Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cerebral Edema
Cerebral Edema
Uploaded by
ScribdTranslationsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cerebral Edema
Cerebral Edema
Uploaded by
ScribdTranslationsCopyright:
Available Formats
Brain edema: causes,
symptoms, diagnosis and
treatment.
Information
Brain edema: causes, symptoms,
diagnosis and treatment.
Swelling of the brain - a dangerous condition that is accompanied by
the accumulation of excess fluid in the tissues of the brain and spinal
cord. This phenomenon threatens very dangerous consequences, as
increased intracranial pressure can cause damage to a particular area of
the cerebral cortex.
Brain swelling and its causes
In fact, this state can be due to several factors. Brain swelling can be
the result of trauma, and occur in the presence of certain diseases. The
following are the most common causes:
traumatic brain injury;
stroke;
diseases involving inflammation of the brain or its membranes,
including meningitis and encephalitis;
brain tumor that grows in size;
anaphylactic shock;
severe intoxication, including drug and alcohol overdose;
serious infectious disease;
some diseases of the cardiovascular system;
burn disease.
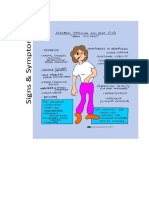
Brain edema: symptoms
This state can be accompanied by a variety of reasons. The main
symptoms depend on the location of edema, its duration and severity.
However, today I decided to allocate three main symptoms:
symptoms associated with increased intracranial pressure -
these include regular raspyrayuschye headaches, feelings of
nausea and vomiting, rarely seizures;
focal symptoms directly related to localized edema. If the
accumulation of fluid puts pressure on one of the parts of the brain,
the symptoms appear relevant. For example, when damaged the
visual center decreases. This group also includes gait, paralysis,
speech problems, etc.;
Stem symptoms are observed in cases where there is swelling in
the brain stem, where important centers of life, including the
centers of heartbeat, breathing, etc. Sometimes in these
conditions there is a violation of the body's thermoregulation,
difficulty breathing, loss of innate reflexes.
Brain edema diagnosis
If the patient is conscious, the doctor first to familiarize himself with
his complaints. However, to establish a precise diagnosis of the
symptoms, additional analyzes and investigations were carried out:
blood;
neurological examination, during which the doctor observes the
presence of unconditioned reflexes, analyzes the mental state and
behavior of the patient;
fundus study also gives the result, especially evident in the area
of optic nerve inflammation;
MRI or CT scan helps determine the size, edema distribution and
location and, therefore, assess the patient's risk to his or her life;
sometimes perform spinal puncture, especially in cases of
suspected infection;
Cerebral angiography - a necessary procedure, to determine the
presence of blood clots and other violations.
Brain edema: treatment
In fact, treatment depends largely on the cause and severity of the
condition. For example, if brain inflammation caused by a bacterial
infection, then antibiotics will be used. However, the therapy includes
some mandatory procedures:
if the basic functions of the nervous system are violated,
including breathing processes and heart rate, then using special
equipment necessary to maintain the patient's normal life
processes;
considered very effective cooling of the brain;
Patients also injected glucose and sodium chloride;
swelling use diuretics that quickly remove excess fluid from the
body, while reducing edema;
and sometimes hormones are used, especially if you want to
reduce the permeability of blood vessels to prevent further
development of edema;
In severe cases, doctors perform craniotomy.
Tsikavenky
Brain edema: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment....
Benign brain tumor, symptoms, diagnosis and...
Benign brain tumor, symptoms, diagnosis and...
What is angioedema? Symptoms, causes, treatment....
Swelling of the brain - signs.
Abrasions - causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment....
Cerebral Ischemia: causes, symptoms, treatment.
Cerebral palsy: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, ...
Causes and symptoms of throat cancer. Diagnosis and
treatment ....
Causes and symptoms of throat cancer. Diagnosis and
treatment ....
Brain cyst, causes and symptoms.
Brain swelling.
Cerebral edema: Causes and
Consequences.
