Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tuckman's Stages of Group Development - WCU of PA
Tuckman's Stages of Group Development - WCU of PA
Uploaded by
tuana.jan.koyuncu.tjOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tuckman's Stages of Group Development - WCU of PA
Tuckman's Stages of Group Development - WCU of PA
Uploaded by
tuana.jan.koyuncu.tjCopyright:
Available Formats
REQUEST VISIT APPLY GIVE
MENU
INFO CAMPUS NOW TODAY
WCU HOME > COLLABORATIVE ON-LINE RESEARCH AND LEARNING > TUCKMAN'S STAGES OF GROUP DEVELOPMENT
COLL ABOR ATIVE ON-LINE RESE ARCH AND
LE ARNING
CONTACT COLLABORATIVE ON-LINE RESEARCH AND LEARNING
HOME COLLABORATIVE RESOURCES TEAMS SCALES ADMINISTRATION
T U CK M A N ' S S TAG E S O F G R O U P D E V E LO P M E N T
Stages of Group Development
These stages are commonly known as: Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing, and Adjourning. Tuckman's model explains that as the team develops maturity and ability, relationships establish, and
leadership style changes to more collaborative or shared leadership.
Tuckman's original work simply described the way he had observed groups evolve, whether they were conscious of it or not. In CORAL, the real value is in recognizing where a team is in the developmental
stage process, and assisting the team to enter a stage consistent with the collaborative work put forth. In the real world, teams are often forming and changing, and each time that happens, they can move to
a different Tuckman Stage. A group might be happily Norming or Performing, but a new member might force them back into Storming, or a team member may miss meetings causing the team to fall back
into Storming. Project guides will be ready for this, and will help the team get back to Performing as quickly as possible.
Forming
The initial forming stage is the process of putting the structure of the team together. Team members feel ambiguous and conflict is avoided at all costs due to the need to be accepted into the group. Team
members look to a group leader for direction and guidance, usually CORAL project guides.
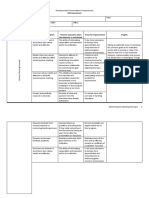
Observable Behaviors Feelings and Thoughts Team Needs Leadership Required
Politeness Many feel excited, optimistic, and full of Team mission and vision Project Guides & Instructors
Tentative joining anticipation Establish specific objectives and tasks provide structure and task direction
Orienting with others personally Others may feel suspicious, fearful, and Identify roles and responsibilities of team Allow for get-acquainted time
Avoids controversy anxious working with others members Create an atmosphere of confidence and
Cliques may form What is expected of me Establish team ground rules optimism
Need for safety and approval Why are they here Team member expectations Active involvement
Attempts to define tasks, processes, and how Uncertainty and Apprehension Operational guidelines for team Team members believe an appointed leader
it will be decided here Effective in class meetings necessary to make decisions
Discussion of problems not relevant to the Effective Chat meetings One-way communication from leader to
task 1st set of feedback from project guides team-members
To advance from this stage to the next stage, each member must relinquish the comfort zone of non-threatening topics and risk the possibility of conflict.
Storming
This stage begins to occur as the process of organizing tasks and processes surface interpersonal conflicts. Leadership, power, and structural issues dominate this stage.
Observable Behaviors Feelings & Thoughts Team Needs Leadership Required
Arguing among members Feel Defensive Inter & intra personal relationships Project guide & Instructors acknowledge
Vying for leadership Confusion, loss of interest can result Identify stylistic and personal differences conflict
Differences in points of view and personal Resistance to tasks Effective listening Project Guides suggest that consensus
style are evident Fluctuations in attitude about the team Giving and receiving feedback among team members
Lack of role clarity Unsure if I agree with teams mission and Conflict resolution Get members to assume more task
Team organizing itself purpose Clarify and understand the team’s purpose responsibility
Power struggles and clashes Question the wisdom of team members Reestablish roles and ground rules Concept of Shared Leadership emerges
Lack of consensus-seeking behaviors Increase in tension and jealousy How to deal with ‘some’ team members Teach conflict resolution methods
Lack of progress Unsure about my personal influence and violating team codes of conduct Offer support and praise
Establishes unrealistic goals freedom in the team Receiving Feedback from project guide Actively involved Team members begin
Concern over excessive work We're not getting anywhere consulting one another – shared leadership
emerging but have difficulty with decision
making
In order to progress to the next stage, group members must move from a "testing and proving" mentality to a problem-solving mentality. The most important trait in helping teams move to the next stage
is the ability of team members to listen to their team mates - what are they trying to say?
