Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Renewable Energy Sources and Their Adoption
Renewable Energy Sources and Their Adoption
Uploaded by
ahmed shaikCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Future of Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesThe Future of Renewable EnergyrkNo ratings yet
- The Future of Renewable EnergyDocument1 pageThe Future of Renewable Energyahlai420No ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Solutions and Climate Change MitigationDocument2 pagesRenewable Energy Solutions and Climate Change Mitigationsetopi8888No ratings yet
- The Role of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate ChangeDocument4 pagesThe Role of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate ChangeNur Ad-DujaNo ratings yet
- 2Document2 pages2Ace NooneNo ratings yet
- 4424Document2 pages4424adrianluczak7No ratings yet
- The Rise of Renewable Energy A Sustainable FutureDocument1 pageThe Rise of Renewable Energy A Sustainable FuturetdctopNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy SourcesDocument1 pageRenewable Energy Sourcestalaxej386No ratings yet
- The Future of Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesThe Future of Renewable EnergyHardik Kashyap VepariNo ratings yet
- The Role of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesThe Role of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate Changequiz-had0nNo ratings yet
- The Future of Renewable EnergyDocument1 pageThe Future of Renewable EnergydotruhadruNo ratings yet
- The Inexorable Transition To Green EnergyDocument2 pagesThe Inexorable Transition To Green EnergyAshwin AshokanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Energy Resources - maneETDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Energy Resources - maneETharjotkaurahuja18No ratings yet
- Renewable Energy - Text ExampleDocument1 pageRenewable Energy - Text ExampleDavi Lucas Lima SousaNo ratings yet
- Title - "The Power of Renewable Energy - Building A Sustainable Future"Document1 pageTitle - "The Power of Renewable Energy - Building A Sustainable Future"mfabregamarinNo ratings yet
- ReachDocument1 pageReachGoga ShoniaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesThe Role of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate ChangeJuan BrattiNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Renewable Energy Harnessing Nature's Power For A Sustainable FutureDocument3 pagesThe Evolution of Renewable Energy Harnessing Nature's Power For A Sustainable FutureHiroNo ratings yet
- Chat GPTed Doc 2Document1 pageChat GPTed Doc 2yourgreatestfear99No ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesRenewable EnergyStormbornNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Renewable Energyvoidmagic200No ratings yet
- Embracing The Renewable Revolution Exploring The Future of Renewable EnergyDocument3 pagesEmbracing The Renewable Revolution Exploring The Future of Renewable Energya_s_1_5No ratings yet
- The Importance of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesThe Importance of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate Changequiz-had0nNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy 1Document1 pageRenewable Energy 1fariri9664No ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesRenewable EnergykyzermainitNo ratings yet
- The Future of Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesThe Future of Renewable EnergyXaine PineraNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Renewable Energy UselDocument8 pagesBenefits of Renewable Energy Uselgeronimo stiltonNo ratings yet
- In Recent YearsDocument2 pagesIn Recent YearsKent MistolaNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3workr285No ratings yet
- The Green Revolution - How Renewable Energy Is Reshaping The WorldDocument3 pagesThe Green Revolution - How Renewable Energy Is Reshaping The WorldMaalav WhorraNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument1 pageEnergyAndrei BazarincaNo ratings yet
- Efficient and Economical Renewable Energy Resources (Research Proposal)Document2 pagesEfficient and Economical Renewable Energy Resources (Research Proposal)UmerShahzadQurashiNo ratings yet
