Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bonding
Bonding
Uploaded by
laraking6060Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bonding
Bonding
Uploaded by
laraking6060Copyright:
Available Formats
Bonding
Ionic bonding
Ionic bonding involves electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
in a lattice.
Compound ions
Sulfate SO4 Hydroxide OH- Ammonium NH3+
Nitrate NO3- Carbonate CO3 2-
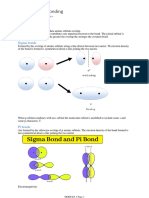
Covalent and dative covalent bonds
A single covalent bond contains a shared pair of electrons.
Multiple bonds contain multiple pairs of electrons.
A dative covalent bond contains a shared pair of electrons with both electrons
Supplied by one atom.A covalent bond should be represented with a line and a
dative covalent bond with an arrow.
Metallic bonding-
Metallic bonding involves attractions between delocalised electrons and positive
ions arranged in a lattice.
Bonding and physical properties-
Four types of crystal structures:
-Ionic
-Metallic
-Macromolecular (giant covalent)
-Molecular
Structure of diamond-
Diamond is a giant covalent structure. in which: each carbon
atom is joined to four other carbon atoms by strong covalent
bonds. The carbon atoms form a regular tetrahedral network
structure.
Structure of graphite-
Graphite has a giant covalent structure in which: each
carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with other carbon
atoms. The carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings.
there are no covalent bonds between the layers.
Structure of ice-
Each water molecule is surrounded by four neighboring H2Os.
two of these are hydrogen-bonded to the oxygen atom on the
central H2O molecule
Structure of iodine-
Iodine has a simple molecular structure. Iodine
atoms are bonded in pairs by covalent bonds.
Structure of magnesium-
Magnesium exists as a large macromolecular
structure (lattice) with strong metallic bonds
between the Magnesium ions and the sea of
delocalised electrons
Structure of sodium chloride-
Sodium chloride is a crystalline lattice structure, where
each sodium ion is surrounded by six chloride ions and
each chloride ion is surrounded by six sodium ions.
Shapes of simple molecules and ions
Bonding pairs and lone pairs have charge clouds that repel each other.
Pairs of electrons in the outer shell arrange themselves as far apart as possible
to minimise repulsion.
Lone pair-lone pair repulsion is greater than lone pair- bond repulsion.
Bond polarity-
Electronegativity is the power of an atom to attract the pair of electrons in a
covalent bond.
The electron distribution in a covalent bond between elements with different
electronegativities will be asymmetrical. This produces a polar covalent bond,
and may cause a molecule to have a permanent dipole.
Forces between molecules-
-permanent dipole-dipole
-van der waals forces
-hydrogen bonding
The melting and boiling points of molecular substances are influenced by the
strengths of these intermolecular forces.
You might also like
- O Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesO Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical Bondingjave_yeongNo ratings yet
- Liquids and SolidsDocument107 pagesLiquids and SolidsMorgan BowersNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument3 pagesStructure and Bondingjordangrierson12No ratings yet
- CH 10Document57 pagesCH 10Akef AfanehNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 2Document32 pagesChemical Bond 2Yak Raj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Notes W4Document5 pagesNotes W4sy.valNo ratings yet
- 1.3. BondingDocument10 pages1.3. BondingdodoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Chemical BondingMini PGNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument34 pagesChemical BondingNihatNo ratings yet
- Principles of Materials Engineering Lec (4 & 5) NewDocument13 pagesPrinciples of Materials Engineering Lec (4 & 5) Newfb6pnfdky9No ratings yet
- Review of IB Chem Topics 4 and 14Document10 pagesReview of IB Chem Topics 4 and 14coolpianocatNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingDocument10 pagesCSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 PHY 351Document14 pagesTutorial 1 PHY 351MUHAMMAD AMMIRUL HAFIZ MD ZAININo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.2 GsDocument19 pagesChapter 6.2 Gszain nNo ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument12 pagesStructure and BondingNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- AQA Chemistry A-Level: 3.1.3: Bonding and StructuresDocument10 pagesAQA Chemistry A-Level: 3.1.3: Bonding and StructuresAshleigh NcubeNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Cha 3Document120 pagesInorganic Cha 3Adugnaw BiksNo ratings yet
