Professional Documents
Culture Documents
As A Network Engineer Must Learn These Protocols
As A Network Engineer Must Learn These Protocols
Uploaded by
Anil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesOriginal Title
As a Network Engineer Must Learn These Protocols
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesAs A Network Engineer Must Learn These Protocols
As A Network Engineer Must Learn These Protocols
Uploaded by
AnilCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
As a Network Engineer Must Learn These Protocols.
Some Important protocols to ensure efficient and reliable communication for enterprise
Companies:
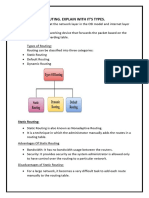
● Routing Protocols
1. BGP (Border Gateway Protocol)
- Used for routing between different autonomous systems, particularly in connecting to
the internet.
2. OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
- An internal gateway protocol used for routing within a single autonomous system.
3. EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
- Cisco proprietary protocol used for efficient and scalable routing within an enterprise.
4. IS-IS (Intermediate System to Intermediate System)
- Used in large service provider networks and sometimes in large enterprise networks
for internal routing.
5. RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
- An older protocol used in small to medium-sized networks, less common in large
enterprises.
● Switching Protocols
1. STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)
- Prevents loops in network topologies by creating a spanning tree that spans all
switches in a network.
2. RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol)
- An enhancement of STP that provides faster convergence.
3. MSTP (Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol)
- Allows multiple VLANs to be mapped to a single spanning tree instance.
4. VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol)
- Manages VLAN configuration across multiple switches.
5. LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol)
- Combines multiple physical links into a single logical link for redundancy and
increased throughput.
6. LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol)
- Used for network devices to advertise their identity and capabilities on a local network.
● Additional Protocols
1. VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol)
- Provides high availability by ensuring that a backup router takes over if the primary
router fails.
2. HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol)
- Cisco's proprietary version of VRRP.
3. IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
- Manages multicast group memberships in IPv4 networks.
4. PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast)
- Used for routing multicast traffic.
● Security Protocols
1. IPSec (Internet Protocol Security)
- Used for securing IP communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet.
2. SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security)
- Provides encrypted communication over the network.
3. 802.1X
- Provides network access control based on authentication.
● Quality of Service (QoS) Protocols
1. DiffServ (Differentiated Services)
- A protocol for specifying and controlling network traffic by class so that certain types
of traffic get precedence.
2. MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
- Directs data from one network node to the next based on short path labels rather than
long network addresses.
These protocols work together to ensure efficient, reliable, and secure network
communication within a large enterprise.
You might also like
- TM 11398Document592 pagesTM 11398krill.copco50% (2)
- Cisco Ccna Flash CardsDocument61 pagesCisco Ccna Flash CardsRemiMoncayoNo ratings yet
- What Is RAID Control PDFDocument6 pagesWhat Is RAID Control PDFAhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Work, Energy and PowerDocument12 pagesChapter 6 Work, Energy and PowerZhu Jiankun100% (1)
- VLANsDocument15 pagesVLANsRafia ShoukatNo ratings yet
- Routing Protocols Explained: PrefaceDocument3 pagesRouting Protocols Explained: PrefaceSai RamNo ratings yet
- Ass SawaibahDocument10 pagesAss Sawaibah70131348No ratings yet
- HPE MSR900 Series Router PerformanceDocument16 pagesHPE MSR900 Series Router PerformanceRobertoRubioNo ratings yet
- RomperDocument8 pagesRomperÁngelLópezNo ratings yet
