Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care
Nursing Care
Uploaded by
ScribdTranslationsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care
Nursing Care
Uploaded by
ScribdTranslationsCopyright:
Available Formats
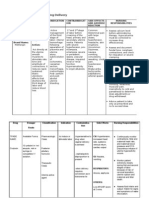
NURSING CARE
Nitroglycerin acts directly on vascular smooth muscles, causing arterial and
venous vasodilation, but the venous effects are more important.
Interaction:
With beta blockers, Neuroleptics, antidepressants, acetylsysteine.
Nursing Care.
Assess The adverse effects of this medication are common, although
mild and transient. Nursing should supervise the appearance of:
Headaches, throbbing and persistent due to vasodilation, which should
disappear after the administration of analgesics.
Tachycardia and collapse as well as skin rash also due to its vasodilator
effect, which is why we will monitor the patient with a cardiac monitor.
At high doses we can find cyanosis, bradycardia and also hypoxia.
In case of severe orthostatic hypotension, we must stop the perfusion, so
we will periodically monitor the patient's blood pressure values.
Control of the appearance of nausea and vomiting.
Administer in special infusion sets, not PVC, as 40-80% of the dose can
be absorbed in common PVC infusion sets.
BP control.
Administer in a continuous infusion pump (do not administer boluses of
medication through the same lumen) – Skin rashes
Discontinue infusion slowly due to possible rebound effect.
Dilute in Dext5% protected from light and heat.
NURSING CARE
It is administered intravenously in infusion with 100 cm every hour.
Before giving this medication, look at the solution carefully. This should be light in color and
free of floating particles.
It is important that you use the medication exactly as directed. Pethidine can cause
dependence.
You might also like
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyGi Ey ElNo ratings yet
- RLE 3 FINAL 2011-03 Emergency NursingDocument47 pagesRLE 3 FINAL 2011-03 Emergency NursingBoni LagunayNo ratings yet
- Spinal Anes Drug StudyDocument12 pagesSpinal Anes Drug StudyNicosia Mae FerrerNo ratings yet
- Ecart For PrintingDocument10 pagesEcart For PrintingbluennaNo ratings yet
- Phenylephrine Hydrochloride PDFDocument5 pagesPhenylephrine Hydrochloride PDFVinz Khyl G. CastillonNo ratings yet
- Phenylephrine HydrochlorideDocument5 pagesPhenylephrine HydrochlorideRoger Jr PumarenNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKristoff CamposNo ratings yet
- ICU Drips: Stephanie Sanderson, RN, MSN, CNS, CCNS, CCRN Medical Cardiac ICU-UNMHDocument32 pagesICU Drips: Stephanie Sanderson, RN, MSN, CNS, CCNS, CCRN Medical Cardiac ICU-UNMHNicole Adkins100% (1)
- Adenosine Prospect Medical in Limba EnglezaDocument5 pagesAdenosine Prospect Medical in Limba EnglezaLaura ZahariaNo ratings yet
- 24 Emergency DrugsDocument7 pages24 Emergency DrugsApple BelicanNo ratings yet
- Medical Emergencies in The Dental OfficeDocument23 pagesMedical Emergencies in The Dental Officeতৌহিদ তপুNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCM 118Document14 pagesCase Study NCM 118Romzy BasañesNo ratings yet
- Common Drug & Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument50 pagesCommon Drug & Nursing ResponsibilitiesRyanMatira100% (1)
- Nursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeDocument5 pagesNursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeSophia limNo ratings yet
- Indication Specific Action Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration/ Patient TeachingDocument6 pagesIndication Specific Action Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration/ Patient TeachingKrista Madranca CastroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CARDIODocument17 pagesDrug Study CARDIODiannetotz Morales100% (1)
- FentanylDocument4 pagesFentanylapi-3797941No ratings yet
- HW2 PharmacologyDocument6 pagesHW2 PharmacologyMICHAEL GABRIEL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Epinephrine Drug StudyDocument7 pagesEpinephrine Drug StudyJhoy Iris SarangayaNo ratings yet
- Hazards of Local AnesthesiaDocument44 pagesHazards of Local AnesthesiaIyad Abou-RabiiNo ratings yet
- Nclex PharmacologyDocument82 pagesNclex PharmacologyMaria Nadia Mihalik100% (3)
- Isosorbide DinitrateDocument1 pageIsosorbide Dinitrate202110439No ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Cardio Vascular SystemDocument138 pagesDrugs Used in Cardio Vascular SystemSagun lohalaNo ratings yet
- EpinephrineDocument6 pagesEpinephrineapi-3797941100% (2)
- Nitroglycerin Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNitroglycerin Drug StudyjuancristoNo ratings yet
- Drugs ORDocument17 pagesDrugs ORCatherine ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic Complications: Leonardo, Perey, Zhong, ZhouDocument29 pagesAnesthetic Complications: Leonardo, Perey, Zhong, ZhouRenee PereyNo ratings yet
- Activated Charcoal: Adverse EffectsDocument14 pagesActivated Charcoal: Adverse EffectsAntonetteNo ratings yet
- Cu Task 2 PharmaDocument5 pagesCu Task 2 PharmaNiña ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vasotec EnalaprilDocument1 pageVasotec EnalaprilCassie100% (1)
- Fluimucil 300mg / 3mlDocument3 pagesFluimucil 300mg / 3mlRezti PratiwiNo ratings yet
- InotropicsDocument20 pagesInotropicsMalathi VarnaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsnurse_nurseNo ratings yet
- HCL Clonipress: 75 MCG & 150 MCG TabletDocument1 pageHCL Clonipress: 75 MCG & 150 MCG TabletShyden Taghap Billones BordaNo ratings yet
- Phenylephrine HydrochlorideDocument5 pagesPhenylephrine HydrochlorideSean Amir S. Savellano100% (1)
- Drugs Affecting Cardiac and Renal Systems LecDocument10 pagesDrugs Affecting Cardiac and Renal Systems LecMichelle ErikaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs - Cardiac DrugsDocument14 pagesEmergency Drugs - Cardiac DrugsKookie JunNo ratings yet
- Practice Midterm Test.Document16 pagesPractice Midterm Test.Marku LeeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenNo ratings yet
