Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Zero Coupon Bond
Zero Coupon Bond
Uploaded by
Shridhar PCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- G4 Bethesda CompanyDocument37 pagesG4 Bethesda CompanySylvia MiraNo ratings yet
- Risk and Return Analysis: Summer Internship Project ReportDocument55 pagesRisk and Return Analysis: Summer Internship Project ReportAmrish PatelNo ratings yet
- Ayodha PMDocument7 pagesAyodha PMaryanboxer786No ratings yet
- PS 2Document13 pagesPS 2Malavika G NairNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-03-07 at 10.33.06 PMDocument12 pagesScreenshot 2022-03-07 at 10.33.06 PMYash ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Oaf 624 Course OutlineDocument8 pagesOaf 624 Course OutlinecmgimwaNo ratings yet
- Bcom433 Inv and Port MGT NotesDocument102 pagesBcom433 Inv and Port MGT NotesramboNo ratings yet
- Proposed Intelligent System To Support Local Businesses in KenyaDocument13 pagesProposed Intelligent System To Support Local Businesses in KenyaGeorge RabarNo ratings yet
- Question 1 - Give The Meaning of Treasury Management. Explain The Need For Specialized Handling of Treasury and Benefits of Treasury. Answer - 1Document8 pagesQuestion 1 - Give The Meaning of Treasury Management. Explain The Need For Specialized Handling of Treasury and Benefits of Treasury. Answer - 1Raghavendra SoniNo ratings yet
- BA Interview Questions and Answers 1698202392Document29 pagesBA Interview Questions and Answers 1698202392Shailendrahasabe@gmail.com100% (1)
- Revised BDM - Sample Q&A SolveDocument13 pagesRevised BDM - Sample Q&A SolveSonam Dema DorjiNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Q3 Module 8Document21 pagesBusiness Finance Q3 Module 8클레어ClaireNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements AnalysisDocument58 pagesFinancial Statements AnalysisenkeltvrelseNo ratings yet
- Types of Project Selection ModelsDocument4 pagesTypes of Project Selection Modelskfasihi92% (24)
- Untitled DocumentDocument9 pagesUntitled DocumentamyNo ratings yet
- Smart Task 2 SubmissionDocument5 pagesSmart Task 2 SubmissionPrateek JoshiNo ratings yet
- Vce Smart Task 2 Project Finance Modelling and AnalysisDocument4 pagesVce Smart Task 2 Project Finance Modelling and AnalysisMd FarmanNo ratings yet
- FM414 LN 3 Master Copy Presentation Solutions - Working Capital MGT - 2024 ColorDocument15 pagesFM414 LN 3 Master Copy Presentation Solutions - Working Capital MGT - 2024 ColorAntonio AguiarNo ratings yet
- Follow Who Know Road: Q1. Define The Following Financial Modeling Terms Business RisksDocument3 pagesFollow Who Know Road: Q1. Define The Following Financial Modeling Terms Business RisksIbrahimm Denis FofanahNo ratings yet
- Q1 Explain What Is CAMELS Framework Used in Banking AnalysisDocument2 pagesQ1 Explain What Is CAMELS Framework Used in Banking Analysisshubham ghodkeNo ratings yet
- AOR QuestionsDocument33 pagesAOR QuestionsAditi SinghNo ratings yet
- Project Management Notes (UNIT - 3)Document29 pagesProject Management Notes (UNIT - 3)DEV BHADANANo ratings yet
- Finance Strategy PDFDocument8 pagesFinance Strategy PDFShahzaib AslamNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering EconomicsDocument12 pagesSoftware Engineering Economicspidrovo_1No ratings yet
- Entry Phase of The AssignmentDocument3 pagesEntry Phase of The AssignmentAbin AntonyNo ratings yet
- VCE Summer Internship Program 2021: Name Email-ID Smart Task No. Project TopicDocument3 pagesVCE Summer Internship Program 2021: Name Email-ID Smart Task No. Project TopicShazmeenNo ratings yet
- VCE Summer Internship Program 2021: Smart Task Submission FormatDocument7 pagesVCE Summer Internship Program 2021: Smart Task Submission FormatNiharika MathurNo ratings yet
- 1437-Khansa Tallat-Finance-Summary of The ChaptersDocument12 pages1437-Khansa Tallat-Finance-Summary of The Chapterswasif sardarNo ratings yet
