Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsP-Block (Zero Group)
P-Block (Zero Group)
Uploaded by
kaleshreyas6Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- ASTM A653-Standard Specification For Steel Sheet, Zinc-Coated (Galvanized) or Zinc-Iron Alloy-Coated (Galvannealed) by The Hot-Dip Process PDFDocument14 pagesASTM A653-Standard Specification For Steel Sheet, Zinc-Coated (Galvanized) or Zinc-Iron Alloy-Coated (Galvannealed) by The Hot-Dip Process PDFMOHAMAD NIZAMUDINNo ratings yet
- Inert GasesDocument42 pagesInert GasesRAVI KUMAR INSANNo ratings yet
- Fischer-Tropsch (FT) ProcessDocument18 pagesFischer-Tropsch (FT) ProcessNur Ainie Baharudin100% (4)
- Special Colours Updated 2006Document16 pagesSpecial Colours Updated 2006Hamilton CopeteNo ratings yet
- P Block Group 18 Revision Notes Jee Mains L Neet L Kota Short Notes L Inorganic Chemistry LDocument1 pageP Block Group 18 Revision Notes Jee Mains L Neet L Kota Short Notes L Inorganic Chemistry LMAnOJ KAnNA JNo ratings yet
- Group 18 Class 12 NotesDocument4 pagesGroup 18 Class 12 NotesRitvik ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Noble Gas PPT Final 211226061542Document41 pagesNoble Gas PPT Final 211226061542Anas 2974No ratings yet
- Group 18 Elements (Noble Gases) Syed Zaffer AliDocument6 pagesGroup 18 Elements (Noble Gases) Syed Zaffer AliAlka Manjaly JaisonNo ratings yet
- Noble Gases: B.Sc. Chemistry Semester I Dr. Ashok Kuingh Assistant Professor University of Lucknow LucknowDocument21 pagesNoble Gases: B.Sc. Chemistry Semester I Dr. Ashok Kuingh Assistant Professor University of Lucknow LucknowSergioNo ratings yet
- Advanced Inorganic Chemistry - ROBERT L. CARTERDocument7 pagesAdvanced Inorganic Chemistry - ROBERT L. CARTERBRUNO RAMOS DE LIMANo ratings yet
- Noble Gas PPT, FinalDocument42 pagesNoble Gas PPT, FinalRAVI KUMAR INSAN100% (2)
- Chemistry of Noble GasesDocument26 pagesChemistry of Noble GasesjaqNo ratings yet
- Dipanjali Project (FinaleDocument28 pagesDipanjali Project (FinaleDipanjali SahooNo ratings yet
- Noble Gases 20 Aug 2022Document2 pagesNoble Gases 20 Aug 2022PLABAN DASNo ratings yet
- 18th GroupDocument12 pages18th GroupSai Sasivardhan GampaNo ratings yet
- IOC Complete Reactions - IOC Complete ReactionsDocument5 pagesIOC Complete Reactions - IOC Complete Reactionsasway933No ratings yet
- 18th GRP NarayanaDocument11 pages18th GRP NarayanaM. FaisalNo ratings yet
- Ch-8:-Redox Reactions: (Pottasium Ferricinite) (Pottasium Ferrocinite)Document21 pagesCh-8:-Redox Reactions: (Pottasium Ferricinite) (Pottasium Ferrocinite)PATEL AUM S.No ratings yet
- P BlockDocument1 pageP BlockYash PatelNo ratings yet
- S-Block For Jee AdvanceDocument38 pagesS-Block For Jee AdvanceSitabai JadhavNo ratings yet
- 1-4 Road MapDocument4 pages1-4 Road Mapipsita lahiriNo ratings yet
- Classroom Rules: NO Scribbling On DesksDocument15 pagesClassroom Rules: NO Scribbling On DesksArjun PasrichaNo ratings yet
- Group18elements 160809012321Document18 pagesGroup18elements 160809012321monicpaul thachilNo ratings yet
- 4.18th Group Elements (173-191) FINALDocument19 pages4.18th Group Elements (173-191) FINALSurya teja cvNo ratings yet
- Roadmap Problem - 1Document1 pageRoadmap Problem - 1Siddharth SharmaNo ratings yet
- P Block Master NcertDocument40 pagesP Block Master Ncertrabindrasahoo1006No ratings yet
- FaziraRazak - HydrogenDocument50 pagesFaziraRazak - HydrogenaieyinHengNo ratings yet
- Water Disinfection Ferrate VI As The Gre PDFDocument10 pagesWater Disinfection Ferrate VI As The Gre PDFalejandra mNo ratings yet
- Benzene Haloalkanes Haloarenes Alcohols Notes (Lakshya JEE 2023)Document9 pagesBenzene Haloalkanes Haloarenes Alcohols Notes (Lakshya JEE 2023)Hinata逍遥No ratings yet
- P - Block ElementsDocument8 pagesP - Block ElementsGyanaranjan RautarayNo ratings yet
- Complete Periodic Table 6Document9 pagesComplete Periodic Table 6Fenil KoratNo ratings yet
