Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SI Sheet #6
SI Sheet #6
Uploaded by
sebastiangon2023Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SI Sheet #6
SI Sheet #6
Uploaded by
sebastiangon2023Copyright:
Available Formats
General Chemistry I: Chapter 6 Handout
SI Leader: Emily Siegelman
Electromagnetic Radiation
Terms to Know:
• Amplitude: Height of the peek
• Wavelength distance between peek
• Frequency # of waves passing a point in a given time
• Speed of Light c = 3* 10^8 m/s
What is the formula for the speed of light?
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency?
DeBroglie Wavelength Formula: λ= h/ (mv)
1. What is the wavelength of light with a frequency of 52.3 GHz?
2. What is the frequency of light with a wavelength of 520 nm?
SI Sessions Tuesdays/ Thursdays @4pm & 6:30pm
esiegelman2021@fau.edu
General Chemistry I: Chapter 6 Handout
SI Leader: Emily Siegelman
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Place the following in order from highest energy to lowest energy and from lowest to
highest wavelength.
• Blue light
• Infrared
• Ultraviolet
• Red light
• Gamma rays
• Radio
• Microwave
Planck’s Constant: Energy of a photon is proportional to its frequency
• h = 6.63 × 10-34 J∙s
• E = hν/ λ
3. What is the energy per mole for light with a wavelength of 960 nm?
SI Sessions Tuesdays/ Thursdays @4pm & 6:30pm
esiegelman2021@fau.edu
General Chemistry I: Chapter 6 Handout
SI Leader: Emily Siegelman
4. What is the wavelength of a photon if 2 moles of that photon have a total of 5.2 × 10J of
energy?
5. What is the energy per mole for a light with a frequency of 9*10^14 Hz?
6. What is the energy (in Joules) of a 455 nm photon?
a. 4.86 ´ 10-36 J
b. 9.04 ´ 10-32 J
c. 4.37 ´ 10-19 J
d. 1.46 ´ 10-18 J
Atomic Spectra
SI Sessions Tuesdays/ Thursdays @4pm & 6:30pm
esiegelman2021@fau.edu
General Chemistry I: Chapter 6 Handout
SI Leader: Emily Siegelman
Bohr model: describe the line spectrum of the hydrogen atoms
Limitation: only for 1 electron systems
Identify the ground state and excited states in the diagram below:
7. Identify which transition emits the highest and lowest wavelength, highest and
lowest energy, and highest and lowest frequency.
Quantum Numbers
What is a quantum number?
Facts about Quantum Numbers
• n = shell
o n>0
• l = subshell
l=0: s; l=1: p; l=2, d; l=3: f
• n-1
• ml = orbital
o ±l
SI Sessions Tuesdays/ Thursdays @4pm & 6:30pm
esiegelman2021@fau.edu
General Chemistry I: Chapter 6 Handout
SI Leader: Emily Siegelman
• ms = spin number
o±½
o Not obtained from Schrodinger’s equation
Fill in all possible quantum numbers for the following:
n l m l
2p
3d
4s
8. Which of the following is a possible set of quantum numbers for an electron in an
atom?
a. n = 1, l = 1, ml = 1
b. n = 2, l = 0, ml = -1
c. n = 0, l = 0, ml = 0
d. n = 3, l = 1, ml = -1
9. What is the maximum number of orbitals that can be occupied by electrons in the n = 2
shell?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 4
d. 9
SI Sessions Tuesdays/ Thursdays @4pm & 6:30pm
esiegelman2021@fau.edu
General Chemistry I: Chapter 6 Handout
SI Leader: Emily Siegelman
10. What is the maximum number of orbitals that can be identified with the following
quantum numbers: n= 5, l = 3?
