Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsIGCSE Geography P4 Key Answers
IGCSE Geography P4 Key Answers
Uploaded by
technabooksCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- AS 1530.2 (Test For Flamability of Materials)Document13 pagesAS 1530.2 (Test For Flamability of Materials)Ibrahim KNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document7 pagesUnit 4api-235865217No ratings yet
- CSS NCII 4rth Quarter Lesson Plan LO3 IsolateDocument2 pagesCSS NCII 4rth Quarter Lesson Plan LO3 IsolateJulius Baldelovar100% (5)
- 2010-2011 Head, Fischer and Elan Bindings Tech Manual From Tyrolia - Techn - Manual - ENDocument91 pages2010-2011 Head, Fischer and Elan Bindings Tech Manual From Tyrolia - Techn - Manual - ENemgyee100% (5)
- Airflow Quantity MeasurementsDocument16 pagesAirflow Quantity Measurementsadam fakhri100% (1)
- 4.2 Geographical Investigation AdditionalDocument24 pages4.2 Geographical Investigation AdditionalTheRealDanNo ratings yet
- Paper 4 Enquiry SkillsDocument40 pagesPaper 4 Enquiry SkillsYixuan JiangNo ratings yet
- Geo SbaDocument17 pagesGeo SbaFalon TomlinNo ratings yet
- GEOGRAPHY RESEARCHDocument26 pagesGEOGRAPHY RESEARCHMazvitaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Social Studies Summary PDFDocument25 pagesGrade 7 Social Studies Summary PDFShikeenga FillipusNo ratings yet
- 1,2,3,6Document4 pages1,2,3,6ريان الحربيNo ratings yet
- River MeasurementsDocument12 pagesRiver Measurementsmahika gaurNo ratings yet
- Paper 4 - Alternative To Coursework - The Geography Study SchoolDocument7 pagesPaper 4 - Alternative To Coursework - The Geography Study SchoolTanatswa TicharwaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Stream FlowDocument6 pagesWhat Is A Stream FlowRheymar Dela Rosa DiwaNo ratings yet
- Weather Unit - Lesson Five Weather ToolsDocument11 pagesWeather Unit - Lesson Five Weather Toolsapi-547152003No ratings yet
- River MeasurementsDocument9 pagesRiver MeasurementsMunir LakhaNo ratings yet
- Case StudiesDocument12 pagesCase StudiesAntara PandeNo ratings yet
- ABEn 145 - Tribunalo - Lab 4Document14 pagesABEn 145 - Tribunalo - Lab 4Jaylou OpondaNo ratings yet
- Navigational InstrumentsDocument2 pagesNavigational InstrumentsAriel MolinaNo ratings yet
- Lab 04Document3 pagesLab 04mekailpervaiz48No ratings yet
- FieldworkDocument28 pagesFieldworkRutendo GandidzanwaNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document9 pagesLab 6ArjayDimapilisNo ratings yet
- Measurements of Water QualityDocument3 pagesMeasurements of Water QualityFuad AhmedinNo ratings yet
- Obinna Geo 5Document48 pagesObinna Geo 5Obinna RichardNo ratings yet
- 20 Hydrometreological Instruments: Prepared By: Kenjie N. Dela CruzDocument41 pages20 Hydrometreological Instruments: Prepared By: Kenjie N. Dela CruzDela Cruz Kenjie N.No ratings yet
- Flow and Cross SectionDocument14 pagesFlow and Cross SectionfrancishozeguevaraNo ratings yet
- Hydrographic Surveys: Lesson 34Document14 pagesHydrographic Surveys: Lesson 34Ma Danica LagacNo ratings yet
- No. Sense Observations Qualitative Quantitative: Fill Up The Table BelowDocument23 pagesNo. Sense Observations Qualitative Quantitative: Fill Up The Table BelowUmmu Umar Wa AisyahNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Doppler Current ProfilerDocument20 pagesAcoustic Doppler Current Profilerashish chauhanNo ratings yet
- The Weather StationDocument13 pagesThe Weather StationgeorgemaposaNo ratings yet
- Hydrometeorological InstrumentsDocument7 pagesHydrometeorological InstrumentsVerra Myza Arat0% (1)
- Lecture 5 - HeightsDocument25 pagesLecture 5 - HeightsMeshai RanchodNo ratings yet
- SNI 7963-2014 Tide Gauge ObservationDocument19 pagesSNI 7963-2014 Tide Gauge Observationseirac.1782No ratings yet
- Stream GaugingDocument13 pagesStream GaugingMomin arNo ratings yet
- Flow Visualisation Using Water Flow Channel AimDocument6 pagesFlow Visualisation Using Water Flow Channel AimesakkimuthuNo ratings yet
- Hydrometeorological InstrumentsDocument4 pagesHydrometeorological InstrumentsAnne WabanNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Lab ManualDocument16 pagesHydrology Lab ManualAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Coasts Practicals Paper 4Document8 pagesCoasts Practicals Paper 4gavazamary1No ratings yet