- Lec1 - Redox I (MUST) PDFDocument14 pagesLec1 - Redox I (MUST) PDFAmeer MohdNo ratings yet
- P-Block - Extra Notes 1 (PJ12MB)Document42 pagesP-Block - Extra Notes 1 (PJ12MB)hsjbsjsNo ratings yet
- Organics: Oxidation: Organic Molecule CO,, (Complete Mineralization)Document13 pagesOrganics: Oxidation: Organic Molecule CO,, (Complete Mineralization)SantJhaNo ratings yet
- Noble GasesDocument5 pagesNoble GasesDevanshi MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen and Its Compounds: ST THDocument8 pagesHydrogen and Its Compounds: ST THAravind NarasimhaluNo ratings yet
- OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS (Redox Reactions) (SJ, P. 316)Document29 pagesOXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS (Redox Reactions) (SJ, P. 316)Jon Bisu Debnath0% (1)
- Redox ReactionsDocument44 pagesRedox ReactionsAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Surface Reactions On Metal and Associated Impact of Salt AnionsDocument2 pagesSurface Reactions On Metal and Associated Impact of Salt AnionsDaniel BenegasNo ratings yet
- 9group ViiaDocument21 pages9group Viiaglaurent487No ratings yet
- Noble GasDocument16 pagesNoble GasNandya AristaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - Ony PDFDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet - Ony PDFSana ImamNo ratings yet
- RCT Class SampleDocument10 pagesRCT Class Samplepanjiyarsamarth08No ratings yet
- ChromimetryDocument1 pageChromimetryĐặng Thu ThảoNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Redox ChemistryDocument20 pagesAquatic Redox ChemistryAsep SaefumillahNo ratings yet
- Organic Synthesis. ReductionsDocument64 pagesOrganic Synthesis. ReductionsKartik RanaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry: Sri ChaitanyaDocument11 pagesInorganic Chemistry: Sri ChaitanyasuryasaiNo ratings yet
- Compounds of Xenon PDFDocument7 pagesCompounds of Xenon PDFÑäñdäñëë ÑäyäkNo ratings yet
- Alkene N BenzeneDocument2 pagesAlkene N Benzenemikumo81No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon: Reagent - Function: NotesDocument46 pagesHydrocarbon: Reagent - Function: NotesSowmya AnandNo ratings yet
- 4.5: Pourbaix DiagramsDocument3 pages4.5: Pourbaix DiagramsDwi PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Group - 16 ElementsDocument24 pagesGroup - 16 ElementsChandra VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Group 15 ElementsDocument24 pagesGroup 15 ElementsAkarshNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDocument64 pagesHydrogen and Its CompoundsAnamikaNo ratings yet
- assignment6ANS PDFDocument11 pagesassignment6ANS PDFKNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Metals and NonmetalsDocument7 pagesSynopsis Metals and NonmetalsSaumya DhokariyaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 302 Stratospheric Chemistry2Document47 pagesCHEM 302 Stratospheric Chemistry2MAGU_MWENYEWENo ratings yet
- HydrogenDocument21 pagesHydrogenAmmritaNo ratings yet
- KimiaDocument28 pagesKimianabila safithriNo ratings yet
- 509 Topper 21 110 1 2 462 Study of First Element Hydrogen Up202004231654 1587641079 979Document9 pages509 Topper 21 110 1 2 462 Study of First Element Hydrogen Up202004231654 1587641079 979Rakesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemical Formula, Naming & Writing Compound: General Chemistry 1Document30 pagesChemical Formula, Naming & Writing Compound: General Chemistry 1Synne Mae BorneaNo ratings yet
- Sgs Cen Issues en 14350 - 2020 en PDF 20 v2Document2 pagesSgs Cen Issues en 14350 - 2020 en PDF 20 v2aminNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulas at A GlanceDocument47 pagesChemical Formulas at A GlanceSubho BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - D BlockDocument47 pagesTopic 7 - D Blockizz isalahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 F3Document14 pagesChapter 4 F3Nurul AqilahNo ratings yet
