Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Map Physiological Changes During Pregnancy
Map Physiological Changes During Pregnancy
Uploaded by
ScribdTranslationsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Map Physiological Changes During Pregnancy
Map Physiological Changes During Pregnancy
Uploaded by
ScribdTranslationsCopyright:
Available Formats
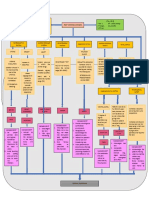
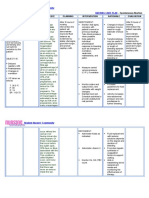
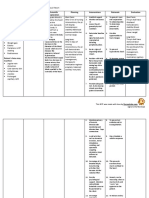
PHYSIOLOGICAL CHANGES
DURING PREGNANCY
RENIN ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM
BLOOD VOLUME PRES SANGUI HEART
AND PROSTAGLANDINS IN
WEIGHT INCREASE ALTERATIO SURE
ARTE NE PREGNANCY
IN PREGNANCY NS
CARDIOVASCULA RIAL
R
The increase in volume Increased intra-abdominal
The normal half blood volume arterial blood pressure Estrogen increases pressure displaces the heart
increase is 12.5kg blood maternal begins to increase decreases by 10-15 mmHg in renin substrate upward and rotates it
On of the represents one of the early pregnancy, systolic pressure and 20-25 synthesis and
important basics of forward; the
e
important reaches its peak at mmHg in diastolic. This caused
hyponatremia The
changes anteroposterior diameter
32 weeks and change has its maximum level by effect
components of and cardiothoracic ratio
pregnancy and produces maintains until reaching mid-pregnancy and natriureti of
Weight gain is the th increase reflecting the more
an increase in minute term . It increases returns to normal
e c horizontal position of the
expansion of the total volume and renal and approximately 1600ml approach the term the
progester stimula heart
aqueous mass of the uterine blood flow. as average in the one tes the
body normal single pregnancy angioten renin-
sin
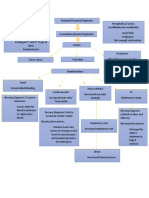
VENOUS PRESSURE PULMONARY VEMTILATION systemCAPACITY OF
ACID-BASE BALANCE
MINUTE VOLUME PHYSIOLOGY AND GASES
DIFFUSIO BLOODY
N
The venous pressure of the The increase in pressure The diffusion capacity from the Durin h pregna
The increase in volume upper extremities does not intra-abdominal causes Minute volume increases alveolus to the pulmonary g e ncy
intravascular produced change, there is an increase in alterations in cavity approximately 40% capillary depends on the arteri h PCO2
w i
during the pregnancy the pressure of the femoral thoracic, he diameter during pregnancy, from 7.5 to thickness of the membranes and al i
approximately o s
leads to a elevation vein
from 9 mm H2O to 10 cross increases 10.5 liters/min. There is no the flow.
blood pulmonary, decre s
mmHg compared r 3
of the minute volume. Most weeks up to 20 mm of approximately two increase in respiratory rate, capacity of t
ases;
to 40 mmHg in 0
N
of the increase occurs H2O at term, which is centimeters, widening of a although there is a substantial increase to the h 3
pregnant women o
during the first trimester, explains for the pressur the lower ribs occurs and th in pregnancy the diffusion
followed by a has a 5
with a peak at 20-24 weeks e
mechanics of the uterus on he
e decrease at 24-27beginning
weeks of
the iliac vein and the inferior costal angle increases from tidal volume. the
vena cava 68
URINARY SYSTEM
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM FUR
HEMATIC SYSTEM
The changes are due Starts with erythroid hyperplasia The increase of the
In the oral cavity the gums
to factors such as which manifests itself from the pigmentation is due to
they soften and we can
mechanical pressure exerted second half of pregnancy excessive deposit of
find gingivorrhagia. In
melanin in the basal layer
through the uterus in brings with it an increase in certain cases, there could be
and
growth, the environment mean corpuscular volume, and giving to present tialism
suprabasal, finding
hormonal and increase increased values of secondary to nausea.