- Unlocking A Sustainable Future - Exploring The Dynamics of EnergyDocument2 pagesUnlocking A Sustainable Future - Exploring The Dynamics of EnergyMariten JohnNo ratings yet
- Some Energy Creating Techniques and How Perpetual Motion Revolutionizes The GameDocument18 pagesSome Energy Creating Techniques and How Perpetual Motion Revolutionizes The GameAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument1 pageRenewable EnergyPinky MNo ratings yet
- Weather Patterns in AccraDocument2 pagesWeather Patterns in AccraDela KayNo ratings yet
- 13Document2 pages13lightsorcerorNo ratings yet
- ZnaczenieDocument1 pageZnaczenieaedfNo ratings yet
- Reading TextDocument1 pageReading TextShafiq BhattiNo ratings yet
- Advancing Towards A Sustainable FutureDocument2 pagesAdvancing Towards A Sustainable Futurevoidmagic200No ratings yet
- Renewable Energy TransitionDocument2 pagesRenewable Energy Transitionmianasadkamal108No ratings yet
- Report Finish 3Document15 pagesReport Finish 3a0925084228No ratings yet
- Climate Change and Renewable Energy: From Evidence to ActionFrom EverandClimate Change and Renewable Energy: From Evidence to ActionNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy and Its Role in Sustainable DevelopmentDocument1 pageRenewable Energy and Its Role in Sustainable Developmentصدقة جاريةNo ratings yet
- The GrothDocument1 pageThe Grothjasonsun91No ratings yet
- The Future of Renewable Energy - A Sustainable Path Towards A Brighter TomorrowDocument2 pagesThe Future of Renewable Energy - A Sustainable Path Towards A Brighter TomorrowBruwnoNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-04-18 at 7.47.33 AMDocument15 pagesScreenshot 2024-04-18 at 7.47.33 AMsauradeeparahaNo ratings yet
- 7 Tech RepDocument13 pages7 Tech RepFe MonteronNo ratings yet
- SustainabilityDocument4 pagesSustainabilityfarzanarohiNo ratings yet
- The Rise of Renewable Energy SourcesDocument1 pageThe Rise of Renewable Energy SourcesSergio RileyNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Renewable Energy Resources: Unit IiDocument34 pagesAdvantages of Renewable Energy Resources: Unit IiAdesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Renewable Energy Resources: Unit IiDocument34 pagesAdvantages of Renewable Energy Resources: Unit IiAdesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument8 pagesGeographyJudith NakazziNo ratings yet
- Green EnergyDocument6 pagesGreen EnergysegarnowbodyNo ratings yet
- Source of EnergyDocument3 pagesSource of Energyshaikhfatimaalvi95No ratings yet
- The Quest For Sustainable Energy - Navigating The Path To A Greener FutureDocument2 pagesThe Quest For Sustainable Energy - Navigating The Path To A Greener FuturePernille MathiasenNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Renewable EnergyDocument9 pagesResearch Paper Renewable EnergyMaíra Prata de AraújoNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy EssayDocument2 pagesRenewable Energy Essayeriksve13No ratings yet
- The Evolution and Impact of Renewable Energy TechnologiesDocument5 pagesThe Evolution and Impact of Renewable Energy Technologiesxadal74291No ratings yet
- JJ LetDocument2 pagesJJ Letpourya mashmoulNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic Compressed Air Energy Storage For Electricity SupplyDocument12 pagesAdiabatic Compressed Air Energy Storage For Electricity SupplysutardiNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Conventional Heat Treatment With Corn Oil Oil Blended With Indian Red Seed OilDocument11 pagesComparative Analysis of Conventional Heat Treatment With Corn Oil Oil Blended With Indian Red Seed Oilk eswariNo ratings yet
- Btech Oe 7 Sem Renewable Energy Resources Koe074 2022Document2 pagesBtech Oe 7 Sem Renewable Energy Resources Koe074 2022मधुसूदन सिंहNo ratings yet
- New PIANC Guidelines For Marine Oil and Petrochemical Terminal DesignDocument8 pagesNew PIANC Guidelines For Marine Oil and Petrochemical Terminal DesignydlewNo ratings yet
- RAC Case StudyDocument11 pagesRAC Case StudyshubhamNo ratings yet
- Appendix: List of Petroleum & Exploration Companies in Nigeria # Name MultinationalsDocument3 pagesAppendix: List of Petroleum & Exploration Companies in Nigeria # Name MultinationalsMuhammad Izzat Saffian100% (1)
- PET524 Saturation 1Document12 pagesPET524 Saturation 1Ronald NgueleNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument32 pagesPDFgharsallah mouna100% (1)