04 April, 2016
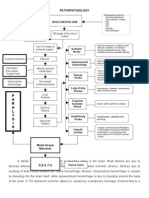
Swelling of the brain, causes and consequences of the emergency of which we will examine in this
article - is a reaction to excessive load, injuries and infections. Typically, this process occurs quickly
enough. Therefore the own and space among them is filled with excess fluid, and the brain as a
result of increases in volume, which, in turn, causes an increase in intracranial pressure,
deterioration of cerebral circulation and leads to the death of cells.
This condition, as you know, requires mandatory and emergency care to avoid serious
consequences or death.
cause of edema
Causes of inflammation of the brain can be different, and are covered, for example, in violation of
cerebral circulation, expressed ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, in traumatic brain injury, in the
presence of intracranial cancer or metastasis of tumors in any place.
inflammatory processes in the brain or
membrane (meningitis or encephalitis), fractures of the cranial vault with damage to the
substance of the brain, as well as common diseases in the form of serious infections,
cardiovascular disorders or severe burns can also cause inflammation of the brain.
In addition, triggering the development of this disease can even be a severe allergic reaction in the
process of anaphylactic shock, or drug and alcohol poisoning.
What is the main danger
edema Swelling of any tissue of the human body - is quite common and is a natural phenomenon,
which usually takes place without any consequences. But the brain is in a confined space with the
dense skull, which cannot increase its volume under pressure of its tissues.
Whatever the cause causes cerebral edema, which ultimately leads to the fact that there is a
compression of its material in a narrow space. This fact carries the greatest danger: neuronal
ischemia is aggravated, increased progression of edema, and at some point lost brain function.
inflammation of the brain in stroke: what
he called
One of the common causes of swelling of such a patient is transferred to them hemorrhagic or
ischemic stroke. Unfortunately, these types of circulatory disorders are almost always accompanied
by the described problem, expressed in varying degrees, and is a kind of indicator of the severity of
the pathological process. Stroke
Ischemic is caused by obstruction of blood flow to particular areas of the brain as a result of blockage
of blood vessels for one reason or another leading to a lack of oxygen, cell death and, as a
consequence, swelling of the brain.
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when bleeding under the shell of the brain becomes the impetus for the
rapid increase in intracranial pressure and therefore causes inflammation of the brain. The reasons
for this type of stroke are usually identical - pressure high blood pressure, stress, physical exertion
that causes blood vessels in the brain to rupture or blood to leak through its walls.
How does edema develop in stroke?
First swelling caused by metabolism (metabolism) in the affected area. In medicine, this
phenomenon is called cytotoxic cerebral edema, and is located mainly in the gray matter. After six
hours, this pathology is joined by vasogenic edema, located in the white matter of the brain. It is
caused by the so-called process propotevanie fluid and proteins from small blood vessels into the
extracellular space by a slowdown of blood flow or stasis (arrest).
simultaneously with such development of cerebral edema and necrosis, which leads to the
accumulation in the intercellular space of osmotically active substances, which cause even greater
production of fluid from the capillary.
Inflammation of the brain in stroke develops very quickly and spontaneously, although it can be
located in the lesion (local inflammation) in one hemisphere (diffuse swelling) in both hemispheres
(generalized edema). It is important to take into account its symptoms, and the time to take
measures, although, of course, in stroke to determine the development of edema is difficult, since the
patient is usually in cloudy consciousness or coma.
signs of brain edema
No matter what causes the classified cause of inflammation of the brain, its symptoms cannot be
considered specific and, therefore, to determine the presence of a dangerous disease in the patient,
focusing only on them is difficult.
In medicine, they are divided into three main groups: symptoms
associated with increased intracranial pressure; Signs
of focal disorders;Signs
they derive pathology.
Typically, cerebral edema (the causes, consequences of which we are considering) is accompanied
by severe headache, nausea and retching - these symptoms can be attributed to signs of intracranial
hypertension.Disorders
Speech, vision, hearing and touch, problems with orientation in space, as well as paresis and
paralysis - are signs of focal anomalies.
cerebral edema, patients often complain of shortness of breath, disturbed breathing, the
development of a feeling of drowsiness, anxiety, increased blood pressure, dizziness develops,
sometimes accompanied by seizures - all signs of cerebral edema brain stem requiring urgent
resuscitation.