- Instrumentation For Ocean ApplicationDocument22 pagesInstrumentation For Ocean ApplicationRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- DischargeDocument20 pagesDischargeanish.bhandariNo ratings yet
- Cec 102 Practical - Introductory HydrologyDocument25 pagesCec 102 Practical - Introductory HydrologyVietHungCao100% (3)
- Measuring and Recording Weather PT 3Document7 pagesMeasuring and Recording Weather PT 3zoeNo ratings yet
- btech7th-CE-WRE LAB (3) - 1Document20 pagesbtech7th-CE-WRE LAB (3) - 1sarojkrmahuwanNo ratings yet
- Windexploration CCDocument16 pagesWindexploration CCapi-340145996No ratings yet
- Economics A Level NotesDocument20 pagesEconomics A Level NotesFatima ZiaNo ratings yet
- Field Work 5Document18 pagesField Work 5Danica Alejo100% (1)
- PROJECT Hydraulic UTHMDocument13 pagesPROJECT Hydraulic UTHMNik Aliff100% (1)
- Beach Profile MethodDocument3 pagesBeach Profile MethodNatarajan MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- Wa0032Document53 pagesWa0032Gerald EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- What Makes Weather Lesson Plan FinalDocument6 pagesWhat Makes Weather Lesson Plan Finalapi-507180911No ratings yet
- The River Channel Alternative To Practical 1Document11 pagesThe River Channel Alternative To Practical 1nicole matsikaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Hannah Wynzelle AbanNo ratings yet
- Coastal ProjectDocument24 pagesCoastal ProjectChris BramaoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Report 2Document23 pagesAssignment Report 2DiegoNo ratings yet
- Weather InstrumentsDocument12 pagesWeather InstrumentsMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Method and Equipment (Longkang)Document6 pagesMethod and Equipment (Longkang)rozaidiabdulrahimNo ratings yet
- Measuring Flow RateDocument1 pageMeasuring Flow RateRaymond KatabaziNo ratings yet
- Velocity Distribution by Current MetreDocument4 pagesVelocity Distribution by Current MetreAashu AnshNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate Atmosphere: "For I Can Do All Things Through Christ Who Gives Me Strength", Phillipians 4:13Document41 pagesWeather and Climate Atmosphere: "For I Can Do All Things Through Christ Who Gives Me Strength", Phillipians 4:13Michael MunyangiNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere Wheather FlyingDocument27 pagesAtmosphere Wheather FlyingRAMA ALFI MUHARAM 181011087No ratings yet
- FWDocument6 pagesFWrychellelaoNo ratings yet
- Navigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsFrom EverandNavigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsNo ratings yet
- 29 GIS SeismicDocument6 pages29 GIS SeismicKhader Abu-daggaNo ratings yet
- P Spice TutorialDocument9 pagesP Spice TutorialPeiHanTseringNo ratings yet
- Lect 10 PDFDocument16 pagesLect 10 PDFshoaib_mohammed_28No ratings yet
- Operation Manual - Amann ASC100Document142 pagesOperation Manual - Amann ASC100David Apaza Hurtado100% (4)
- PCC41NG2 Series Component Cleanliness Cabinet: FeaturesDocument2 pagesPCC41NG2 Series Component Cleanliness Cabinet: FeaturesSamNo ratings yet
- Value Chain AnalysisDocument18 pagesValue Chain AnalysisjainsonaNo ratings yet
- Aphex - Aural - Exciter Type B and CDocument6 pagesAphex - Aural - Exciter Type B and CRichard PowersNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Procedure To Run A Program On FPGA BoardDocument11 pagesStep by Step Procedure To Run A Program On FPGA BoardAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Bibliography For AntennasDocument16 pagesBibliography For AntennasFrancisco ArrudaNo ratings yet
- Analisis Pencatatan Dan Penilaian Persediaan Pada Pt. Sumber Mutiara PrimaDocument12 pagesAnalisis Pencatatan Dan Penilaian Persediaan Pada Pt. Sumber Mutiara PrimaferferferferinNo ratings yet
- Basic Vibration Analysis Condition MonitoringDocument5 pagesBasic Vibration Analysis Condition MonitoringMohamed Nawar50% (2)
- Refer DXF or DWG File For Laser Cutting. 2. Part Inspection Is On Finished DimensionDocument1 pageRefer DXF or DWG File For Laser Cutting. 2. Part Inspection Is On Finished DimensionBala MuruganNo ratings yet
- Ices Indian Universities InstitutionsDocument3 pagesIces Indian Universities InstitutionsOperationNo ratings yet
- Alpha1 Series PC Communication Protocol561785 PDFDocument1 pageAlpha1 Series PC Communication Protocol561785 PDFpancawawanNo ratings yet
