Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kinetic Theory of Matter
Kinetic Theory of Matter
Uploaded by
ellenjune632Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Maele Le DitlhalosoDocument2 pagesMaele Le Ditlhalosowengiemotshegwe100% (1)
- MET 387 Course PackDocument85 pagesMET 387 Course PackWilliam ShultsNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Skin Material With ZBrush and Single Pass BPR PabloMunozGDocument29 pagesA Guide To Skin Material With ZBrush and Single Pass BPR PabloMunozGJackes David Lemos Lemos100% (3)
- CH 1 - Survey of CGDocument67 pagesCH 1 - Survey of CGReem YouNo ratings yet
- TP1 Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument2 pagesTP1 Kinetic Theory of MatterThabang Sbo PhokontsiNo ratings yet
- Third Form Packet WorkDocument19 pagesThird Form Packet WorkLizbeth Chi100% (1)
- Unit 2 Thermal Physics CIEDocument27 pagesUnit 2 Thermal Physics CIEShrirang ChandankhedeNo ratings yet
- VIII Chemistry HO 01Document9 pagesVIII Chemistry HO 01AINo ratings yet
- 2-Thermal PhysicsDocument26 pages2-Thermal PhysicsSamah Hafez100% (1)
- Notes - Matter in Our Surroundings - ExpDocument6 pagesNotes - Matter in Our Surroundings - Expdeborah hildaNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings ( Prashant Kirad ) (1)Document41 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings ( Prashant Kirad ) (1)nidhimathapati123No ratings yet
- Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - Free Exam AcademyDocument14 pagesSimple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - Free Exam AcademysinojiayogNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument10 pagesStates of Matterm.umerfaizan1895No ratings yet
- Thermal Transfer IDocument6 pagesThermal Transfer Iashane dwightNo ratings yet
- Resource 1Document13 pagesResource 1eeren41789No ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Particulate Nature of Matter 2023 Year 10Document10 pagesCh. 1 Particulate Nature of Matter 2023 Year 10sarah awadNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryDocument8 pagesThe Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryVibinraj K NileshwarNo ratings yet
- Y9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesDocument10 pagesY9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesTeck TieNo ratings yet
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 9Document10 pagesCSO Olympiad Book For Class 9Malith MadushanNo ratings yet
- Stages of AggregationDocument6 pagesStages of AggregationgrandayaizaNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Document15 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Keeertththana SaravananNo ratings yet
- Understanding Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument50 pagesUnderstanding Kinetic Particle TheoryozmanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledNana MinNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of ParticlesDocument14 pagesKinetic Theory of ParticlesMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Study Guide KMTDocument6 pagesStudy Guide KMT9Wezen Jowelyn Mae G. TabuzoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundingsshashi kumar sinhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesChapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsAshrafNo ratings yet
- G9-Chem-Matter 1-NotesDocument11 pagesG9-Chem-Matter 1-NotesvijahatNo ratings yet
- G9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2Document35 pagesG9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2hk6sd6cf7vNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its ClassificationDocument13 pagesMatter and Its ClassificationChandraSekharNo ratings yet
- 6463 Topper 21 101 1 2 18 1122 States of Matter Up201701031203 1483425218 7346Document5 pages6463 Topper 21 101 1 2 18 1122 States of Matter Up201701031203 1483425218 7346avantikajethani20No ratings yet
- The States of Matter CWDocument3 pagesThe States of Matter CWPraveenaNo ratings yet
- PHY111A 1.1.1 - Kinetic Particle Model PDFDocument28 pagesPHY111A 1.1.1 - Kinetic Particle Model PDFanton petrovNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument9 pagesStates of Mattervidya pmNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Kinetic Model of MatterDocument17 pages1.2 Kinetic Model of MatterHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Notes - Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument7 pagesNotes - Kinetic Theory of MatterAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Term 1 NotesDocument28 pagesChemistry Term 1 Notesepicfortnite063No ratings yet