Causes of cerebral edema in newborns
We must consider this pathology has just been born children.It causes swelling of the brain that
causes often found in their mother's grave during labor and birth trauma baby.But it can cause birth
defects or acquired diseases.Abscesses, tumors, meningitis, encephalitis, intrauterine hypoxia - all of
which can cause inflammation of the brain in babies.
By the way, during the described pathology in children it is somewhat different than in adults,
because their bodies are still very limited possibility of maintaining the regulation of the vascular tone
of the intracranial pressure and the dynamics of the cerebrospinal fluid.The only salvation for the
child in a Such a situation is especially the connection of the bones of the skull, between which is
either soft cartilage, or gap (fontanels). By the way, this anatomical feature protects the baby from
compression and swelling of the brain, which could reach at any cry crumbs.
Characteristics symptoms of cerebral
edema in babies
Inflammation of the brain in newborns differs fulminant. At the beginning of the pathology the baby
usually becomes sluggish, drowsiness, which may appear convulsions, disconnection of
consciousness. Some children, on the contrary, cause inflammation of the excited state, which is
reflects a constant non-stop crying.
SPRING swells even at rest, the volume of the head increases, the baby appears vomiting, fever.
In newborns with cerebral edema, a characteristic feature of this disease is a very rapid deterioration
of the general condition and, unfortunately, in many cases it ends in death.
Brain inflammation: implications
The sooner a patient with this diagnosis will be provided with fully qualified medical assistance, the
higher his chances of recovery. But recovery is often only partial - it all depends on the severity of the
pathological process.
A consequence is sometimes, for example, the development of epilepsy caused by a violation of the
blood supply to certain areas of the brain. The patient may increase intracranial pressure, which in
turn leads to constant headaches, dizziness, delirium, and even a reduction in social communication
skills.
Many patients with a diagnosis of "inflammation of the brain" to the consequences of the pathology
observed in the adhesions in their ventricles between the shells, or spaces of cerebrospinal fluid,
which leads not only to occasional headaches, but also to a state depression and disorders of
nervous and mental activity.
If the swelling has expanded, it may be the result of brain damage and decreased mental ability.
How do the effects of cerebral edema
manifest in children?
Consequences of reporting illness in children can also be serious, depending on the severity of the
illness.
These include the development of cerebral palsy and hydrocephalus, epilepsy, as well as violations
of the formation of internal organs.Edema
brain in some children can cause problems with speech, as well as coordination of movements.
Moved pathology, unfortunately causes some patients neuro-psychological instability and mental
retardation.
From the above it is clear that inflammation of the brain in children is a very serious pathology that
requires continuous monitoring by a child neurologist and pediatrician, and its duration depends on
the severity of the consequences of this disease.
You might also like
- Reflective Essay-Rexson A. DalanginDocument3 pagesReflective Essay-Rexson A. DalanginRexson Alcantara DalanginNo ratings yet
- Complete Denture ManualDocument23 pagesComplete Denture ManualCitra PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Bundle PDFDocument94 pagesCritical Care Bundle PDFسلطان محمد فوزي سلمانNo ratings yet
- Format - Case Prentation 1Document6 pagesFormat - Case Prentation 1Ej CasareoNo ratings yet
- Critical CareDocument120 pagesCritical CareJoanna Ephraim CruzNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument30 pagesCerebrovascular AccidentRichard Charles UmlasNo ratings yet
- STROKE: Handbook with activities, exercises and mental challengesFrom EverandSTROKE: Handbook with activities, exercises and mental challengesNo ratings yet
- Stoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Document7 pagesStoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Mark Anthony Taña GabiosaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System DiseasesDocument16 pagesNervous System DiseasesShahzad ShameemNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument4 pagesCerebrovascular AccidentRjohn IsiderioNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorDocument18 pagesBrain TumorSKSAIDINESH100% (1)
