Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nasm 21
Nasm 21
Uploaded by
shahzaibgul5160 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views1 pageOriginal Title
NASM 21
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views1 pageNasm 21
Nasm 21
Uploaded by
shahzaibgul516Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
THE CARDIORESPIRATORY SYSTEM
The cardiorespiratory system is composed of two closely related systems, the
cardiovascular system consisting of the heart, blood vessels, and blood and the
respiratory system, which includes the trachea, bronchi, alveoli, and the lungs.
These systems work together to provide the body with adequate oxygen and
nutrients and to remove waste products such as CO2 from cells in the body.
THE HEART
The heart is a muscular pump that rhythmically contracts to push blood
throughout the body. The adult heart is approximately the size of a adult fist and
weighs roughly 300 g. Cardiac muscle is one of three major types of muscle, the
others being skeletal and smooth muscle. Cardiac muscle is similar to skeletal
muscle in that cardiac muscle cells contain myofibrils and sarcomeres aligned side
by side, which give them their striated appearance. Whereas skeletal muscle is a
voluntary muscle, cardiac muscle is involuntary muscle, meaning that it cannot
typically be consciously controlled.
Cardiac Muscle Contraction
Cardiac muscle fibers are shorter and more tightly connected than skeletal muscle
. Another unique feature of cardiac muscle is the presence of irregularly spaced
dark bands between cardiac cells called intercalated discs. Intercalated discs help
hold muscle cells together during contraction and create an electrical connection
between the cells that allows the heart to contract as one functional unit. The
heart has its own built-in conduction system, unlike skeletal muscle, that sends an
electrical signal rapidly throughout all the cardiac cells. The typical resting heart
rate is between 70 and 80 beats per minute.
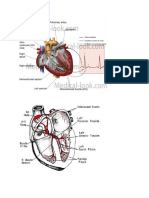
The electrical conduction system of the
heart consists of specialized cells that allow
an electrical signal to be transmitted from
the sinoatrial (SA) node through both atria
and down into the ventricles. Thus, the
electrical conduction system of the heart is
what stimulates the mechanical myocardial
cells to contract in a regular rhythmic
pattern The SA node, located in the right
atrium, is referred to as the pacemaker for
the heart because it initiates the electrical
signal that causes the heart to beat. The
internodal pathways transfer the impulse
from the SA node to the atrioventricular (AV)
node. The AV node delays the impulse
before allowing it to move on to the
ventricles. The AV bundle conducts the
impulse to the ventricles for contraction via
the left and right bundle branches of the
Purkinje fibers.
You might also like
- Chest X-RayDocument135 pagesChest X-RayLeeza Servidad100% (1)
- Human Heart AssignmentDocument12 pagesHuman Heart AssignmentMonica SreeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Cardiovascular SystemElvira Wisakhadewi100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Heart and Blood Vessels - PatientDocument9 pagesAnatomy of The Heart and Blood Vessels - Patientaasuman123No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology The HeartDocument21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology The Heartkheng100% (4)
- The Cardiovascular System: Arteries VeinsDocument27 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: Arteries VeinsMark Anthony DiegoNo ratings yet
- What Are The Heart and Blood Vessels?Document7 pagesWhat Are The Heart and Blood Vessels?phbnaiduNo ratings yet
- Notes 231213 134139-1Document14 pagesNotes 231213 134139-1idlydumpfvckNo ratings yet
- Group1 Presentation On The HeartDocument14 pagesGroup1 Presentation On The HeartchukwukerechimezirimNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 5Document10 pagesBiology Unit 5Aaditya MenonNo ratings yet
- The Heart Weighs Between 7 and 15 OuncesDocument2 pagesThe Heart Weighs Between 7 and 15 OunceshengkyhengkyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemAnkit PattnayakNo ratings yet
- Cardiovasuclar SystemDocument13 pagesCardiovasuclar SystemGreatle Mae D. BasbañoNo ratings yet
