Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer Key - Carboxylic Acid-18-6-24
Answer Key - Carboxylic Acid-18-6-24
Uploaded by
HARSHIL GAMERCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer Key - Carboxylic Acid-18-6-24
Answer Key - Carboxylic Acid-18-6-24
Uploaded by
HARSHIL GAMERCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer key – Carboxylic Acid – 18-6-24 Mercury chloride –
1 a 2 b 3 d 4 c 5 a
6 b 7 a 8 d 9 a 10 d
11 c 12 b 13 c 14 d 15 c 25. (a) Activated charcoal adsorbed the impurity of
16 c 17 c acetic acid by which the concentration of acetic
acid solution decrease.
18. (a) Phenol is a weaker acid than carboxylic
acids. 26. (d) Intermolecular hydrogen bonding leads to
dimerisation of carboxylic acid in non-
aqueous solvents.
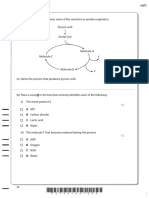
19. (a)
27. (c)
evolve with brisk effervescence.
28. (b) It is known as Schotten Baumann reaction.
20. (d)
29. (a) Due to –I effect of three F atom
O
is a strong acid.
COOH || CONH2
21. (a) +NH3 OH OCOCH3
COOH C COOH COOH COOH
||
30. (d) + (CH3CO)2O +
22. (b)
Salicylic acid Acetic anhydride Aspirin or
Acetyl
23. (a)
24. (d) Tollen’s reagent -
Fehling solution –
You might also like
- Module 7 KISS Notes (HSC Chemistry)Document15 pagesModule 7 KISS Notes (HSC Chemistry)rsorani8No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Chemistry AssignmentDocument28 pagesBiomolecules Chemistry AssignmentAmarendra Shukla74% (243)
- Common Names of Organic CompoundsDocument10 pagesCommon Names of Organic CompoundsGear Less Gamer65% (17)
- 2019 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Zhonghua Secondary AnswerDocument10 pages2019 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Zhonghua Secondary AnswerUZAIR MAHBUB BHUYAINNo ratings yet
- ASTM B201 (2014r)Document3 pagesASTM B201 (2014r)PubcrawlNo ratings yet
- 18 Acids and Esters NotesDocument13 pages18 Acids and Esters NotesSherazNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Feb 2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 05 Feb 2024krishrajput88888888No ratings yet
- 18 Acids and Esters NotesDocument13 pages18 Acids and Esters NotesAwais BodlaNo ratings yet
- Compounds of Nitrogen: Formative Worksheet Conceptive WorksheetDocument4 pagesCompounds of Nitrogen: Formative Worksheet Conceptive WorksheetMEGHNA BAGCHINo ratings yet
- Formula and EquationsDocument28 pagesFormula and EquationsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- 5 The Diagram Below Summarises Some of The Reactions in Aerobic RespirationDocument3 pages5 The Diagram Below Summarises Some of The Reactions in Aerobic RespirationEricka AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Ak Carboxylic AcidDocument2 pagesAk Carboxylic AcidsuryaisonemailNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Allen QuestionsDocument20 pagesOrganic Chemistry Allen Questionstiruvalarnayatty100% (1)
- Common Names of Organic CompoundsDocument21 pagesCommon Names of Organic CompoundsAnujNo ratings yet
- Harpic Study PDFDocument12 pagesHarpic Study PDFbala krishnaNo ratings yet
- Loudon 5 Ech 20 Sec 02Document2 pagesLoudon 5 Ech 20 Sec 02Imad MadaniNo ratings yet
- Case Based Question Aldehyde Ketones CarboxylicDocument4 pagesCase Based Question Aldehyde Ketones Carboxylicjiyakhurana243No ratings yet
- Strong & Weak Acids - pH, pKa, Kw 2 QPDocument13 pagesStrong & Weak Acids - pH, pKa, Kw 2 QPangelachan1853spcsNo ratings yet
- RQ Group Tuition: Pre-Board Examination 2015Document7 pagesRQ Group Tuition: Pre-Board Examination 2015Riders RoughNo ratings yet
- 08 S and P Block Elements Sol. Final EDocument20 pages08 S and P Block Elements Sol. Final EgnkstarNo ratings yet
- TB ch16 Carboxylic Acids Esters and Other Acid DerivativesDocument15 pagesTB ch16 Carboxylic Acids Esters and Other Acid Derivativeslexfred55No ratings yet
- EGSB ReactorDocument48 pagesEGSB ReactorNanofold100% (1)
- Structured Questions: CC CC C S S S S CC CDocument3 pagesStructured Questions: CC CC C S S S S CC Ctjun kit minNo ratings yet
- CH 12. Carboxylic Acids - Derivatives - Carbonyl Compounds TatvaDocument47 pagesCH 12. Carboxylic Acids - Derivatives - Carbonyl Compounds TatvaSajag GargNo ratings yet
- 03-Ionic equilibrium-Sol-Final-EDocument19 pages03-Ionic equilibrium-Sol-Final-ESubbu SarabuNo ratings yet
- SSLC 2024 Chemistry Answer Kery EM by Ebrabim Vathimattom SirDocument2 pagesSSLC 2024 Chemistry Answer Kery EM by Ebrabim Vathimattom Sirnaaji8824No ratings yet