- Week 1: Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument31 pagesWeek 1: Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsCrizza Mae CuregNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 1 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument68 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 1 Matter in Our SurroundingsParesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- MATTERDocument4 pagesMATTERRajiv BiswasNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 HandoutDocument10 pagesWEEK 1 HandoutWeCareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 States of MattersDocument7 pagesChapter 2 States of MattersMd Ahsan Habib MizanNo ratings yet
- O LVL Chem - Chap 1Document3 pagesO LVL Chem - Chap 1montyredNo ratings yet
- Grade-09 - Science - Chapter01 - Matter-in-Our-Surroundings by Raminder ChopraDocument11 pagesGrade-09 - Science - Chapter01 - Matter-in-Our-Surroundings by Raminder ChopraRaminder ChopraNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4Document11 pagesiGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4SimonNo ratings yet
- Ngss Particle Model PDFDocument2 pagesNgss Particle Model PDFDarwinEspinoza100% (1)
- IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument70 pagesIGCSE Chemistry NotesKim Seng OnnNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)Document28 pagesPhysics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)salma salNo ratings yet
- Physics: Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument11 pagesPhysics: Kinetic Particle Theoryanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument3 pagesKinetic Molecular TheorykimNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory, Phase Changes, Brownian MotionDocument10 pagesKinetic Theory, Phase Changes, Brownian MotionRamesh GoldbergNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Model of MatterDocument25 pagesKinetic Model of MatterHafiza JaweriaNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic TheoryDocument4 pagesThe Kinetic TheoryMystica InnissNo ratings yet
- 3 1Document90 pages3 1Joy MercadoNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1 States of Matter CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 Save My ExamsDocument1 page2.1.1 States of Matter CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 Save My Examsyichenlin111No ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument108 pagesChapter-1 Matter in Our SurroundingsNodiaNo ratings yet
- S2 A Chemistry New Class JuneDocument25 pagesS2 A Chemistry New Class Junethiri hsuNo ratings yet
- 1 States of MatterDocument7 pages1 States of MatterAiman SanobarNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1 - KINETIC MOLECULAR MODEL - IngallaDocument4 pagesACTIVITY 1 - KINETIC MOLECULAR MODEL - Ingallajet tolintinoNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesIgcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsCHIO SHEUNG YONGNo ratings yet
- Phyw 2Document42 pagesPhyw 2Sajjad FaisalNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument32 pagesStates of MatterKeith BansrajNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Globalisation 2Document11 pagesGlobalisation 2wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- (H2 Bio) Chapter 1 Cell BiologyDocument29 pages(H2 Bio) Chapter 1 Cell BiologywengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- Parts of The EyeDocument9 pagesParts of The EyewengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- GP6 - Pressure 1Document3 pagesGP6 - Pressure 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- TP5 - Heat Capacity & Latent Heat 1Document5 pagesTP5 - Heat Capacity & Latent Heat 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- GP5 - Energy, Work & Power 1Document8 pagesGP5 - Energy, Work & Power 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- Diane Ka Ga Botsalano - Iafrika - SetswanaDocument1 pageDiane Ka Ga Botsalano - Iafrika - SetswanawengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- 1002 S2 - 1002 T2Document2 pages1002 S2 - 1002 T2Manjunath ShettyNo ratings yet
- Euler's PathDocument10 pagesEuler's PathSatish Kumar0% (1)
- 3341104Document7 pages3341104Vani YamaniNo ratings yet
- Catalogue - 35 - 40 Kva PDFDocument4 pagesCatalogue - 35 - 40 Kva PDFsunil varmaNo ratings yet
- Blast Chiller 1Document66 pagesBlast Chiller 1Rfsdjr AceNo ratings yet