- Information System ManagementDocument10 pagesInformation System ManagementAmrita SinghNo ratings yet
- Project Management MaharishiDocument29 pagesProject Management Maharishiankita choudharyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Concept, Scope and Objectives of FinanceDocument7 pagesUnit 1: Concept, Scope and Objectives of FinanceVanshika Srivastava 17IFT017No ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting RulesDocument22 pagesCapital Budgeting Rulesshweta shuklaNo ratings yet
- Financial Engineering Section A Definition of Financial EngineeringDocument10 pagesFinancial Engineering Section A Definition of Financial Engineeringqari saibNo ratings yet
- Master of Business AdministrationDocument31 pagesMaster of Business Administrationoshank12No ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management at Capital One (UKDocument25 pagesCustomer Relationship Management at Capital One (UKRakesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2 M.Com Sem 4thDocument7 pagesAssignment - 2 M.Com Sem 4thVishwas JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Module-III Analytical Tools in Sourcing, Pricing Analysis: Foreign Exchange Currency ManagementDocument10 pagesModule-III Analytical Tools in Sourcing, Pricing Analysis: Foreign Exchange Currency ManagementumeshNo ratings yet
- Answers MS 42Document13 pagesAnswers MS 42SHRIYA TEWARINo ratings yet
- Financial EngineeringDocument42 pagesFinancial Engineeringqari saibNo ratings yet
- PB6MAT - PB6MAT - Financial Technology Week 6Document43 pagesPB6MAT - PB6MAT - Financial Technology Week 6James LieNo ratings yet
- 201511-Semester II-MB0049-Project Management-DEDocument12 pages201511-Semester II-MB0049-Project Management-DEDhaniram SharmaNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument18 pagesProject ManagementShehryar KhanNo ratings yet
- ExpendituresDocument5 pagesExpendituresSheikh MarufNo ratings yet
- Sen MPDocument13 pagesSen MPPushkar rane 1oth,B,ROLL NO.47No ratings yet
- EEA - Data Analyst - Case Study - CFDocument4 pagesEEA - Data Analyst - Case Study - CFLUDOVICMEKNo ratings yet
- Course12 2 PDFDocument36 pagesCourse12 2 PDFYony LaurenteNo ratings yet
- 1 Assignment-1Document4 pages1 Assignment-1Tushar Gupta100% (1)
- Syllabus EMBA12weeksDocument19 pagesSyllabus EMBA12weeksakcelik04No ratings yet
- Super Day Secrets - Your Technical Interview GuideDocument24 pagesSuper Day Secrets - Your Technical Interview GuideJithin RajanNo ratings yet
- Equity Valuation ThesisDocument5 pagesEquity Valuation ThesisJose Katab100% (2)
- Se Economics AutoRecovered AutoRecoveredDocument25 pagesSe Economics AutoRecovered AutoRecoveredArslan GujjarNo ratings yet
- Entre Marking Scheme 2018Document14 pagesEntre Marking Scheme 2018Philomina GomezNo ratings yet
- CA - NotesDocument6 pagesCA - NotessharonNo ratings yet
- Credit AnalystDocument9 pagesCredit AnalystJimsy Antu100% (1)
- Project Selection ModelsDocument26 pagesProject Selection ModelsAbdul Rehman100% (1)
- Assignment Semester-Ii Subject-Project Management Code-MB 0049 ANS1. Phases of Project Management: Project Management Is A Rationally Planned andDocument7 pagesAssignment Semester-Ii Subject-Project Management Code-MB 0049 ANS1. Phases of Project Management: Project Management Is A Rationally Planned andAnonymous 61Kx8L3No ratings yet
- Hints For BSBRSK501 Manage RiskDocument26 pagesHints For BSBRSK501 Manage Riskhossain alviNo ratings yet
- Summary of Michael L. George, John Maxey, David T. Rowlands & Mark Price's The Lean Six Sigma Pocket ToolbookFrom EverandSummary of Michael L. George, John Maxey, David T. Rowlands & Mark Price's The Lean Six Sigma Pocket ToolbookNo ratings yet
- Summary of Don McGreal & Ralph Jocham's The Professional Product OwnerFrom EverandSummary of Don McGreal & Ralph Jocham's The Professional Product OwnerNo ratings yet