a. 1
b. 3
c. 5
d. 7
11. A particular orbital has n = 4, l = 2. Identify the orbital.
a. 2f
b. 2g
c. 4p
d. 4d
12. Of the following orbitals choices- 1p, 2d, 3d, 4f- are proper?
SI Sessions Tuesdays/ Thursdays @4pm & 6:30pm
esiegelman2021@fau.edu
You might also like
- Gen Chem Q2 - 1 2Document8 pagesGen Chem Q2 - 1 2Frenalyn Cerilla SantiagoNo ratings yet
- ExamQuestionsTroChapter7 8 TrimmedDocument8 pagesExamQuestionsTroChapter7 8 TrimmedAli TarekNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument27 pagesGeneral ChemistryRick AndrewsNo ratings yet
- 6A Practice MT2 F13Document4 pages6A Practice MT2 F13Aileen LiangNo ratings yet
- Final Exam ReviewDocument16 pagesFinal Exam Reviewsebastiangon2023No ratings yet
- Chem Basic FB Answer Key CH 05 (06.13.16)Document6 pagesChem Basic FB Answer Key CH 05 (06.13.16)amalieroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument41 pagesChapter 1 - Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDan DinhNo ratings yet
- Chem 11 2016 WorksheetDocument4 pagesChem 11 2016 Worksheettemesgenor21No ratings yet
- One Mark QuestionsDocument4 pagesOne Mark Questionshari95No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Quantum Numbers and Electronics ConfigurationDocument18 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Quantum Numbers and Electronics ConfigurationLynette LicsiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document9 pagesChapter 7alexcw92No ratings yet
- Question Bank CHEM 1201Document12 pagesQuestion Bank CHEM 1201SHASHANK VISHWAKARMANo ratings yet
- Chemistry: A Free Web Support in EducationDocument4 pagesChemistry: A Free Web Support in EducationHarman SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Remedial Test 1 2015Document3 pagesChemistry Remedial Test 1 2015getnetdejen13No ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Form 6Document5 pagesSTPM Chemistry Form 6BabasChong100% (1)
- Q2 Sci.9 Mod.1 v1.0Document25 pagesQ2 Sci.9 Mod.1 v1.0April Lavenia Barrientos100% (3)
- Science Module 1 q2Document20 pagesScience Module 1 q2rylacantubaNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument2 pagesActivitycamille lei CalderonNo ratings yet
- Code:: Part 1. Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesCode:: Part 1. Multiple Choice QuestionsChiến NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Exercise 1 - Atomic SymbolsDocument6 pagesTopic 1 Exercise 1 - Atomic SymbolsKotori Choi IshikawaNo ratings yet
- q2 Sci9 Mod1 v10 NationalDocument26 pagesq2 Sci9 Mod1 v10 NationalGian YadaooNo ratings yet
- Mediterranean Institute of Technology Midterm Exam Spring 2021 1/6Document6 pagesMediterranean Institute of Technology Midterm Exam Spring 2021 1/6Aya Hachana0% (1)
- EDocument13 pagesESultan Hadi PrabowoNo ratings yet
- 1st SUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 9 Q2Document5 pages1st SUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 9 Q2Sabnahis Batongbuhay Extension100% (1)
- Ch. 7 Practice Quiz Answer KeyDocument3 pagesCh. 7 Practice Quiz Answer KeyMysticNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 9th Unit 2 EnglishDocument1 pageChemistry 9th Unit 2 Englisha.basheer089No ratings yet
- PH-Model Paper-03 - 092131Document32 pagesPH-Model Paper-03 - 092131p1hx0wyNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument4 pagesAnswer KeyNajwa KayyaliNo ratings yet
- ESP Test 1 Part 1 AnswersDocument5 pagesESP Test 1 Part 1 Answerschemistry_mwuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Atomic Electron Configurations and PeriodicityDocument40 pagesChapter 8: Atomic Electron Configurations and PeriodicityRuben FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 11 TH 12 THDocument52 pagesChemistry 11 TH 12 THSudhir ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Insert Image Related To The Topic Which Occupy Full Box.: Class: Subject: Unit No.: Unit Name: TopicDocument7 pagesInsert Image Related To The Topic Which Occupy Full Box.: Class: Subject: Unit No.: Unit Name: TopicMayank ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvansDocument22 pagesWelcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvanseraborNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Introductory Chemistry 6th Edition Tro Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument29 pages(Download PDF) Introductory Chemistry 6th Edition Tro Solutions Manual Full Chapterhodosynorlis100% (8)