Norming
In this stage, team members are creating new ways of doing and being together. As the group develops cohesion, leadership changes from ‘one’ teammate in charge to shared leadership. Team members
learn they have to trust one another for shared leadership to be effective.
Observable Behaviors Feelings & Thoughts Team Needs Leadership Required
Processes and procedures are agreed upon Sense of belonging to a team Develop a decision making process Shared leadership
Comfortable with relationships Confidence is high Be prepared to offer ideas and suggestions Give feedback and support from Project
Focus and energy on tasks Team members feel a new ability to express Problem solving is shared Guides
Effective conflict resolution skills criticism constructively Utilizing all resources to support the team Allow for less structure
Sincere attempt to make consensual Acceptance of all members in the team effort Promotes team interaction
decisions General sense of trust Team members take responsibility in shared Asks for contributions from all team members
Balanced influence, shared problem solving Assured that everything is going to work out leadership skills Collaboration becomes clearer
Develop team routines okay Receiving Feedback from project guides Encouraging others in making decisions
Sets and achieves task milestones Freedom to express and contribute Continues to build strong relationships
The major task function of stage three is the data flow between group members: They share feelings and ideas, solicit and give feedback to one another, and explore actions related to the task. Creativity is
high. Collaboration emerges during this stage when team work ethic and shared leadership is understood.
The major drawback of the norming stage is that members may begin to fear the inevitable future breakup of the team; they may resist change of any sort.
Per forming
True interdependence is the norm of this stage of group development. The team is flexible as individuals adapt to meet the needs of other team members. This is a highly productive stage both personally
and professionally.
Observable Behaviors Feelings & Thoughts Team Needs Leadership Required
Fully functional teams Empathy for one another Project guides assure team is moving in Shared Leadership being practiced
Roles are clearer High commitment collaborative direction Observing, Inquiring, Fulfilling, team needs
Team develops independence Begin understanding collaborative work ethic Maintain team flexibility Collaborative efforts among team members
Team able to organize itself Tight bonds emerge Measure knowledge performance – post test Project guides provides little direction
Flexible members function well individually, Fun and excitement Provide information Team members offer positive reinforcement
in subgroups or as a team Lots of personal development and creativity Giving and Receiving and support
Better understand each other’s strengths and General sense of satisfaction Feedback and Dialogue with project guides Share new information
weaknesses and insights into group Continual discovery of how to sustain feelings
processes of momentum and enthusiasm
The Performing stage is not reached by all groups. If group members are able to evolve to stage four, their capacity, range, and depth of personal relations expand to true interdependence. In this stage,
people can work independently, in subgroups, or as a total unit with equal competencies.
Adjourning
In this stage typically team members are ready to leave (course termination) causing significant change to the team structure, membership, or purpose and the team during the last week of class. They
experience change and transition. While the group continues to perform productively they also need time to manage their feelings of termination and transition.
Observable Behaviors Feelings & Thoughts Team Needs Leadership Required
Visible signs of grief Sadness Evaluate the efforts of the team Project guides help team develop options for
Momentum slows down Humor (that to outsiders could appear cruel) Tie up loose ends and tasks termination
Restless Behavior Glad it is over – relief Recognize and reward team efforts Good listening
Bursts of extreme energy usually followed by Reflection and carry forth collaborative
lack of energy learning to next opportunity
The final stage, adjourning, involves the termination of task behaviors and disengagement from relationships. A planned conclusion usually includes recognition for participation and achievement and an
opportunity for members to say personal goodbyes. Concluding a group can create some apprehension – in effect, a minor crisis. The termination of the group is a regressive movement from giving up
control to giving up inclusion in the group.