- Atoms CombiningDocument12 pagesAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding PPT 2023-2024Document52 pagesChemical Bonding PPT 2023-2024Naim RahmanNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document19 pagesCH 12api-256509209No ratings yet
- Fbise Chapter 4 (I)Document7 pagesFbise Chapter 4 (I)Zarish ZubairNo ratings yet
- STRUCTURE AND BONDING PowerPoint For Fourth Form.Document54 pagesSTRUCTURE AND BONDING PowerPoint For Fourth Form.tsteadmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument44 pagesChemical Bondingjas_ong_man_ling1996No ratings yet
- Bonding and Naming CompoundsDocument10 pagesBonding and Naming CompoundsDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document37 pagesChemical Bonding 1palal123No ratings yet
- Notes Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesNotes Chemical BondingRammohan Balaji PrasadNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument39 pagesIonic and Covalent Bondingchickuwa pawawawaNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids Definition: Solid State ChemistryDocument9 pagesBonding in Solids Definition: Solid State Chemistryhaimanot yibeltalNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document21 pagesWeek 2JeffersonTalanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Grade 11 Unit 3: By: Addis Ababa Education Bureau APRIL 2020Document22 pagesChemistry Grade 11 Unit 3: By: Addis Ababa Education Bureau APRIL 2020Abdi sunNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and CatalysisDocument66 pagesChemical Bonding and CatalysisKaran Padvi 03No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument25 pagesChemical Bondingjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - UNIT 4 - COMPOUNDSDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - UNIT 4 - COMPOUNDSRaffaella LaxaldeNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding in SolidsDocument3 pagesAtomic Bonding in Solidsazmatshahzad786786No ratings yet
- BondsDocument24 pagesBondsPavithran Kamaleswari Year 10No ratings yet
- 1 Engineering Materials, Processes and Testing (Me136p-2)Document21 pages1 Engineering Materials, Processes and Testing (Me136p-2)JeffersonTalanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10.2 The Solid StateDocument14 pagesLesson 10.2 The Solid StatefitriNo ratings yet
- Condensed Matter Physics Materials Science Greek Solid Long-Range Order Crystal Glass Glass Transition Gels Thin FilmsDocument6 pagesCondensed Matter Physics Materials Science Greek Solid Long-Range Order Crystal Glass Glass Transition Gels Thin FilmsimnasNo ratings yet
- MME365 Glass and Ceramics Engineering: Bonding in Ceramic MaterialsDocument12 pagesMME365 Glass and Ceramics Engineering: Bonding in Ceramic MaterialsZahir Rayhan JhonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond Typesapi-287081563No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding NotesAyesha Awan100% (1)
- Assignment - 2Document15 pagesAssignment - 2padhiyararpitaNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Inch 2101Document80 pagesCh3 Inch 2101liyou eshetuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Notes For ExamDocument4 pagesChemical Bonding Notes For ExamMermz96No ratings yet
- 3.2 Properties of Solids StudentDocument7 pages3.2 Properties of Solids StudentZachary Daniel UyNo ratings yet
- Giant Ionic and Giant CovalentDocument8 pagesGiant Ionic and Giant CovalentSamuelNo ratings yet
- Bonding PacketDocument24 pagesBonding PacketIra Munirah100% (2)
- Csec Chemistry Chapter 5 - Structures and BondingDocument18 pagesCsec Chemistry Chapter 5 - Structures and Bondingchelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- C2 Knowledge PowerpointsDocument33 pagesC2 Knowledge PowerpointsMrs S BakerNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chemical BondingDocument14 pagesNotes - Chemical Bonding黄心盈No ratings yet
- Article (Bonding&Structure)Document3 pagesArticle (Bonding&Structure)Fawzan Fahad MDNo ratings yet
- Ib PPT 4 SL PDFDocument103 pagesIb PPT 4 SL PDFzarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChemical BondingdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Document11 pagesCh3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding1Document35 pagesChemical Bonding1drchewieNo ratings yet
- 4 Lewis Dot Structure and Types of BondDocument71 pages4 Lewis Dot Structure and Types of BondEren Micaella100% (1)
