Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 Ocular Refraction
2 Ocular Refraction
Uploaded by
majd danOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 Ocular Refraction
2 Ocular Refraction
Uploaded by
majd danCopyright:
Available Formats
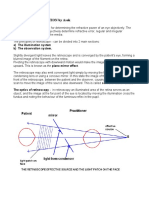
The ocular refraction
The eye = adaptive optical system, 64D refractive power: 70% air-corneal
interface, 30% crystalline (it can supplement the refractive power of the eye
through an accommodation mechanism that allows a clear view of nearby
objects).
Ocular refraction = balance between 4 fundamental refractive variables:
1. the axial length of the eyeball
2. the dioptric power of the cornea
3. the dioptric power of the lens
4. the depth of the anterior chamber
Refraction: -static component
- dynamic component (accommodation)
Emmetropia = the refraction of the eye in an accommodative resting state,
when the image of the objects is formed on the retina and the 4 fundamental
refractive variables are in equilibrium.
Ametropia = the situation in which the beam of light coming from infinity is
formed at one point or more points, in front of or behind the retina. The
ametropic eye is an eye with abnormal vision without correction.
Eye refraction: - subjective methods
- objective methods
Subjective methods = are based on the response of the patient who chooses the
correction that offers the best visual acuity
Basic materials: lens box, test frame, Snellen test
The patient reads the smallest row of a Snellen test at a distance of 6m.
Evaluation of the spherical component
Corrects with progressively increasing lenses.
It starts with a monocular test. If the subject reads the last line of a Snellen
chart, he is emmetropic or small hypermetropic. Lenses from +0.50 Dsf or +
1Dsf are added to the sample frame. If a better view is not obtained, it means
that the subject is emmetropic. If the visual acuity improves after the lens is
added, the patient is hypermetropic and the highest spherical value with the
maximum visual acuity will be prescribed.
If the patient does not read the last line, he is myopic or astigmatized, has a
high value of hypermetropia or has an organic eye disorder. Initially the + 1dsf
spherical lens is applied. If a better visual acuity is not obtained, the patient is
myopic or astigmatized. Add the concave spherical lens with which the best
view is obtained and the lowest value with which the maximum visual acuity is
obtained is prescribed.
If the patient does not read better after correction with + or - lenses, it means
that they have astigmatism and cylindrical lenses will be used.
The autorefraction test
Autorefractors measure refractive error in just seconds and automatically
determines a person's refractive errors.
After informing the patient of the need to fix the look, refraction is measured
in both eyes.
The results of the test are used to diagnose the following conditions:
- astigmatism, a refractive problem with the eye related to the shape of the
lens, which causes blurry vision
- hyperopia, which is also known as farsightedness
- myopia, which is also known as nearsightedness
- presbyopia, a condition related to aging that causes lens of the eye to have
trouble focusing
You might also like
- Literature Review of Refractive ErrorDocument7 pagesLiterature Review of Refractive Errorafdtsdece100% (1)
- Dispensing NotesDocument103 pagesDispensing Notesjancok100% (1)
- Ophtalmo Lab AllDocument27 pagesOphtalmo Lab Allmajd danNo ratings yet
- Re TinosDocument31 pagesRe TinosAn Da100% (1)
- Mri MachineDocument16 pagesMri Machineمحمد المدنيNo ratings yet
- Baghdad University College of Medicine Ophthalmology DepartmentDocument20 pagesBaghdad University College of Medicine Ophthalmology DepartmentMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- What Is Retinoscopy?: Myopia HyperopiaDocument4 pagesWhat Is Retinoscopy?: Myopia HyperopiababyswitNo ratings yet
- Errors of Refraction - Presbyopia, AstigmatismDocument16 pagesErrors of Refraction - Presbyopia, AstigmatismVid MirosevicNo ratings yet
- Optics of The EyeDocument19 pagesOptics of The EyeObansa JohnNo ratings yet