- Dispersion For CeramicDocument5 pagesDispersion For CeramicThanhNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids, Esters, and Other Acid Derivatives: Test BankDocument14 pagesCarboxylic Acids, Esters, and Other Acid Derivatives: Test BankAda VessaliusNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pagesCarboxylic AcidssuryaisonemailNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Dec 16, 2022Document4 pagesAdobe Scan Dec 16, 2022Pankaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Grade X-ScienceDocument3 pagesAnswer Key Grade X-ScienceAkshithaNo ratings yet
- My TestDocument39 pagesMy TestkrisnuNo ratings yet
- Acid Base and Salt: 1. Objective QuestionsDocument8 pagesAcid Base and Salt: 1. Objective QuestionsKabir MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- 13 - BhattiAcademy - Com - Chemistry - 5. Scholar Series (Obj)Document11 pages13 - BhattiAcademy - Com - Chemistry - 5. Scholar Series (Obj)Amir FarooqNo ratings yet
- 02-Carboxylic Acids and Their derivatives-Que.-Final-EDocument13 pages02-Carboxylic Acids and Their derivatives-Que.-Final-EAbhishek RavirajNo ratings yet
- Organic Chmeistry Chapter 10Document9 pagesOrganic Chmeistry Chapter 10yoojh100No ratings yet
- Asnwer Key Sci-9Document5 pagesAsnwer Key Sci-9Ferna Joy LapinigNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Acetic AcidDocument6 pagesLecture 5 Acetic AcidYan LaksanaNo ratings yet
- X - CH - 4 - Carbon and Its CompoundDocument16 pagesX - CH - 4 - Carbon and Its CompoundMathanNo ratings yet
- S FZB MCKP PHAVR5 T4 J900Document6 pagesS FZB MCKP PHAVR5 T4 J900Damn GoodNo ratings yet
- 02 - Carboxylic Acid (Theory) Module-5Document12 pages02 - Carboxylic Acid (Theory) Module-5Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 WorksheetDocument1 page1 WorksheetJuan Ramón González RubioNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ObjectiveDocument7 pagesChemistry Objectivekargil defence academyNo ratings yet
- IAS Mains Mechanical Engineering 2001Document7 pagesIAS Mains Mechanical Engineering 2001ChetanmdNo ratings yet
- Skema Kimia K123 Trial SPM SBP 2019 PDFDocument39 pagesSkema Kimia K123 Trial SPM SBP 2019 PDFSiti Hajar Abd Hamid100% (1)
- 17-8-23 Q XI Prep.Document1 page17-8-23 Q XI Prep.tomod26971No ratings yet
- Ss 1 First Term Chemistry ExaminationDocument3 pagesSs 1 First Term Chemistry ExaminationUzoma ObasiNo ratings yet
- AQA A Level Chem CH30 Practice Question AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA A Level Chem CH30 Practice Question AnswersMahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- CET Org Chem Carbonyl CompoundsDocument10 pagesCET Org Chem Carbonyl CompoundsSourabh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Tybsc-Cs Sem5 Ai Apr19Document2 pagesTybsc-Cs Sem5 Ai Apr19riyuc0456No ratings yet
- 0 PM 8 Lbyqslmw QHe 2 WDL TDocument8 pages0 PM 8 Lbyqslmw QHe 2 WDL TShashwat Shaw 9H 35No ratings yet
- Chemistry Full BookDocument4 pagesChemistry Full BookUmer TariqNo ratings yet
- A A AN N NSSSW W Weeer R RSSS: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesA A AN N NSSSW W Weeer R RSSS: Multiple Choice QuestionsAashi SinghNo ratings yet
- At The End of The Topic, Students Should Be Able To:: Tutorial 19: Amino AcidsDocument5 pagesAt The End of The Topic, Students Should Be Able To:: Tutorial 19: Amino AcidsizabelNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases QP - 2Document48 pagesAcids Bases QP - 2wnh8wyq97gNo ratings yet
- 2021 SEM 4 CC 9 OrganicDocument3 pages2021 SEM 4 CC 9 OrganicGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Please Check Whether You Have Got The Right Question PaperDocument1 pagePlease Check Whether You Have Got The Right Question PaperPranesh JewalikarNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document5 pagesCH 12Himanshu SangwanNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesOrganic ChemistryAndrea Jarani LinezoNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Questions: Linkage) (NDocument4 pagesCritical Thinking Questions: Linkage) (NAbhishek RavirajNo ratings yet
- Closed Form Expressions For Monoprotic Weak Acid Aqueous SolutionsDocument9 pagesClosed Form Expressions For Monoprotic Weak Acid Aqueous Solutionslilvk12No ratings yet