- Starting Right CorporationDocument18 pagesStarting Right CorporationLyka Marie Pajares100% (1)
- LT Cost of CapitalDocument17 pagesLT Cost of CapitalAnmol YadavNo ratings yet
- Managing The Marketing FunctionDocument15 pagesManaging The Marketing Functionjerick garlejoNo ratings yet
- MF QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesMF QuestionnaireVINEETA KAPOORNo ratings yet
- Method Nifty 50 ArbitrageDocument8 pagesMethod Nifty 50 ArbitrageTesthdjNo ratings yet
- Fund Industry Assignment PDFDocument12 pagesFund Industry Assignment PDFFedericoNo ratings yet
- Dec 2022Document4 pagesDec 2022Jesus VillalongaNo ratings yet
- Present Value of Principal (8,000,000 X 0.6756) 5,404,800 Jan-01 Present Value of Semi Annual Interest (400,000 X 8.11) 3,244,000 Purchase Price 8,648,800 Jul-01Document2 pagesPresent Value of Principal (8,000,000 X 0.6756) 5,404,800 Jan-01 Present Value of Semi Annual Interest (400,000 X 8.11) 3,244,000 Purchase Price 8,648,800 Jul-01AnonnNo ratings yet
- Stealth Income Strategies For InvestorsDocument116 pagesStealth Income Strategies For Investorsrypai50% (4)
- Sonali Bank Intern Report 1Document72 pagesSonali Bank Intern Report 1Nazmul Alam FarukiNo ratings yet
- Comfort ShoesDocument32 pagesComfort ShoesGrace Priscilla SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Q PP 4 BondsDocument1 pageQ PP 4 BondsJoebel CristalesNo ratings yet
- Coca Cola Company Is A Global Soft Drink Beverage Company TickeDocument3 pagesCoca Cola Company Is A Global Soft Drink Beverage Company TickeAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis Toyota Indus Motors Company Limited: Lquidity RatiosDocument9 pagesRatio Analysis Toyota Indus Motors Company Limited: Lquidity RatiosArsl331No ratings yet
- Insider TradingDocument49 pagesInsider TradingRavi Joshi100% (1)
- Chapter 7. Bonds and Their Valuation: A B C D E F G H I 1 2 3 4Document13 pagesChapter 7. Bonds and Their Valuation: A B C D E F G H I 1 2 3 4Naufal IhsanNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2019Document395 pagesAnnual Report 2019Aji WijanarkoNo ratings yet
- Mega TrustDocument50 pagesMega Trustbribriinsf100% (1)
- (Quiz Uas Take Home) Akl-1 PDFDocument7 pages(Quiz Uas Take Home) Akl-1 PDFStephani ElvinaNo ratings yet
- All About Stock Market - Read ItDocument44 pagesAll About Stock Market - Read ItShekhar SumanNo ratings yet
- FINA 4011 Exam 2 OutlineDocument4 pagesFINA 4011 Exam 2 OutlineRavi PatelNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Capital Accounts Reporting and Managing Intellectual CapitalDocument81 pagesIntellectual Capital Accounts Reporting and Managing Intellectual CapitalirfantanjungNo ratings yet
- Chap005a - The Value of BondDocument35 pagesChap005a - The Value of Bondnt.phuongnhu1912No ratings yet
- Difference Between GDR and IDRDocument18 pagesDifference Between GDR and IDRpriyanka chawlaNo ratings yet
- Istilah Istilah EkoTekDocument24 pagesIstilah Istilah EkoTeki putu andre artha wardanaNo ratings yet
- Crypto Vs GoldDocument22 pagesCrypto Vs GoldResearchtimeNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Assignment 1Document6 pagesCorporate Finance Assignment 1Kûnãl SälîañNo ratings yet
- Variance Swaps - An IntroductionDocument5 pagesVariance Swaps - An IntroductionAngelo TorresNo ratings yet
- The Banking Law Reviewer Hot JuristDocument28 pagesThe Banking Law Reviewer Hot Juristgrego centillas100% (3)
Zero Coupon Bond
Zero Coupon Bond
Uploaded by
Shridhar POriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Zero Coupon Bond
Zero Coupon Bond
Uploaded by
Shridhar PCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Zero coupon bond
Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not pay interest during the life of the bonds. Instead,
investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount
the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due.