- Cloxacillin, Sodium: How Should I Take Cloxacillin?Document7 pagesCloxacillin, Sodium: How Should I Take Cloxacillin?Stacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- Bacaan Autonomic DysreflexiaDocument5 pagesBacaan Autonomic DysreflexiaPatriationkNo ratings yet
- Adult and Pediatric Emergency DrugsDocument61 pagesAdult and Pediatric Emergency DrugsYu, Denise Kyla BernadetteNo ratings yet
- Drug FileDocument20 pagesDrug FileSanjeevNo ratings yet
- CH 21 Obstetric AnaesthesiaDocument39 pagesCH 21 Obstetric AnaesthesiaChristian LeepoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Therapeutic Action Indication & Dosage Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument5 pagesDrug Name Therapeutic Action Indication & Dosage Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationArvan SebastianNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study Neh Jai2xDocument10 pagesDrugs Study Neh Jai2xjai2xNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Body SystemsDocument159 pagesPharmacology Body SystemsHezielErispeTaligatosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyTeanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- Bebdrugs DECDocument7 pagesBebdrugs DECAaron Angelo DillaNo ratings yet
- RUSS Emergency DrugDocument6 pagesRUSS Emergency DrugKat BausaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Emergency DrugsDocument5 pagesPharmacology Emergency DrugsAce RegellanaNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- On Emergency DrugsDocument25 pagesOn Emergency DrugsBikram Chhetry100% (1)
- Name of DrugDocument6 pagesName of Drug私 シャーロット100% (1)
- Cue CardsDocument2 pagesCue CardsSuzette Bartolome AgresorNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCharm LorenzoNo ratings yet
- DiclofenacDocument22 pagesDiclofenacintan kusumaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Drugs in The Neonatal Unit: 1 Julia PettyDocument5 pagesDrugs in The Neonatal Unit: 1 Julia PettyMarjoNo ratings yet
- Natural History of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument49 pagesNatural History of Parkinson's DiseaseScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Application of Copper Sulfate in AquacultureDocument2 pagesApplication of Copper Sulfate in AquacultureScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Retirement Instructions Unemployment PorvenirDocument6 pagesRetirement Instructions Unemployment PorvenirScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Sixth Grade Reading Comprehension AssessmentDocument8 pagesSixth Grade Reading Comprehension AssessmentScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Tourist PlanningDocument39 pagesTourist PlanningScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Ethnicity, Language and IdentityDocument4 pagesEthnicity, Language and IdentityScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Abbreviated File-Process Case 01 Marco A. and CounterclaimDocument25 pagesAbbreviated File-Process Case 01 Marco A. and CounterclaimScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter X. Precision Shooting From Naval Air PlatformsDocument24 pagesChapter X. Precision Shooting From Naval Air PlatformsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS Mechanical Drawing 2Document7 pagesSYLLABUS Mechanical Drawing 2ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Practical Work The Familiar PDFDocument1 pagePractical Work The Familiar PDFScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- History and Evolution of Reciprocating MotorsDocument32 pagesHistory and Evolution of Reciprocating MotorsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- PH Portfolio Recovery ProposalDocument3 pagesPH Portfolio Recovery ProposalScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Musical Instruments of EuropeDocument3 pagesMusical Instruments of EuropeScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Boxing PDFDocument49 pagesBoxing PDFScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension and Contextual Vocabulary Exercises 4th Middle #8.Document5 pagesReading Comprehension and Contextual Vocabulary Exercises 4th Middle #8.ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Comparative Table of Rationalism and EmpiricismDocument7 pagesComparative Table of Rationalism and EmpiricismScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects GuatemalaDocument20 pagesLegal Aspects GuatemalaScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- iTEP in - House PDFDocument12 pagesiTEP in - House PDFScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade Plan - Block 4 GeographyDocument12 pages5th Grade Plan - Block 4 GeographyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Application of Regulations in The Financial SystemDocument74 pagesApplication of Regulations in The Financial SystemScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Examples of Operant ConditioningDocument1 pageExamples of Operant ConditioningScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Project On Electricity For ChildrenDocument13 pagesProject On Electricity For ChildrenScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Expo22 Daily ExperienceDocument6 pagesExpo22 Daily ExperienceScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Driver's Manual in TexasDocument109 pagesDriver's Manual in TexasScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Types of Banks Based On OwnershipDocument2 pagesTypes of Banks Based On OwnershipScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Laboratory Report 1Document14 pagesChemistry Laboratory Report 1ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Security of Accounting Information SystemsDocument2 pagesSecurity of Accounting Information SystemsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Applied StatisticsDocument209 pagesApplied StatisticsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Vibrational Sound Therapy ManualDocument12 pagesVibrational Sound Therapy ManualScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Event Security ProtocolDocument7 pagesEvent Security ProtocolScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet