Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsColor Models
Color Models
Uploaded by
Patil TanishkCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Color ModelsDocument34 pagesColor ModelsSinduja BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Q1. Disitinguish Between Random and Raster Scan Display Devices. Ans: Raster ScanDocument4 pagesQ1. Disitinguish Between Random and Raster Scan Display Devices. Ans: Raster ScanahsNo ratings yet
- Chap 15 Colour ModelDocument14 pagesChap 15 Colour ModelShivangi Bansal 204020No ratings yet
- Color Space: Color Model Colors Tuples RGB Cmyk Absolute Color SpaceDocument20 pagesColor Space: Color Model Colors Tuples RGB Cmyk Absolute Color SpaceDinesh ScorpNo ratings yet
- HSL and HSVDocument15 pagesHSL and HSVs_paraisoNo ratings yet
- Colour ModelsDocument5 pagesColour ModelsKrishanu Modak100% (1)
- Colour (Compatibility Mode)Document30 pagesColour (Compatibility Mode)PradeepvenugopalNo ratings yet
- Art Color Systems HandbookDocument9 pagesArt Color Systems HandbookAli HosenNo ratings yet
- Color Models in Figma DesignDocument4 pagesColor Models in Figma DesignVeluanna VadiNo ratings yet
- Digital Image ProcessingDocument11 pagesDigital Image ProcessingAlina RehmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Color Image ProcessingDocument34 pagesChapter 6 Color Image ProcessingGarvit TyagiNo ratings yet
- Color Model 1Document20 pagesColor Model 1sharmilaNo ratings yet
- Color Models: UltravioletDocument18 pagesColor Models: UltravioletSyawal Dina SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document25 pagesChapter 7MuhdFikriNo ratings yet
- Color SpaceDocument6 pagesColor SpaceMoji Piyapong0% (1)
- Color Model YUV CMYKDocument5 pagesColor Model YUV CMYKPatil TanishkNo ratings yet
- Color: CSE 320 Graphics ProgrammingDocument34 pagesColor: CSE 320 Graphics ProgrammingIsaac Joel RajNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document129 pagesModule 2survey ssNo ratings yet
- Chap1 2 3Document27 pagesChap1 2 3Hàng Không Mẫu HạmNo ratings yet
- ImageProcessing12 ColourImageProcessingDocument76 pagesImageProcessing12 ColourImageProcessingPurushotham Prasad KNo ratings yet
- Hsi - HSL - HSVDocument27 pagesHsi - HSL - HSVspahicdaniloNo ratings yet
- RGB To HSVDocument2 pagesRGB To HSVnikwplayNo ratings yet
- Color FeatureDocument3 pagesColor Featureart101988No ratings yet
- Color ModelsDocument33 pagesColor ModelsAditya PugaliaNo ratings yet
- Color Order SystemsDocument30 pagesColor Order SystemsBeyene DumechaNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics: Color ModelsDocument35 pagesComputer Graphics: Color Modelsمروة عبدالله محمد علي حبيبانNo ratings yet
- Colour Image ProcessingDocument60 pagesColour Image ProcessingkondurukarthikNo ratings yet
- Lect 8Document73 pagesLect 8Asif FiazNo ratings yet
- CIT 2211 - Lecture 4 - ColourDocument27 pagesCIT 2211 - Lecture 4 - Colourrisksentinel.objNo ratings yet
- Hunter Color labDocument32 pagesHunter Color lab6jdxwpmj26No ratings yet
- Color Image Processing: Prepared by T. Ravi Kumar NaiduDocument60 pagesColor Image Processing: Prepared by T. Ravi Kumar NaiduRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- DA2042 ColorDocument29 pagesDA2042 ColorVanathi PriyadharshiniNo ratings yet
- CV 3Document10 pagesCV 3Bilal KhanNo ratings yet
- Collor IpDocument29 pagesCollor IpMALAKONDA REDDY BOILLANo ratings yet
- Graph TheoryDocument18 pagesGraph Theoryjaved khanNo ratings yet
- Quiz DIPDocument7 pagesQuiz DIPayesha bashirNo ratings yet
- MC 4Document28 pagesMC 4Muskan KhannNo ratings yet
- CS8092 Computer Graphics and Multimedia Notes WatermarkDocument169 pagesCS8092 Computer Graphics and Multimedia Notes WatermarkRameez NNo ratings yet
- Light and ColorDocument29 pagesLight and ColorSuman BhandariNo ratings yet