2. Types of equity
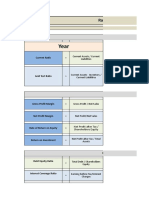
3. What are the 4 Agile Ceremony?
The sprint planning meeting, the daily stand-up meeting, the sprint review meeting, and the
sprint retrospective meeting.
4. What things to do during Backlog Grooming?
adding user stories, prioritizing items (like user stories), updating items, adding or removing
items, splitting user stories and evaluating and reevaluating estimates
5. Different techniques in the prioritization?
MoSCoW prioritization method
The MoSCoW method is a simple technique for prioritizing tasks where you assign every task on
your to-do list to one of four categories:
M – Must do: M tasks are things you absolutely have to do.
S – Should do: S tasks are things you should do, but they're a lower priority than M tasks.
C – Could do: C tasks are nice-to-dos. You'd like to do them, but if you don't, it's probably not a
big deal.
W – Won't do: W tasks are things that just aren't worth doing.
6. Difference between BRD, FSD, RTM
Requirements Traceability Matrix is a document used to verify that all of the requirements are
connected to test cases. The principal reason project managers use RTM is to confirm that all
requirements will be accounted for in the testing phase. RTM usually helps to evaluate the
impact of project requirements.
7. Instrument of Capital Markets?
Capital market instruments encompass a broad range of financial tools, including equities,
bonds, derivatives, ETFs, and foreign exchange instruments. They play a crucial role in
fundraising for entities and offering diverse investment opportunities, crucial for economic
growth, risk management, and wealth generation.
8. What is Data Flow & Components used in Data Flow?
A data flow diagram (DFD) maps out the flow of information for any process or system. It uses
defined symbols like rectangles, circles and arrows, plus short text labels, to show data inputs,
outputs, storage points and the routes between each destination. progressively deeper into how
the data is handled
9. Personas and its use cases?
10. Bond Yield?
11. How do you decide the story Points during the stories?
1. Effort: Work volume and intensity required
Effort refers to the amount of work required to complete different user stories. The relative
estimation process includes answering questions like:
How many tasks are involved?
What preparation and follow-up activities should you expect?
How much effort will each task and prep activity require?
2. Risk: Uncertainty and potential obstacles
This measure involves considering process risks, dependencies on internal tasks or external
factors, and the unknowns in the development process. Each story point value adds to the risk
score.
So, high-risk stories will warrant more story points as they require an additional buffer period to
cushion the unforeseen challenges that pop up. Agile teams may use the points to reject certain
stories or manage and mitigate risks more effectively.
3. Complexity: Technical difficulty and intricacies
Complexity is not just about how hard the task is but also how intricate and involved the
solution needs to be. This includes the use of new or unfamiliar technologies, the need to rely
on innovative or untested solutions, and the level of intellectual challenge.
12. Where Clearing house comes into Picture
A Clearinghouse is an intermediary between a buyer and a seller in the financial markets, whose
job is to ensure that both parties honor their obligations.
Clearing house never gets in touch between both Buyer and Seller.
1. On T Day Buyer has brought some securities from Seller.
2. On T Day Amount will be deducted from the Buyer and credited to Clearing Members
account (Brokers account).
3. On T+1 day Clearing members sends that amount to Clearing bank of the buyer.
4. On T+2 day Clearing Bank of buyer sends that amount to Clearing Bank Sellers Account.
5. On T+2 Day Seller will receive the amount.
6. On T Day seller will sell his securities and those securities will be credited to Clearing
members account (Brokers account).
7. On T+1 Day Securities will be sent from Clearing members account to Depository of Sellers
Pool account
8. On T+2 Day Depository of Sellers pool account will transfer those securities to Buyers
Depository Pools Account.
9. On T+2 Buyer will receive those securities to his D-mat account from Buyers depository.
13. What is Reconciliation?
Reconciliation is an accounting process in which two sets of records are compared to ensure
that the results are accurate and consistent.
