Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Original 1
Original 1
Uploaded by
raptorosaurusrexfanclub0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesHi another paper for you
Original Title
original-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHi another paper for you
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal 1
Original 1
Uploaded by
raptorosaurusrexfanclubHi another paper for you
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
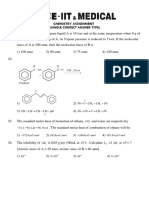
PRACTICE TEST
Test No. : 34 Duration : 30 min M.M. : 60 Batch : XII
TOPICS COVERED
CHEMISTRY
Electrolysis
Choose the correct () answer:
1. The electric charge required for electrode deposition of 6. If 0.50 L of a 0.60 M SnSO4 solution is electrolyzed
one gram-equivalent of a substance is for a period of 30.0 min using a current of 9.65 A. If
inert electrodes are used, what is the final
(1) One ampere per second
concentration of Sn2+ remaining in the solution?
(2) 96500 coulombs per second
[Atomic wt. of Sn = 119]
(3) One ampere for one hour
(1) 0.32 M (2) 0.42 M
(4) Charge on one mole of electrons
(3) 0.542 M (4) 0.18 M
2. The amount of an ion liberated on an electrode during
7. In the electrolysis of aqueous NaCl, what volume of
electrolysis does not depend upon
Cl2(g) is produced in the time that it takes to liberate
(1) Conductance of the solution 5.0 liter of H 2(g)? Assume that both gases are
(2) Current strength measured at STP.
(3) Time (1) 5.0 (2) 2.50
(4) Electrochemical equivalent of the element (3) 7.50 (4) 10.0
3. Electrolysis can be used to determine atomic masses. 8. In the electrolysis of a CuSO4 solution, how many
A current of 0.550 A deposits 0.55 g of a certain metal grams of Cu are deposited on the cathode in the time
in 100 minutes. Calculate the atomic mass of the metal that it takes to liberate 5.6 litre of O2(g), measured at
if equivalent wt. = molecular wt./3 1 atm and 273 K at the anode?
(1) 100 (1) 31.75
(2) 45.0 (2) 14.2
(3) 48.25 (3) 4.32
(4) 144.75 (4) 63.5
4. Beryllium occurs naturally in the form of beryl. The 9. The function of a salt bridge is to
metal is produced from its ore by electrolysis after the (1) Maintain electrical neutrality of both half cells
ore has been converted to the oxide and then to the
chloride. How many grams of Be(s) is deposited from (2) Increase the cell potential at the positive electrode
a BeCl2 solution by a current of 5.0 A that flows for (3) Decrease the cell potential at the negative
1.0 h? (atomic weight : Be = 9) electrode
(1) 0.840 (2) 1.68 (4) Eliminate the impurities present in the electrolyte
(3) 1.42 (4) 1.08 10. Electrolytic conduction is due to the movement of
5. Total charge required for the oxidation of two moles (1) Electrons
Mn3O4 into MnO24 in presence of alkaline medium is (2) Ions
(1) 5 F (2) 10 F (3) Atoms
(3) 20 F (4) 26 F (4) Electrons as well as ions
2 XII-S/Chem-34/2020-21/XXI-VII-20
11. Resistance of a decimolar solution between two
electrodes 0.02 meter apart and 0.0004 m2 in area was 13.