- Reduce Carbon Footprint LeafletDocument2 pagesReduce Carbon Footprint LeafletaajwennerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Exam Style QuestionsDocument13 pagesChapter 10 Exam Style QuestionsAmanda AnushaNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction LANTHANIDE SEPARATIONDocument4 pagesSolvent Extraction LANTHANIDE SEPARATIONGandiyaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Chemistry Lab - Exploring The 5 Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument2 pagesGrade 11 Chemistry Lab - Exploring The 5 Types of Chemical Reactionsapi-212579279No ratings yet
- Glaze MaterialsDocument7 pagesGlaze MaterialssmiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/04Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/04Yasir Akhun0% (1)
- G8TOT Matter Modules 2 3Document20 pagesG8TOT Matter Modules 2 3Jestony Matilla50% (2)
- Moles Formulae Equations QuestionsDocument148 pagesMoles Formulae Equations QuestionsShifa RizwanNo ratings yet
- D Block Notes Part - 1Document44 pagesD Block Notes Part - 1Altaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics 1 QPDocument12 pagesChemical Energetics 1 QPMohammed AnwerNo ratings yet
- RSC Nutrients and FertilisersDocument2 pagesRSC Nutrients and FertilisersduongchitrungNo ratings yet
- Ammonia 101011060743 Phpapp01Document3 pagesAmmonia 101011060743 Phpapp01Muhd IqbalNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Trends ProjectDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table Trends Projectapi-239702286No ratings yet
- Chapter 02 ISM Chang 14eDocument7 pagesChapter 02 ISM Chang 14elsytb2000No ratings yet
- 0653 w15 Ms 62Document4 pages0653 w15 Ms 62yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- Some Atypical Properties of Beryllium Compounds - Chemistry LibretextsDocument6 pagesSome Atypical Properties of Beryllium Compounds - Chemistry Libretextsapi-368121935No ratings yet
- Electrolysis 3 MSDocument14 pagesElectrolysis 3 MSEnoch AdebiyiNo ratings yet
- Periodic LawDocument2 pagesPeriodic LawenzoNo ratings yet
- A213Document14 pagesA213Juan Vicente Reyes LimaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument2 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesNirvana Adithya Visiobibliophobiatic GuyNo ratings yet
- - (Appendix B Lennard–Jones Constants) PDFDocument2 pages- (Appendix B Lennard–Jones Constants) PDFYaiselle FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties and Trends TamDocument22 pagesPeriodic Properties and Trends TamMonkeNo ratings yet
- Fluorspar Acid Grade PDFDocument2 pagesFluorspar Acid Grade PDFBurhani WicaksonoNo ratings yet
P-Block (Zero Group)
P-Block (Zero Group)
Uploaded by
kaleshreyas60 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageP-Block (Zero Group)
P-Block (Zero Group)
Uploaded by
kaleshreyas6Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
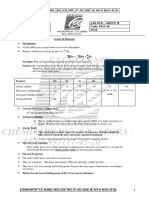
p-BLOCK
18th-GROUP NOBLE GAS
1. Relative Abundance:
Ø In Dewar's method, the separation of noble gases is
summerized below
Ar > Ne > Kr > He > Xe > Rn
Mixture of noble gases (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe)
2. Melting and Boiling point:
in contact with coconut charcoal at 173 K
Rn > Xe > Kr > Ar > Ne > He
3. He has the lowest boiling point among all element
Unadsorbed adsorbed
4. Noble gases are monoatomic, colourless, odourless, (He, Ne) (Ar, Kr, Xe)
spraingly soluble in water and diffusing through most in contact with charcoal at 93 K in contact with another charcoal at
liquid air temperature.
commonly used laboratry materials.
5. O2[PtF6] is the first noble gas compound. Adsorbed Unadsorbed
6. Ar, Kr and Xe form clathrate compound when pass Ne He In the first charcoal Second charcoal
Kr, Xe. Temp. raised Ar
in ice with high pressure. to 183 K
A.6H2O (A = Ar/Kr/Xe)
Evolved Kr Remained adsorbed Xe
Ø The viscosity of He is extermely low, about 1/100th of
hydrogen gas.