You might also like
- G4 Bethesda CompanyDocument37 pagesG4 Bethesda CompanySylvia MiraNo ratings yet
- Risk and Return Analysis: Summer Internship Project ReportDocument55 pagesRisk and Return Analysis: Summer Internship Project ReportAmrish PatelNo ratings yet
- Ayodha PMDocument7 pagesAyodha PMaryanboxer786No ratings yet
- PS 2Document13 pagesPS 2Malavika G NairNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-03-07 at 10.33.06 PMDocument12 pagesScreenshot 2022-03-07 at 10.33.06 PMYash ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Oaf 624 Course OutlineDocument8 pagesOaf 624 Course OutlinecmgimwaNo ratings yet
- Bcom433 Inv and Port MGT NotesDocument102 pagesBcom433 Inv and Port MGT NotesramboNo ratings yet
- Proposed Intelligent System To Support Local Businesses in KenyaDocument13 pagesProposed Intelligent System To Support Local Businesses in KenyaGeorge RabarNo ratings yet
- Question 1 - Give The Meaning of Treasury Management. Explain The Need For Specialized Handling of Treasury and Benefits of Treasury. Answer - 1Document8 pagesQuestion 1 - Give The Meaning of Treasury Management. Explain The Need For Specialized Handling of Treasury and Benefits of Treasury. Answer - 1Raghavendra SoniNo ratings yet
- BA Interview Questions and Answers 1698202392Document29 pagesBA Interview Questions and Answers 1698202392Shailendrahasabe@gmail.com100% (1)
- Revised BDM - Sample Q&A SolveDocument13 pagesRevised BDM - Sample Q&A SolveSonam Dema DorjiNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Q3 Module 8Document21 pagesBusiness Finance Q3 Module 8클레어ClaireNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements AnalysisDocument58 pagesFinancial Statements AnalysisenkeltvrelseNo ratings yet
- Types of Project Selection ModelsDocument4 pagesTypes of Project Selection Modelskfasihi92% (24)
- Untitled DocumentDocument9 pagesUntitled DocumentamyNo ratings yet
- Smart Task 2 SubmissionDocument5 pagesSmart Task 2 SubmissionPrateek JoshiNo ratings yet
- Vce Smart Task 2 Project Finance Modelling and AnalysisDocument4 pagesVce Smart Task 2 Project Finance Modelling and AnalysisMd FarmanNo ratings yet
- FM414 LN 3 Master Copy Presentation Solutions - Working Capital MGT - 2024 ColorDocument15 pagesFM414 LN 3 Master Copy Presentation Solutions - Working Capital MGT - 2024 ColorAntonio AguiarNo ratings yet
- Follow Who Know Road: Q1. Define The Following Financial Modeling Terms Business RisksDocument3 pagesFollow Who Know Road: Q1. Define The Following Financial Modeling Terms Business RisksIbrahimm Denis FofanahNo ratings yet
- Q1 Explain What Is CAMELS Framework Used in Banking AnalysisDocument2 pagesQ1 Explain What Is CAMELS Framework Used in Banking Analysisshubham ghodkeNo ratings yet
- AOR QuestionsDocument33 pagesAOR QuestionsAditi SinghNo ratings yet
- Project Management Notes (UNIT - 3)Document29 pagesProject Management Notes (UNIT - 3)DEV BHADANANo ratings yet
- Finance Strategy PDFDocument8 pagesFinance Strategy PDFShahzaib AslamNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering EconomicsDocument12 pagesSoftware Engineering Economicspidrovo_1No ratings yet
- Entry Phase of The AssignmentDocument3 pagesEntry Phase of The AssignmentAbin AntonyNo ratings yet
- VCE Summer Internship Program 2021: Name Email-ID Smart Task No. Project TopicDocument3 pagesVCE Summer Internship Program 2021: Name Email-ID Smart Task No. Project TopicShazmeenNo ratings yet
- VCE Summer Internship Program 2021: Smart Task Submission FormatDocument7 pagesVCE Summer Internship Program 2021: Smart Task Submission FormatNiharika MathurNo ratings yet