- Tradesman - Sheet metal-TEDDocument5 pagesTradesman - Sheet metal-TEDDeekshith DileepNo ratings yet
- 2nd Revised Application Form For DPWH MeDocument2 pages2nd Revised Application Form For DPWH MeKagare KageNo ratings yet
- Advanced Training Institute, DGT, MSDE, Mumbai - MCQ Test 4 - POT / ETDocument4 pagesAdvanced Training Institute, DGT, MSDE, Mumbai - MCQ Test 4 - POT / ETpriyanka lariyaNo ratings yet
- 700 Series Rubber Seated Butterfly Valves: Features and BenefitsDocument2 pages700 Series Rubber Seated Butterfly Valves: Features and BenefitsqcselvaNo ratings yet
- Equations: Hvac Equations, Data, and Rules of ThumbDocument21 pagesEquations: Hvac Equations, Data, and Rules of ThumbzodedNo ratings yet
- Surface Catenary Interventions PsDocument2 pagesSurface Catenary Interventions Psditer najarNo ratings yet
- Pages From Siemens Tcpip EthernetDocument1 pagePages From Siemens Tcpip EthernettinhmdcNo ratings yet
- "Greater Baku Regional Development Plan" (GBRDP) ProjectDocument114 pages"Greater Baku Regional Development Plan" (GBRDP) ProjectRyan French100% (2)
- 50 Top Design of Masonry Structures Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pages50 Top Design of Masonry Structures Multiple Choice Questionssaikiran1493No ratings yet
- NDT Radiation SafetyDocument33 pagesNDT Radiation SafetyRamakrishnan AmbiSubbiahNo ratings yet
- Irc Gov in SP 090 2010 PDFDocument92 pagesIrc Gov in SP 090 2010 PDFSubramanian ArulNo ratings yet
- Material HandlingDocument26 pagesMaterial HandlingRohit AroraNo ratings yet
- Exp-8 Staircase WiringDocument3 pagesExp-8 Staircase WiringUjjwal GargNo ratings yet
IGCSE Geography P4 Key Answers
IGCSE Geography P4 Key Answers
Uploaded by
technabooks0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesOriginal Title
IGCSE Geography P4 key answers
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesIGCSE Geography P4 Key Answers
IGCSE Geography P4 Key Answers
Uploaded by
technabooksCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
How to measure gradient
- Measure a distance of 10m
- Put two ranging poles on the ends of the river bed and make sure it is vertical
- Use a tape to create a line between the poles
- Hold a clinometer at the angle of the line
- Then using the clinometer, measure the angle
- Repeat the measurement several times and calculate average
- Record the results
How to measure channel width
- Put poles on either sides of the river bank
- Stretch a tape measure across the river and ensure that it is tight
- Then look at the point where the tape measure touches/ reaches the bank
- Repeat several times and get the average
- Record the result
How to measure the channel depth
- Use ranging rod
- Record the depth by reading the scale
- Measure from the river bed to the water surface
- Repeat multiple times across the section to find the average
- Repeat with different sections and record results
How to read min and max thermometer
- Put stevenson screen outside
- Read the temperatures and record it every 24 hours at the same time of the day
- Read the value from the bottom of the index of both thermometers
- Record the min and max temperatures
- Be sure to read the value perpendicular to the scale
How to measure rainfall
- Attach the rain gauge to post
- Rainfall into the funnel and into a jar
- Measure the volume of water using a measuring cylinder and read the value from
below the meniscus
- The volume is measured in mm
- Measure every day and same time for 24 hours
- Be sure to empty the container before putting the jar back into the post
How to measure wind speed
- Use an anemometer
- Place in a high area on top of buildings
- The cups of the anemometer will rotate as the wind blow
- There will a reading displayed on the screen
- Reading is recorded as knots or miles per hour
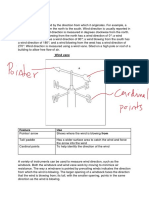
How to measure wind direction
- Use a wind vane
- Wind will exert force on the pointer which causes it to rotate to the direction the wind
is coming from
- The pointer will point to a direction and the direction is determined by using the
compass direction below the pointer
Features of a good questionnaire
- Explanation of who is asking questions and the topic of the questionnaire
- Aimed at a target group
- Easy to read and understand
- Explain the purpose of the questionnaire
- Contains space to write answers
- The questionnaire is anonymous it doesn’t violate the person’s personal life
- Include thank you at the end
How to measure beach profile
- Put poles at each break of slopes
- Measure the distance between slopes
- Make sure the poles are vertical
- Hold the clinometer next to top
- Use a clinometer to measure the angle
- Repeat along the different places up the beach
Fieldwork for pollution
- Decide types of pollution
- Create a 1-5 scale/ environment index
- Decide on a sampling method
- Use a quadrat and throw over the shoulder
- Count the litter
- Photograph the types of pollution
How to measure wave frequency
- Place a pole in the sea near the shore
- Make sure the pole is vertical
- Count the number of waves breaking and hitting the pole
- Record it in a table/ tally
- Use a stopwatch to measure the time - the number of waves breaking for 1 minute
- Repeat the measurements and work out average
How to use a sunshine recorder
- Place the sunshine recorder outside in an open area
- Insert a paper card in the instrument
- The sun’s ray will burn the paper which creates a line
- The burn line on the paper determines the hours of sunshine
- Record for every 24 hours at the same time
- Make sure to replace the card each day
How to use quadrat to collect results (unsure)
- Throw the quadrat over the shoulder (so it’s random)
- Count the number of squares which different materials can be found
- Do more than one measurement at different sites and calculate average
Measure angle of slopes
- Place a ranging pole on top & bottom of beach
- Make sure the poles are vertical
- Use a tape measure, measure the distance
- Use a clinometer and hold it at an agreed height
- Measure the angle
- Repeat the measurement for several times and calculate the average
How to measure river velocity using floats
- Measure a distance of 10m using a tape measure
- Place ranging poles on each end of the 10m
- Make sure the poles are vertical
- Put an orange at the starting point
- Start the timer when it’s released
- When orange reaches end point, stop the timer
- Use the formula speed = distance/ time to calculate the speed
- Repeat the measurement and calculate the average
How to measure river velocity using flowmeter
- Submerge the flowmeter into the river
- The propeller should be facing upstream
- Make sure there is no obstacles infront of the propeller
- Read the digital reading of the speed displayed on the screen of the instrument
- Repeat the measurement and calculate the average
- Record the results
How to measure the depth of a river
- Extend the tape measure from bank to bank and measure the distance
- Using 0.5 m interval, put a pole at each interval as a marking
- Make sure the pole is vertical
- Identify the wet part of the pole and measure the height
- Record all the heights
- Add all the heights together and divide to obtain the mean height
How to measure the roundness of the beach materials (unsure)
- Using a random/ systematic method pick out 10 pebbles
- Using a scale determine the roundness by observing (may be unreliable as it is
subjective)
- Repeat downstream
How to measure river discharge
- Use hydrograph
- Discharge (m^3/2) = cross-sectional area (m^2) x velocity (m/2)
- Highest point on hydrograph shows peak discharge
- Usually increases downstream
How to measure wetted perimeter
- Using a long chain/ tape measure, stretch it across the river bed from one bank to
another
- Have someone to walk on the tape measure/ chain to make sure it’s on the river bed
- Read the measurement on the tape measure
- Repeat and calculate the average
- Record the result
How to measure longshore drift (rate)
- Measure a distance of 10m of the beach
- Mark the start and end point of the 10m distance
- Using a float (orange) and put it in the water at the start point
- Release the orange and start the timer
- When it reaches the end point, stop the timer
- Calculate the speed
+or
- Measure a distance of 10m of the beach
- Mark the start and end point of the 10m
- Using a float (orange) and put it in the water at the start point
- Release it and you will be able to observe the movement of longshore drift
Factors to consider for river fieldwork
- Accessibility/ is it a private area?