- Color Transformations: I R R R T S R R R F (M, N), Whereas S S SDocument11 pagesColor Transformations: I R R R T S R R R F (M, N), Whereas S S SAbhi TailorNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing, Color ModelsDocument40 pagesDigital Image Processing, Color Modelsk_kunarajNo ratings yet
- CGMM 3Document3 pagesCGMM 3nishita patidarNo ratings yet
- DipDocument4 pagesDipLekshmi Devi RanjithNo ratings yet
- Colour ModelsDocument6 pagesColour ModelsPIYUSH PAWAR100% (1)
- Unit - IiiDocument12 pagesUnit - Iiigauravrokade762No ratings yet
- Experiment No.5Document4 pagesExperiment No.5Tejas PatilNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structures For Computer Science: Lecture - 13 DR DPRV Subba RaoDocument29 pagesDiscrete Structures For Computer Science: Lecture - 13 DR DPRV Subba RaoPandu DoradlaNo ratings yet
- CH 15Document28 pagesCH 15Maisa ArhamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Colour Image ProcessingDocument53 pagesChapter 9 Colour Image ProcessingSaikarNo ratings yet
- Color Model: Submitted by Jagtap Aishwarya NitinDocument4 pagesColor Model: Submitted by Jagtap Aishwarya Nitinshriyash jagtapNo ratings yet
- Machine Vision Exp 2 (Mumbai Univesrity)Document6 pagesMachine Vision Exp 2 (Mumbai Univesrity)Om BhamareNo ratings yet
- Color Space Image ProcessingDocument11 pagesColor Space Image ProcessingSushant SawantNo ratings yet
- Color Image ProcessingDocument13 pagesColor Image ProcessingBrijesh KumarNo ratings yet
- EE 604 Image ProcessingDocument16 pagesEE 604 Image Processingmuskan agarwalNo ratings yet
- Pengolahan Citra Berwarna: Kuliah Ke-3 PPCDDocument55 pagesPengolahan Citra Berwarna: Kuliah Ke-3 PPCDaditya nur johansyahNo ratings yet
- HSL and HSV - Wikipedia, Th..Document15 pagesHSL and HSV - Wikipedia, Th..ramu.paturi7712No ratings yet
- Basic Vision-Maslab 2004Document45 pagesBasic Vision-Maslab 2004demoNo ratings yet
- Color Model: Understanding the Spectrum of Computer Vision: Exploring Color ModelsFrom EverandColor Model: Understanding the Spectrum of Computer Vision: Exploring Color ModelsNo ratings yet
- Colour Image ProcessingDocument57 pagesColour Image ProcessingANANG SANJAYANo ratings yet
- Color Matching Function: Understanding Spectral Sensitivity in Computer VisionFrom EverandColor Matching Function: Understanding Spectral Sensitivity in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Soft engg1 0Document4 pagesSoft engg1 0Patil TanishkNo ratings yet
- Types of Images Based On ColourDocument3 pagesTypes of Images Based On ColourPatil TanishkNo ratings yet
- Unit1 3Document10 pagesUnit1 3Patil TanishkNo ratings yet
- Unit1 4Document7 pagesUnit1 4Patil TanishkNo ratings yet
- Unit1 p2Document7 pagesUnit1 p2Patil TanishkNo ratings yet
- Design PrinciplesDocument4 pagesDesign PrinciplesPatil TanishkNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Patil TanishkNo ratings yet
- DMGTDocument139 pagesDMGTPatil TanishkNo ratings yet
Color Models
Color Models
Uploaded by
Patil Tanishk0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views5 pagesColor Models
Color Models
Uploaded by
Patil TanishkCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
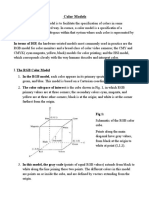
Color Model
• A color model is an abstract mathematical model that describes how
colors can be represented as a set of numbers (e.g., a triple in RGB or
a quad in CMYK).
• Color models can usually be described using a coordinate system, and
each color in the system is represented by a single point in the
coordinate space.
• For a given color model, to interpret a tuple or quad as a color, we can
define a set of rules and definitions used to accurately calibrate and
generate colors, i.e. a mapping function.
• A color space identifies a specific combination of color models and
mapping functions. Identifying the color space automatically identifies
the associated color model. For example, Adobe RGB and sRGB are
two different color spaces, both based on the RGB color model.
RGB
• RGB color model stores individual values for red, green, and blue.