AgCl can be obtained
found to be 50 ohm. Specific conductance ( ) is
(1) By extraplotation of the graph and C to zero
(1) 25 S cm–1 concentration
(2) 1 S cm–1
(2) By known values of of AgNO3, HCl and HNO3
(3) 100 S cm–1 (3) Both (1) and (2)
(4) 0.01 S cm–1 (4) None of these
14. The conductivity of a strong electrolyte
12. Ionisation constant of a weak acid (HA) in terms of m (1) Increases rapidly on dilution
and m is (2) Increases slightly on dilution
(3) Does not change with dilution
2
cm cm (4) Decreases on dilution
(1) K a (2) K a
( m ) m ( m m ) 15. Molar conductance of Ba(NO3)2, KCl and KNO3 are
x, y and z respectively at infinite dilution. Molar
2 2
conductance of BaCl2 at infinite dilution is
c( m ) cm
(3) K a (4) K a 2
(1) x + y – z (2) x + 2y – z
m ( m m ) ( m )
x
(3) x + 2y – 2z (4) yz
2
You might also like
- Airline Cabin Crew Training IATA Training Course PDFDocument3 pagesAirline Cabin Crew Training IATA Training Course PDFwin computer0% (1)
- Boxing Tactics of Foreign MastersDocument4 pagesBoxing Tactics of Foreign Mastersirishmike12345100% (2)
- 324 (High Court) Muhammas SaifDocument17 pages324 (High Court) Muhammas SaifHiskeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ElectrochemistryDocument18 pagesWorksheet Electrochemistryyatan kapoorNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024Document5 pagesElectrochemistry - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024anshulNo ratings yet
- NTSE - SAT Sample PaperDocument4 pagesNTSE - SAT Sample Papersneha sharmaNo ratings yet
- Incoming SR - Iit - (Mains - Model) - 5-05-05-2024 - Q. Paper & KeyDocument17 pagesIncoming SR - Iit - (Mains - Model) - 5-05-05-2024 - Q. Paper & Keymaheshlight3213No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - (Single Type) QDocument6 pagesElectrochemistry - (Single Type) QRupesh Kumar ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- CT 1Document7 pagesCT 1anushreej078No ratings yet
- Electro ChemistryDocument14 pagesElectro ChemistryABHIIEET WAGHMARENo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Assignment - Ankit Sir - D9tiDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry Assignment - Ankit Sir - D9timythirdacc0401No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - DPP 09 (Of Lec 11) - Lakshya JEE 2024Document3 pagesElectrochemistry - DPP 09 (Of Lec 11) - Lakshya JEE 20244ourballsNo ratings yet
- MCQ Test ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesMCQ Test Electrochemistryyatan kapoorNo ratings yet
- 4-Poll ChemistryDocument2 pages4-Poll Chemistryprathikmstar55No ratings yet
- XII Chemistry Chapter Test 3 ElectrochemistryDocument4 pagesXII Chemistry Chapter Test 3 ElectrochemistryVishwaaNo ratings yet
- Xicbse Electrochemistry Ass 2 QPDocument3 pagesXicbse Electrochemistry Ass 2 QPtanishkakannan3253No ratings yet
- Practice Test 02 - Test Paper (Chemistry) - Lakshya JEE 2024Document3 pagesPractice Test 02 - Test Paper (Chemistry) - Lakshya JEE 2024Krish bansalNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument6 pagesElectrochemistryShlok BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Assignment CBSE 2020Document4 pagesElectrochemistry Assignment CBSE 2020mitsuhaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Uti Module 3Document8 pagesElectrochemistry Uti Module 3arunarajeshwaryNo ratings yet
- Dpps ElectroDocument14 pagesDpps ElectroVanshika MiglaniNo ratings yet
- Plus Two ElectrochemistryDocument1 pagePlus Two ElectrochemistryAbhijithNo ratings yet
- BITSAT Chemistry SET 1Document8 pagesBITSAT Chemistry SET 1Sara MannNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument7 pagesChemistry AssignmentYASH GOSAVINo ratings yet
- 27 March Electro ChemDocument16 pages27 March Electro ChemManas JainNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument11 pagesElectrochemistrysaranya ganesanNo ratings yet
- Xi Centre Che 18.03.24Document16 pagesXi Centre Che 18.03.24pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Toppers Neet Practice Sheet-05Document6 pagesToppers Neet Practice Sheet-05RussNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry & Atomic Structure, Power TestDocument3 pagesStoichiometry & Atomic Structure, Power TestulluchutiyaNo ratings yet