- Away from buildings
- Depth of river
- Safety - may have dangerous wild animals
Advantages of pilot survey
- Allow group to agree on what measurements to make
- Reduces error
- Allow students to experience working as a team
- Practice the fieldwork techniques
How to carry out traffic count fieldwork
- Get into groups/ pair at several different sites
- One student count the number of cars passing by by using a clicker
- Another student record the numbers
- Count for 30 minutes
- Make sure to synchronise start and finish time with other groups at different sites
+another situation (vehicles are characterised e.g number of lorries, cars, bus…)
- Get into groups at different sites
- Each student of the group is assigned to count a certain type of vehicle
- Another is in charge of recording the numbers
- Count for 30 minutes
- Make sure to synchronise start and finish time
You might also like
- AS 1530.2 (Test For Flamability of Materials)Document13 pagesAS 1530.2 (Test For Flamability of Materials)Ibrahim KNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document7 pagesUnit 4api-235865217No ratings yet
- CSS NCII 4rth Quarter Lesson Plan LO3 IsolateDocument2 pagesCSS NCII 4rth Quarter Lesson Plan LO3 IsolateJulius Baldelovar100% (5)
- 2010-2011 Head, Fischer and Elan Bindings Tech Manual From Tyrolia - Techn - Manual - ENDocument91 pages2010-2011 Head, Fischer and Elan Bindings Tech Manual From Tyrolia - Techn - Manual - ENemgyee100% (5)
- Airflow Quantity MeasurementsDocument16 pagesAirflow Quantity Measurementsadam fakhri100% (1)
- 4.2 Geographical Investigation AdditionalDocument24 pages4.2 Geographical Investigation AdditionalTheRealDanNo ratings yet
- Paper 4 Enquiry SkillsDocument40 pagesPaper 4 Enquiry SkillsYixuan JiangNo ratings yet
- Geo SbaDocument17 pagesGeo SbaFalon TomlinNo ratings yet
- GEOGRAPHY RESEARCHDocument26 pagesGEOGRAPHY RESEARCHMazvitaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Social Studies Summary PDFDocument25 pagesGrade 7 Social Studies Summary PDFShikeenga FillipusNo ratings yet
- 1,2,3,6Document4 pages1,2,3,6ريان الحربيNo ratings yet
- River MeasurementsDocument12 pagesRiver Measurementsmahika gaurNo ratings yet
- Paper 4 - Alternative To Coursework - The Geography Study SchoolDocument7 pagesPaper 4 - Alternative To Coursework - The Geography Study SchoolTanatswa TicharwaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Stream FlowDocument6 pagesWhat Is A Stream FlowRheymar Dela Rosa DiwaNo ratings yet
- Weather Unit - Lesson Five Weather ToolsDocument11 pagesWeather Unit - Lesson Five Weather Toolsapi-547152003No ratings yet
- River MeasurementsDocument9 pagesRiver MeasurementsMunir LakhaNo ratings yet
- Case StudiesDocument12 pagesCase StudiesAntara PandeNo ratings yet
- ABEn 145 - Tribunalo - Lab 4Document14 pagesABEn 145 - Tribunalo - Lab 4Jaylou OpondaNo ratings yet
- Navigational InstrumentsDocument2 pagesNavigational InstrumentsAriel MolinaNo ratings yet
- Lab 04Document3 pagesLab 04mekailpervaiz48No ratings yet
- FieldworkDocument28 pagesFieldworkRutendo GandidzanwaNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document9 pagesLab 6ArjayDimapilisNo ratings yet
- Measurements of Water QualityDocument3 pagesMeasurements of Water QualityFuad AhmedinNo ratings yet
- Obinna Geo 5Document48 pagesObinna Geo 5Obinna RichardNo ratings yet
- 20 Hydrometreological Instruments: Prepared By: Kenjie N. Dela CruzDocument41 pages20 Hydrometreological Instruments: Prepared By: Kenjie N. Dela CruzDela Cruz Kenjie N.No ratings yet
- Flow and Cross SectionDocument14 pagesFlow and Cross SectionfrancishozeguevaraNo ratings yet