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase StudyAndrei HoNo ratings yet
- Buzzard Field Development - UK North Sea Zeron 100X TIG Wire SpecifiedDocument2 pagesBuzzard Field Development - UK North Sea Zeron 100X TIG Wire SpecifiedElMacheteDelHuesoNo ratings yet
- DRAGADOS Offshore by Oscar Del SantoDocument3 pagesDRAGADOS Offshore by Oscar Del SantoOscar César Del Santo, PhDNo ratings yet
- Biodigestor NRELDocument48 pagesBiodigestor NRELjorge AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Mister MeshDocument4 pagesMister MeshSiwa SiwananNo ratings yet
- Carbon Steel Pipe Standards & SpecificationsDocument9 pagesCarbon Steel Pipe Standards & SpecificationsTunji AminuNo ratings yet
- Lloyds Register - Future IMO Legislation (August 2013)Document0 pagesLloyds Register - Future IMO Legislation (August 2013)metallourgosNo ratings yet
- ( cAMERON: Certification of ComplianceDocument4 pages( cAMERON: Certification of ComplianceOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Guide To Chinese Climate Policy - 2019Document169 pagesGuide To Chinese Climate Policy - 2019ASIAANALYSISNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas DehydrationDocument12 pagesNatural Gas DehydrationSagar DadhichNo ratings yet
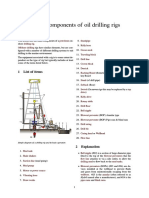
- List of Components of Oil Drilling RigsDocument4 pagesList of Components of Oil Drilling RigsIjlal Ahmad100% (1)
- 4CH0 2C Que 20170118Document20 pages4CH0 2C Que 20170118abhayNo ratings yet
- Delloite Oil and Gas Reality Check 2015 PDFDocument32 pagesDelloite Oil and Gas Reality Check 2015 PDFAzik KunouNo ratings yet
- Colour Codes, Notes & FAQ: WBCSD Cement Sustainability Initiative CO2 Emissions Inventory Protocol, Version 2.0Document33 pagesColour Codes, Notes & FAQ: WBCSD Cement Sustainability Initiative CO2 Emissions Inventory Protocol, Version 2.0Rodrigo DíazNo ratings yet
- Public Bus Energy Consumption Investigation For Transition To Electric Power and Semi-Dynamic ChargingDocument6 pagesPublic Bus Energy Consumption Investigation For Transition To Electric Power and Semi-Dynamic ChargingGurdeep singhNo ratings yet
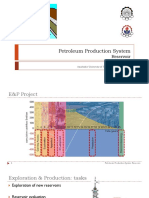
- 2 - Petroleum Production SystemDocument46 pages2 - Petroleum Production Systemفاطمه پویانNo ratings yet
- Excise TaxDocument13 pagesExcise Taxlantern san juanNo ratings yet
- 11-6703 WP AcidGas Amines Final PDFDocument15 pages11-6703 WP AcidGas Amines Final PDFАнтон КоробейниковNo ratings yet
- Catalog - COSCO Filter & StrainerDocument26 pagesCatalog - COSCO Filter & Strainerkhunmyominoo100% (1)
- Elegant Group BookDocument8 pagesElegant Group BookTrevor MupasiNo ratings yet
- As 4553-2008 Gas Space Heating AppliancesDocument8 pagesAs 4553-2008 Gas Space Heating AppliancesSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Wind and WaterDocument225 pagesWind and WaterbugstermanNo ratings yet
Renewable Energy Sources and Their Adoption
Renewable Energy Sources and Their Adoption
Uploaded by
ahmed shaikOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Renewable Energy Sources and Their Adoption
Renewable Energy Sources and Their Adoption
Uploaded by
ahmed shaikCopyright:
Available Formats
Renewable Energy Sources and Their Adoption
Introduction to Renewable Energy
Renewable energy refers to energy derived from natural sources that are replenished
on a human timescale, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal
heat. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable energy sources do not produce greenhouse gases
or other pollutants during their operation. The adoption of renewable energy is
essential for mitigating climate change and achieving sustainable development
goals.
Types of Renewable Energy
There are several types of renewable energy sources, including solar power, wind
power, hydroelectric power, biomass, and geothermal energy. Solar power harnesses
energy from the sun using photovoltaic cells, while wind power generates
electricity through wind turbines. Hydroelectric power utilizes the energy of
flowing water to produce electricity. Biomass energy is derived from organic
materials, such as plant and animal waste, and geothermal energy exploits the heat
from the Earth's interior.