- Novel Carbon Materials and Composites: Synthesis, Properties and ApplicationsFrom EverandNovel Carbon Materials and Composites: Synthesis, Properties and ApplicationsXin JiangNo ratings yet
- Ans & Solution - P-Block ElementDocument22 pagesAns & Solution - P-Block ElementHARSHIL GAMERNo ratings yet
- Ans & Sol - Sound Wave - 18-6-24Document10 pagesAns & Sol - Sound Wave - 18-6-24HARSHIL GAMERNo ratings yet
- ANSWER KEY - Gravitation - 11-6-2024Document12 pagesANSWER KEY - Gravitation - 11-6-2024HARSHIL GAMERNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - X-Ray - 12-6-24Document4 pagesAnswer Key - X-Ray - 12-6-24HARSHIL GAMERNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - Transverse Wave-15-6-24Document9 pagesAnswer Key - Transverse Wave-15-6-24HARSHIL GAMERNo ratings yet
- Ans & Sol - Solution - Chem - 24-6-24Document1 pageAns & Sol - Solution - Chem - 24-6-24HARSHIL GAMERNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument1 pagePresentationHARSHIL GAMERNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals Revision NotesDocument22 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals Revision Notesrohan thakurNo ratings yet
- Steel Making - Open-Hearth TehniqueDocument5 pagesSteel Making - Open-Hearth TehniqueMarcelo Rodriguez FujimotoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Membrane ProcessesDocument26 pagesChapter 13: Membrane ProcessesJason ConnorNo ratings yet
- TRPlast BrochureDocument8 pagesTRPlast Brochureluis hernandezNo ratings yet
- Exercises of Analytical Chemistry - Part 1: A. Stoichiometry ReminderDocument16 pagesExercises of Analytical Chemistry - Part 1: A. Stoichiometry ReminderTeresa RiosNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Agra: Chemistry ProjectDocument14 pagesDelhi Public School Agra: Chemistry Projectkrish kanteNo ratings yet
- Pptim 170504095620 PDFDocument31 pagesPptim 170504095620 PDFashoku24007No ratings yet
- Sublimation and RecrystallizationDocument4 pagesSublimation and RecrystallizationAIRAH SALALIMANo ratings yet
- The Big TEGO. Products Services Data Sheets-75-150-16!76!31-61Document31 pagesThe Big TEGO. Products Services Data Sheets-75-150-16!76!31-61DWI RAHMASARI FATMAWATINo ratings yet
- What Are Synthetic Resins Applications and UsesDocument11 pagesWhat Are Synthetic Resins Applications and UsesBansal Trading CompanyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15application of Aqueous EquilibriaDocument5 pagesChapter 15application of Aqueous EquilibriaKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 - Post Lab QuestionsDocument3 pagesMODULE 2 - Post Lab QuestionsAnne Therese / Annie KanaanNo ratings yet
- MaterialeManoperaUtilajeTransport PDFDocument259 pagesMaterialeManoperaUtilajeTransport PDFMihai SchiopuNo ratings yet
- Hemipleat Nooval Oval To Round Replacement Cartridge enDocument2 pagesHemipleat Nooval Oval To Round Replacement Cartridge enherysyam1980No ratings yet
- Chlorine TabletsDocument6 pagesChlorine TabletsNobelion WolfNo ratings yet
- B OCR A Chemistry 1st Year Specification PointsDocument23 pagesB OCR A Chemistry 1st Year Specification PointsAbdiNo ratings yet
- Full Chemistry NotesDocument21 pagesFull Chemistry NotesluckybuddyNo ratings yet
- A 105 Vs A 350Document3 pagesA 105 Vs A 350shNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete - History, Properties & Durability PDFDocument5 pagesReinforced Concrete - History, Properties & Durability PDFLvisionNo ratings yet
- Shriver-5thEd-Answers To Self Tests and ExercisesDocument50 pagesShriver-5thEd-Answers To Self Tests and ExercisesJuan E SotoNo ratings yet
- Captex 300 TDS I-10Document2 pagesCaptex 300 TDS I-10Erik SteinbergNo ratings yet
- CCB 231 Supp ExamDocument6 pagesCCB 231 Supp ExamTumisang100% (1)
- Vanillin Production From Lignin and Its Use As A Renewable ChemicalDocument24 pagesVanillin Production From Lignin and Its Use As A Renewable ChemicalMary Cristel de LeonNo ratings yet
- Reinolds Caffenol RecipesDocument1 pageReinolds Caffenol RecipesvimmariNo ratings yet
- Base Stock Study ComparisonDocument43 pagesBase Stock Study ComparisonChristian CotteNo ratings yet
- FiloSeal+HD FIREDocument5 pagesFiloSeal+HD FIREMoeen Iqbal ShahNo ratings yet
- Kalviexpress Che Name Reaction.1pdfDocument42 pagesKalviexpress Che Name Reaction.1pdfYashveer RaiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional Isolasi DNADocument6 pagesJurnal Internasional Isolasi DNAGregorius SimbolonNo ratings yet