet
- Identification of High Surge Pressure in LNG Loading Lines SystemDocument5 pagesIdentification of High Surge Pressure in LNG Loading Lines SystemnapoleonmNo ratings yet
- Tissot Touch ManualDocument14 pagesTissot Touch ManualnapoleonmNo ratings yet
- Models - Sme.postbuckling ShellDocument12 pagesModels - Sme.postbuckling ShellnapoleonmNo ratings yet
- 11468-Article Text - Manuscript-32620-2-10-20170707Document8 pages11468-Article Text - Manuscript-32620-2-10-20170707napoleonmNo ratings yet
- Stress Concentrations - How To Identify and Reduce Them in Your DesignsDocument11 pagesStress Concentrations - How To Identify and Reduce Them in Your DesignsnapoleonmNo ratings yet
- Comsol Composite Materials Module Users GuideDocument68 pagesComsol Composite Materials Module Users GuidenapoleonmNo ratings yet
- The United States Navy and Israeli NavyDocument66 pagesThe United States Navy and Israeli NavynapoleonmNo ratings yet
- Few Layer Graphne Based Superlattices As Efficient Thermal InsulatorsDocument7 pagesFew Layer Graphne Based Superlattices As Efficient Thermal InsulatorsnapoleonmNo ratings yet
- Cryogenic Characteristics of Graphene CompositesDocument39 pagesCryogenic Characteristics of Graphene CompositesnapoleonmNo ratings yet
- Offer: Offer Address Delivery AdressDocument2 pagesOffer: Offer Address Delivery AdressnapoleonmNo ratings yet
- LH2 Safety and Design Considerations ImportantDocument47 pagesLH2 Safety and Design Considerations ImportantnapoleonmNo ratings yet
- ISO TS 18683-2021 Ed.2 Id.76811 Publication PDF (En)Document49 pagesISO TS 18683-2021 Ed.2 Id.76811 Publication PDF (En)napoleonmNo ratings yet
- Gutteling Datasheet 2016 Hoses Multi-LNG WhiteDocument2 pagesGutteling Datasheet 2016 Hoses Multi-LNG WhitenapoleonmNo ratings yet
- Pre-Normative REsearch For Safe Use of Liquid HydrogenDocument151 pagesPre-Normative REsearch For Safe Use of Liquid HydrogennapoleonmNo ratings yet
- Part Lis Pump KSB ViktorindoDocument2 pagesPart Lis Pump KSB Viktorindopnni minastimur15No ratings yet
- ColorQube 8870 PartsDocument7 pagesColorQube 8870 PartsGeorgeguillotinesNo ratings yet
- Biomekanika Cedera KepalaDocument14 pagesBiomekanika Cedera KepalaramadhankurniawanNo ratings yet
- Chap 41 PDFDocument22 pagesChap 41 PDFnelson escuderoNo ratings yet
- Happy Diwali Practice PaperDocument16 pagesHappy Diwali Practice PaperTutorial VideoNo ratings yet
- 019 - OM Hollowgram Wheel Sets - 134944 - ENDocument16 pages019 - OM Hollowgram Wheel Sets - 134944 - ENLowman JuniorNo ratings yet
- E12 Cluster Removal and Odometer RepairDocument6 pagesE12 Cluster Removal and Odometer RepairVicente PerezNo ratings yet
- JC70DB Draw Works Parts ListDocument22 pagesJC70DB Draw Works Parts ListLakshmi Kishore100% (1)
- Diamatre Teava - PEDDocument72 pagesDiamatre Teava - PEDAlin TomozeiNo ratings yet
- Ds BurnDocument63 pagesDs BurnmahsaNo ratings yet
- Tribology of Polymers Adhesion, Friction, Wear, and Mass-TransferDocument12 pagesTribology of Polymers Adhesion, Friction, Wear, and Mass-TransferDersein SaraozNo ratings yet
- Singly Reinforced Concrete Beam Design ExampleDocument16 pagesSingly Reinforced Concrete Beam Design Exampleyamen0% (1)
- Pajero Full 2008 13Document1,059 pagesPajero Full 2008 13Antonio GasparNo ratings yet
- Increase of Wear Resistance of The Drill Pipe Thread Connection by Electromechanical Surface HardeningDocument5 pagesIncrease of Wear Resistance of The Drill Pipe Thread Connection by Electromechanical Surface HardeningQuality controllerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PDFDocument40 pagesChapter 5 PDFImran Rasheed100% (1)
- A3G4I2 - Attachment 2 - A Process and Instrumentation DiagramsDocument11 pagesA3G4I2 - Attachment 2 - A Process and Instrumentation DiagramsAlfonsus W.M.No ratings yet
- CompressorDocument456 pagesCompressorsatfasNo ratings yet
- Bike - Speed Vs RPMDocument6 pagesBike - Speed Vs RPMjohari23No ratings yet
- IVECO NEF SeriesDocument36 pagesIVECO NEF SeriesOlivier ORMANNo ratings yet
- TUFF Static Scissor Lift TablesDocument1 pageTUFF Static Scissor Lift TablesRarisgrup OficialNo ratings yet
- Study of Influence of Notch Root RadiusDocument12 pagesStudy of Influence of Notch Root RadiusLuan CaetanoNo ratings yet
- Allowable Deflection of PipesDocument4 pagesAllowable Deflection of PipesTAMER RAGAANo ratings yet
- A320LEAP1A-B12-0008.5 Cont&Ind R1 220517Document78 pagesA320LEAP1A-B12-0008.5 Cont&Ind R1 220517simsimsomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Design of Low Friction SurfacesDocument28 pagesChapter 11 Design of Low Friction SurfacesShivam AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Hvac AssignmentDocument9 pagesHvac AssignmentCharu GargNo ratings yet
- Eriksson 2009Document12 pagesEriksson 2009sxasxasxNo ratings yet
- 4 - Review Notes - MOTORS & ENGINESDocument17 pages4 - Review Notes - MOTORS & ENGINESJoebert SabidoNo ratings yet
- Commande 12.21Document2 pagesCommande 12.21M B F SOLUTIONNo ratings yet