- 1437-Khansa Tallat-Finance-Summary of The ChaptersDocument12 pages1437-Khansa Tallat-Finance-Summary of The Chapterswasif sardarNo ratings yet
- Information System ManagementDocument10 pagesInformation System ManagementAmrita SinghNo ratings yet
- Project Management MaharishiDocument29 pagesProject Management Maharishiankita choudharyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Concept, Scope and Objectives of FinanceDocument7 pagesUnit 1: Concept, Scope and Objectives of FinanceVanshika Srivastava 17IFT017No ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting RulesDocument22 pagesCapital Budgeting Rulesshweta shuklaNo ratings yet
- Financial Engineering Section A Definition of Financial EngineeringDocument10 pagesFinancial Engineering Section A Definition of Financial Engineeringqari saibNo ratings yet
- Master of Business AdministrationDocument31 pagesMaster of Business Administrationoshank12No ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management at Capital One (UKDocument25 pagesCustomer Relationship Management at Capital One (UKRakesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2 M.Com Sem 4thDocument7 pagesAssignment - 2 M.Com Sem 4thVishwas JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Module-III Analytical Tools in Sourcing, Pricing Analysis: Foreign Exchange Currency ManagementDocument10 pagesModule-III Analytical Tools in Sourcing, Pricing Analysis: Foreign Exchange Currency ManagementumeshNo ratings yet
- Answers MS 42Document13 pagesAnswers MS 42SHRIYA TEWARINo ratings yet
- Financial EngineeringDocument42 pagesFinancial Engineeringqari saibNo ratings yet
- PB6MAT - PB6MAT - Financial Technology Week 6Document43 pagesPB6MAT - PB6MAT - Financial Technology Week 6James LieNo ratings yet
- 201511-Semester II-MB0049-Project Management-DEDocument12 pages201511-Semester II-MB0049-Project Management-DEDhaniram SharmaNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument18 pagesProject ManagementShehryar KhanNo ratings yet
- ExpendituresDocument5 pagesExpendituresSheikh MarufNo ratings yet
- Sen MPDocument13 pagesSen MPPushkar rane 1oth,B,ROLL NO.47No ratings yet
- EEA - Data Analyst - Case Study - CFDocument4 pagesEEA - Data Analyst - Case Study - CFLUDOVICMEKNo ratings yet
- Course12 2 PDFDocument36 pagesCourse12 2 PDFYony LaurenteNo ratings yet
- 1 Assignment-1Document4 pages1 Assignment-1Tushar Gupta100% (1)
- Syllabus EMBA12weeksDocument19 pagesSyllabus EMBA12weeksakcelik04No ratings yet
- Super Day Secrets - Your Technical Interview GuideDocument24 pagesSuper Day Secrets - Your Technical Interview GuideJithin RajanNo ratings yet
- Equity Valuation ThesisDocument5 pagesEquity Valuation ThesisJose Katab100% (2)
- Se Economics AutoRecovered AutoRecoveredDocument25 pagesSe Economics AutoRecovered AutoRecoveredArslan GujjarNo ratings yet
- Entre Marking Scheme 2018Document14 pagesEntre Marking Scheme 2018Philomina GomezNo ratings yet
- CA - NotesDocument6 pagesCA - NotessharonNo ratings yet
- Credit AnalystDocument9 pagesCredit AnalystJimsy Antu100% (1)
- Project Selection ModelsDocument26 pagesProject Selection ModelsAbdul Rehman100% (1)
- Assignment Semester-Ii Subject-Project Management Code-MB 0049 ANS1. Phases of Project Management: Project Management Is A Rationally Planned andDocument7 pagesAssignment Semester-Ii Subject-Project Management Code-MB 0049 ANS1. Phases of Project Management: Project Management Is A Rationally Planned andAnonymous 61Kx8L3No ratings yet
- Hints For BSBRSK501 Manage RiskDocument26 pagesHints For BSBRSK501 Manage Riskhossain alviNo ratings yet
- Summary of Michael L. George, John Maxey, David T. Rowlands & Mark Price's The Lean Six Sigma Pocket ToolbookFrom EverandSummary of Michael L. George, John Maxey, David T. Rowlands & Mark Price's The Lean Six Sigma Pocket ToolbookNo ratings yet