- Chapter 7 Chem HWDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Chem HWSpringSpaethNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Structure of Atom Important Questions With AnswersDocument16 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Structure of Atom Important Questions With AnswersPriyanshuNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Important Question Answer of Chapter 2 (Structure of Atom) &chapter 3 (Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument38 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Important Question Answer of Chapter 2 (Structure of Atom) &chapter 3 (Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Propertiessriram.j.athreyaNo ratings yet
- 9th Chem CHP 2-mcqsDocument2 pages9th Chem CHP 2-mcqsshahid khanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nasim Zafar: COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Virtual Campus IslamabadDocument43 pagesDr. Nasim Zafar: COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Virtual Campus IslamabadAhmerz Chillz WinterzNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Flame Test Manual Oktober2021Document4 pagesExperiment 2 Flame Test Manual Oktober2021NORHELENA ALEESA ZULKEPLINo ratings yet
- Practice Exam: InstructionsDocument12 pagesPractice Exam: Instructionsneemine329No ratings yet
- Chem I (EM) BLM 2021-22Document66 pagesChem I (EM) BLM 2021-22Tanzeela Hashmi75% (8)
- PART I: MULTIPLE CHOICE (Each Question Has A 2-Point Value)Document6 pagesPART I: MULTIPLE CHOICE (Each Question Has A 2-Point Value)Saige RedNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2Nd Edition by Zumdahl Isbn 1305079248 9781305079243 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2Nd Edition by Zumdahl Isbn 1305079248 9781305079243 Full Chapter PDFmarc.herman362100% (12)
- MT Exam 2022Document6 pagesMT Exam 2022ultrasonic.205No ratings yet
- Addis Ababa City Government Education BureauDocument11 pagesAddis Ababa City Government Education BureauErmias100% (1)
- Atoms: Neutrons ProtonsDocument8 pagesAtoms: Neutrons ProtonsMelke JasinNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory and The Electronic Structure of Atoms: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument69 pagesQuantum Theory and The Electronic Structure of Atoms: Multiple Choice QuestionsRs Remo KookieNo ratings yet
- hss17c0400t Ir ReviewDocument5 pageshss17c0400t Ir ReviewLara AminNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Inorg18Document6 pagesActivity 1 Inorg18JoelNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry by Annitah 1Document57 pagesInorganic Chemistry by Annitah 1mukisajob586No ratings yet
- Introductory Chemistry 6th Edition Tro Solutions Manual instant download all chapterDocument29 pagesIntroductory Chemistry 6th Edition Tro Solutions Manual instant download all chaptersenatsfera100% (2)
- Atomic Structure HL Multiple Choice Questions AnswersDocument3 pagesAtomic Structure HL Multiple Choice Questions AnswersMalak AlqaidoomNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledFarah EssidNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 7th Edition McMurry Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesChemistry 7th Edition McMurry Solutions Manual 1shaneclaywityaogbdk100% (22)
- Chemistry 7th Edition McMurry Solutions Manual 1Document11 pagesChemistry 7th Edition McMurry Solutions Manual 1philip100% (36)
- Chemistry 7Th Edition Mcmurry Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument32 pagesChemistry 7Th Edition Mcmurry Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFjuliette.brewer310100% (20)
- SI Sheet #4 Copy 2Document5 pagesSI Sheet #4 Copy 2sebastiangon2023No ratings yet
- Exam #2 ReviewDocument9 pagesExam #2 Reviewsebastiangon2023No ratings yet
- Final Exam Review 3Document17 pagesFinal Exam Review 3sebastiangon2023No ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesThermodynamicssebastiangon2023No ratings yet
