Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Tachment
Science Tachment
Uploaded by
Leona KokeraiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Tachment
Science Tachment
Uploaded by
Leona KokeraiCopyright:
Available Formats
The Alveoli
The role of the alveoli
these are the air sacs through which gaseous exchange takes place in the
lungs.
They are numerous and their large surface area is good for intake of
oxygenated air and expulsion of deoxygenated air.
The lining of the alveoli is semi permeable(allowing air only to pass
through).
Capillaries surrounding the alveolus contain less oxygen than present in
the air sac, thus oxygen diffuse through into the capillaries.
Carbon dioxide is more in the capillaries than in the air sacs, thus diffuse
through into the air sacs.
Functions of parts of the respiratory system.
1. VOICE BOX
-Is held open by the trachea to allow passage of air
2. TRACHEA
- Is a cartilage structure
- Lining has cilia which are in constant motion and traps dust and dirt
- It also helps in moisturising air
Notes compiled by M. MLILO “TO GOD BE THE GLORY” Page 40
3. BRONCHUS AND BRONCHIOLES
- Channels air to and from the alveoli
- Containing mucus and cilia to trap dust an micro organisms
4. ALVEOLI
- These are small thin walled semi permeable air sacs
- They are numerous and provide a large surface area for gaseous
exchange; this ensures that sufficient oxygen is obtained.
5. Ribs
- Protect lungs
- Are raised during inhalation and lowered to reduce volume and expel
waste gases during exhalation
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN INHALED AND EXHALED AIR
SUBSTANCE INHALED AIR EXHALED AIR
OXYGEN 20% 16%
CARBON DIOXIDE 0.03% 4%
WATER Usually dry Usually moist(high)
TEMPERATURE Lower than exhaled air Higher than inhaled
NITROGEN 79% 79%
GERMS Has Usually does not have
DUST PARTICLES Has Does not have
1 EXPERIMENT
COMPARING INHALED AND EXHALED AIR
MATERIAL
-Beakers, small pipes, limewater
Notes compiled by M. MLILO “TO GOD BE THE GLORY” Page 41
METHOD
-BLOW IN AND OUT THROUGH THE PIPE
RESULTS
-The limewater in ‘A’ turn milky white and in ‘B’ remains the same.
CONCLUISION
-carbon dioxide is present in ‘A’, thus inhaled air has carbon dioxide
RESPIRATION
-The process whereby glucose is broken down to release energy in the presence
of oxygen.
-Occurs inside the cells of living organisms, during the process, carbon dioxide
and water are released.
WORD EQUETION
GLUCOSE+OXYGEN CARBONDIOXIDE+WATER+HEAT ENERGY
-the process is known as aerobic respiration
-the energy produced is used for moving and other activities
-oxygen is used up and carbon dioxide released.
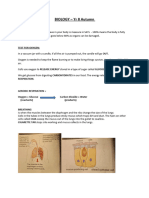
2. EXPERIMENT
Notes compiled by M. MLILO “TO GOD BE THE GLORY” Page 42
-WHICH GAS IS RELEASED DURING RESPIRATION
MATERIALS
-small animal e.g. rat, frog; limewater; three test tubes; potassium hydroxide;
glass/rubber tubing
METHOD
-Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram
-the apparatus compare the amount of carbon dioxide in inhaled and exhaled air
DIAGRAM
RESULTS
-limewater in ‘B’ turned milky white and that in ‘A’ remained clear
CONCLUISION
-limewater in ‘B’ turned milky white because the carbon dioxide concentration is
high.
Notes compiled by M. MLILO “TO GOD BE THE GLORY” Page 43
COMPARING RESPIRATION AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS
RESPIRATION PHOTOSYTHESIS
Catabolic-carbohydrates are broken Anabolic- carbohydrates are
down. manufactured
Oxygen is taken in Oxygen is taken in
Carbon dioxide is given off Carbon dioxide is taken in
Energy is released Energy is absorbed and stored
3 EXPERIMENT
TO SHOW THAT HEAT IS PRODUCED DURING RESPIRATION
MATERIAL
-two thermo flasks; germinating seeds; cotton wool; thermometers
METHOD
1. Divide the germinating seeds into two equal sets
2. Boil one set and disinfect it
3. Place the two sets of seeds and thermometers into the thermo flasks
4. Record temperature at the beginning and after 30 minutes
RESULTS
- The temperature in ‘A’ will be higher than ‘B’ because dead seeds do not
germinate
CONCLUISION
- Germinating seeds produce heat through respiration.