- Network Routing Protocols Back To Basics SSDocument8 pagesNetwork Routing Protocols Back To Basics SSGhayas AliNo ratings yet
- Minor Project Report-OSPF ChampDocument5 pagesMinor Project Report-OSPF Champsmrutiranjan1991100% (1)
- A Detail Qualitative Performance Evaluation of Integrated EIGRP/IS-IS and RIP/IS-IS Routing Protocols in Hybrid NetworksDocument90 pagesA Detail Qualitative Performance Evaluation of Integrated EIGRP/IS-IS and RIP/IS-IS Routing Protocols in Hybrid NetworksNancyNo ratings yet
- HPE Networking Comware Router Series MSR2000-c04123120Document21 pagesHPE Networking Comware Router Series MSR2000-c04123120R HastomoNo ratings yet
- Hpe Flexnetwork msr950 Router Series JDocument16 pagesHpe Flexnetwork msr950 Router Series Jodalrich78No ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document5 pagesCase Study 1Marlo CondeNo ratings yet
- Powered by D-Link Rg-S5750e Series Security and Multi-Services Switch Da...Document21 pagesPowered by D-Link Rg-S5750e Series Security and Multi-Services Switch Da...Kapil SinghNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Routing: Agus SetiawanDocument39 pagesDynamic Routing: Agus SetiawanRandi AfrianNo ratings yet
- AMEYODocument8 pagesAMEYOYashi GuptaNo ratings yet
- ND_Assignment2_Roshan Kumar ThapaDocument6 pagesND_Assignment2_Roshan Kumar Thapasw.dvbimalNo ratings yet
- Routing Questions-Part-IDocument7 pagesRouting Questions-Part-Isumai BagwanNo ratings yet
- Ass 4 FatimaDocument13 pagesAss 4 Fatima70131348No ratings yet
- WWW h3c Com PDFDocument5 pagesWWW h3c Com PDFJamez STNo ratings yet
- Etti - RST IV - Sem.I - Rezolvari - RSDocument25 pagesEtti - RST IV - Sem.I - Rezolvari - RSbeiculescugeorgeNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Routing Protocols Based On Performance: Ms. Pallavi R, Tanviaggarwal, Ullas GuptaDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Routing Protocols Based On Performance: Ms. Pallavi R, Tanviaggarwal, Ullas GuptaInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- What Is Routing. Explain With It'S TypesDocument9 pagesWhat Is Routing. Explain With It'S TypesChaitra kharviNo ratings yet
- ART Assignment FinalDocument5 pagesART Assignment FinalABU ANAS SIDDIKNo ratings yet
- Protocols Governing WebDocument5 pagesProtocols Governing WebRicha Tekriwal100% (1)
- Basics NetworkingDocument2 pagesBasics NetworkingSesmaNo ratings yet
- 151x CCNA 2 EJW Rev3e CH 6 AnswersDocument17 pages151x CCNA 2 EJW Rev3e CH 6 Answersapi-3842231100% (3)
- Graduation Project - FinalpreDocument34 pagesGraduation Project - FinalprePhương ThảoNo ratings yet
- Ccna QuestionsDocument7 pagesCcna QuestionsMadan Mohan KannojiyaNo ratings yet
- NWK 507 Q AnswersDocument16 pagesNWK 507 Q AnswersBhupendra ThapaNo ratings yet
- Routing ProtocolsDocument3 pagesRouting ProtocolsUmutoni VanessaNo ratings yet
- CCNA InterviewDocument8 pagesCCNA InterviewAli MerajNo ratings yet
- Ответы Unit 1. Lesson 5. Static vs dynamic rDocument3 pagesОтветы Unit 1. Lesson 5. Static vs dynamic rМакс КальмусNo ratings yet
- Dynamic RoutingDocument14 pagesDynamic RoutingRattlexnake666No ratings yet
- Dum It Rache 2017Document6 pagesDum It Rache 2017MAwais QarniNo ratings yet
- Explain OSPF in Detail?Document4 pagesExplain OSPF in Detail?mystuff stuffNo ratings yet
- Networking Plus 2005 Notes 1. Standard TopologiesDocument10 pagesNetworking Plus 2005 Notes 1. Standard TopologieseyenstynNo ratings yet
- Routing RoutedDocument32 pagesRouting RoutedMangesh KakadeNo ratings yet
- Ethernet SOMEip and POSIX 1693270550Document7 pagesEthernet SOMEip and POSIX 1693270550toanfetNo ratings yet
- (Document Title) : DECEMBER 31, 2021 Submitted To Dr. Sosina MengistuDocument9 pages(Document Title) : DECEMBER 31, 2021 Submitted To Dr. Sosina MengistuMihret BerheNo ratings yet
- Isaaa Review 2Document25 pagesIsaaa Review 2Azisz PaudelNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 of CNDocument31 pagesAssignment 3 of CNHira WaheedNo ratings yet
- What Is IP RoutingDocument1 pageWhat Is IP RoutingChaminda ICTCNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Lesson 5. Static Vs Dynamic Routing, ProtocolsDocument9 pagesUnit 1. Lesson 5. Static Vs Dynamic Routing, ProtocolsМакс КальмусNo ratings yet
- Assignment NetworkDocument7 pagesAssignment Networkangelanemes5No ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument8 pagesTCP IpGauravNo ratings yet