- Final Exam ReviewDocument16 pagesFinal Exam Reviewsebastiangon2023No ratings yet
- Acousto Optics Modulator 1Document9 pagesAcousto Optics Modulator 1SURESH SURAGANINo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument1 pageElectromagnetic WavesJessicaMarizMagpocMendaroNo ratings yet
- Exponential Horn PhysicsDocument29 pagesExponential Horn PhysicshasiraqNo ratings yet
- Radio-Frequency Circuits6Document18 pagesRadio-Frequency Circuits6mumtazNo ratings yet
- Quantum MechanicsDocument87 pagesQuantum MechanicsNaveenjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Physics Improve ScoreDocument2 pagesPhysics Improve ScoreCHANON KIATKAWINWONGNo ratings yet
- Dipole Antenna 68 ... 87.5 MHZ Vertical Polarization: Type NoDocument2 pagesDipole Antenna 68 ... 87.5 MHZ Vertical Polarization: Type NoIvanNo ratings yet
- Oscillations - Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesOscillations - Lesson PlanpratikwalimbeusaNo ratings yet
- Physlab Report 7Document2 pagesPhyslab Report 7Pugee ChavezNo ratings yet
- Q4 STEM General Physics 2 Week 6Document4 pagesQ4 STEM General Physics 2 Week 6Renz PerlasNo ratings yet
- Branislav Kisa Canin Eric K. Zhang Draft Version: 2011-2018 Solutions ManualDocument16 pagesBranislav Kisa Canin Eric K. Zhang Draft Version: 2011-2018 Solutions Manualbus9No ratings yet
- Waves and Sound WorksheetDocument12 pagesWaves and Sound WorksheetprosenNo ratings yet
- Interference of Light Waves..Document17 pagesInterference of Light Waves..Aditya Kumar DwivediNo ratings yet
- Radiation Heat Transfer PDFDocument6 pagesRadiation Heat Transfer PDFعبدالمؤمن خالد محمودNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Seismic WavesDocument30 pagesWeek 1 Seismic WavesvriannaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Sciences - Co-Ordinated (Double) (0654) : P15 - SpectraDocument3 pagesCambridge IGCSE Sciences - Co-Ordinated (Double) (0654) : P15 - SpectraJuliaNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Exercise 1 (7) Digital RMZSDocument37 pages01 Laboratory Exercise 1 (7) Digital RMZSrenzsantos0825No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Practice Problems Review and AssessmentDocument42 pagesChapter 14 Practice Problems Review and Assessmentra.yakout85No ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Grade 10 Term 1 RevisionDocument15 pagesPhysical Sciences Grade 10 Term 1 RevisionleatissiakngoieNo ratings yet
- NW NSC Physical Sciences P 1 MG Afr-Eng Sept 2023 - FinalDocument16 pagesNW NSC Physical Sciences P 1 MG Afr-Eng Sept 2023 - Final5n0wm4n504No ratings yet
- Important Questions For Annual Examination - Physics 2023 I Puc - Physics PROBLEMS (45 - 48)Document5 pagesImportant Questions For Annual Examination - Physics 2023 I Puc - Physics PROBLEMS (45 - 48)Shaheena BegumNo ratings yet
- 5 Year Solved QB - EC 6503 TLWDocument181 pages5 Year Solved QB - EC 6503 TLWmaheswarisubramaniNo ratings yet
- AVE Uides: Eneral Olutions For Rbitrary WaveguideDocument16 pagesAVE Uides: Eneral Olutions For Rbitrary WaveguideDush AkilaNo ratings yet
- Vibrations and Its Types: Presented By: Er. Sahil Sharma Department of Civil EngineeringDocument12 pagesVibrations and Its Types: Presented By: Er. Sahil Sharma Department of Civil EngineeringSaHil ShaRmaNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature and RadiationDocument39 pagesDual Nature and RadiationWedger RealmeNo ratings yet
- S Mahalingam 1957 Br. J. Appl. Phys. 8 145Document5 pagesS Mahalingam 1957 Br. J. Appl. Phys. 8 145Oussama AkrmiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - 1 (Planar Optical Waveguides) : PYL-791 (Fiber Optics), Ist Semester 2020-2021Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet - 1 (Planar Optical Waveguides) : PYL-791 (Fiber Optics), Ist Semester 2020-2021deepanshuNo ratings yet
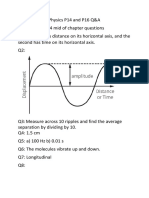
- Physics P14 and P16 EndDocument11 pagesPhysics P14 and P16 EndAum AcharyaNo ratings yet
- L1 1 Introduction and Fundamental of SoundDocument41 pagesL1 1 Introduction and Fundamental of SoundShivika AgrawalNo ratings yet
- B1.2.Intro To AcousticsDocument29 pagesB1.2.Intro To AcousticsMuhammad RidwanNo ratings yet