- Retinoscopy by AzmatDocument29 pagesRetinoscopy by AzmatMazhar Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Direct OphthalmoscopeDocument16 pagesDirect OphthalmoscopeMuhammed AbdulmajeedNo ratings yet
- Special Senses-Vision I-2Document21 pagesSpecial Senses-Vision I-2Ram LakshmanNo ratings yet
- Biophysics of The Visual SystemDocument5 pagesBiophysics of The Visual SystemIfe AzeezNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocument52 pagesOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDShahar ShababNo ratings yet
- RetinosDocument60 pagesRetinosnickno1100% (1)
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Klien Dengan Gangguan RefraksiDocument21 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Klien Dengan Gangguan RefraksiHerly KakaNo ratings yet
- Week 8: Topic: Application of Light WavesDocument45 pagesWeek 8: Topic: Application of Light WavespraiseNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mamta Dept of Ophthalmology RNT Medical College, UdaipurDocument56 pagesDr. Mamta Dept of Ophthalmology RNT Medical College, UdaipurGideon IrwandaNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan ObejktifDocument12 pagesPemeriksaan ObejktifMuhammad FadhilNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocument52 pagesOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDHidayadNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Sadia Qasim Submitted To: Mam Sania Aslam Subject: Management of Refractive Error HESC19113023 Bs Optometry 5ADocument14 pagesSubmitted By: Sadia Qasim Submitted To: Mam Sania Aslam Subject: Management of Refractive Error HESC19113023 Bs Optometry 5AŠadïįaQasimNo ratings yet
- OphthalDocument10 pagesOphthaldrjanggeum0% (1)
- Refractive Errors (Najla) - 1Document74 pagesRefractive Errors (Najla) - 1Muhammad LukmanNo ratings yet
- Retsimp 2013Document9 pagesRetsimp 2013ijudoptoNo ratings yet
- Daa Objective RefractionDocument56 pagesDaa Objective RefractiondwindaNo ratings yet
- Retinoscopy and Its Principles: Presenter: DR - Rasika Thakur Moderator: DR - Monica Samant MR - Kunal KishorDocument67 pagesRetinoscopy and Its Principles: Presenter: DR - Rasika Thakur Moderator: DR - Monica Samant MR - Kunal KishorHenok BirukNo ratings yet
- Clinical RefractionDocument46 pagesClinical RefractionMuhammed Abdulmajeed100% (1)
- Accommodation: Shubhangi ShuklaDocument17 pagesAccommodation: Shubhangi ShuklaShubhangi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect FinalDocument31 pagesDirect and Indirect Finalmeenali karnNo ratings yet
- ScribdDocument3 pagesScribdAndrew CoatesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Introduction To OpticsDocument3 pagesChapter 9 Introduction To OpticsFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- Indirect OphthalmosDocument8 pagesIndirect OphthalmosAnumeha JindalNo ratings yet
- Anisometropia 4Document18 pagesAnisometropia 4Mamtha MMNo ratings yet
- Publication 4 8578 1650Document9 pagesPublication 4 8578 1650NIKHILA RAKESHNo ratings yet
- 2 Dioptrique de Loeil Normal 2021.anglaisDocument7 pages2 Dioptrique de Loeil Normal 2021.anglaisHoussemNo ratings yet
- Objective Refraction Technique: Retinoscopy: Aao ReadingDocument57 pagesObjective Refraction Technique: Retinoscopy: Aao ReadingKhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- AmblyopiaDocument33 pagesAmblyopiaSujon PaulNo ratings yet
- Eye ExaminationDocument6 pagesEye ExaminationChellamani UmakanthanNo ratings yet
- Review: True or FalseDocument18 pagesReview: True or FalseAdorio JillianNo ratings yet
- Examination of Case of StrabismusDocument76 pagesExamination of Case of StrabismusDr-SunitaVimal100% (2)
- RefraksiDocument42 pagesRefraksiGalihNo ratings yet
- Error of RefractionDocument37 pagesError of RefractionIka KrastanayaNo ratings yet
- College of Medicine and Health Science, Department of OptometryDocument47 pagesCollege of Medicine and Health Science, Department of Optometryhenok birukNo ratings yet
- Dynamic RetinosDocument6 pagesDynamic RetinosguybarnettNo ratings yet
- Optometry Department OPTO 374 The Synoptophore Dr. Safiah Mulla Name: Fatima Ahmad Abo-Qoaied ID: 426200452Document25 pagesOptometry Department OPTO 374 The Synoptophore Dr. Safiah Mulla Name: Fatima Ahmad Abo-Qoaied ID: 426200452zecemariNo ratings yet