Adoption Rates and Challenges
The adoption rates of renewable energy vary by region and energy source. Countries
like Germany and Denmark have made significant strides in renewable energy
adoption, with substantial investments in wind and solar power. However, challenges
to widespread adoption include high initial costs, infrastructure limitations, and
regulatory barriers. Additionally, the intermittent nature of some renewable energy
sources, such as solar and wind, requires the development of efficient energy
storage solutions to e...
Case Studies
Several countries have successfully integrated renewable energy into their energy
mix. For example, Iceland generates nearly 100% of its electricity from renewable
sources, primarily geothermal and hydroelectric power. Germany's Energiewende
(energy transition) policy has led to significant investments in wind and solar
power, making the country a leader in renewable energy adoption. These case studies
demonstrate the feasibility and benefits of transitioning to renewable energy.
Future Prospects
The future prospects for renewable energy are promising. Technological advancements
continue to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of renewable energy
systems. Innovations in energy storage, such as advanced battery technologies, are
addressing the intermittency issues associated with solar and wind power.
Furthermore, international agreements and national policies aimed at reducing
greenhouse gas emissions are driving the global transition to renewable energy. As
the world moves towards a sus...
You might also like
- The Future of Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesThe Future of Renewable EnergyrkNo ratings yet
- The Future of Renewable EnergyDocument1 pageThe Future of Renewable Energyahlai420No ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Solutions and Climate Change MitigationDocument2 pagesRenewable Energy Solutions and Climate Change Mitigationsetopi8888No ratings yet
- The Role of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate ChangeDocument4 pagesThe Role of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate ChangeNur Ad-DujaNo ratings yet
- 2Document2 pages2Ace NooneNo ratings yet
- 4424Document2 pages4424adrianluczak7No ratings yet
- The Rise of Renewable Energy A Sustainable FutureDocument1 pageThe Rise of Renewable Energy A Sustainable FuturetdctopNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy SourcesDocument1 pageRenewable Energy Sourcestalaxej386No ratings yet
- The Future of Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesThe Future of Renewable EnergyHardik Kashyap VepariNo ratings yet
- The Role of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesThe Role of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate Changequiz-had0nNo ratings yet
- The Future of Renewable EnergyDocument1 pageThe Future of Renewable EnergydotruhadruNo ratings yet
- The Inexorable Transition To Green EnergyDocument2 pagesThe Inexorable Transition To Green EnergyAshwin AshokanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Energy Resources - maneETDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Energy Resources - maneETharjotkaurahuja18No ratings yet
- Renewable Energy - Text ExampleDocument1 pageRenewable Energy - Text ExampleDavi Lucas Lima SousaNo ratings yet
- Title - "The Power of Renewable Energy - Building A Sustainable Future"Document1 pageTitle - "The Power of Renewable Energy - Building A Sustainable Future"mfabregamarinNo ratings yet
- ReachDocument1 pageReachGoga ShoniaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesThe Role of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate ChangeJuan BrattiNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Renewable Energy Harnessing Nature's Power For A Sustainable FutureDocument3 pagesThe Evolution of Renewable Energy Harnessing Nature's Power For A Sustainable FutureHiroNo ratings yet
- Chat GPTed Doc 2Document1 pageChat GPTed Doc 2yourgreatestfear99No ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesRenewable EnergyStormbornNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Renewable Energyvoidmagic200No ratings yet