- Physio Individual CardioDocument4 pagesPhysio Individual CardioAyunie ZulkeflyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology The HeartDocument21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology The HeartUfuq Azmi BasyarNo ratings yet
- Heart PhysiologyDocument11 pagesHeart Physiologyzzahraadam80No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesCardiovascular SystemDevendra RawatNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartJoan Devera100% (1)
- Cardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryDocument73 pagesCardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryAparna RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Peer TutorialDocument6 pagesPeer Tutorialmashe1No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 (Heart)Document10 pagesLecture 5 (Heart)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 (Cardiac & Respiratory Therapy Equipment) FinalDocument37 pagesUnit - 1 (Cardiac & Respiratory Therapy Equipment) FinalanniepersiasNo ratings yet
- PALMA, LYCA D. - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (Heart and Blood Vessels)Document6 pagesPALMA, LYCA D. - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (Heart and Blood Vessels)G-Palma, Lyca D.No ratings yet
- CVS 2Document153 pagesCVS 2khalidtalal8000No ratings yet
- Heart AnatomyDocument3 pagesHeart Anatomymuskaan.kukrejaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (Heart) : o o o o oDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System (Heart) : o o o o okayaldrNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Heart Made Easy Part 1Document22 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Heart Made Easy Part 1adedayodavid860No ratings yet
- Module 5 CardioVascular SystemDocument7 pagesModule 5 CardioVascular SystemWai KikiNo ratings yet
- Concept On Oxygenation: Gas TransportDocument135 pagesConcept On Oxygenation: Gas TransportNikko MelencionNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: Agriscience 332 Animal Science #8646-A TEKS: (C) (2) (A) and (C) (2) (B)Document111 pagesThe Circulatory System: Agriscience 332 Animal Science #8646-A TEKS: (C) (2) (A) and (C) (2) (B)brdaisyNo ratings yet
- The Mammalian Circulatory SystemDocument58 pagesThe Mammalian Circulatory Systemirisgoldcaster100% (1)
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument7 pagesAnatomy of The HeartJanice ScatesNo ratings yet
- Conduction System of The HeartDocument9 pagesConduction System of The Hearthirap50% (2)
- Cardiac CycleDocument3 pagesCardiac CycleKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Transportation 1Document28 pagesCardiovascular System - Transportation 1Louise Mica Lee100% (1)
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardio Vascular SystemguptaasitNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Cycles of Heart Contraction Drive Double Circulate in MammalsDocument5 pagesCoordinated Cycles of Heart Contraction Drive Double Circulate in MammalsMayar HasanNo ratings yet
- Our Heart BeatsDocument7 pagesOur Heart BeatsferyNo ratings yet
- Cardio PulmonaryDocument4 pagesCardio PulmonaryAyessa CortesNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument11 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystemBlack QueenNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory System Systemleah rualesNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiolgy. Lec4Document22 pagesAnimal Physiolgy. Lec4ao868598No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Syrculation System, 2013Document92 pagesCardiovascular and Syrculation System, 2013Santi Purnama SariNo ratings yet
- The Equine Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesThe Equine Cardiovascular SystemSavannah Simone PetrachenkoNo ratings yet
- احلام 1 PDFDocument7 pagesاحلام 1 PDFEhab Alaa Abd Al-AmeerNo ratings yet
- The HeartDocument2 pagesThe HeartSonkapoponkaNo ratings yet
- الجهاز الدوريDocument16 pagesالجهاز الدوريHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- Technical DefinitionDocument3 pagesTechnical DefinitionErin BarnesNo ratings yet
- Blue Orange Creative Diabetes Presentation - 20231108 - 194927 - 0000Document10 pagesBlue Orange Creative Diabetes Presentation - 20231108 - 194927 - 0000thea ramosNo ratings yet