- Hydrographic Surveys: Lesson 34Document14 pagesHydrographic Surveys: Lesson 34Ma Danica LagacNo ratings yet
- No. Sense Observations Qualitative Quantitative: Fill Up The Table BelowDocument23 pagesNo. Sense Observations Qualitative Quantitative: Fill Up The Table BelowUmmu Umar Wa AisyahNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Doppler Current ProfilerDocument20 pagesAcoustic Doppler Current Profilerashish chauhanNo ratings yet
- The Weather StationDocument13 pagesThe Weather StationgeorgemaposaNo ratings yet
- Hydrometeorological InstrumentsDocument7 pagesHydrometeorological InstrumentsVerra Myza Arat0% (1)
- Lecture 5 - HeightsDocument25 pagesLecture 5 - HeightsMeshai RanchodNo ratings yet
- SNI 7963-2014 Tide Gauge ObservationDocument19 pagesSNI 7963-2014 Tide Gauge Observationseirac.1782No ratings yet
- Stream GaugingDocument13 pagesStream GaugingMomin arNo ratings yet
- Flow Visualisation Using Water Flow Channel AimDocument6 pagesFlow Visualisation Using Water Flow Channel AimesakkimuthuNo ratings yet
- Hydrometeorological InstrumentsDocument4 pagesHydrometeorological InstrumentsAnne WabanNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Lab ManualDocument16 pagesHydrology Lab ManualAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Coasts Practicals Paper 4Document8 pagesCoasts Practicals Paper 4gavazamary1No ratings yet
- Instrumentation For Ocean ApplicationDocument22 pagesInstrumentation For Ocean ApplicationRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- DischargeDocument20 pagesDischargeanish.bhandariNo ratings yet
- Cec 102 Practical - Introductory HydrologyDocument25 pagesCec 102 Practical - Introductory HydrologyVietHungCao100% (3)
- Measuring and Recording Weather PT 3Document7 pagesMeasuring and Recording Weather PT 3zoeNo ratings yet
- btech7th-CE-WRE LAB (3) - 1Document20 pagesbtech7th-CE-WRE LAB (3) - 1sarojkrmahuwanNo ratings yet
- Windexploration CCDocument16 pagesWindexploration CCapi-340145996No ratings yet
- Economics A Level NotesDocument20 pagesEconomics A Level NotesFatima ZiaNo ratings yet
- Field Work 5Document18 pagesField Work 5Danica Alejo100% (1)
- PROJECT Hydraulic UTHMDocument13 pagesPROJECT Hydraulic UTHMNik Aliff100% (1)
- Beach Profile MethodDocument3 pagesBeach Profile MethodNatarajan MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- Wa0032Document53 pagesWa0032Gerald EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- What Makes Weather Lesson Plan FinalDocument6 pagesWhat Makes Weather Lesson Plan Finalapi-507180911No ratings yet
- The River Channel Alternative To Practical 1Document11 pagesThe River Channel Alternative To Practical 1nicole matsikaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Hannah Wynzelle AbanNo ratings yet
- Coastal ProjectDocument24 pagesCoastal ProjectChris BramaoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Report 2Document23 pagesAssignment Report 2DiegoNo ratings yet
- Weather InstrumentsDocument12 pagesWeather InstrumentsMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Method and Equipment (Longkang)Document6 pagesMethod and Equipment (Longkang)rozaidiabdulrahimNo ratings yet
- Measuring Flow RateDocument1 pageMeasuring Flow RateRaymond KatabaziNo ratings yet
- Velocity Distribution by Current MetreDocument4 pagesVelocity Distribution by Current MetreAashu AnshNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate Atmosphere: "For I Can Do All Things Through Christ Who Gives Me Strength", Phillipians 4:13Document41 pagesWeather and Climate Atmosphere: "For I Can Do All Things Through Christ Who Gives Me Strength", Phillipians 4:13Michael MunyangiNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere Wheather FlyingDocument27 pagesAtmosphere Wheather FlyingRAMA ALFI MUHARAM 181011087No ratings yet