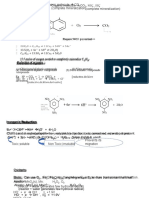
Prepration of Xe-Fluoride:
F2, 673K, 1 bar
XeF2
2F2, 873K, 7 bar O2F2
Xe XeF4 XeF6 + O2
143K
3F2, 573K, 70 bar
XeF6
Properties:
Fluoride donor: Eg. XeF2 + MF5 ¾¾® [XeF4 ]+ [MF6 ]-
(M =As / Sb / P)
Fluoride acceptor: Eg. XeF6 + MF ¾¾® M + [XeF7 ]-
(M =Na /K / Rb / Cs)
SF4 / Pt
Fluorinating agents: Eg. XeF4 ¾¾¾¾ ® PtF4 / SF6 + Xe
XeF2 + NO ¾¾® 2NOF + Xe
Reaction with SiO2 : Eg. 2XeF6 + SiO2 ¾¾® SiF4 + XeOF4
Hydrolysis:
H2O 1
Xe + 2HF + O
2 2
XeF2
1
Xe + 2F – + H2O + O
2OH
–
2 2
6XeF4 + 12H2O ¾¾® 4Xe + 2XeO3 + 24HF + 3O2
Partial hydrolysis
H2O
XeOF4 + 2HF
XeF6 XeO3 + 6HF
3H2O
7OH – – –
HXeO4 + 3H2O + F
–
ex. OH
1
(XeO64–¯ + Xe + 2H2O + O2 )
2
You might also like
- ASTM A653-Standard Specification For Steel Sheet, Zinc-Coated (Galvanized) or Zinc-Iron Alloy-Coated (Galvannealed) by The Hot-Dip Process PDFDocument14 pagesASTM A653-Standard Specification For Steel Sheet, Zinc-Coated (Galvanized) or Zinc-Iron Alloy-Coated (Galvannealed) by The Hot-Dip Process PDFMOHAMAD NIZAMUDINNo ratings yet
- Inert GasesDocument42 pagesInert GasesRAVI KUMAR INSANNo ratings yet
- Fischer-Tropsch (FT) ProcessDocument18 pagesFischer-Tropsch (FT) ProcessNur Ainie Baharudin100% (4)
- Special Colours Updated 2006Document16 pagesSpecial Colours Updated 2006Hamilton CopeteNo ratings yet
- P Block Group 18 Revision Notes Jee Mains L Neet L Kota Short Notes L Inorganic Chemistry LDocument1 pageP Block Group 18 Revision Notes Jee Mains L Neet L Kota Short Notes L Inorganic Chemistry LMAnOJ KAnNA JNo ratings yet
- Group 18 Class 12 NotesDocument4 pagesGroup 18 Class 12 NotesRitvik ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Noble Gas PPT Final 211226061542Document41 pagesNoble Gas PPT Final 211226061542Anas 2974No ratings yet
- Group 18 Elements (Noble Gases) Syed Zaffer AliDocument6 pagesGroup 18 Elements (Noble Gases) Syed Zaffer AliAlka Manjaly JaisonNo ratings yet
- Noble Gases: B.Sc. Chemistry Semester I Dr. Ashok Kuingh Assistant Professor University of Lucknow LucknowDocument21 pagesNoble Gases: B.Sc. Chemistry Semester I Dr. Ashok Kuingh Assistant Professor University of Lucknow LucknowSergioNo ratings yet
- Advanced Inorganic Chemistry - ROBERT L. CARTERDocument7 pagesAdvanced Inorganic Chemistry - ROBERT L. CARTERBRUNO RAMOS DE LIMANo ratings yet
- Noble Gas PPT, FinalDocument42 pagesNoble Gas PPT, FinalRAVI KUMAR INSAN100% (2)
- Chemistry of Noble GasesDocument26 pagesChemistry of Noble GasesjaqNo ratings yet
- Dipanjali Project (FinaleDocument28 pagesDipanjali Project (FinaleDipanjali SahooNo ratings yet
- Noble Gases 20 Aug 2022Document2 pagesNoble Gases 20 Aug 2022PLABAN DASNo ratings yet
- 18th GroupDocument12 pages18th GroupSai Sasivardhan GampaNo ratings yet
- IOC Complete Reactions - IOC Complete ReactionsDocument5 pagesIOC Complete Reactions - IOC Complete Reactionsasway933No ratings yet
- 18th GRP NarayanaDocument11 pages18th GRP NarayanaM. FaisalNo ratings yet
- Ch-8:-Redox Reactions: (Pottasium Ferricinite) (Pottasium Ferrocinite)Document21 pagesCh-8:-Redox Reactions: (Pottasium Ferricinite) (Pottasium Ferrocinite)PATEL AUM S.No ratings yet
- P BlockDocument1 pageP BlockYash PatelNo ratings yet
- S-Block For Jee AdvanceDocument38 pagesS-Block For Jee AdvanceSitabai JadhavNo ratings yet
- 1-4 Road MapDocument4 pages1-4 Road Mapipsita lahiriNo ratings yet
- Classroom Rules: NO Scribbling On DesksDocument15 pagesClassroom Rules: NO Scribbling On DesksArjun PasrichaNo ratings yet
- Group18elements 160809012321Document18 pagesGroup18elements 160809012321monicpaul thachilNo ratings yet
- 4.18th Group Elements (173-191) FINALDocument19 pages4.18th Group Elements (173-191) FINALSurya teja cvNo ratings yet