CAMPUS MAP RIGHT TO KNOW REQUESTS
WCU ALERT TEXT MESSAGING HEA STUDENT CONSUMER
WCU WEATHER FRAUD, WASTE, & ABUSE
West Chester University
700 South High Street EMERGENCY SERVICES PA WHISTLEBLOWER LAW
West Chester, PA 19383
FACILITIES NEWS & REPORTS NON-DISCRIMINATION STATEMENT
610-436-1000
© West Chester University LAST UPDATED 9/28/22
You might also like
- Managing TeamsDocument42 pagesManaging TeamsAudrey Cawis50% (2)
- Stages of Group Development / Tuckman's Stages: ReferenceDocument2 pagesStages of Group Development / Tuckman's Stages: ReferenceshalinaNo ratings yet
- Tuckmans Stages HandoutDocument2 pagesTuckmans Stages HandoutshalinaNo ratings yet
- Building Working Teams-Student Notes - Monday June 19TH 2023Document12 pagesBuilding Working Teams-Student Notes - Monday June 19TH 2023Fatma HusseinNo ratings yet
- Participative ManagementDocument71 pagesParticipative ManagementAngie FiguraNo ratings yet
- Media 358180 enDocument2 pagesMedia 358180 enapi-429910234No ratings yet
- Team FormationDocument24 pagesTeam FormationJhon Ariel VillaruelNo ratings yet
- The Art of Practicle LeadershipDocument28 pagesThe Art of Practicle LeadershipHamis ShekibulaNo ratings yet
- Tuckmans Stages of Group Development 1Document20 pagesTuckmans Stages of Group Development 1gelolana18No ratings yet
- Ob Assignment Siimret TesDocument21 pagesOb Assignment Siimret TessimretNo ratings yet
- 4A Team Building and Team Work 1Document18 pages4A Team Building and Team Work 1Pan DhanaNo ratings yet
- Team BuildingDocument13 pagesTeam BuildingFoto ShackNo ratings yet
- Team Types: Functional Cross Functional Virtual Self DirectedDocument47 pagesTeam Types: Functional Cross Functional Virtual Self DirectedpepeNo ratings yet
- TuckmanDocument7 pagesTuckmanOnward TangwaraNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 ODCDocument12 pagesTopic 3 ODCAraysya SSNo ratings yet
- Teams Lect 5Document12 pagesTeams Lect 5api-3696879No ratings yet
- Leadership Skills: Prepared By: Ms - AtiahDocument30 pagesLeadership Skills: Prepared By: Ms - AtiahsandhiyaNo ratings yet
- COG's Ladder: Group/Team Development ModelDocument2 pagesCOG's Ladder: Group/Team Development ModelKayla JohnsonNo ratings yet
- OB-58-OB Ch09-Work Teams and GroupsDocument26 pagesOB-58-OB Ch09-Work Teams and GroupsberitahrNo ratings yet
- Bello SW013 ELA6Document2 pagesBello SW013 ELA6Deocarn Ivan F. BelloNo ratings yet
- Pmi DassmDocument68 pagesPmi DassmErik BRENA LORANo ratings yet
- Leadership & TeamworkDocument23 pagesLeadership & Teamworkmr2781225No ratings yet
- T3 Team ChangeDocument23 pagesT3 Team ChangeAmirah ShamimieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Work Teams and GroupsDocument26 pagesChapter 8 Work Teams and Groupsmukesh paridaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Groups and TeamsDocument38 pagesChapter 7 Groups and TeamsJohn Leo Caballero DagcutanNo ratings yet
- Report - Work Teams and GroupsDocument13 pagesReport - Work Teams and GroupsShinjiNo ratings yet
- 1slide Presentation For Rich May, Tetra TechDocument72 pages1slide Presentation For Rich May, Tetra TechkarlNo ratings yet
- 2015-2016 Leadership For Food Services StaffDocument25 pages2015-2016 Leadership For Food Services StaffTotdi AicragNo ratings yet
- DCL Individual Output - Self AssessmentDocument2 pagesDCL Individual Output - Self AssessmentShanNo ratings yet
- Summary Chapter 10 "Group Dynamics" Organizational BehaviourDocument4 pagesSummary Chapter 10 "Group Dynamics" Organizational BehaviourReza MarganaNo ratings yet