- Brainstem Stroke SymptomsDocument3 pagesBrainstem Stroke SymptomsMirza AriandiNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Ns-Reeves and SwensonDocument112 pagesDisorders of Ns-Reeves and SwensonSuganya BalachandranNo ratings yet
- Stroke - FAST, Symptoms, Causes, Types, Treatment, PreventionDocument20 pagesStroke - FAST, Symptoms, Causes, Types, Treatment, PreventionMustafa AL ShlashNo ratings yet
- Neurological System DisordersDocument41 pagesNeurological System DisordersJoanna Ephraim CruzNo ratings yet
- Stroke 1Document7 pagesStroke 1mildred alidonNo ratings yet
- Hemiplegia Resource Book ModifiedDocument60 pagesHemiplegia Resource Book ModifiedAnonymous czrvb3hNo ratings yet
- Focus On StrokeDocument92 pagesFocus On StrokeDIAH RETNO WULAN100% (2)
- PBLDocument6 pagesPBLzuhaldarwisNo ratings yet
- Stroke Causes: SkullDocument10 pagesStroke Causes: SkullMohd Farid Bin RosliNo ratings yet
- AneurysmDocument7 pagesAneurysmLillabinNo ratings yet
- Cerebral EdemaDocument5 pagesCerebral EdemaSimranNo ratings yet
- Meningitides, Which Are Responsible For The Majority of Cases in Bacterial Meningitis of Adults. in AsepticDocument18 pagesMeningitides, Which Are Responsible For The Majority of Cases in Bacterial Meningitis of Adults. in AsepticNuay LaoNo ratings yet
- Stroke: Cerebrovascular Accident: The Sudden Death of Some Brain Cells Due To Lack of Oxygen WhenDocument7 pagesStroke: Cerebrovascular Accident: The Sudden Death of Some Brain Cells Due To Lack of Oxygen WhenRose SalviejoNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesCentral Nervous SystemJT RoseguardNo ratings yet
- Brain Stroke 2.0Document17 pagesBrain Stroke 2.0krutarthgohil21No ratings yet
- 13 Neurologic Diseases and ConditionsDocument3 pages13 Neurologic Diseases and ConditionsNeida Caro-BooneNo ratings yet
- DisordersDocument3 pagesDisordersDaniel GitauNo ratings yet
- Human Body QuizDocument9 pagesHuman Body QuizAnoshaNo ratings yet
- Stroke: DefinitionDocument8 pagesStroke: DefinitionKasuganti koteshwar raoNo ratings yet
- Syncope (Medicine)Document7 pagesSyncope (Medicine)Wira SentanuNo ratings yet
- Ayeni MotunrayoDocument5 pagesAyeni Motunrayoayenimotunrayo40No ratings yet
- Brain and Cognition 2 NotesDocument6 pagesBrain and Cognition 2 Noteskimnoij25No ratings yet
- Classification of Hemorrhagic StrokesDocument7 pagesClassification of Hemorrhagic StrokesRavinr9No ratings yet
- Epidural Hematom FersiDocument11 pagesEpidural Hematom FersiMuhammad SolehNo ratings yet
- Examples: A Drunk Friend Walking Out To His Car With Keys in Hand, A Drunk Couple Heading Into ADocument8 pagesExamples: A Drunk Friend Walking Out To His Car With Keys in Hand, A Drunk Couple Heading Into ASitti NaifaNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument4 pagesHemorrhagic StrokeIamanamay TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Disease of Nervous System Lect 2Document62 pagesDisease of Nervous System Lect 2Monirul IslamNo ratings yet
- Care of Unconscious PatientDocument6 pagesCare of Unconscious PatientSuparna SinghaNo ratings yet
- Wala Pa Conclusion ToDocument17 pagesWala Pa Conclusion ToLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- What Is A StrokeDocument5 pagesWhat Is A StrokeLintsuNo ratings yet
- Brain Attack: NR-75D Diana Diaz RN, MSDocument66 pagesBrain Attack: NR-75D Diana Diaz RN, MSJoshua SmithNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident: Types Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Outlook PreventionDocument6 pagesCerebrovascular Accident: Types Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Outlook PreventionAlfrien Ivanovich LarchsonNo ratings yet
- Definition:: IschemicDocument4 pagesDefinition:: IschemicKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Cerebral InfarctionDocument2 pagesCerebral InfarctionMarie Aurora Gielbert MarianoNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Neurologic Deficit or RIND.: Amaurosis FugaxDocument11 pagesIschemic Neurologic Deficit or RIND.: Amaurosis FugaxErwin BrionesNo ratings yet
- Mathias Blessings AinaDocument16 pagesMathias Blessings AinamikealsonjuwonNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation in Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument19 pagesRehabilitation in Cerebrovascular AccidentIsaac OmwengaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accidentgeohanna_mariefNo ratings yet