- Roadmap Problem - 1Document1 pageRoadmap Problem - 1Siddharth SharmaNo ratings yet
- P Block Master NcertDocument40 pagesP Block Master Ncertrabindrasahoo1006No ratings yet
- FaziraRazak - HydrogenDocument50 pagesFaziraRazak - HydrogenaieyinHengNo ratings yet
- Water Disinfection Ferrate VI As The Gre PDFDocument10 pagesWater Disinfection Ferrate VI As The Gre PDFalejandra mNo ratings yet
- Benzene Haloalkanes Haloarenes Alcohols Notes (Lakshya JEE 2023)Document9 pagesBenzene Haloalkanes Haloarenes Alcohols Notes (Lakshya JEE 2023)Hinata逍遥No ratings yet
- P - Block ElementsDocument8 pagesP - Block ElementsGyanaranjan RautarayNo ratings yet
- Complete Periodic Table 6Document9 pagesComplete Periodic Table 6Fenil KoratNo ratings yet
- Lec1 - Redox I (MUST) PDFDocument14 pagesLec1 - Redox I (MUST) PDFAmeer MohdNo ratings yet
- P-Block - Extra Notes 1 (PJ12MB)Document42 pagesP-Block - Extra Notes 1 (PJ12MB)hsjbsjsNo ratings yet
- Organics: Oxidation: Organic Molecule CO,, (Complete Mineralization)Document13 pagesOrganics: Oxidation: Organic Molecule CO,, (Complete Mineralization)SantJhaNo ratings yet
- Noble GasesDocument5 pagesNoble GasesDevanshi MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen and Its Compounds: ST THDocument8 pagesHydrogen and Its Compounds: ST THAravind NarasimhaluNo ratings yet
- OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS (Redox Reactions) (SJ, P. 316)Document29 pagesOXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS (Redox Reactions) (SJ, P. 316)Jon Bisu Debnath0% (1)
- Redox ReactionsDocument44 pagesRedox ReactionsAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Surface Reactions On Metal and Associated Impact of Salt AnionsDocument2 pagesSurface Reactions On Metal and Associated Impact of Salt AnionsDaniel BenegasNo ratings yet
- 9group ViiaDocument21 pages9group Viiaglaurent487No ratings yet
- Noble GasDocument16 pagesNoble GasNandya AristaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - Ony PDFDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet - Ony PDFSana ImamNo ratings yet
- RCT Class SampleDocument10 pagesRCT Class Samplepanjiyarsamarth08No ratings yet
- ChromimetryDocument1 pageChromimetryĐặng Thu ThảoNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Redox ChemistryDocument20 pagesAquatic Redox ChemistryAsep SaefumillahNo ratings yet
- Organic Synthesis. ReductionsDocument64 pagesOrganic Synthesis. ReductionsKartik RanaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry: Sri ChaitanyaDocument11 pagesInorganic Chemistry: Sri ChaitanyasuryasaiNo ratings yet
- Compounds of Xenon PDFDocument7 pagesCompounds of Xenon PDFÑäñdäñëë ÑäyäkNo ratings yet
- Alkene N BenzeneDocument2 pagesAlkene N Benzenemikumo81No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon: Reagent - Function: NotesDocument46 pagesHydrocarbon: Reagent - Function: NotesSowmya AnandNo ratings yet
- 4.5: Pourbaix DiagramsDocument3 pages4.5: Pourbaix DiagramsDwi PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Group - 16 ElementsDocument24 pagesGroup - 16 ElementsChandra VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Group 15 ElementsDocument24 pagesGroup 15 ElementsAkarshNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDocument64 pagesHydrogen and Its CompoundsAnamikaNo ratings yet
- assignment6ANS PDFDocument11 pagesassignment6ANS PDFKNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Metals and NonmetalsDocument7 pagesSynopsis Metals and NonmetalsSaumya DhokariyaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 302 Stratospheric Chemistry2Document47 pagesCHEM 302 Stratospheric Chemistry2MAGU_MWENYEWENo ratings yet