- Agile Leadership Workbook 1 CommunicationDocument44 pagesAgile Leadership Workbook 1 CommunicationGaryNo ratings yet
- Summary Presentation of Team Building CourseDocument33 pagesSummary Presentation of Team Building Courseaizaz65No ratings yet
- Group Formation and Team Building - BB Second PptsDocument46 pagesGroup Formation and Team Building - BB Second PptsAditya D Tanwar100% (1)
- B102 Organisational Behaviour:::::: OB10: 6th PresentationDocument22 pagesB102 Organisational Behaviour:::::: OB10: 6th PresentationJoJo asdfNo ratings yet
- Parag. Ob Ppt.2Document33 pagesParag. Ob Ppt.2paragbuddheNo ratings yet
- Coaching For Better ImprovementDocument25 pagesCoaching For Better ImprovementAbu Bakr100% (2)
- Team Working-Main by Ramesh.PDocument22 pagesTeam Working-Main by Ramesh.Plalit.knowledgeNo ratings yet
- Steps in Successful Team BuildingDocument25 pagesSteps in Successful Team BuildingOBED ASAMOAH-GYARKONo ratings yet
- Group 9Document32 pagesGroup 9Yda Nur ImanNo ratings yet
- STORMING en Un EquipoDocument6 pagesSTORMING en Un Equipodiosaegipcia8626No ratings yet
- Group Dynamics at Work PlaceDocument7 pagesGroup Dynamics at Work PlaceKHUSHI ALTHAFNo ratings yet
- Team Behavior and ToolsDocument16 pagesTeam Behavior and ToolsmichsantosNo ratings yet
- NT TeamworkDocument13 pagesNT Teamworkrahul221No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 TeamworkDocument17 pagesChapter 6 TeamworkBerk TekinNo ratings yet
- Class PPT - Team Dynamics Module 2Document27 pagesClass PPT - Team Dynamics Module 2Ramesh DhamiNo ratings yet
- Organizational Change PracticeDocument11 pagesOrganizational Change PracticeRio AlbaricoNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document26 pagesCH 2soul12345No ratings yet
- Leadership in Organizational SettingDocument17 pagesLeadership in Organizational SettingAnonymous bmaJWEQcGnNo ratings yet
- Why Teams Fail: By: Saloni MaheshwariDocument15 pagesWhy Teams Fail: By: Saloni MaheshwariyuvrajNo ratings yet
- Leading Self-Managed TeamsDocument25 pagesLeading Self-Managed TeamsMuhd AqibNo ratings yet
- CSC 171 Sprint 2018 Four Stages of Team Development: in Small GroupsDocument6 pagesCSC 171 Sprint 2018 Four Stages of Team Development: in Small Groupsfariez79No ratings yet
- Teams Download FileDocument25 pagesTeams Download Fileluis anchayhua pradoNo ratings yet
- Group Life Cycle-1Document5 pagesGroup Life Cycle-1Aidrouz LipanNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument41 pagesFinal ProjectAmeerNo ratings yet
- Group2 - DivisionB - Team Building Skills For R&D Project TeamsDocument6 pagesGroup2 - DivisionB - Team Building Skills For R&D Project TeamsAshish GargNo ratings yet
- Five Stage Model of Group DevelopmentDocument4 pagesFive Stage Model of Group DevelopmentFatimah TariqNo ratings yet
- Do You Have A Traditional Organization or A Leadership Organization?Document2 pagesDo You Have A Traditional Organization or A Leadership Organization?Anonymous GDOULL9No ratings yet
- Poised for Excellence: Fundamental Principles of Effective Leadership in the Boardroom and BeyondFrom EverandPoised for Excellence: Fundamental Principles of Effective Leadership in the Boardroom and BeyondNo ratings yet
- The Leadership PIN Code: Unlocking the Key to Willing and Winning RelationshipsFrom EverandThe Leadership PIN Code: Unlocking the Key to Willing and Winning RelationshipsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Skyrocket Your Team's Performance: Nurture a Mentoring CultureFrom EverandSkyrocket Your Team's Performance: Nurture a Mentoring CultureNo ratings yet
- Trends in ManagementDocument9 pagesTrends in ManagementMerinNo ratings yet