- Embracing The Renewable Revolution Exploring The Future of Renewable EnergyDocument3 pagesEmbracing The Renewable Revolution Exploring The Future of Renewable Energya_s_1_5No ratings yet
- The Importance of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesThe Importance of Renewable Energy in Combating Climate Changequiz-had0nNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy 1Document1 pageRenewable Energy 1fariri9664No ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesRenewable EnergykyzermainitNo ratings yet
- The Future of Renewable EnergyDocument2 pagesThe Future of Renewable EnergyXaine PineraNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Renewable Energy UselDocument8 pagesBenefits of Renewable Energy Uselgeronimo stiltonNo ratings yet
- In Recent YearsDocument2 pagesIn Recent YearsKent MistolaNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3workr285No ratings yet
- The Green Revolution - How Renewable Energy Is Reshaping The WorldDocument3 pagesThe Green Revolution - How Renewable Energy Is Reshaping The WorldMaalav WhorraNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument1 pageEnergyAndrei BazarincaNo ratings yet
- Efficient and Economical Renewable Energy Resources (Research Proposal)Document2 pagesEfficient and Economical Renewable Energy Resources (Research Proposal)UmerShahzadQurashiNo ratings yet
- Unlocking A Sustainable Future - Exploring The Dynamics of EnergyDocument2 pagesUnlocking A Sustainable Future - Exploring The Dynamics of EnergyMariten JohnNo ratings yet
- Some Energy Creating Techniques and How Perpetual Motion Revolutionizes The GameDocument18 pagesSome Energy Creating Techniques and How Perpetual Motion Revolutionizes The GameAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Renewable EnergyDocument1 pageRenewable EnergyPinky MNo ratings yet
- Weather Patterns in AccraDocument2 pagesWeather Patterns in AccraDela KayNo ratings yet
- 13Document2 pages13lightsorcerorNo ratings yet
- ZnaczenieDocument1 pageZnaczenieaedfNo ratings yet
- Reading TextDocument1 pageReading TextShafiq BhattiNo ratings yet
- Advancing Towards A Sustainable FutureDocument2 pagesAdvancing Towards A Sustainable Futurevoidmagic200No ratings yet
- Renewable Energy TransitionDocument2 pagesRenewable Energy Transitionmianasadkamal108No ratings yet
- Report Finish 3Document15 pagesReport Finish 3a0925084228No ratings yet
- Climate Change and Renewable Energy: From Evidence to ActionFrom EverandClimate Change and Renewable Energy: From Evidence to ActionNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy and Its Role in Sustainable DevelopmentDocument1 pageRenewable Energy and Its Role in Sustainable Developmentصدقة جاريةNo ratings yet
- The GrothDocument1 pageThe Grothjasonsun91No ratings yet
- The Future of Renewable Energy - A Sustainable Path Towards A Brighter TomorrowDocument2 pagesThe Future of Renewable Energy - A Sustainable Path Towards A Brighter TomorrowBruwnoNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-04-18 at 7.47.33 AMDocument15 pagesScreenshot 2024-04-18 at 7.47.33 AMsauradeeparahaNo ratings yet
- 7 Tech RepDocument13 pages7 Tech RepFe MonteronNo ratings yet
- SustainabilityDocument4 pagesSustainabilityfarzanarohiNo ratings yet
- The Rise of Renewable Energy SourcesDocument1 pageThe Rise of Renewable Energy SourcesSergio RileyNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Renewable Energy Resources: Unit IiDocument34 pagesAdvantages of Renewable Energy Resources: Unit IiAdesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Renewable Energy Resources: Unit IiDocument34 pagesAdvantages of Renewable Energy Resources: Unit IiAdesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument8 pagesGeographyJudith NakazziNo ratings yet
- Green EnergyDocument6 pagesGreen EnergysegarnowbodyNo ratings yet
- Source of EnergyDocument3 pagesSource of Energyshaikhfatimaalvi95No ratings yet
- The Quest For Sustainable Energy - Navigating The Path To A Greener FutureDocument2 pagesThe Quest For Sustainable Energy - Navigating The Path To A Greener FuturePernille MathiasenNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Renewable EnergyDocument9 pagesResearch Paper Renewable EnergyMaíra Prata de AraújoNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy EssayDocument2 pagesRenewable Energy Essayeriksve13No ratings yet