- Defects of VisionDocument2 pagesDefects of VisionMohamad Rizal MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Direct OphthalmosocopeDocument19 pagesDirect OphthalmosocopeissemoiseNo ratings yet
- Clinical Skills Week 1Document3 pagesClinical Skills Week 1Aishah SiddiqahNo ratings yet
- Refractive ErrorsDocument38 pagesRefractive ErrorszahraaNo ratings yet
- Physics of Eye and Vision - Updated DR Bakhtiar 2023Document46 pagesPhysics of Eye and Vision - Updated DR Bakhtiar 2023mhamadmhamad1184No ratings yet
- INFOCUS MANUAL CATARACT SCREENINGF Primary-Eye-Care-Manual-Summary1Document21 pagesINFOCUS MANUAL CATARACT SCREENINGF Primary-Eye-Care-Manual-Summary1Si PuputNo ratings yet
- Intoduction and MethodologyDocument11 pagesIntoduction and MethodologyKarthikNo ratings yet
- Clinical OpticDocument43 pagesClinical OpticReinhard TuerahNo ratings yet
- l7 - Clinical RefractionDocument11 pagesl7 - Clinical Refractionteamtruth50No ratings yet
- Refraction and PrescribingDocument6 pagesRefraction and PrescribingawaisNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 MicrosDocument28 pagesChap 4 MicrosPatricio ArruéNo ratings yet
- Bo 405 (32301721022)Document8 pagesBo 405 (32301721022)AvinabaNo ratings yet
- Indirect OphthalmosDocument3 pagesIndirect Ophthalmosbijujc100% (1)
- TimRoot - Chapter 9 - Introduction To OpticsDocument1 pageTimRoot - Chapter 9 - Introduction To OpticsBaeyerNo ratings yet
- RefraksiDocument11 pagesRefraksiMagfirah HalimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Pregnancy HTDocument18 pagesLecture 10 Pregnancy HTmajd danNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 CKD - Chronic Kidney Disease 1 _ 2Document54 pagesLecture 7 CKD - Chronic Kidney Disease 1 _ 2majd danNo ratings yet
- Curs 1+2 Adenophaty and splenomegaly 2Document41 pagesCurs 1+2 Adenophaty and splenomegaly 2majd danNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document18 pagesLecture 1majd danNo ratings yet
- VS-V GT Medical Manual 1160 2015Document16 pagesVS-V GT Medical Manual 1160 2015Jorge Luis OrtizNo ratings yet
- Anisometropia 4Document18 pagesAnisometropia 4Mamtha MMNo ratings yet
- Lasik Eye Surgery Research PaperDocument7 pagesLasik Eye Surgery Research Paperwkzcoprhf100% (1)
- Eye PPT For Nursing Students by DR - Reshma AjayDocument46 pagesEye PPT For Nursing Students by DR - Reshma AjayRESHMA AJAY100% (2)
- 02 Patient Profile and Case HistoryDocument7 pages02 Patient Profile and Case HistoryNikoleta TuleaNo ratings yet
- Working of Human Eye LensDocument18 pagesWorking of Human Eye LensNupur LolgeNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 Nov 2016 Memo EngDocument9 pagesLife Sciences P1 Nov 2016 Memo EngOlerato NtsimaneNo ratings yet
- Ch-10 Science PYQsDocument10 pagesCh-10 Science PYQsglusac261No ratings yet
- Module 9 EASA AME Question BankDocument28 pagesModule 9 EASA AME Question Bankshameeel18No ratings yet
- Near and Far-SightednessDocument1 pageNear and Far-SightednessHarrinishri MANo ratings yet
- 8.3 IclcDocument96 pages8.3 IclcAce RNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument8 pagesHuman Eyeanitaagarwal19891984No ratings yet
- Module 5 1Document35 pagesModule 5 1Rejie Nel AquinoNo ratings yet
- The Eye - Grade11Document4 pagesThe Eye - Grade11joshua NaulthyNo ratings yet
- Eye School ScreeningDocument2 pagesEye School ScreeningriyadbanayotNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sashwat RayDocument98 pagesDr. Sashwat RayDikshant DaswatNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Refractive ErrorsDocument5 pagesLiterature Review On Refractive Errorsafmzfvlopbchbe100% (1)
- Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices Towards Refractive Error Amongs StudentDocument7 pagesKnowledge, Attitudes and Practices Towards Refractive Error Amongs Student0039 NURUL HANI IZZUANI BINTI AFRIZANNo ratings yet
- Intro To 21 StepsDocument28 pagesIntro To 21 StepsZoey SanNo ratings yet
- April 23Document125 pagesApril 23V HasagalNo ratings yet
- Vision BPTDocument110 pagesVision BPTAkshay BadoreNo ratings yet