- With Each HeartbeatDocument6 pagesWith Each HeartbeatnahlajovialNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesCardiovascular SystemAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Heart and Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesHeart and Circulatory SystemBryent GawNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 GcsDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 3 GcsNurse NotesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument34 pagesCardiovascular Systemurooj100% (1)
- Oral RevDocument6 pagesOral RevjjolaguerNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory System - Study NotesDocument8 pagesHuman Circulatory System - Study NotesrockyajeetNo ratings yet
- Carpio - Learning Objective StratMedDocument29 pagesCarpio - Learning Objective StratMedaemancarpioNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Heart Muscle Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHeart Muscle Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Using The Surface Electrocardiogram To Localization of Idiopathic Ventricular TachycardiaDocument12 pagesUsing The Surface Electrocardiogram To Localization of Idiopathic Ventricular TachycardiaNavojit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Pacienti 2020 1-220Document28 pagesPacienti 2020 1-220crilala23No ratings yet
- Chest Xray PT 2Document41 pagesChest Xray PT 2pvs5155No ratings yet
- Pediatric Spinal Schwannoma RAADocument17 pagesPediatric Spinal Schwannoma RAArakeNo ratings yet
- Practical Checklist PD CVS OnlyDocument6 pagesPractical Checklist PD CVS OnlyardiandawoodNo ratings yet
- Truncus ArteriosusDocument4 pagesTruncus ArteriosuskemalahmadNo ratings yet
- Heart AnatomyDocument7 pagesHeart AnatomyFolarin EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- PowerpointDocument12 pagesPowerpointapi-585922320No ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesMakalah Bahasa InggrisOlga RevalinaNo ratings yet
- Atrioventricular Septal Defect From Embryonic DeveDocument13 pagesAtrioventricular Septal Defect From Embryonic DeveGuțaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Surgery 2Document24 pagesCardiovascular Surgery 2Ernesto KangNo ratings yet
- FitriDHP - Cardiomegaly Dan Efusion PericardiumDocument40 pagesFitriDHP - Cardiomegaly Dan Efusion PericardiumIlham PrayogoNo ratings yet
- Thorax and Abdomen Muscle NotesDocument2 pagesThorax and Abdomen Muscle NotesJean OpallaNo ratings yet
- KROK 2-CardioDocument12 pagesKROK 2-CardioberdaderagaNo ratings yet
- Four Chambers of The HeartDocument7 pagesFour Chambers of The HeartJohn TecsonNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of HeartDocument51 pagesBlood Supply of HeartHema Malani MurthiNo ratings yet
- Bates Chapter 8 Lung and ThoraxDocument15 pagesBates Chapter 8 Lung and ThoraxAdrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Assessment BeforeDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Assessment BeforeBinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Examination:: General InspectionDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Examination:: General InspectionPhysician AssociateNo ratings yet
- Venous System Arterial System: A. Artery A.A. Arteries L. Left R. Right v. Vein V.V. VeinsDocument2 pagesVenous System Arterial System: A. Artery A.A. Arteries L. Left R. Right v. Vein V.V. VeinsJann ericka Jao100% (2)
- 1-Cardiac AnatomyDocument5 pages1-Cardiac AnatomyZintan HospitalNo ratings yet
- Care of Patient On I C DDocument15 pagesCare of Patient On I C DGeorge John Jeelu SusanNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument13 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystemCaraDeleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Spine and ThoraxDocument24 pagesChapter 4 - Spine and ThoraxmassagekevinNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Thorax and LungsDocument15 pagesAssessment of Thorax and LungsmakathrinasanchezNo ratings yet
- Human Heart Coloring Sheet With QR CodesDocument2 pagesHuman Heart Coloring Sheet With QR Codesapi-280337641No ratings yet
- Viewer (v5.7.000)Document1 pageViewer (v5.7.000)Faisal freakNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument122 pagesCardioAdrian Rosell Carrillo EnriquezNo ratings yet
- DIAG Y MANEJO TerapéuticoDocument12 pagesDIAG Y MANEJO TerapéuticoCORONARIA QUILMESNo ratings yet