Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antihypertensive Medications Nursing Care
Antihypertensive Medications Nursing Care
Uploaded by
ScribdTranslations0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageThis document provides information on nursing care for various antihypertensive and anticoagulant medications. For angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors such as captopril, nurses should monitor blood pressure, electrolyte levels, and signs of angioedema. For angiotensin II receptor antagonists such as losartan, heart rate, blood pressure, and possible effects on the skin or nervous system should be monitored.
Original Description:
This document provides information on nursing care for various antihypertensive and anticoagulant medications. For angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors such as captopril, nurses should monitor blood pressure, electrolyte levels, and signs of angioedema. For angiotensin II receptor antagonists such as losartan, heart rate, blood pressure, and possible effects on the skin or nervous system should be monitored.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on nursing care for various antihypertensive and anticoagulant medications. For angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors such as captopril, nurses should monitor blood pressure, electrolyte levels, and signs of angioedema. For angiotensin II receptor antagonists such as losartan, heart rate, blood pressure, and possible effects on the skin or nervous system should be monitored.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageAntihypertensive Medications Nursing Care
Antihypertensive Medications Nursing Care
Uploaded by
ScribdTranslationsThis document provides information on nursing care for various antihypertensive and anticoagulant medications. For angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors such as captopril, nurses should monitor blood pressure, electrolyte levels, and signs of angioedema. For angiotensin II receptor antagonists such as losartan, heart rate, blood pressure, and possible effects on the skin or nervous system should be monitored.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
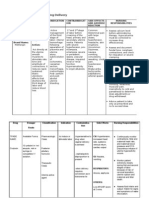
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE MEDICATIONS NURSING CARE
1. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors : CAPTOPRIL
After washing hands, 12 correct.
Monitor vital signs, especially blood pressure.
Monitor for signs of angioedema, monitor blood sodium and potassium levels
during treatment
Inform the patient that it may take several weeks for the desired therapeutic
effects to occur.
Warn the patient not to take any supplements containing potassium.
If there is an increase in potassium levels in the blood, take arterial blood gases
to rule out possible metabolic acidosis.
2. Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist : LOZARTAN
After washing hands, 12 correct
Monitor vital signs, especially heart rate and blood pressure.
Monitor photosensitivity, rashes, changes in the central nervous system.
Take electrocardiograms on the patient to see if changes occur in the condition
of the heart.
Inform the patient not to change position so abruptly because it may cause
dizziness or cause orthostatic hypotension.
Educate the patient.
Suggest that the patient have some laboratory tests.
3. Calcium Channel Blockers : AMLODIPINO
After washing hands, 12 correct times, taking blood pressure before and
after administration of the medication.
Use caution when administering IV due to interaction with beta blockers
Monitor ECG for AV block (may increase PR interval.
Inquire about atrioventricular conduction disorders due to the risk of
blockage due to myocardial and sinus node depression.
monitor for the presence of adverse reactions.
ANTICOAGULANT MEDICATIONS NURSING CARE
1) Low molecular weight heparin: ENOXAPARIN
Administer after lunch
Monitor clotting time
Observe presence of hum
Monitor for signs of digestive disorders
Platelet count value, presence of bleeding, abdominal pain, dyspepsia,
gastritis, constipation, skin disorders
In the administration of fibrinolytics, constant monitoring for possible
adverse reactions
Monitor for the presence of possible neurological signs that may be due to a
cerebral hemorrhage.
If you intend to use streptokinase, you must ask the patient if they have
been administered it in the previous 12 months; if so, it should not be used
due to the danger of producing an adverse reaction.
During fibrinolytic treatment up to two days later, no drug should be
administered IM.
During administration in myocardial infarction, the appearance of
arrhythmias should be monitored.