figures of up to 46% in the
of renal blood flow reticulocytes
presence of melasma in
pregnant
You might also like
- Porsche 912E Service InformationDocument47 pagesPorsche 912E Service InformationOscar Hamer100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Spontaneous AbortionDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Spontaneous Abortionderic97% (36)
- NCP TbiDocument4 pagesNCP TbiWyen CabatbatNo ratings yet
- Hiatal Hernia FinalDocument7 pagesHiatal Hernia FinalbabiNo ratings yet
- Map Physiological Changes During PregnancyDocument1 pageMap Physiological Changes During PregnancyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram 2Document2 pagesSchematic Diagram 2NICHOLE MOJELLONo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Case ScenarioDocument5 pagesActivity 1 - Case ScenarioHannah CaseriaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Pregnancy 2ndDocument61 pagesPhysiology of Pregnancy 2ndLeo SSNo ratings yet
- (BatMC MedSurg) Palma - NCPDocument4 pages(BatMC MedSurg) Palma - NCPJann Reinna PALMANo ratings yet
- Mannitol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMannitol Drug StudyNo Vem BerNo ratings yet
- Systemic and Local ChangesDocument4 pagesSystemic and Local ChangesAristia ObeliaNo ratings yet
- NCM 109L NCP FormatDocument3 pagesNCM 109L NCP FormataaronjosephsilvaNo ratings yet
- BFMC Drug StudyDocument25 pagesBFMC Drug StudyJoshua Dumanjug SyNo ratings yet
- Eclampsia: Group 3Document21 pagesEclampsia: Group 3Trisha Mae MarquezNo ratings yet
- HHHHHDocument15 pagesHHHHHHamza JubranNo ratings yet
- PBL - Renal Git Neuro MuscuDocument3 pagesPBL - Renal Git Neuro Muscugie sarcedaNo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinnylix23No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionMurugham DineshNo ratings yet
- OXYTOCINDocument3 pagesOXYTOCINJaye Aprile Adrianne KuizonNo ratings yet
- FruitflowDocument9 pagesFruitflowDimas01003125No ratings yet
- Final Drug Study and Nursing Care For Cs Final Na GidDocument7 pagesFinal Drug Study and Nursing Care For Cs Final Na GidMor Shi DA BalutintikNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format 1Document3 pagesDrug Study Format 1Janeenne Fe Nicole SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco80% (5)
- Nejmra 1404726Document10 pagesNejmra 1404726Daniel LamNo ratings yet
- Vii. NCP and Case Study: Learn The DemonstrateDocument4 pagesVii. NCP and Case Study: Learn The DemonstrateVenus Glaze Verzola100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFrancis BelotindosNo ratings yet
- Altered Uteroplacental Tissue PerfusionDocument5 pagesAltered Uteroplacental Tissue PerfusionArielle BajalaNo ratings yet
- 14 Physio OB - Maternal Physiology IIDocument7 pages14 Physio OB - Maternal Physiology IINeil Vincent De AsisNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument2 pagesDrug Study ICUErryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Spontaneous AbortionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Spontaneous Abortionderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Spontaneous AbortionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Spontaneous AbortionAbigael Rubio de LeonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationer balotNo ratings yet
- 0 CardioDocument33 pages0 CardioOmar khalidNo ratings yet
- Readiness For Enhanced Health ManagementDocument6 pagesReadiness For Enhanced Health ManagementJIMENEZ, TRISHA MARIE D.No ratings yet
- In Gel Finger 2015Document10 pagesIn Gel Finger 2015Dumitrache VicentiuNo ratings yet
- Data Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesData Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationmarielfmerlanNo ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirDocument2 pagesNCP Liver CirBhabykhrishNo ratings yet
- Format, Drug StudyDocument23 pagesFormat, Drug StudyKrizzle Mae NeypesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan AbortionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Abortionnengsk84% (19)
- NCP HmoleDocument5 pagesNCP HmolemeriiNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output EclampsiasteffiNo ratings yet
- CT 11 - HPNDocument12 pagesCT 11 - HPNLycah RotoneNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SampleDocument2 pagesDrug Study SampleRoselle Oquiton FuertesNo ratings yet
- System 1st 2nd 3rd Reproductive System: Approximately 1 CM Longer On RadiographDocument2 pagesSystem 1st 2nd 3rd Reproductive System: Approximately 1 CM Longer On RadiographIncheon GalNo ratings yet
- Iloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing: West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo CityDocument2 pagesIloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing: West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo CityAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studychinchin ramosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyAysaaa DCNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Chronic Hypertension With Superimposed Preeclampsia (Obstetrical Complex)Document13 pagesCase Study of Chronic Hypertension With Superimposed Preeclampsia (Obstetrical Complex)Ivan Laurentine AceretNo ratings yet
- Final NCPDocument21 pagesFinal NCPkoringring100% (1)
- Abdominal Compartment Syndrome: Neil Berry Simon FletcherDocument8 pagesAbdominal Compartment Syndrome: Neil Berry Simon FletchernucaiceNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SengdocxDocument4 pagesDrug Study SengdocxMica OmotsosircNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TemplateDocument2 pagesDrug Study TemplateKistlerzane CABALLERONo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Application of Copper Sulfate in AquacultureDocument2 pagesApplication of Copper Sulfate in AquacultureScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Natural History of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument49 pagesNatural History of Parkinson's DiseaseScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Abbreviated File-Process Case 01 Marco A. and CounterclaimDocument25 pagesAbbreviated File-Process Case 01 Marco A. and CounterclaimScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Retirement Instructions Unemployment PorvenirDocument6 pagesRetirement Instructions Unemployment PorvenirScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter X. Precision Shooting From Naval Air PlatformsDocument24 pagesChapter X. Precision Shooting From Naval Air PlatformsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Tourist PlanningDocument39 pagesTourist PlanningScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Ethnicity, Language and IdentityDocument4 pagesEthnicity, Language and IdentityScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Project On Electricity For ChildrenDocument13 pagesProject On Electricity For ChildrenScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- History and Evolution of Reciprocating MotorsDocument32 pagesHistory and Evolution of Reciprocating MotorsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Comparative Table of Rationalism and EmpiricismDocument7 pagesComparative Table of Rationalism and EmpiricismScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS Mechanical Drawing 2Document7 pagesSYLLABUS Mechanical Drawing 2ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Musical Instruments of EuropeDocument3 pagesMusical Instruments of EuropeScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Sixth Grade Reading Comprehension AssessmentDocument8 pagesSixth Grade Reading Comprehension AssessmentScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Boxing PDFDocument49 pagesBoxing PDFScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension and Contextual Vocabulary Exercises 4th Middle #8.Document5 pagesReading Comprehension and Contextual Vocabulary Exercises 4th Middle #8.ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Practical Work The Familiar PDFDocument1 pagePractical Work The Familiar PDFScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade Plan - Block 4 GeographyDocument12 pages5th Grade Plan - Block 4 GeographyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- PH Portfolio Recovery ProposalDocument3 pagesPH Portfolio Recovery ProposalScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects GuatemalaDocument20 pagesLegal Aspects GuatemalaScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Applied StatisticsDocument209 pagesApplied StatisticsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- iTEP in - House PDFDocument12 pagesiTEP in - House PDFScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Types of Banks Based On OwnershipDocument2 pagesTypes of Banks Based On OwnershipScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Driver's Manual in TexasDocument109 pagesDriver's Manual in TexasScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Laboratory Report 1Document14 pagesChemistry Laboratory Report 1ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Expo22 Daily ExperienceDocument6 pagesExpo22 Daily ExperienceScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Application of Regulations in The Financial SystemDocument74 pagesApplication of Regulations in The Financial SystemScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Examples of Operant ConditioningDocument1 pageExamples of Operant ConditioningScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Security of Accounting Information SystemsDocument2 pagesSecurity of Accounting Information SystemsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Vibrational Sound Therapy ManualDocument12 pagesVibrational Sound Therapy ManualScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Event Security ProtocolDocument7 pagesEvent Security ProtocolScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- AlpsDocument4 pagesAlpsciohaniNo ratings yet
- Leica TM6100A Brochure enDocument6 pagesLeica TM6100A Brochure enCarlos CostaNo ratings yet
- Web Server Log Analysis SysytemDocument3 pagesWeb Server Log Analysis SysytemNexgen TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Probability in Everyday LifeDocument11 pagesProbability in Everyday LifeMwendalubi Chiholyonga0% (1)
- Maheka Ajitama 3.22.19.0.15 KE 2A Tugas Ke 1Document8 pagesMaheka Ajitama 3.22.19.0.15 KE 2A Tugas Ke 1Aji SuryoNo ratings yet
- SFC 332G: Dual Streams With Independent Products Can Be Measured, As Well AsDocument2 pagesSFC 332G: Dual Streams With Independent Products Can Be Measured, As Well AsadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Civil Lab ManualDocument17 pagesCivil Lab ManualShakil KhanNo ratings yet
- Lexus Toyota ManualDocument37 pagesLexus Toyota Manualjorge morillo100% (1)
- Shannon Boettcher SeminarDocument45 pagesShannon Boettcher SeminarUCSBieeNo ratings yet
- Geotech Chapter 4Document16 pagesGeotech Chapter 4Casao JonroeNo ratings yet
- The Node - Js HandbookDocument189 pagesThe Node - Js Handbookmel GobanNo ratings yet
- Ligatures Nov19Document13 pagesLigatures Nov19mntoaderNo ratings yet
- Heat PinchDocument6 pagesHeat PinchYeeXuan TenNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 44Document5 pagesChapter - 44tito cuadrosNo ratings yet
- How Can Theory-Based Evaluation Make Greater HeadwayDocument25 pagesHow Can Theory-Based Evaluation Make Greater HeadwayRuby GarciaNo ratings yet
- ISMC 2016 Primary 5 Answer SheetDocument2 pagesISMC 2016 Primary 5 Answer SheetAileen MimeryNo ratings yet
- Automotive Sumative TestDocument5 pagesAutomotive Sumative TestRAndy rodelas100% (2)
- Template Laporan DEDDocument2 pagesTemplate Laporan DEDaminNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Official Course: Implementing Active Directory Domain Services Sites and ReplicationDocument31 pagesMicrosoft Official Course: Implementing Active Directory Domain Services Sites and ReplicationasegunloluNo ratings yet
- 22 Bollinger Band RulesDocument4 pages22 Bollinger Band Rulesravee100% (2)
- 6 Relational Database DesignDocument9 pages6 Relational Database DesignAmrit BabuNo ratings yet
- Team Member Application Team Member Application Team Member Application Team Member ApplicationDocument35 pagesTeam Member Application Team Member Application Team Member Application Team Member ApplicationAnanth Nag PusalaNo ratings yet
- Muzon Pabahay Elementary SchoolDocument3 pagesMuzon Pabahay Elementary SchoolCristeta ToqueroNo ratings yet
- Using The Phase Plot Tool For MATLABDocument3 pagesUsing The Phase Plot Tool For MATLABJojo KawayNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Costs, Scale of Production and Break-Even Analysis - LearnerDocument23 pages4.2 Costs, Scale of Production and Break-Even Analysis - LearnerDhivya Lakshmirajan100% (1)
- Optimal Boiler Size and Its Relation To Seasonal EfficiencyDocument45 pagesOptimal Boiler Size and Its Relation To Seasonal EfficiencybobbobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 Excercises Part IIDocument5 pagesChapter 09 Excercises Part IIFatbardha MorinaNo ratings yet
- Deep Sea Electronics: Model 5220 Installation and Configuration InstructionsDocument2 pagesDeep Sea Electronics: Model 5220 Installation and Configuration Instructionsdhani_is100% (1)
- Weather Criterion Explained PDFDocument14 pagesWeather Criterion Explained PDFDeep SeaNo ratings yet