• With a color space based on the RGB color model, the three primaries
are added together to create colors from completely white to
completely black.
• https://www.dynamsoft.com/blog/insights/image-processing/image-
processing-101-color-models/
HSV (hue, saturation, value)
• The HSV model space can be described as an inverted hexagonal pyramid.
• The top surface is a regular hexagon, showing the change in hue in the H
direction, from 0 ° to 360 ° is the entire spectrum of visible light. The six
corners of the hexagon represent the positions of the six colors of red,
yellow, green, cyan, blue, and magenta, each of which is 60 ° apart.
• The saturation S is represented by the S direction from the center to the
hexagonal boundary, and the value varies from 0 to 1. The closer to the
hexagonal boundary, the higher the color saturation. The color of the
hexagonal boundary is the most saturated, i.e. S = 1; the color saturation at
the center of the hexagon is 0, i.e. S = 0.
• The height of the hexagonal pyramid (also known as the central axis) is
denoted by V, which represents a black to white gradation from bottom to
top. The bottom of V is black, V = 0; the top of V is white, V = 1.
You might also like
- Color ModelsDocument34 pagesColor ModelsSinduja BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Q1. Disitinguish Between Random and Raster Scan Display Devices. Ans: Raster ScanDocument4 pagesQ1. Disitinguish Between Random and Raster Scan Display Devices. Ans: Raster ScanahsNo ratings yet
- Chap 15 Colour ModelDocument14 pagesChap 15 Colour ModelShivangi Bansal 204020No ratings yet
- Color Space: Color Model Colors Tuples RGB Cmyk Absolute Color SpaceDocument20 pagesColor Space: Color Model Colors Tuples RGB Cmyk Absolute Color SpaceDinesh ScorpNo ratings yet
- HSL and HSVDocument15 pagesHSL and HSVs_paraisoNo ratings yet
- Colour ModelsDocument5 pagesColour ModelsKrishanu Modak100% (1)
- Colour (Compatibility Mode)Document30 pagesColour (Compatibility Mode)PradeepvenugopalNo ratings yet
- Art Color Systems HandbookDocument9 pagesArt Color Systems HandbookAli HosenNo ratings yet
- Color Models in Figma DesignDocument4 pagesColor Models in Figma DesignVeluanna VadiNo ratings yet
- Digital Image ProcessingDocument11 pagesDigital Image ProcessingAlina RehmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Color Image ProcessingDocument34 pagesChapter 6 Color Image ProcessingGarvit TyagiNo ratings yet
- Color Model 1Document20 pagesColor Model 1sharmilaNo ratings yet
- Color Models: UltravioletDocument18 pagesColor Models: UltravioletSyawal Dina SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document25 pagesChapter 7MuhdFikriNo ratings yet
- Color SpaceDocument6 pagesColor SpaceMoji Piyapong0% (1)
- Color Model YUV CMYKDocument5 pagesColor Model YUV CMYKPatil TanishkNo ratings yet
- Color: CSE 320 Graphics ProgrammingDocument34 pagesColor: CSE 320 Graphics ProgrammingIsaac Joel RajNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document129 pagesModule 2survey ssNo ratings yet
- Chap1 2 3Document27 pagesChap1 2 3Hàng Không Mẫu HạmNo ratings yet
- ImageProcessing12 ColourImageProcessingDocument76 pagesImageProcessing12 ColourImageProcessingPurushotham Prasad KNo ratings yet
- Hsi - HSL - HSVDocument27 pagesHsi - HSL - HSVspahicdaniloNo ratings yet
- RGB To HSVDocument2 pagesRGB To HSVnikwplayNo ratings yet
- Color FeatureDocument3 pagesColor Featureart101988No ratings yet
- Color ModelsDocument33 pagesColor ModelsAditya PugaliaNo ratings yet
- Color Order SystemsDocument30 pagesColor Order SystemsBeyene DumechaNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics: Color ModelsDocument35 pagesComputer Graphics: Color Modelsمروة عبدالله محمد علي حبيبانNo ratings yet
- Colour Image ProcessingDocument60 pagesColour Image ProcessingkondurukarthikNo ratings yet
- Lect 8Document73 pagesLect 8Asif FiazNo ratings yet