- 11th ND 12th - 1714104498666Document18 pages11th ND 12th - 1714104498666gamer8281929No ratings yet
- Chemistry: NTSE Stage I - 2015 Worksheet - 01 Nature of Matter, Atoms and Its Behavior and RadioactivityDocument3 pagesChemistry: NTSE Stage I - 2015 Worksheet - 01 Nature of Matter, Atoms and Its Behavior and RadioactivityNitishNo ratings yet
- Jitendra Hirwani: Problem Solving Techniques of Physical Chemistry For NeetDocument19 pagesJitendra Hirwani: Problem Solving Techniques of Physical Chemistry For NeetabhishekNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 04 PDFDocument1 page12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 04 PDFShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Cet - 03 03 2024Document34 pagesCet - 03 03 2024sknoushad126No ratings yet
- Allen NTSE Statewise Sample Paper With Solution-34Document6 pagesAllen NTSE Statewise Sample Paper With Solution-34ASDFNo ratings yet
- AITS Practice Paper (Chemistry) - Dropper NEETDocument4 pagesAITS Practice Paper (Chemistry) - Dropper NEETsharvilchaturvedi52No ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument17 pagesElectrochemistryzohaibsalamNo ratings yet
- 01 JEEMains 1Document3 pages01 JEEMains 1Aditya GoyalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (SPP) - 1: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument12 pagesChemistry (SPP) - 1: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryBishnu Prasad JenaNo ratings yet
- 2.electrochemistry QB (2023-24)Document6 pages2.electrochemistry QB (2023-24)Shana Chandran 18083No ratings yet
- 2IIT1920 (IIT Camp) (Main) CWS01 (Atomic Structure, Periodic Properties and Chemical Bonding) (SAG Mam) PDFDocument3 pages2IIT1920 (IIT Camp) (Main) CWS01 (Atomic Structure, Periodic Properties and Chemical Bonding) (SAG Mam) PDFvidhit dlNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Structure of Atom: NEET-11RT-1Document4 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Structure of Atom: NEET-11RT-1Jai 5.0No ratings yet
- Paper - Ii Chemical Sciences: Note: Attempt All The Questions. Each Question Carries Two (2) MarksDocument14 pagesPaper - Ii Chemical Sciences: Note: Attempt All The Questions. Each Question Carries Two (2) MarksashaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper: Ntse Stage - I (Delhi State) (2020 - 21) (For Class - X) Scholastic Aptitude TestDocument11 pagesQuestion Paper: Ntse Stage - I (Delhi State) (2020 - 21) (For Class - X) Scholastic Aptitude Testzenith view filmsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Assignment 25Document6 pagesChemistry Assignment 2518 BhavinNo ratings yet
- Topic: Electrochemistry: Neet/JeeDocument6 pagesTopic: Electrochemistry: Neet/Jeesumitkachare6No ratings yet
- 2 - Che - 29-08-22 - N.S - N.cum.t-05 - Mouli Sir - eDocument5 pages2 - Che - 29-08-22 - N.S - N.cum.t-05 - Mouli Sir - eAnonymous A6Jnef04No ratings yet
- KCET2011 Chemistry AnswerkeyDocument12 pagesKCET2011 Chemistry AnswerkeyLokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- SSLC Pre Model Examination - 2023: ChemistryDocument2 pagesSSLC Pre Model Examination - 2023: ChemistryhadiyxxNo ratings yet
- BHU ch2011Document15 pagesBHU ch2011LORD RAVANNo ratings yet
- Year Test - Ii: (Batch - A)Document11 pagesYear Test - Ii: (Batch - A)sachin sakuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Cet-11Document2 pagesChemistry Cet-11VenomNo ratings yet
- CT 2Document7 pagesCT 2anushreej078No ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument5 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYsarahNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry FDocument8 pagesElectrochemistry FAshwin Balaji100% (1)
- Mole, Atomic Periodic, BondingDocument15 pagesMole, Atomic Periodic, Bondingfa1075900No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Past Papers 2022-14Document4 pagesElectrochemistry Past Papers 2022-1410 A Pratyush Dubey0% (1)