- Optimum Population GrowthDocument6 pagesOptimum Population GrowthFahad Mahmud MarutNo ratings yet
- Attitudes and Social CognitionDocument30 pagesAttitudes and Social CognitionIkram khanNo ratings yet
- The Unity of Descartess Thought PDFDocument10 pagesThe Unity of Descartess Thought PDFAnonymous pZ2FXUycNo ratings yet
- XI Sociology Chapt4 HssliveDocument4 pagesXI Sociology Chapt4 HssliveShriram NageswaranNo ratings yet
- MACKENZIE - The Cheviot, Stag and The White White RockDocument24 pagesMACKENZIE - The Cheviot, Stag and The White White Rockpinkanna100% (1)
- The Contemporary World SyllabusDocument10 pagesThe Contemporary World SyllabusJulie CabalanNo ratings yet
- Procedures of Translating Culture-Specific ConceptsDocument5 pagesProcedures of Translating Culture-Specific ConceptsWilliam BosichNo ratings yet
- CONFLICT RESOLUTION Individual AssignmentDocument8 pagesCONFLICT RESOLUTION Individual AssignmentCaxton mwashitaNo ratings yet
- Becoming A Reflexive ResearcherDocument3 pagesBecoming A Reflexive ResearcherSohvi ReitmaaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Community and Association PDFDocument2 pagesBasic Concepts of Community and Association PDFSuneel Kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- The Psychology of Physical SensationDocument295 pagesThe Psychology of Physical SensationGabriel DelfinoNo ratings yet
- Unit2-Culture & SocietyDocument16 pagesUnit2-Culture & SocietyShobana SubramanianNo ratings yet
- NFA To DFA Subset Construction Notes Module 2Document7 pagesNFA To DFA Subset Construction Notes Module 2Sindhu PNo ratings yet
- PESManual FinalDocument115 pagesPESManual FinalravenheadmanonNo ratings yet
- Citizenship Education Training Manual UpdateDocument22 pagesCitizenship Education Training Manual Updategamedas100No ratings yet
- 16PF ReportDocument15 pages16PF ReportKarunya ReddyNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Criminological Theory and The Problem of Causation PDFDriveDocument98 pagesAn Introduction To Criminological Theory and The Problem of Causation PDFDriveResteer John LumbabNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam in Economic DevelopmentDocument3 pagesMidterm Exam in Economic DevelopmentJason Mables100% (1)
- The Self From Various PerspectivesDocument32 pagesThe Self From Various PerspectivesMariah GolzNo ratings yet
- Forming ImpressionsDocument5 pagesForming ImpressionsLyla FarooghNo ratings yet
- Admin, DocumentDocument18 pagesAdmin, DocumentRichard FereirraNo ratings yet
- The Essence of Existence and The Quest For Survival in The Poetry of Dennis BrutusDocument5 pagesThe Essence of Existence and The Quest For Survival in The Poetry of Dennis BrutusIjahss JournalNo ratings yet
- Literature Review 1Document7 pagesLiterature Review 1api-609504422No ratings yet
- Bully Target ResearchDocument18 pagesBully Target ResearchNattha SaravutanukulNo ratings yet
- 88-Article Text-167-1-10-20150920Document22 pages88-Article Text-167-1-10-20150920Ansori DanuzNo ratings yet
- Sustainable TourismDocument26 pagesSustainable TourismRavi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Chapter 9 and 10Document2 pagesSummary of Chapter 9 and 10Alto Del Nacho ADRIANONo ratings yet
- Disciplines and Ideas in The Social Sciences Quarter 1 - Module 2: Nature and Functions of Social Sciences DisciplinesDocument11 pagesDisciplines and Ideas in The Social Sciences Quarter 1 - Module 2: Nature and Functions of Social Sciences DisciplinesFumia LutzNo ratings yet
- OB Chapter 3Document120 pagesOB Chapter 3Abhilasha MeshramNo ratings yet