- Chemistry NotesDocument3 pagesChemistry NotesfezthebombNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Pets in Fonts - Google SearchDocument1 pagePets in Fonts - Google Searchlaraking6060No ratings yet
- Powerpuffs - Google SearchDocument1 pagePowerpuffs - Google Searchlaraking6060No ratings yet
- FamilyDocument1 pageFamilylaraking6060No ratings yet
- Can Science and Religion CoexistDocument2 pagesCan Science and Religion Coexistlaraking6060No ratings yet
- Cell Recognition and The Immune SystemDocument3 pagesCell Recognition and The Immune Systemlaraking6060No ratings yet
- AlkenesDocument6 pagesAlkeneslaraking6060No ratings yet
- Australian/New Zealand StandardDocument2 pagesAustralian/New Zealand StandardShyanaka0% (1)
- Bk-6-Latest EIC-B-1002-0 (PV2R Series Single Pumps)Document30 pagesBk-6-Latest EIC-B-1002-0 (PV2R Series Single Pumps)RAYNo ratings yet
- !!!smart Virtual Screening Part1Document8 pages!!!smart Virtual Screening Part1நமச்சிவாயம் பாலகிருஷ்ணன்No ratings yet
- Use and Abuse of The DPPH - RadicalDocument12 pagesUse and Abuse of The DPPH - RadicalKim Dong Yoo100% (1)
- WIS5 - Appendix 2Document86 pagesWIS5 - Appendix 2Reza Fakhrizal100% (1)
- MCQQQQQQQQQDocument7 pagesMCQQQQQQQQQNaveen PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Sampel Daun StroberiDocument6 pagesSampel Daun StroberiI Made Astawa Ari Putra 245No ratings yet
- Spinning and Applications of Bioinspired Fiber SystemsDocument24 pagesSpinning and Applications of Bioinspired Fiber SystemsEliton Medeiros Candido de MacêdoNo ratings yet
- Pipe Class: Rating: Base Material: Corrosion Allowance: Special Requirement: Temperature (Deg. C) and Pressure (Kg/Sq. CM G) RatingsDocument1 pagePipe Class: Rating: Base Material: Corrosion Allowance: Special Requirement: Temperature (Deg. C) and Pressure (Kg/Sq. CM G) RatingsRajendra LabadeNo ratings yet
- Cblechpu 13Document8 pagesCblechpu 13वरदान गंजूNo ratings yet
- Brosur - NP GasluxDocument4 pagesBrosur - NP GasluxYudiNo ratings yet
- Act-Sat (Recent Vocab List)Document322 pagesAct-Sat (Recent Vocab List)Sayed MikoNo ratings yet
- Studies of Structural, Optical, and Electrical Properties Associated With Defects in Sodium-Doped Copper Oxide (Cuo/Na) NanostructuresDocument18 pagesStudies of Structural, Optical, and Electrical Properties Associated With Defects in Sodium-Doped Copper Oxide (Cuo/Na) NanostructuresBilal JuttNo ratings yet
- The Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument28 pagesThe Second Law of ThermodynamicsSpace MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Design Guidelines For PE & ROTO Lined Carbon Steel PipingDocument8 pagesDesign Guidelines For PE & ROTO Lined Carbon Steel PipingKamatchi Nathan100% (1)
- DPPS-5 Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesDPPS-5 Chemical BondingshubhamNo ratings yet
- HalflifeDocument17 pagesHalflifeMinnie InarapmasNo ratings yet
- Serum Protein Multi-Calibrator InsertDocument6 pagesSerum Protein Multi-Calibrator InsertDaniel VargasNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Principles of Biochemistry 4th Edition Horton PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Principles of Biochemistry 4th Edition Horton PDF Full Chapterstronginsanelyu8yx100% (21)
- Molecules 28 03379 v2Document61 pagesMolecules 28 03379 v2Pratap ShettyNo ratings yet
- Wa0001Document16 pagesWa0001Rafique SarderNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Pyq LectureDocument25 pagesSemiconductor Pyq LectureAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Insulation ProductsDocument1 pageInsulation ProductsDygoPalNo ratings yet
- Craft, B - .C. and Hawkins - M - Applied Petroleum Reservoir Engineering (102-114)Document14 pagesCraft, B - .C. and Hawkins - M - Applied Petroleum Reservoir Engineering (102-114)Medina Gonzalez Oscar ManuelNo ratings yet
- Q. 7. Differentiate Between: (I) DNA and RNADocument7 pagesQ. 7. Differentiate Between: (I) DNA and RNAFari NaheedNo ratings yet
- Purestab Md1024: Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesPurestab Md1024: Technical Data SheetHadyan AdliNo ratings yet
- 290923-Data Sheet Hi-Grid MGDocument8 pages290923-Data Sheet Hi-Grid MGTeknik produksi wikonNo ratings yet
- Examples of Pharmaceutical Ingredients-AnselDocument5 pagesExamples of Pharmaceutical Ingredients-AnselKyla Mariz TablizoNo ratings yet
- Materials Chemistry B: Journal ofDocument10 pagesMaterials Chemistry B: Journal ofShashikant PathakNo ratings yet
- New Way Chemistry For Hong Kong A-Level Book 3A 1Document40 pagesNew Way Chemistry For Hong Kong A-Level Book 3A 1MARENG BERNABENo ratings yet