- CVABDocument4 pagesCVABRobby BanjarNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Evaluation of Stroke - UpToDateDocument57 pagesOverview of The Evaluation of Stroke - UpToDateclarissa suryaNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular DiseaseDocument37 pagesHemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular Diseasejbvaldez100% (1)
- Neurogenic Shock PresentationDocument9 pagesNeurogenic Shock PresentationrohitNo ratings yet
- Case 1 FinalDocument70 pagesCase 1 FinalMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Neuropathology Autopsy Practice Post Mortem Examination in Cerebrovascular Disease StrokeDocument15 pagesNeuropathology Autopsy Practice Post Mortem Examination in Cerebrovascular Disease Strokelisboa_rodriNo ratings yet
- Stroke: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDocument9 pagesStroke: Causes, Incidence, and Risk Factorsthona_shirleneNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accidentzairajoy07No ratings yet
- Stupor and Coma in Adults: Author: Section Editors: Deputy EditorDocument30 pagesStupor and Coma in Adults: Author: Section Editors: Deputy EditorYessenia BarrantesNo ratings yet
- Causes: Aneurysm Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Encephalitis HydrocephalusDocument12 pagesCauses: Aneurysm Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Encephalitis Hydrocephalusemuelle12No ratings yet
- Cerebral Edema, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCerebral Edema, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- History and Evolution of Reciprocating MotorsDocument32 pagesHistory and Evolution of Reciprocating MotorsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Abbreviated File-Process Case 01 Marco A. and CounterclaimDocument25 pagesAbbreviated File-Process Case 01 Marco A. and CounterclaimScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Retirement Instructions Unemployment PorvenirDocument6 pagesRetirement Instructions Unemployment PorvenirScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Boxing PDFDocument49 pagesBoxing PDFScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Application of Copper Sulfate in AquacultureDocument2 pagesApplication of Copper Sulfate in AquacultureScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Natural History of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument49 pagesNatural History of Parkinson's DiseaseScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Practical Work The Familiar PDFDocument1 pagePractical Work The Familiar PDFScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter X. Precision Shooting From Naval Air PlatformsDocument24 pagesChapter X. Precision Shooting From Naval Air PlatformsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Comparative Table of Rationalism and EmpiricismDocument7 pagesComparative Table of Rationalism and EmpiricismScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS Mechanical Drawing 2Document7 pagesSYLLABUS Mechanical Drawing 2ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Tourist PlanningDocument39 pagesTourist PlanningScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Ethnicity, Language and IdentityDocument4 pagesEthnicity, Language and IdentityScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Musical Instruments of EuropeDocument3 pagesMusical Instruments of EuropeScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Expo22 Daily ExperienceDocument6 pagesExpo22 Daily ExperienceScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade Plan - Block 4 GeographyDocument12 pages5th Grade Plan - Block 4 GeographyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Laboratory Report 1Document14 pagesChemistry Laboratory Report 1ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Examples of Operant ConditioningDocument1 pageExamples of Operant ConditioningScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Driver's Manual in TexasDocument109 pagesDriver's Manual in TexasScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- iTEP in - House PDFDocument12 pagesiTEP in - House PDFScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension and Contextual Vocabulary Exercises 4th Middle #8.Document5 pagesReading Comprehension and Contextual Vocabulary Exercises 4th Middle #8.ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects GuatemalaDocument20 pagesLegal Aspects GuatemalaScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Sixth Grade Reading Comprehension AssessmentDocument8 pagesSixth Grade Reading Comprehension AssessmentScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- PH Portfolio Recovery ProposalDocument3 pagesPH Portfolio Recovery ProposalScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Project On Electricity For ChildrenDocument13 pagesProject On Electricity For ChildrenScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Application of Regulations in The Financial SystemDocument74 pagesApplication of Regulations in The Financial SystemScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Types of Banks Based On OwnershipDocument2 pagesTypes of Banks Based On OwnershipScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Security of Accounting Information SystemsDocument2 pagesSecurity of Accounting Information SystemsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Applied StatisticsDocument209 pagesApplied StatisticsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Event Security ProtocolDocument7 pagesEvent Security ProtocolScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Vibrational Sound Therapy ManualDocument12 pagesVibrational Sound Therapy ManualScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- TechDS DV1800AP-DV28500WPDocument4 pagesTechDS DV1800AP-DV28500WPHendri KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet Avoil FCDocument4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet Avoil FCfs1640No ratings yet
- Sec 3 Welding Imperfections (Defects)Document31 pagesSec 3 Welding Imperfections (Defects)Abdullah100% (1)
- © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaDocument154 pages© The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaJattu TatiNo ratings yet
- Royal College Grade 07 English Second Term Paper (221119 110652Document10 pagesRoyal College Grade 07 English Second Term Paper (221119 110652sandeepsubasinghe23No ratings yet
- Maze ProblemDocument2 pagesMaze ProblemBhuvaneswari RamamurthyNo ratings yet
- Past Tenses ReviewDocument9 pagesPast Tenses ReviewmariaNo ratings yet
- Usg Epsilon1 enDocument53 pagesUsg Epsilon1 enTonatiuh RamirezNo ratings yet
- CTA Pocket CardDocument2 pagesCTA Pocket CardBreitbart News100% (1)
- Divyesh ResumeDocument2 pagesDivyesh ResumeDivyeshNo ratings yet
- MESFETDocument2 pagesMESFETKarthik KichuNo ratings yet
- TR - 2D Game Art Development NC IIIDocument66 pagesTR - 2D Game Art Development NC IIIfor pokeNo ratings yet
- Touch FootballDocument75 pagesTouch FootballIon Balda MarinNo ratings yet
- Sansulin R Suspensi Injeksi 100 IU, ML - Rekombinan Insulin Manusia - DKI0708100443A1 - 2016Document2 pagesSansulin R Suspensi Injeksi 100 IU, ML - Rekombinan Insulin Manusia - DKI0708100443A1 - 2016Yessi VirginiaNo ratings yet
- MBA Global Management Technische Hochschule Ingolstadt - IngolstadtDocument7 pagesMBA Global Management Technische Hochschule Ingolstadt - IngolstadtHieu NguyenNo ratings yet
- ToR For Individual Film Makers On LTADocument6 pagesToR For Individual Film Makers On LTARoshil VermaNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow TemplateDocument9 pagesCash Flow Templatealdi ruNo ratings yet
- Approval Sheet and Evaluation FormDocument8 pagesApproval Sheet and Evaluation FormDannet Frondozo DelmonteNo ratings yet
- CDP 22 FinalDocument8 pagesCDP 22 FinalAnonymous GMUQYq8No ratings yet
- CESTARO - Plan-Tonificacion Inicial MujerDocument14 pagesCESTARO - Plan-Tonificacion Inicial MujerLucas Javier VidalNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) in Power SuppliesDocument41 pagesElectromagnetic Interference (EMI) in Power SuppliesAmarnath M DamodaranNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Loss - Bir.or - Car.1.2020Document1 pageAffidavit of Loss - Bir.or - Car.1.2020black stalkerNo ratings yet
- TLNB SeriesRules 7.35Document24 pagesTLNB SeriesRules 7.35Pan WojtekNo ratings yet
- MSP 430 G 2553Document75 pagesMSP 430 G 2553diosb3No ratings yet
- OpAudCh02 CBET 01 501E ToraldeMa - KristineE.Document4 pagesOpAudCh02 CBET 01 501E ToraldeMa - KristineE.Kristine Esplana ToraldeNo ratings yet
- Ni Based Superalloy: Casting Technology, Metallurgy, Development, Properties and ApplicationsDocument46 pagesNi Based Superalloy: Casting Technology, Metallurgy, Development, Properties and ApplicationsffazlaliNo ratings yet
- Amazon Intern Job DescriptionsDocument15 pagesAmazon Intern Job Descriptionschirag_dceNo ratings yet
- PHP Lab ProgrammsDocument10 pagesPHP Lab Programmsakshaya100% (1)
- Design Thinking WorksheetDocument5 pagesDesign Thinking Worksheetsujal patel100% (1)