- Shear Wall Design: Hord EsignDocument1 pageShear Wall Design: Hord EsignkirubaNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment PlantDocument24 pagesWater Treatment PlantHarendra RathnayakeNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics ReviewerDocument2 pagesThermodynamics ReviewerRogelioB.AlobII100% (1)
- Review 2Document7 pagesReview 2usman ghaniNo ratings yet
- Specification - Sectic TankDocument2 pagesSpecification - Sectic TankpeakfortuneNo ratings yet
- 07 DiagnosticsDocument132 pages07 DiagnosticsJosué Soldera100% (2)
- Test Bank Questions Chapter 6Document3 pagesTest Bank Questions Chapter 6Anonymous 8ooQmMoNs1No ratings yet
- Process Control SystemsDocument3 pagesProcess Control SystemsHammad Ansari100% (1)
- Schmidt Analysis (Updated 12-28-2011)Document5 pagesSchmidt Analysis (Updated 12-28-2011)أمير معروفNo ratings yet
- Solenoid Valve (Proportional Reducing) - Calibrate - Negative Flow ControlDocument37 pagesSolenoid Valve (Proportional Reducing) - Calibrate - Negative Flow ControlBrahian Mijael Garrado Gonzales100% (2)
- Chart Smart:: Linear AcceleratorsDocument2 pagesChart Smart:: Linear AcceleratorsClaudia Morales UlloaNo ratings yet
- DiffeqDocument126 pagesDiffeqRaghavendra GondabalNo ratings yet
- Ch4 - Elastic Properties of SolidsDocument2 pagesCh4 - Elastic Properties of Solidsنايف محمد القباتليNo ratings yet
- UT BOTOL ANGIN - KMP. KranaaDocument10 pagesUT BOTOL ANGIN - KMP. KranaaSatriya GunawanNo ratings yet
- Coupled TanksDocument32 pagesCoupled TanksbgizachewNo ratings yet
- C X G F DX X G X G F: 4.5 Integration by SubstitutionDocument11 pagesC X G F DX X G X G F: 4.5 Integration by SubstitutionAndres TorricoNo ratings yet
- LGMMA Acrylic Coating Resin Brochure 2017 EDocument2 pagesLGMMA Acrylic Coating Resin Brochure 2017 EFausa Okta Ananta LaksaNo ratings yet
- Romax Spin FlyerDocument2 pagesRomax Spin FlyerDionisie LefterNo ratings yet
- Naphtha Steam Reforming For Hydrogen ProductionDocument9 pagesNaphtha Steam Reforming For Hydrogen ProductionsatishchemengNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectricalDocument178 pagesBasics of Electricaludayakumart50% (2)
- 12 Fiber Multi Mode Multitube Fiber Optic Cable: Part No. Data SheetDocument1 page12 Fiber Multi Mode Multitube Fiber Optic Cable: Part No. Data SheetAde DwinantoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Electrical SystemsDocument18 pagesMechanical and Electrical SystemsAlexander PiniliNo ratings yet
Kinetic Theory of Matter
Kinetic Theory of Matter
Uploaded by
ellenjune632Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kinetic Theory of Matter
Kinetic Theory of Matter
Uploaded by
ellenjune632Copyright:
Available Formats
1
KINETIC THEORY OF MATTER
Matter is made up of small particles called atoms or a group of atoms called
molecules. The size of each particle is different for different materials.
The distance between molecules can change depending on the Internal Energy
(kinetic + potential) of the molecule or atom.
Particles are always in motion (moving). The higher the temperature the faster the
molecules move/vibrates.
At the same temperature, all molecules have the same energy. Small particles move
faster while heavy particles moves slowly.
States Of Matter
States of SOLID LIQUID GAS
matter
Have a definite Have a definite Have no definite shape and
volume and volume but no definite volume. (wholly fills up the
definite shape. shape (takes the shape container and takes the shape
Properties
Not compressible of the container). of the container). Highly
Slightly compressible compressible
Molecules are very Molecules slightly Molecules are much further
Distance close to each other further apart than in apart. So gases can be
between solids but still close compressed or squeezed in
molecules together to have a smaller space.
definite volume
Forces Held by strong Particle held by less No or less forces of attraction.
between forces of attraction strong forces. Molecules are free to move in
molecules called bonds. any direction.
Molecules vibrate Free to move Moves freely at high speed
Motion to and fro at a fixed colliding with each other and
position. the walls of the container.
Motion of Gas Molecules and its Temperature and Pressure.
If a gas is heated in a closed container, its molecules gain kinetic energy and begin to hit the
walls of the container more frequently than before. This causes an increase in pressure on the
walls of the container. The faster the gas molecules move, the higher the temperature they
attain. The gas container can explode if it can’t withstand the pressure build up.