- FWDocument6 pagesFWrychellelaoNo ratings yet
- Navigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsFrom EverandNavigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsNo ratings yet
- 29 GIS SeismicDocument6 pages29 GIS SeismicKhader Abu-daggaNo ratings yet
- P Spice TutorialDocument9 pagesP Spice TutorialPeiHanTseringNo ratings yet
- Lect 10 PDFDocument16 pagesLect 10 PDFshoaib_mohammed_28No ratings yet
- Operation Manual - Amann ASC100Document142 pagesOperation Manual - Amann ASC100David Apaza Hurtado100% (4)
- PCC41NG2 Series Component Cleanliness Cabinet: FeaturesDocument2 pagesPCC41NG2 Series Component Cleanliness Cabinet: FeaturesSamNo ratings yet
- Value Chain AnalysisDocument18 pagesValue Chain AnalysisjainsonaNo ratings yet
- Aphex - Aural - Exciter Type B and CDocument6 pagesAphex - Aural - Exciter Type B and CRichard PowersNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Procedure To Run A Program On FPGA BoardDocument11 pagesStep by Step Procedure To Run A Program On FPGA BoardAdiseshuMiddeNo ratings yet
- Bibliography For AntennasDocument16 pagesBibliography For AntennasFrancisco ArrudaNo ratings yet
- Analisis Pencatatan Dan Penilaian Persediaan Pada Pt. Sumber Mutiara PrimaDocument12 pagesAnalisis Pencatatan Dan Penilaian Persediaan Pada Pt. Sumber Mutiara PrimaferferferferinNo ratings yet
- Basic Vibration Analysis Condition MonitoringDocument5 pagesBasic Vibration Analysis Condition MonitoringMohamed Nawar50% (2)
- Refer DXF or DWG File For Laser Cutting. 2. Part Inspection Is On Finished DimensionDocument1 pageRefer DXF or DWG File For Laser Cutting. 2. Part Inspection Is On Finished DimensionBala MuruganNo ratings yet
- Ices Indian Universities InstitutionsDocument3 pagesIces Indian Universities InstitutionsOperationNo ratings yet
- Alpha1 Series PC Communication Protocol561785 PDFDocument1 pageAlpha1 Series PC Communication Protocol561785 PDFpancawawanNo ratings yet
- Tradesman - Sheet metal-TEDDocument5 pagesTradesman - Sheet metal-TEDDeekshith DileepNo ratings yet
- 2nd Revised Application Form For DPWH MeDocument2 pages2nd Revised Application Form For DPWH MeKagare KageNo ratings yet
- Advanced Training Institute, DGT, MSDE, Mumbai - MCQ Test 4 - POT / ETDocument4 pagesAdvanced Training Institute, DGT, MSDE, Mumbai - MCQ Test 4 - POT / ETpriyanka lariyaNo ratings yet
- 700 Series Rubber Seated Butterfly Valves: Features and BenefitsDocument2 pages700 Series Rubber Seated Butterfly Valves: Features and BenefitsqcselvaNo ratings yet
- Equations: Hvac Equations, Data, and Rules of ThumbDocument21 pagesEquations: Hvac Equations, Data, and Rules of ThumbzodedNo ratings yet
- Surface Catenary Interventions PsDocument2 pagesSurface Catenary Interventions Psditer najarNo ratings yet
- Pages From Siemens Tcpip EthernetDocument1 pagePages From Siemens Tcpip EthernettinhmdcNo ratings yet
- "Greater Baku Regional Development Plan" (GBRDP) ProjectDocument114 pages"Greater Baku Regional Development Plan" (GBRDP) ProjectRyan French100% (2)
- 50 Top Design of Masonry Structures Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pages50 Top Design of Masonry Structures Multiple Choice Questionssaikiran1493No ratings yet
- NDT Radiation SafetyDocument33 pagesNDT Radiation SafetyRamakrishnan AmbiSubbiahNo ratings yet
- Irc Gov in SP 090 2010 PDFDocument92 pagesIrc Gov in SP 090 2010 PDFSubramanian ArulNo ratings yet
- Material HandlingDocument26 pagesMaterial HandlingRohit AroraNo ratings yet
- Exp-8 Staircase WiringDocument3 pagesExp-8 Staircase WiringUjjwal GargNo ratings yet