Notes compiled by M. MLILO “TO GOD BE THE GLORY” Page 44
You might also like
- Kin 2G03 - Sleep Assign #1Document5 pagesKin 2G03 - Sleep Assign #1YurNo ratings yet
- General and Unique Characteristics of The Different Organ Systems in Representative AnimalsDocument51 pagesGeneral and Unique Characteristics of The Different Organ Systems in Representative AnimalsAliah Jeonelle Ramos100% (2)
- Comb Scie Notes-Bio Section-1Document5 pagesComb Scie Notes-Bio Section-1Leona KokeraiNo ratings yet
- L - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkDocument7 pagesL - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkNotImmortalNo ratings yet
- B6.2 Revision Notes ZwhjilDocument3 pagesB6.2 Revision Notes ZwhjilwellingtonNo ratings yet
- Respiration: - Respiration Is The Release of Energy From Food Substances in All Living CellsDocument8 pagesRespiration: - Respiration Is The Release of Energy From Food Substances in All Living CellsMandla RebirthNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument9 pagesRespiration in Organismsshreya kashyapNo ratings yet
- Chapter XI - Gas Exchange in HumansDocument1 pageChapter XI - Gas Exchange in Humansghostoast123No ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument36 pagesRESPIRATIONnyemarichardssvgNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 Revision Notes 19hzxf3Document3 pagesTopic 11 Revision Notes 19hzxf3salmasomaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-The Air Around UsDocument50 pagesChapter 5-The Air Around UsGenevieve Yong100% (1)
- 1 Respiration Summary SlidesDocument23 pages1 Respiration Summary SlidesAseel Elghazeli100% (1)
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4edain84No ratings yet
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Faida Hamid87% (23)
- 9 Human Gas ExchangeDocument78 pages9 Human Gas ExchangezaeNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasDocument7 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasParasNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumansDocument8 pagesGas Exchange in Humanstawana nyikaNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument7 pagesAnaerobic RespirationvictoriaNo ratings yet
- Air Around UsDocument30 pagesAir Around UsSugandha JainNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Gas ExchangeDocument19 pagesRespiratory Gas ExchangeRahul MeenaNo ratings yet
- Living Organisms Require Energy: The Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionDocument38 pagesLiving Organisms Require Energy: The Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionWen Shan ChuaNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyDocument5 pagesRespiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyTechnical AyushNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans Grade 9Document49 pagesGas Exchange in Humans Grade 9harliv2.5chandhokNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.3 - Human Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesTopic 2.3 - Human Respiratory Systembienfrancis.reyes.jhsNo ratings yet
- Respiration Ch-5 Life ProcessesDocument18 pagesRespiration Ch-5 Life Processes7B06Asher kharaNo ratings yet
- Sheniblog-Class 9 Biology Chapter 4 (Eng Med) NotesDocument3 pagesSheniblog-Class 9 Biology Chapter 4 (Eng Med) Notesdevu fav MohanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SytemsDocument9 pagesRespiratory Sytemstatendachimbandi1No ratings yet
- Unit 7 - RevisionDocument5 pagesUnit 7 - RevisionusbdetailsNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument6 pagesBreathingtnkele73No ratings yet
- 3 - Oxygen Is Needed in RespirationDocument13 pages3 - Oxygen Is Needed in RespirationmizwhiteNo ratings yet