Physics Notes: KINETIC THEORY OF MATTER. leemok productions 2012©
2
Brownian Motion
Brownian motion gives us the evidence that molecules in suspension (gases) are constantly
moving. When smoke is trapped in a glass box (smoke cell) and is observed with a
microscope, the smoke particle can be seen as bright specks moving around in a random and
haphazard manner.
This is because they collide with gas molecules that move at high velocities at random paths.
Smoke particles are bigger compared to air particles. The specks of light seen is where
collision between smoke particles and air particles occur. This phenomena is known as
Brownian motion..
Evaporation
Evaporation is the escape of high energy molecules from the surface of a liquid. Evaporation
results in a drop in the temperature of the liquid from which the molecules escaped. This is
because the molecules that escape acquire energy to do so from those which remain in the
liquid.Evaporation only takes place at the surface of the liquid and occurs at any temperature.
Factors That Affect Evaporation
A number of factors affect the rate of evaporation. These are;
Wind speed (drought).An increase in wind speed causes an increase in rate of
evaporation
Surface area. The larger the surface area the higher the rate of evaporation.
Temperature. The higher the temperature the higher the rate of evaporation
Humidity. The higher the humidity the lower the rate of evaporation.
Applications of evaporeation
Ether is used in fridges to cool their interiors
Water sacks are put under the shade and moistened with water so that the water inside
cools as the molecules outside evaporate.
Organisms cool themselves by evaporation using different ways,
. Dogs = Panting
Elephants= Flap their ears
Humans= Perspiration
Plants=Evaporation from leaves
Physics Notes: KINETIC THEORY OF MATTER. leemok productions 2012©
You might also like
- Maele Le DitlhalosoDocument2 pagesMaele Le Ditlhalosowengiemotshegwe100% (1)
- MET 387 Course PackDocument85 pagesMET 387 Course PackWilliam ShultsNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Skin Material With ZBrush and Single Pass BPR PabloMunozGDocument29 pagesA Guide To Skin Material With ZBrush and Single Pass BPR PabloMunozGJackes David Lemos Lemos100% (3)
- CH 1 - Survey of CGDocument67 pagesCH 1 - Survey of CGReem YouNo ratings yet
- TP1 Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument2 pagesTP1 Kinetic Theory of MatterThabang Sbo PhokontsiNo ratings yet
- Third Form Packet WorkDocument19 pagesThird Form Packet WorkLizbeth Chi100% (1)
- Unit 2 Thermal Physics CIEDocument27 pagesUnit 2 Thermal Physics CIEShrirang ChandankhedeNo ratings yet
- VIII Chemistry HO 01Document9 pagesVIII Chemistry HO 01AINo ratings yet
- 2-Thermal PhysicsDocument26 pages2-Thermal PhysicsSamah Hafez100% (1)
- Notes - Matter in Our Surroundings - ExpDocument6 pagesNotes - Matter in Our Surroundings - Expdeborah hildaNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings ( Prashant Kirad ) (1)Document41 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings ( Prashant Kirad ) (1)nidhimathapati123No ratings yet
- Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - Free Exam AcademyDocument14 pagesSimple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - Free Exam AcademysinojiayogNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument10 pagesStates of Matterm.umerfaizan1895No ratings yet
- Thermal Transfer IDocument6 pagesThermal Transfer Iashane dwightNo ratings yet
- Resource 1Document13 pagesResource 1eeren41789No ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Particulate Nature of Matter 2023 Year 10Document10 pagesCh. 1 Particulate Nature of Matter 2023 Year 10sarah awadNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryDocument8 pagesThe Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryVibinraj K NileshwarNo ratings yet
- Y9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesDocument10 pagesY9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesTeck TieNo ratings yet
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 9Document10 pagesCSO Olympiad Book For Class 9Malith MadushanNo ratings yet
- Stages of AggregationDocument6 pagesStages of AggregationgrandayaizaNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Document15 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Keeertththana SaravananNo ratings yet