You might also like
- 50 Item Pharmacology Exam With Answers and RationaleDocument17 pages50 Item Pharmacology Exam With Answers and Rationalebibot189% (18)
- Nursing Drug CardsDocument32 pagesNursing Drug CardsJenna Rasmussen100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyGi Ey ElNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management: PD: Kevin M. Reeves January 20, 2016Document16 pagesClassroom Management: PD: Kevin M. Reeves January 20, 2016Samiullah Durrani100% (2)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Study Guide For The Dental Technician ExaminationDocument64 pagesStudy Guide For The Dental Technician ExaminationAurora100% (3)
- Pharma - Week 2 Course TaskDocument6 pagesPharma - Week 2 Course TaskLou KristofferNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology CaptoprilDocument14 pagesPharmacology Captoprildalilaarshad31No ratings yet
- Drug Dosage Mechanism of Action Specific Indication Contraindicati ON Adverse Effect Nursing PrecautionDocument11 pagesDrug Dosage Mechanism of Action Specific Indication Contraindicati ON Adverse Effect Nursing PrecautionIzabela UyNo ratings yet
- E - Cart DrugsDocument18 pagesE - Cart Drugs'SheenMarkReal'100% (2)
- Drug Dosage Mechanism of Action Specific Indicatio N Contraindicat ION Adverse Effect Nursing PrecautionDocument14 pagesDrug Dosage Mechanism of Action Specific Indicatio N Contraindicat ION Adverse Effect Nursing PrecautionIzabela UyNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventDocument6 pagesAmlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Route/Dose Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects/Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument9 pagesName of Drug Route/Dose Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects/Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiespauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCarson BirthNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJoy Jarin100% (1)
- DrugsDocument113 pagesDrugsCARE CATH LABNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesCardiovascular SystemRegineCuasSulibNo ratings yet
- Cu Task 2 PharmaDocument5 pagesCu Task 2 PharmaNiña ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Practice Midterm Test.Document16 pagesPractice Midterm Test.Marku LeeNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument22 pagesFinal Drug StudyPaula Xavier AlfalahiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Perioperative ManagementDocument14 pagesChapter 3: Perioperative ManagementpoddataNo ratings yet
- Legaspi Course Task 2Document7 pagesLegaspi Course Task 2FATIMA AIRA LEGASPINo ratings yet
- Drug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesDocument12 pagesDrug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesBernie Evan Oidem ForlajeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- Course Task 2Document2 pagesCourse Task 2John Elton TangpuzNo ratings yet
- Anti-Tuberculosis AgentsDocument15 pagesAnti-Tuberculosis AgentsNick van ExelNo ratings yet
- Drug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesDocument11 pagesDrug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesBernie Evan Oidem ForlajeNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin 500mg Tab (Zithromax)Document6 pagesAzithromycin 500mg Tab (Zithromax)Mayownski TejeroNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibutors MailDocument5 pagesAce Inhibutors MailWendy AdaoNo ratings yet
- Pharma From GPTDocument30 pagesPharma From GPTManisha ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Medications: LorsartanDocument3 pagesMedications: LorsartanJoy DunwanNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCM 118Document14 pagesCase Study NCM 118Romzy BasañesNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyTeanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- Drug RationaleDocument77 pagesDrug RationaleYolanda WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyKenneth ManalangNo ratings yet
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine Tramadol Ketorolac Ampicillin Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument10 pagesRanitidine Tramadol Ketorolac Ampicillin Paracetamol Drug StudyMarco MoralesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NCM 118 FinalDocument15 pagesDrug Study NCM 118 FinalSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- WEEK2 Course Task (ALFEREZ, DINIELA)Document4 pagesWEEK2 Course Task (ALFEREZ, DINIELA)DINIELA ALLAINE ALFEREZNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Medication Nurse)Document42 pagesDrug Study (Medication Nurse)Ellen Grace CalayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboDocument7 pagesNursing Pharmacology Handouts For ZamboAlexa Abidin Oldenborg100% (8)