- CIT 2211 - Lecture 4 - ColourDocument27 pagesCIT 2211 - Lecture 4 - Colourrisksentinel.objNo ratings yet
- Hunter Color labDocument32 pagesHunter Color lab6jdxwpmj26No ratings yet
- Color Image Processing: Prepared by T. Ravi Kumar NaiduDocument60 pagesColor Image Processing: Prepared by T. Ravi Kumar NaiduRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- DA2042 ColorDocument29 pagesDA2042 ColorVanathi PriyadharshiniNo ratings yet
- CV 3Document10 pagesCV 3Bilal KhanNo ratings yet
- Collor IpDocument29 pagesCollor IpMALAKONDA REDDY BOILLANo ratings yet
- Graph TheoryDocument18 pagesGraph Theoryjaved khanNo ratings yet
- Quiz DIPDocument7 pagesQuiz DIPayesha bashirNo ratings yet
- MC 4Document28 pagesMC 4Muskan KhannNo ratings yet
- CS8092 Computer Graphics and Multimedia Notes WatermarkDocument169 pagesCS8092 Computer Graphics and Multimedia Notes WatermarkRameez NNo ratings yet
- Light and ColorDocument29 pagesLight and ColorSuman BhandariNo ratings yet
- Color Transformations: I R R R T S R R R F (M, N), Whereas S S SDocument11 pagesColor Transformations: I R R R T S R R R F (M, N), Whereas S S SAbhi TailorNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing, Color ModelsDocument40 pagesDigital Image Processing, Color Modelsk_kunarajNo ratings yet
- CGMM 3Document3 pagesCGMM 3nishita patidarNo ratings yet
- DipDocument4 pagesDipLekshmi Devi RanjithNo ratings yet
- Colour ModelsDocument6 pagesColour ModelsPIYUSH PAWAR100% (1)
- Unit - IiiDocument12 pagesUnit - Iiigauravrokade762No ratings yet
- Experiment No.5Document4 pagesExperiment No.5Tejas PatilNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structures For Computer Science: Lecture - 13 DR DPRV Subba RaoDocument29 pagesDiscrete Structures For Computer Science: Lecture - 13 DR DPRV Subba RaoPandu DoradlaNo ratings yet
- CH 15Document28 pagesCH 15Maisa ArhamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Colour Image ProcessingDocument53 pagesChapter 9 Colour Image ProcessingSaikarNo ratings yet
- Color Model: Submitted by Jagtap Aishwarya NitinDocument4 pagesColor Model: Submitted by Jagtap Aishwarya Nitinshriyash jagtapNo ratings yet
- Machine Vision Exp 2 (Mumbai Univesrity)Document6 pagesMachine Vision Exp 2 (Mumbai Univesrity)Om BhamareNo ratings yet
- Color Space Image ProcessingDocument11 pagesColor Space Image ProcessingSushant SawantNo ratings yet
- Color Image ProcessingDocument13 pagesColor Image ProcessingBrijesh KumarNo ratings yet
- EE 604 Image ProcessingDocument16 pagesEE 604 Image Processingmuskan agarwalNo ratings yet
- Pengolahan Citra Berwarna: Kuliah Ke-3 PPCDDocument55 pagesPengolahan Citra Berwarna: Kuliah Ke-3 PPCDaditya nur johansyahNo ratings yet
- HSL and HSV - Wikipedia, Th..Document15 pagesHSL and HSV - Wikipedia, Th..ramu.paturi7712No ratings yet
- Basic Vision-Maslab 2004Document45 pagesBasic Vision-Maslab 2004demoNo ratings yet
- Color Model: Understanding the Spectrum of Computer Vision: Exploring Color ModelsFrom EverandColor Model: Understanding the Spectrum of Computer Vision: Exploring Color ModelsNo ratings yet
- Colour Image ProcessingDocument57 pagesColour Image ProcessingANANG SANJAYANo ratings yet
- Color Matching Function: Understanding Spectral Sensitivity in Computer VisionFrom EverandColor Matching Function: Understanding Spectral Sensitivity in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Soft engg1 0Document4 pagesSoft engg1 0Patil TanishkNo ratings yet
- Types of Images Based On ColourDocument3 pagesTypes of Images Based On ColourPatil TanishkNo ratings yet
- Unit1 3Document10 pagesUnit1 3Patil TanishkNo ratings yet
- Unit1 4Document7 pagesUnit1 4Patil TanishkNo ratings yet
- Unit1 p2Document7 pagesUnit1 p2Patil TanishkNo ratings yet
- Design PrinciplesDocument4 pagesDesign PrinciplesPatil TanishkNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Patil TanishkNo ratings yet
- DMGTDocument139 pagesDMGTPatil TanishkNo ratings yet