- Understanding Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument50 pagesUnderstanding Kinetic Particle TheoryozmanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledNana MinNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of ParticlesDocument14 pagesKinetic Theory of ParticlesMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Study Guide KMTDocument6 pagesStudy Guide KMT9Wezen Jowelyn Mae G. TabuzoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundingsshashi kumar sinhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesChapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsAshrafNo ratings yet
- G9-Chem-Matter 1-NotesDocument11 pagesG9-Chem-Matter 1-NotesvijahatNo ratings yet
- G9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2Document35 pagesG9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2hk6sd6cf7vNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its ClassificationDocument13 pagesMatter and Its ClassificationChandraSekharNo ratings yet
- 6463 Topper 21 101 1 2 18 1122 States of Matter Up201701031203 1483425218 7346Document5 pages6463 Topper 21 101 1 2 18 1122 States of Matter Up201701031203 1483425218 7346avantikajethani20No ratings yet
- The States of Matter CWDocument3 pagesThe States of Matter CWPraveenaNo ratings yet
- PHY111A 1.1.1 - Kinetic Particle Model PDFDocument28 pagesPHY111A 1.1.1 - Kinetic Particle Model PDFanton petrovNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument9 pagesStates of Mattervidya pmNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Kinetic Model of MatterDocument17 pages1.2 Kinetic Model of MatterHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Notes - Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument7 pagesNotes - Kinetic Theory of MatterAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Term 1 NotesDocument28 pagesChemistry Term 1 Notesepicfortnite063No ratings yet
- Week 1: Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument31 pagesWeek 1: Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsCrizza Mae CuregNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 1 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument68 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 1 Matter in Our SurroundingsParesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- MATTERDocument4 pagesMATTERRajiv BiswasNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 HandoutDocument10 pagesWEEK 1 HandoutWeCareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 States of MattersDocument7 pagesChapter 2 States of MattersMd Ahsan Habib MizanNo ratings yet
- O LVL Chem - Chap 1Document3 pagesO LVL Chem - Chap 1montyredNo ratings yet
- Grade-09 - Science - Chapter01 - Matter-in-Our-Surroundings by Raminder ChopraDocument11 pagesGrade-09 - Science - Chapter01 - Matter-in-Our-Surroundings by Raminder ChopraRaminder ChopraNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4Document11 pagesiGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4SimonNo ratings yet
- Ngss Particle Model PDFDocument2 pagesNgss Particle Model PDFDarwinEspinoza100% (1)
- IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument70 pagesIGCSE Chemistry NotesKim Seng OnnNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)Document28 pagesPhysics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)salma salNo ratings yet
- Physics: Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument11 pagesPhysics: Kinetic Particle Theoryanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument3 pagesKinetic Molecular TheorykimNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory, Phase Changes, Brownian MotionDocument10 pagesKinetic Theory, Phase Changes, Brownian MotionRamesh GoldbergNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Model of MatterDocument25 pagesKinetic Model of MatterHafiza JaweriaNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic TheoryDocument4 pagesThe Kinetic TheoryMystica InnissNo ratings yet
- 3 1Document90 pages3 1Joy MercadoNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1 States of Matter CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 Save My ExamsDocument1 page2.1.1 States of Matter CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 Save My Examsyichenlin111No ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument108 pagesChapter-1 Matter in Our SurroundingsNodiaNo ratings yet
- S2 A Chemistry New Class JuneDocument25 pagesS2 A Chemistry New Class Junethiri hsuNo ratings yet
- 1 States of MatterDocument7 pages1 States of MatterAiman SanobarNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1 - KINETIC MOLECULAR MODEL - IngallaDocument4 pagesACTIVITY 1 - KINETIC MOLECULAR MODEL - Ingallajet tolintinoNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesIgcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsCHIO SHEUNG YONGNo ratings yet
- Phyw 2Document42 pagesPhyw 2Sajjad FaisalNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument32 pagesStates of MatterKeith BansrajNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Globalisation 2Document11 pagesGlobalisation 2wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- (H2 Bio) Chapter 1 Cell BiologyDocument29 pages(H2 Bio) Chapter 1 Cell BiologywengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
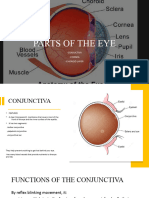
- Parts of The EyeDocument9 pagesParts of The EyewengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- GP6 - Pressure 1Document3 pagesGP6 - Pressure 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- TP5 - Heat Capacity & Latent Heat 1Document5 pagesTP5 - Heat Capacity & Latent Heat 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- GP5 - Energy, Work & Power 1Document8 pagesGP5 - Energy, Work & Power 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- Diane Ka Ga Botsalano - Iafrika - SetswanaDocument1 pageDiane Ka Ga Botsalano - Iafrika - SetswanawengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- 1002 S2 - 1002 T2Document2 pages1002 S2 - 1002 T2Manjunath ShettyNo ratings yet
- Euler's PathDocument10 pagesEuler's PathSatish Kumar0% (1)
- 3341104Document7 pages3341104Vani YamaniNo ratings yet
- Catalogue - 35 - 40 Kva PDFDocument4 pagesCatalogue - 35 - 40 Kva PDFsunil varmaNo ratings yet
- Blast Chiller 1Document66 pagesBlast Chiller 1Rfsdjr AceNo ratings yet
- Shear Wall Design: Hord EsignDocument1 pageShear Wall Design: Hord EsignkirubaNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment PlantDocument24 pagesWater Treatment PlantHarendra RathnayakeNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics ReviewerDocument2 pagesThermodynamics ReviewerRogelioB.AlobII100% (1)
- Review 2Document7 pagesReview 2usman ghaniNo ratings yet
- Specification - Sectic TankDocument2 pagesSpecification - Sectic TankpeakfortuneNo ratings yet
- 07 DiagnosticsDocument132 pages07 DiagnosticsJosué Soldera100% (2)
- Test Bank Questions Chapter 6Document3 pagesTest Bank Questions Chapter 6Anonymous 8ooQmMoNs1No ratings yet
- Process Control SystemsDocument3 pagesProcess Control SystemsHammad Ansari100% (1)
- Schmidt Analysis (Updated 12-28-2011)Document5 pagesSchmidt Analysis (Updated 12-28-2011)أمير معروفNo ratings yet
- Solenoid Valve (Proportional Reducing) - Calibrate - Negative Flow ControlDocument37 pagesSolenoid Valve (Proportional Reducing) - Calibrate - Negative Flow ControlBrahian Mijael Garrado Gonzales100% (2)
- Chart Smart:: Linear AcceleratorsDocument2 pagesChart Smart:: Linear AcceleratorsClaudia Morales UlloaNo ratings yet
- DiffeqDocument126 pagesDiffeqRaghavendra GondabalNo ratings yet
- Ch4 - Elastic Properties of SolidsDocument2 pagesCh4 - Elastic Properties of Solidsنايف محمد القباتليNo ratings yet
- UT BOTOL ANGIN - KMP. KranaaDocument10 pagesUT BOTOL ANGIN - KMP. KranaaSatriya GunawanNo ratings yet
- Coupled TanksDocument32 pagesCoupled TanksbgizachewNo ratings yet
- C X G F DX X G X G F: 4.5 Integration by SubstitutionDocument11 pagesC X G F DX X G X G F: 4.5 Integration by SubstitutionAndres TorricoNo ratings yet
- LGMMA Acrylic Coating Resin Brochure 2017 EDocument2 pagesLGMMA Acrylic Coating Resin Brochure 2017 EFausa Okta Ananta LaksaNo ratings yet
- Romax Spin FlyerDocument2 pagesRomax Spin FlyerDionisie LefterNo ratings yet
- Naphtha Steam Reforming For Hydrogen ProductionDocument9 pagesNaphtha Steam Reforming For Hydrogen ProductionsatishchemengNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectricalDocument178 pagesBasics of Electricaludayakumart50% (2)
- 12 Fiber Multi Mode Multitube Fiber Optic Cable: Part No. Data SheetDocument1 page12 Fiber Multi Mode Multitube Fiber Optic Cable: Part No. Data SheetAde DwinantoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Electrical SystemsDocument18 pagesMechanical and Electrical SystemsAlexander PiniliNo ratings yet