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocument14 pagesNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Medication LectureDocument23 pagesCardiac Medication LectureilikeedsheeranNo ratings yet
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- RX - Citicoline, Kalium, Ketosteril, Methycobal, Myonal, Lipolin GelDocument6 pagesRX - Citicoline, Kalium, Ketosteril, Methycobal, Myonal, Lipolin GelntootNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ranitidine TramadolDocument10 pagesDrug Study Ranitidine TramadolSitti Zhainab0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyEzshkha OngueNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care in BenzodiazepinesDocument8 pagesNursing Care in BenzodiazepinesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Drug Data Generic Name: Losartan Brand Name: Losartan RitemedDocument2 pagesDrug Data Generic Name: Losartan Brand Name: Losartan RitemedKristina Ana ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Med Surg Medication Study GuideDocument8 pagesMed Surg Medication Study Guidetina100% (1)
- Pre and Post OperationDocument5 pagesPre and Post Operationhacker ammerNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument3 pagesDrugsMarl Gale TahumNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutics in ObstetricsDocument103 pagesPharmacotherapeutics in Obstetricssanthanalakshmi100% (4)
- Anti Tuberculosis AgentsDocument15 pagesAnti Tuberculosis Agentsejg26100% (1)
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- HW2 PharmacologyDocument6 pagesHW2 PharmacologyMICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology CardiovascularDocument86 pagesPharmacology Cardiovascularamasoud96 amasoud96No ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Abbreviated File-Process Case 01 Marco A. and CounterclaimDocument25 pagesAbbreviated File-Process Case 01 Marco A. and CounterclaimScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Natural History of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument49 pagesNatural History of Parkinson's DiseaseScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Tourist PlanningDocument39 pagesTourist PlanningScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Application of Copper Sulfate in AquacultureDocument2 pagesApplication of Copper Sulfate in AquacultureScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Ethnicity, Language and IdentityDocument4 pagesEthnicity, Language and IdentityScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Retirement Instructions Unemployment PorvenirDocument6 pagesRetirement Instructions Unemployment PorvenirScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- History and Evolution of Reciprocating MotorsDocument32 pagesHistory and Evolution of Reciprocating MotorsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS Mechanical Drawing 2Document7 pagesSYLLABUS Mechanical Drawing 2ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter X. Precision Shooting From Naval Air PlatformsDocument24 pagesChapter X. Precision Shooting From Naval Air PlatformsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Musical Instruments of EuropeDocument3 pagesMusical Instruments of EuropeScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Boxing PDFDocument49 pagesBoxing PDFScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Practical Work The Familiar PDFDocument1 pagePractical Work The Familiar PDFScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Comparative Table of Rationalism and EmpiricismDocument7 pagesComparative Table of Rationalism and EmpiricismScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Event Security ProtocolDocument7 pagesEvent Security ProtocolScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade Plan - Block 4 GeographyDocument12 pages5th Grade Plan - Block 4 GeographyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- iTEP in - House PDFDocument12 pagesiTEP in - House PDFScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Expo22 Daily ExperienceDocument6 pagesExpo22 Daily ExperienceScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension and Contextual Vocabulary Exercises 4th Middle #8.Document5 pagesReading Comprehension and Contextual Vocabulary Exercises 4th Middle #8.ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects GuatemalaDocument20 pagesLegal Aspects GuatemalaScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Project On Electricity For ChildrenDocument13 pagesProject On Electricity For ChildrenScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- PH Portfolio Recovery ProposalDocument3 pagesPH Portfolio Recovery ProposalScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Sixth Grade Reading Comprehension AssessmentDocument8 pagesSixth Grade Reading Comprehension AssessmentScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Laboratory Report 1Document14 pagesChemistry Laboratory Report 1ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Applied StatisticsDocument209 pagesApplied StatisticsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Types of Banks Based On OwnershipDocument2 pagesTypes of Banks Based On OwnershipScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Application of Regulations in The Financial SystemDocument74 pagesApplication of Regulations in The Financial SystemScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Security of Accounting Information SystemsDocument2 pagesSecurity of Accounting Information SystemsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Driver's Manual in TexasDocument109 pagesDriver's Manual in TexasScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Vibrational Sound Therapy ManualDocument12 pagesVibrational Sound Therapy ManualScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Examples of Operant ConditioningDocument1 pageExamples of Operant ConditioningScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Fundamentals of Nursing Care Concepts Connections and Skills 3rd Edition Marti Burton PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Fundamentals of Nursing Care Concepts Connections and Skills 3rd Edition Marti Burton PDF Full Chaptersorryabrammanhrv3100% (22)
- BirthweightDocument1 pageBirthweightmaria morariuNo ratings yet
- Ida Jean Orlando - SoftDocument5 pagesIda Jean Orlando - SoftBenjamin TanNo ratings yet
- Genetic Roulette The Gamble of Our LivesDocument5 pagesGenetic Roulette The Gamble of Our LivessgyulusNo ratings yet
- Obe VeridicalityDocument6 pagesObe VeridicalityKarina PsNo ratings yet
- Gender and DisabilityDocument17 pagesGender and DisabilityLucian LourençoNo ratings yet
- Life Orientation September 2021 MG EngDocument22 pagesLife Orientation September 2021 MG EngHitekani ImargineNo ratings yet
- Week 009 Module A Concept of Activity ManagementDocument4 pagesWeek 009 Module A Concept of Activity ManagementMark John Paul CablingNo ratings yet
- MHFA Youth Participant Processing Guide+Document43 pagesMHFA Youth Participant Processing Guide+Sophia BrummNo ratings yet
- Community Family Studies Preliminary NotesDocument12 pagesCommunity Family Studies Preliminary NotesJade LyNo ratings yet
- Alien Mind Contrtol CommandsDocument62 pagesAlien Mind Contrtol Commandshilly8100% (3)
- Society For The Scientific Study of Religion, Wiley Journal For The Scientific Study of ReligionDocument22 pagesSociety For The Scientific Study of Religion, Wiley Journal For The Scientific Study of ReligionPetruPavălNo ratings yet
- Articulo 2Document6 pagesArticulo 2Alexander RuizNo ratings yet
- KSSM SCIENCE Form 4 Chapter 10 10.1 StudentsDocument36 pagesKSSM SCIENCE Form 4 Chapter 10 10.1 StudentsTSENo ratings yet
- 3 - Vitamin CDocument12 pages3 - Vitamin CskyeandoNo ratings yet
- Safety Practices During Construction: Oisd - GDN - 192Document59 pagesSafety Practices During Construction: Oisd - GDN - 192yash shahNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument2 pagesAntibioticsShalini PanchalNo ratings yet
- How It Works?: Mueller Hinton Agar (MHA)Document9 pagesHow It Works?: Mueller Hinton Agar (MHA)dragusriyadi01No ratings yet
- Case ReportDocument5 pagesCase ReportJenesse Kacy GalugaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: General ObjectiveDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: General ObjectiveSarita yadavNo ratings yet
- Bahayaamaran: Baca Helaian Data Keselamatan'Sebelum DigunakanDocument1 pageBahayaamaran: Baca Helaian Data Keselamatan'Sebelum DigunakanMuhammad Farhan Bin IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Sensory Profile Scores of Young Children With and Without Autism Spectrum DisordersDocument8 pagesComparison of Sensory Profile Scores of Young Children With and Without Autism Spectrum DisordersDaniela Sánchez AcostaNo ratings yet
- Sigma MP 101 (US) EN SdsDocument9 pagesSigma MP 101 (US) EN SdsEduardo GarzaNo ratings yet
- TRX Six Procedures PDFDocument8 pagesTRX Six Procedures PDFBabis XNo ratings yet
- 5K 30 - 40 MILES: September 4Document5 pages5K 30 - 40 MILES: September 4joogNo ratings yet
- By Michael J. EllisonDocument12 pagesBy Michael J. EllisonA MNo ratings yet
- Articles: Thermal Comfort Assessment of Metro Manila Development Authority (Mmda) Traffic Enforcers in Pasig City, PhilippinesDocument5 pagesArticles: Thermal Comfort Assessment of Metro Manila Development Authority (Mmda) Traffic Enforcers in Pasig City, PhilippinesCheska ValmonteNo ratings yet
- Medgluv - Gloves - Certifications - OpulentDocument35 pagesMedgluv - Gloves - Certifications - Opulentsaisridhar99100% (1)