- Summary of Don McGreal & Ralph Jocham's The Professional Product OwnerFrom EverandSummary of Don McGreal & Ralph Jocham's The Professional Product OwnerNo ratings yet
- Starting Right CorporationDocument18 pagesStarting Right CorporationLyka Marie Pajares100% (1)
- LT Cost of CapitalDocument17 pagesLT Cost of CapitalAnmol YadavNo ratings yet
- Managing The Marketing FunctionDocument15 pagesManaging The Marketing Functionjerick garlejoNo ratings yet
- MF QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesMF QuestionnaireVINEETA KAPOORNo ratings yet
- Method Nifty 50 ArbitrageDocument8 pagesMethod Nifty 50 ArbitrageTesthdjNo ratings yet
- Fund Industry Assignment PDFDocument12 pagesFund Industry Assignment PDFFedericoNo ratings yet
- Dec 2022Document4 pagesDec 2022Jesus VillalongaNo ratings yet
- Present Value of Principal (8,000,000 X 0.6756) 5,404,800 Jan-01 Present Value of Semi Annual Interest (400,000 X 8.11) 3,244,000 Purchase Price 8,648,800 Jul-01Document2 pagesPresent Value of Principal (8,000,000 X 0.6756) 5,404,800 Jan-01 Present Value of Semi Annual Interest (400,000 X 8.11) 3,244,000 Purchase Price 8,648,800 Jul-01AnonnNo ratings yet
- Stealth Income Strategies For InvestorsDocument116 pagesStealth Income Strategies For Investorsrypai50% (4)
- Sonali Bank Intern Report 1Document72 pagesSonali Bank Intern Report 1Nazmul Alam FarukiNo ratings yet
- Comfort ShoesDocument32 pagesComfort ShoesGrace Priscilla SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Q PP 4 BondsDocument1 pageQ PP 4 BondsJoebel CristalesNo ratings yet
- Coca Cola Company Is A Global Soft Drink Beverage Company TickeDocument3 pagesCoca Cola Company Is A Global Soft Drink Beverage Company TickeAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis Toyota Indus Motors Company Limited: Lquidity RatiosDocument9 pagesRatio Analysis Toyota Indus Motors Company Limited: Lquidity RatiosArsl331No ratings yet
- Insider TradingDocument49 pagesInsider TradingRavi Joshi100% (1)
- Chapter 7. Bonds and Their Valuation: A B C D E F G H I 1 2 3 4Document13 pagesChapter 7. Bonds and Their Valuation: A B C D E F G H I 1 2 3 4Naufal IhsanNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2019Document395 pagesAnnual Report 2019Aji WijanarkoNo ratings yet
- Mega TrustDocument50 pagesMega Trustbribriinsf100% (1)
- (Quiz Uas Take Home) Akl-1 PDFDocument7 pages(Quiz Uas Take Home) Akl-1 PDFStephani ElvinaNo ratings yet
- All About Stock Market - Read ItDocument44 pagesAll About Stock Market - Read ItShekhar SumanNo ratings yet
- FINA 4011 Exam 2 OutlineDocument4 pagesFINA 4011 Exam 2 OutlineRavi PatelNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Capital Accounts Reporting and Managing Intellectual CapitalDocument81 pagesIntellectual Capital Accounts Reporting and Managing Intellectual CapitalirfantanjungNo ratings yet
- Chap005a - The Value of BondDocument35 pagesChap005a - The Value of Bondnt.phuongnhu1912No ratings yet
- Difference Between GDR and IDRDocument18 pagesDifference Between GDR and IDRpriyanka chawlaNo ratings yet
- Istilah Istilah EkoTekDocument24 pagesIstilah Istilah EkoTeki putu andre artha wardanaNo ratings yet
- Crypto Vs GoldDocument22 pagesCrypto Vs GoldResearchtimeNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Assignment 1Document6 pagesCorporate Finance Assignment 1Kûnãl SälîañNo ratings yet
- Variance Swaps - An IntroductionDocument5 pagesVariance Swaps - An IntroductionAngelo TorresNo ratings yet
- The Banking Law Reviewer Hot JuristDocument28 pagesThe Banking Law Reviewer Hot Juristgrego centillas100% (3)