- HydrogenDocument21 pagesHydrogenAmmritaNo ratings yet
- KimiaDocument28 pagesKimianabila safithriNo ratings yet
- 509 Topper 21 110 1 2 462 Study of First Element Hydrogen Up202004231654 1587641079 979Document9 pages509 Topper 21 110 1 2 462 Study of First Element Hydrogen Up202004231654 1587641079 979Rakesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemical Formula, Naming & Writing Compound: General Chemistry 1Document30 pagesChemical Formula, Naming & Writing Compound: General Chemistry 1Synne Mae BorneaNo ratings yet
- Sgs Cen Issues en 14350 - 2020 en PDF 20 v2Document2 pagesSgs Cen Issues en 14350 - 2020 en PDF 20 v2aminNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulas at A GlanceDocument47 pagesChemical Formulas at A GlanceSubho BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - D BlockDocument47 pagesTopic 7 - D Blockizz isalahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 F3Document14 pagesChapter 4 F3Nurul AqilahNo ratings yet
- Reduce Carbon Footprint LeafletDocument2 pagesReduce Carbon Footprint LeafletaajwennerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Exam Style QuestionsDocument13 pagesChapter 10 Exam Style QuestionsAmanda AnushaNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction LANTHANIDE SEPARATIONDocument4 pagesSolvent Extraction LANTHANIDE SEPARATIONGandiyaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Chemistry Lab - Exploring The 5 Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument2 pagesGrade 11 Chemistry Lab - Exploring The 5 Types of Chemical Reactionsapi-212579279No ratings yet
- Glaze MaterialsDocument7 pagesGlaze MaterialssmiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/04Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/04Yasir Akhun0% (1)
- G8TOT Matter Modules 2 3Document20 pagesG8TOT Matter Modules 2 3Jestony Matilla50% (2)
- Moles Formulae Equations QuestionsDocument148 pagesMoles Formulae Equations QuestionsShifa RizwanNo ratings yet
- D Block Notes Part - 1Document44 pagesD Block Notes Part - 1Altaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics 1 QPDocument12 pagesChemical Energetics 1 QPMohammed AnwerNo ratings yet
- RSC Nutrients and FertilisersDocument2 pagesRSC Nutrients and FertilisersduongchitrungNo ratings yet
- Ammonia 101011060743 Phpapp01Document3 pagesAmmonia 101011060743 Phpapp01Muhd IqbalNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Trends ProjectDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table Trends Projectapi-239702286No ratings yet
- Chapter 02 ISM Chang 14eDocument7 pagesChapter 02 ISM Chang 14elsytb2000No ratings yet
- 0653 w15 Ms 62Document4 pages0653 w15 Ms 62yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- Some Atypical Properties of Beryllium Compounds - Chemistry LibretextsDocument6 pagesSome Atypical Properties of Beryllium Compounds - Chemistry Libretextsapi-368121935No ratings yet
- Electrolysis 3 MSDocument14 pagesElectrolysis 3 MSEnoch AdebiyiNo ratings yet
- Periodic LawDocument2 pagesPeriodic LawenzoNo ratings yet
- A213Document14 pagesA213Juan Vicente Reyes LimaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument2 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesNirvana Adithya Visiobibliophobiatic GuyNo ratings yet
- - (Appendix B Lennard–Jones Constants) PDFDocument2 pages- (Appendix B Lennard–Jones Constants) PDFYaiselle FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties and Trends TamDocument22 pagesPeriodic Properties and Trends TamMonkeNo ratings yet
- Fluorspar Acid Grade PDFDocument2 pagesFluorspar Acid Grade PDFBurhani WicaksonoNo ratings yet