- Biology - RespirationDocument2 pagesBiology - RespirationMN IzhharuddinNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemsDocument41 pagesRespiratory SystemsDenzel MusaNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 6 - Chapter 16Document11 pagesExp SC 6 - Chapter 16megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Respiratory SystemDocument43 pagesChapter 2 - Respiratory SystemSYAZWANINo ratings yet
- 1 Respiratory SystemDocument70 pages1 Respiratory SystemJan IceNo ratings yet
- Aerobic & Anaerobic Respiration: Biology Form 4Document36 pagesAerobic & Anaerobic Respiration: Biology Form 4Natalia SandyNo ratings yet
- Practical Note and HeredityDocument18 pagesPractical Note and HeredityCalifornia KnightNo ratings yet
- Respiration Biology NotesDocument4 pagesRespiration Biology NotesChal WijeNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument30 pagesThe Respiratory SystemvnakshatrNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange..Document6 pagesGaseous Exchange..sunoyebimpeNo ratings yet
- Biology AutumnDocument4 pagesBiology AutumnlucylubuNo ratings yet
- Air and Atmosphere: Class 6 by Aditi PandeyDocument14 pagesAir and Atmosphere: Class 6 by Aditi PandeyNeha TiwariNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Oxygen Sugar Industries M.Noman Raza CHDocument7 pagesAssignment: Oxygen Sugar Industries M.Noman Raza CHGlobal PMC100% (1)
- The Life Process of Respiration: Biology Unit 7Document23 pagesThe Life Process of Respiration: Biology Unit 7giscaamiliaNo ratings yet
- FORM-2_3.-GASEOUS-EXCHANGE-ADocument5 pagesFORM-2_3.-GASEOUS-EXCHANGE-AaskofumakutesaNo ratings yet
- #5 Midterm Bacte Lab - Anaerobic CulturingDocument2 pages#5 Midterm Bacte Lab - Anaerobic CulturingJared SicorNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsDocument51 pagesGaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsJesimie OriasNo ratings yet
- AlveoliDocument6 pagesAlveoliMukundan PolurNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System of Frog: External RespirationDocument3 pagesRespiratory System of Frog: External RespirationShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Bio TestDocument24 pagesBio Testjunaid mehmoodNo ratings yet
- 08-Respiration and Gaseous Exchange-1Document22 pages08-Respiration and Gaseous Exchange-1Maku MichaelNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument4 pagesRESPIRATIONTumisang PitiroseNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange 1 (Autosaved)Document42 pagesGas Exchange 1 (Autosaved)suhaylanadiif6No ratings yet
- Respiratory - Gas ExchangeDocument3 pagesRespiratory - Gas ExchangeChris P. BeaconNo ratings yet
- Bio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .Document21 pagesBio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .naazim mohamedNo ratings yet
- Biology Ch. 7Document9 pagesBiology Ch. 7sumsumNo ratings yet
- AAU1 - TopicDocument14 pagesAAU1 - TopicnorafaizalNo ratings yet
- Respiration G810FD6Document10 pagesRespiration G810FD6Tifa NassimNo ratings yet
- The 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksFrom EverandThe 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksNo ratings yet
- Types of Cells infographic in green white blue illustrative style_20240105_011741_0000Document1 pageTypes of Cells infographic in green white blue illustrative style_20240105_011741_0000Leona KokeraiNo ratings yet
- Clinical-biochemistryDocument1 pageClinical-biochemistryLeona KokeraiNo ratings yet
- PopulationDocument3 pagesPopulationLeona KokeraiNo ratings yet
- The Periodic TableDocument1 pageThe Periodic TableLeona KokeraiNo ratings yet
- Maths Nov 2015 P1Document28 pagesMaths Nov 2015 P1Leona KokeraiNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument9 pagesHuman ReproductionLeona KokeraiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System and Plant HormonesDocument11 pagesEndocrine System and Plant HormonesLeona KokeraiNo ratings yet
- Edoofa Scholarship ProgramDocument33 pagesEdoofa Scholarship ProgramLeona KokeraiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Leona KokeraiNo ratings yet