- IP Overview PDFDocument4 pagesIP Overview PDFruletriplexNo ratings yet
- Common Metric: The OneDocument27 pagesCommon Metric: The OneABHISHEK KUMAR SAHNo ratings yet
- InterviewDocument27 pagesInterviewJomelyne MangarinNo ratings yet
- HPE FlexNetwork MSR95x Router Series PDFDocument25 pagesHPE FlexNetwork MSR95x Router Series PDFNakpane SonhayeNo ratings yet
- Network+ 2009 Odds and EndsDocument4 pagesNetwork+ 2009 Odds and EndsdarkpageyNo ratings yet
- Cis701 ExamDocument17 pagesCis701 ExamfadedsimplicityNo ratings yet
- Computer-Network-Cheetsheet 2Document18 pagesComputer-Network-Cheetsheet 2Nguyễn Ngọc PhụngNo ratings yet
- 03 Introduction To Dynamic Routing ProtocolsDocument13 pages03 Introduction To Dynamic Routing Protocolshuda1989No ratings yet
- Ip Multicast OverviewDocument6 pagesIp Multicast OverviewwoodksdNo ratings yet
- Imp QuestionsDocument10 pagesImp QuestionsraveendraNo ratings yet
- CCNA 3 Study Guide Answers-AllDocument33 pagesCCNA 3 Study Guide Answers-AllgeertvdhNo ratings yet
- Viva PracticeDocument8 pagesViva PracticeQuad TurboNo ratings yet
- Mec R2018Document227 pagesMec R2018Kishore Kumar RNo ratings yet
- AbseilingDocument12 pagesAbseilingMurah Rezeki Cikgu WafiNo ratings yet
- 02 - D03 - Basic Funtion of SIPROTEC 5Document7 pages02 - D03 - Basic Funtion of SIPROTEC 5DianaNo ratings yet
- Surveillance, Torture and Contr - Rosanne Marie SchneiderDocument135 pagesSurveillance, Torture and Contr - Rosanne Marie SchneiderMagic MikeNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification: 1) Filter Feed Pump With Motor 1 NosDocument4 pagesTechnical Specification: 1) Filter Feed Pump With Motor 1 NosKamatchi NathanNo ratings yet
- Exercise # 1: Statistics and ProbabilityDocument6 pagesExercise # 1: Statistics and ProbabilityAszyla ArzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Practice TestDocument19 pagesChapter 20 Practice TestCorei'Ana Conrad0% (1)
- HT Billing System - May'2022Document2 pagesHT Billing System - May'2022V.Sampath RaoNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Audit Into The Success Rate of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block Analgesia in General Dental PracticeDocument4 pagesA Clinical Audit Into The Success Rate of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block Analgesia in General Dental PracticeGina CastilloNo ratings yet
- CD Dye RD0005Document7 pagesCD Dye RD0005Juan CarlosNo ratings yet
- Gear Trains: 8.1. Angular Velocity RatioDocument16 pagesGear Trains: 8.1. Angular Velocity RatioaddisudagneNo ratings yet
- Hillfoot Data Sheets V5 1Document4 pagesHillfoot Data Sheets V5 1Kristijan IlicNo ratings yet
- ASTM GradesDocument4 pagesASTM GradesSaurabh MundheNo ratings yet
- Ignatian SpiritualityDocument16 pagesIgnatian SpiritualityMihai Frentz100% (2)
- Industrial RoboticsDocument77 pagesIndustrial RoboticsIslam Fouad100% (4)
- Relative Color Pickup of Three Different Knits and Predictive Dyeing Recipe FormulationDocument17 pagesRelative Color Pickup of Three Different Knits and Predictive Dyeing Recipe FormulationNguyễn Huy CườngNo ratings yet
- 6 Landforms - SCIENCEDocument9 pages6 Landforms - SCIENCEArianne RealNo ratings yet
- Snag SummmariesDocument171 pagesSnag Summmarieslaltu adgiriNo ratings yet
- 12 2f17 Vegetarian Argumentative EssayDocument7 pages12 2f17 Vegetarian Argumentative Essayapi-413258549No ratings yet
- Model 621 LR B Data SheetDocument1 pageModel 621 LR B Data SheetMohammed GallowNo ratings yet
- Understanding Your Electricity Bill in PakistanDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Your Electricity Bill in PakistanGhayas Ud-din DarNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Diet Manual: DIRECTIVE #4311Document27 pagesTherapeutic Diet Manual: DIRECTIVE #4311DuNo ratings yet
- UVU Jungle Marathon 2012 BookDocument41 pagesUVU Jungle Marathon 2012 BookGerhard FlatzNo ratings yet
- Md. Rizwanur Rahman - CVDocument4 pagesMd. Rizwanur Rahman - CVHimelNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0264127522004105 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0264127522004105 MainAsimov RiyazNo ratings yet
- LAB 2 - Running Speed (Method 2) OEL 1Document3 pagesLAB 2 - Running Speed (Method 2) OEL 1ZULFAQAR BIN MOHAMMAD NIZAMNo ratings yet
- Low Noise Amplifier Basics: by V. M. García-ChocanoDocument4 pagesLow Noise Amplifier Basics: by V. M. García-ChocanoPranjal Jalan100% (1)