- ATOMS - Practice Sheet & Solution - Vijeta 2023Document5 pagesATOMS - Practice Sheet & Solution - Vijeta 2023siyaNo ratings yet
- G11 - Third Term Examination (2015)Document12 pagesG11 - Third Term Examination (2015)Xiao ShadowlordNo ratings yet
- Test Series: Test - 16: PhysicsDocument20 pagesTest Series: Test - 16: PhysicsRajkumar JainNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Past Papers 2022-14Document4 pagesElectrochemistry Past Papers 2022-14Venugopal JujhavarappuNo ratings yet
- Endohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideFrom EverandEndohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideNo ratings yet
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesFrom EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNo ratings yet
- JournalsDocument9 pagesJournalsapi-302089675No ratings yet
- Adf11 7Document1,182 pagesAdf11 7Parashar ChinniNo ratings yet
- Management of Eclampsia by Nursing StaffDocument42 pagesManagement of Eclampsia by Nursing Staffمالك مناصرةNo ratings yet
- Izumi: Strong Hero 3 3Document3 pagesIzumi: Strong Hero 3 3cold juneNo ratings yet
- Letter MIX 02Document76 pagesLetter MIX 02Tanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- AirAsia India Fees and ChargesDocument1 pageAirAsia India Fees and ChargesIrfanNo ratings yet
- M I N D Mentalism in New Directions TwoDocument268 pagesM I N D Mentalism in New Directions TwoDherendra Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Ada Blackjack Answers (11-09-2021)Document4 pagesAda Blackjack Answers (11-09-2021)Blob BlobbyNo ratings yet
- Thematic Apperception Test: Administration and ScoringDocument15 pagesThematic Apperception Test: Administration and ScoringadcpdevilsNo ratings yet
- Converters: DC-to-DC and AC-to-ACDocument35 pagesConverters: DC-to-DC and AC-to-ACjck07100% (1)
- Real Solutions ProfileDocument12 pagesReal Solutions ProfileFahad MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Science-Grade 9 Learner Activity Sheets Quarter 1-Week 5: Biodiversity and Species Extinction First Edition, 2021Document10 pagesScience-Grade 9 Learner Activity Sheets Quarter 1-Week 5: Biodiversity and Species Extinction First Edition, 2021Ria Lalene S. TabamoNo ratings yet
- PushkalavatiDocument5 pagesPushkalavatiSana KhanNo ratings yet
- Design of A Material Handling Equipment: Belt Conveyor System For Crushed Limestone Using 3 Roll IdlersDocument10 pagesDesign of A Material Handling Equipment: Belt Conveyor System For Crushed Limestone Using 3 Roll IdlersJake OkuyeNo ratings yet
- Test 3 MаrlinsDocument2 pagesTest 3 MаrlinsStaicy ErmakovitchNo ratings yet
- Step by Wicked StepDocument4 pagesStep by Wicked Stepmyl0No ratings yet
- PWC Stock Based Compensation Second EditionDocument392 pagesPWC Stock Based Compensation Second EditionmzurzdcoNo ratings yet
- Oral Health ProgramDocument11 pagesOral Health Programapi-233877887No ratings yet
- Kalyan Sap BW Bi Bo 1Document7 pagesKalyan Sap BW Bi Bo 1jay_kay706348100% (1)
- 60 Free TB ActivitiesDocument11 pages60 Free TB ActivitiesochioreanuNo ratings yet
- Al QiyasDocument10 pagesAl QiyasBellaNo ratings yet
- Fishery Company Surabaya-SidoarjoDocument4 pagesFishery Company Surabaya-SidoarjoTigana OscarNo ratings yet
- R.C.C Project Upto Plinth Level: Abstract SheetDocument10 pagesR.C.C Project Upto Plinth Level: Abstract SheetVivÊk Síngh PâlNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle (Vehicle DTC Information) Document ID# 910473Document20 pagesDiagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle (Vehicle DTC Information) Document ID# 910473Carlos Alberto CruzNo ratings yet
- The Definite Integral and Its ApplicationsDocument13 pagesThe Definite Integral and Its Applicationsapi-312673653100% (1)
- 民用航空器维修人员执照英语等级测试参考试题(第二版)2024.5.13Document1,020 pages民用航空器维修人员执照英语等级测试参考试题(第二版)2024.5.13大雄弗里曼No ratings yet
- North Jersey Jewish Standard, April 17, 2015Document64 pagesNorth Jersey Jewish Standard, April 17, 2015New Jersey Jewish StandardNo ratings yet