- SyllaDocument2 pagesSyllaLeona KokeraiNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Antiagina TTMDocument83 pagesFarmakologi Antiagina TTMEpha Lumban GaolNo ratings yet
- R7 - Reference - Part 0Document8 pagesR7 - Reference - Part 0danielNo ratings yet
- Set A Suggested Answer Mosys SB025 - 230430 - 191516Document4 pagesSet A Suggested Answer Mosys SB025 - 230430 - 191516nursyakiramailanNo ratings yet
- Inflamation: DR Wiwit Ade FW, M Biomed, SppaDocument49 pagesInflamation: DR Wiwit Ade FW, M Biomed, Sppa'Danang ヌグロホNo ratings yet
- Dr.M.Kannan MD DA Professor and HOD of Anaesthesiology Tirunelveli Medical CollegeDocument26 pagesDr.M.Kannan MD DA Professor and HOD of Anaesthesiology Tirunelveli Medical CollegeAlina CiubotariuNo ratings yet
- Common Ecg Abnormalities PDFDocument2 pagesCommon Ecg Abnormalities PDFRonNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Sodium: Submitted By: Milosantos, John Francis D. Tuibeo, Ma. Arlyn P. Yu, Aldrin Anthony LDocument6 pagesElectrolyte Imbalance: Sodium: Submitted By: Milosantos, John Francis D. Tuibeo, Ma. Arlyn P. Yu, Aldrin Anthony Lnospekiko21No ratings yet
- SCIENTIFIC BASIS OF HUMAN MOVEMENT EFFECTS OF EXERCISE ON RESPIRATORY SYSTEM - Wbshce PDFDocument9 pagesSCIENTIFIC BASIS OF HUMAN MOVEMENT EFFECTS OF EXERCISE ON RESPIRATORY SYSTEM - Wbshce PDFlancetNo ratings yet
- Parasympathomimetic AgentsDocument26 pagesParasympathomimetic Agentsrushikesh ugaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 57Document21 pagesChapter 572071317No ratings yet
- Stevic Et Al 2021 Lung Recruitability Evaluated by Recruitment To Inflation Ratio and Lung Ultrasound in Covid 19 AcuteDocument3 pagesStevic Et Al 2021 Lung Recruitability Evaluated by Recruitment To Inflation Ratio and Lung Ultrasound in Covid 19 AcuteJenny ACNo ratings yet
- Spirometry Report Group-14Document11 pagesSpirometry Report Group-14Mwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure and Its Drug ClassificationDocument37 pagesHeart Failure and Its Drug ClassificationMaham AzmatNo ratings yet
- Unit 05 (A) Cardiac Glycosides, Educational PlatformDocument41 pagesUnit 05 (A) Cardiac Glycosides, Educational PlatformSajid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis SS2Document4 pagesHomeostasis SS2Ezeh PrincessNo ratings yet
- NRP 1Document12 pagesNRP 1syasyaNo ratings yet
- Body System ChecklistDocument8 pagesBody System Checklistapi-421876369No ratings yet
- Control Coordination (Prashant Kirad)Document16 pagesControl Coordination (Prashant Kirad)shrikantmisal17No ratings yet
- Checklist Cardiac AssessmentDocument8 pagesChecklist Cardiac AssessmentLovely GopezNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Handout 2Document15 pagesHealth Assessment Handout 2ApRil Anne BalanonNo ratings yet
- CIE A2 Biology Notes PhotosynthesisDocument30 pagesCIE A2 Biology Notes Photosynthesisciebiologynotesfora267% (3)
- Grade 9 Biology - Lesson Note April 8,2020Document10 pagesGrade 9 Biology - Lesson Note April 8,2020micahxNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ECG Interpretation January 2023Document101 pagesIntroduction To ECG Interpretation January 2023davidjoejoekidNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart Disease - Patho - DiagramDocument10 pagesRheumatic Heart Disease - Patho - DiagramJoann100% (12)
- AHA ACLS Written Test: Ready To Study? Start With FlashcardsDocument8 pagesAHA ACLS Written Test: Ready To Study? Start With FlashcardssallyNo ratings yet
- Sample Pages of CRISP Physiology 3rd EditionDocument20 pagesSample Pages of CRISP Physiology 3rd EditionskNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Respiratory SystemDocument22 pagesGrade 9 Respiratory SystemMelanie Tagudin TrinidadNo ratings yet
- 2.health AssessmentDocument7 pages2.health Assessment2BGrp3Plaza, Anna MaeNo ratings yet