- The Evolution and Impact of Renewable Energy TechnologiesDocument5 pagesThe Evolution and Impact of Renewable Energy Technologiesxadal74291No ratings yet
- JJ LetDocument2 pagesJJ Letpourya mashmoulNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic Compressed Air Energy Storage For Electricity SupplyDocument12 pagesAdiabatic Compressed Air Energy Storage For Electricity SupplysutardiNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Conventional Heat Treatment With Corn Oil Oil Blended With Indian Red Seed OilDocument11 pagesComparative Analysis of Conventional Heat Treatment With Corn Oil Oil Blended With Indian Red Seed Oilk eswariNo ratings yet
- Btech Oe 7 Sem Renewable Energy Resources Koe074 2022Document2 pagesBtech Oe 7 Sem Renewable Energy Resources Koe074 2022मधुसूदन सिंहNo ratings yet
- New PIANC Guidelines For Marine Oil and Petrochemical Terminal DesignDocument8 pagesNew PIANC Guidelines For Marine Oil and Petrochemical Terminal DesignydlewNo ratings yet
- RAC Case StudyDocument11 pagesRAC Case StudyshubhamNo ratings yet
- Appendix: List of Petroleum & Exploration Companies in Nigeria # Name MultinationalsDocument3 pagesAppendix: List of Petroleum & Exploration Companies in Nigeria # Name MultinationalsMuhammad Izzat Saffian100% (1)
- PET524 Saturation 1Document12 pagesPET524 Saturation 1Ronald NgueleNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument32 pagesPDFgharsallah mouna100% (1)
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase StudyAndrei HoNo ratings yet
- Buzzard Field Development - UK North Sea Zeron 100X TIG Wire SpecifiedDocument2 pagesBuzzard Field Development - UK North Sea Zeron 100X TIG Wire SpecifiedElMacheteDelHuesoNo ratings yet
- DRAGADOS Offshore by Oscar Del SantoDocument3 pagesDRAGADOS Offshore by Oscar Del SantoOscar César Del Santo, PhDNo ratings yet
- Biodigestor NRELDocument48 pagesBiodigestor NRELjorge AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Mister MeshDocument4 pagesMister MeshSiwa SiwananNo ratings yet
- Carbon Steel Pipe Standards & SpecificationsDocument9 pagesCarbon Steel Pipe Standards & SpecificationsTunji AminuNo ratings yet
- Lloyds Register - Future IMO Legislation (August 2013)Document0 pagesLloyds Register - Future IMO Legislation (August 2013)metallourgosNo ratings yet
- ( cAMERON: Certification of ComplianceDocument4 pages( cAMERON: Certification of ComplianceOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Guide To Chinese Climate Policy - 2019Document169 pagesGuide To Chinese Climate Policy - 2019ASIAANALYSISNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas DehydrationDocument12 pagesNatural Gas DehydrationSagar DadhichNo ratings yet
- List of Components of Oil Drilling RigsDocument4 pagesList of Components of Oil Drilling RigsIjlal Ahmad100% (1)
- 4CH0 2C Que 20170118Document20 pages4CH0 2C Que 20170118abhayNo ratings yet
- Delloite Oil and Gas Reality Check 2015 PDFDocument32 pagesDelloite Oil and Gas Reality Check 2015 PDFAzik KunouNo ratings yet
- Colour Codes, Notes & FAQ: WBCSD Cement Sustainability Initiative CO2 Emissions Inventory Protocol, Version 2.0Document33 pagesColour Codes, Notes & FAQ: WBCSD Cement Sustainability Initiative CO2 Emissions Inventory Protocol, Version 2.0Rodrigo DíazNo ratings yet
- Public Bus Energy Consumption Investigation For Transition To Electric Power and Semi-Dynamic ChargingDocument6 pagesPublic Bus Energy Consumption Investigation For Transition To Electric Power and Semi-Dynamic ChargingGurdeep singhNo ratings yet
- 2 - Petroleum Production SystemDocument46 pages2 - Petroleum Production Systemفاطمه پویانNo ratings yet
- Excise TaxDocument13 pagesExcise Taxlantern san juanNo ratings yet
- 11-6703 WP AcidGas Amines Final PDFDocument15 pages11-6703 WP AcidGas Amines Final PDFАнтон КоробейниковNo ratings yet
- Catalog - COSCO Filter & StrainerDocument26 pagesCatalog - COSCO Filter & Strainerkhunmyominoo100% (1)
- Elegant Group BookDocument8 pagesElegant Group BookTrevor MupasiNo ratings yet
- As 4553-2008 Gas Space Heating AppliancesDocument8 pagesAs 4553-2008 Gas Space Heating AppliancesSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Wind and WaterDocument225 pagesWind and WaterbugstermanNo ratings yet