Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jess 402
Jess 402
Uploaded by
VNR HeroCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jess 402
Jess 402
Uploaded by
VNR HeroCopyright:
Available Formats
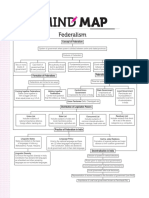
Federalism
Overview
Chapter 2
In the previous chapter, we noted that vertical division of power among
different levels of government is one of the major forms of power-sharing
in modern democracies. In this chapter, we focus on this form of power-
sharing. It is most commonly referred to as federalism. We begin by
describing federalism in general terms. The rest of the chapter tries to
understand the theory and practice of federalism in India. A discussion
of the federal constitutional provisions is followed by an analysis of the
policies and politics that has strengthened federalism in practice. Towards
the end of the chapter, we turn to the local government, a new and third
tier of Indian federalism.
Federalism
2024-25 13
Chapter 2.indd 13 08-04-2022 12:30:48
What is federalism?
Let us get back to the contrast to be, for all practical purposes, a
between Belgium and Sri Lanka unitary system where the national
that we saw in the last chapter. You government has all the powers.
would recall that one of the key Tamil leaders want Sri Lanka to
changes made in the Constitution become a federal system.
of Belgium was to reduce the
Federalism is a system of
power of the Central Government
I am confused.
government in which the power is
and to give these powers to the
What do we divided between a central authority
regional governments. Regional
call the Indian and various constituent units of the
governments existed in Belgium
government? Is it country. Usually, a federation has
even earlier. They had their roles
Union, Federal or and powers. But all these powers two levels of government. One is the
Central? were given to these governments government for the entire country
and could be withdrawn by the that is usually responsible for a
Central Government. The change few subjects of common national
that took place in 1993 was that the interest. The others are governments
regional governments were given at the level of provinces or states
constitutional powers that were that look after much of the day-
no longer dependent on the central to-day administering of their state.
government. Thus, Belgium shifted Both these levels of governments
from a unitary to a federal form of enjoy their power independent of
government. Sri Lanka continues the other.
Federal
political systems
Germany Russia
Canada
Belgium
Austria
Switzerland
United States
of America Spain
Bosnia and Pakistan
Herzegovina
St. Kitts India
Mexico and Nevis Nigeria Pacific Ocean
United
Venezuela Arab
Ethiopia
D e m o c ra t i c Po l i t i c s
Emirates
Atlantic Comoros Malaysia
Pacific Ocean Brazil Ocean Indian
Ocean
Micronesia Australia
Argentina
South Africa
Source: Montreal and Kingston, Handbook of Federal Countries: 2002, McGill-Queen’s University Press, 2002.
Though only 25 of the world’s 193 countries have federal political systems, their citizens make up 40 per cent of the
world’s population. Most of the large countries of the world are federations. Can you notice an exception to this rule in
this map?
2024-25
14
Chapter 2.indd 14 08-04-2022 12:30:50
In this sense, federations are 7 The federal system thus has dual
contrasted with unitary governments. objectives: to safeguard and promote
Under the unitary system, either unity of the country, while at the
there is only one level of government same time accommodate regional
or the sub-units are subordinate to diversity. Therefore, two aspects
the central government. The central are crucial for the institutions and
government can pass on orders to the practice of federalism. Governments
provincial or the local government. at different levels should agree to If federalism
But in a federal system, the central some rules of power-sharing. They works only in
government cannot order the state should also trust that each would big countries,
government to do something. State abide by its part of the agreement. why did Belgium
government has powers of its own An ideal federal system has both adopt it?
for which it is not answerable aspects : mutual trust and agreement
to the central government. Both
to live together.
these governments are separately
answerable to the people. The exact balance of power
between the central and the state
Let us look at some of the key
government varies from one
features of federalism :
federation to another. This balance
1 There are two or more levels (or
depends mainly on the historical
tiers) of government.
context in which the federation was
2 Different tiers of government
formed. There are two kinds of routes
govern the same citizens, but
through which federations have been
each tier has its own jurisdiction
formed. The first route involves
in specific matters of legislation,
independent States coming together
taxation and administration.
on their own to form a bigger unit,
3 The jurisdictions of the respective
so that by pooling sovereignty and
levels or tiers of government are
specified in the constitution. So the retaining identity, they can increase
existence and authority of each tier their security. This type of ‘coming
of government is constitutionally together’ federations include the
guaranteed. USA, Switzerland and Australia. In
4 The fundamental provisions this first category of federations, all
of the constitution cannot be the constituent States usually have
unilaterally changed by one level of equal power and are strong vis-à-vis
government. Such changes require the federal government.
the consent of both the levels of The second route is where a
government. large country decides to divide its
5 Courts have the power to power between the constituent
interpret the constitution and States and the national government.
the powers of different levels of India, Spain and Belgium are
government. The highest court examples of this kind of ‘holding Jurisdiction: The
acts as an umpire if disputes arise together’ federations. In this second area over which
between different levels of category, the Central Government
Federalism
someone has legal
government in the exercise of their tends to be more powerful vis-à- authority. The area
respective powers. vis the States. Very often different may be defined in
terms of geographical
6 Sources of revenue for each level constituent units of the federation boundaries or in terms
of government are clearly specified have unequal powers. Some units of certain kinds of
to ensure its financial autonomy. are granted special powers. subjects.
2024-25 15
Chapter 2.indd 15 08-04-2022 12:30:50
Some Nepalese citizens were discussing the proposals on the
adoption of federalism in their new constitution. This is what some of
them said:
Khag Raj: I don’t like federalism. It would lead to reservation of seats for
different caste groups as in India.
Sarita: Ours in not a very big country. We don’t need federalism.
Babu Lal: I am hopeful that the Terai areas will get more autonomy if they get
their own state government.
Ram Ganesh: I like federalism because it will mean that powers that were earlier
enjoyed by the king will now be exercised by our elected representatives.
If you were participating in this conversation, what would be your response to each
of these? Which of these reflect a wrong understanding of what federalism is?
What makes India a federal country?
What makes India a federal country?
in the form of Panchayats and
We have earlier seen how small Municipalities. As in any federation,
countries like Belgium and Sri Lanka these different tiers enjoy separate
face so many problems of managing jurisdiction. The Constitution
diversity. What about a vast country clearly provided a three-fold
like India, with so many languages, distribution of legislative powers
religions and regions? What are between the Union Government
the power sharing arrangements in and the State Governments. Thus,
our country? it contains three lists:
Let us begin with the Constitution. Union List includes subjects
India had emerged as an independent of national importance, such as
nation after a painful and bloody defence of the country, foreign
Isn’t that partition. Soon after Independence, affairs, banking, communications
strange? Did several princely states became a part and currency. They are included
our constitution of the country. The Constitution in this list because we need a
makers not declared India as a Union of States. uniform policy on these matters
know about Although it did not use the word throughout the country. The Union
federalism? Or federation, the Indian Union is based Government alone can make laws
did they wish on the principles of federalism. relating to the subjects mentioned
to avoid talking in the Union List.
Let us go back to the seven
about it? State List contains subjects
features of federalism mentioned
D e m o c ra t i c Po l i t i c s
above. We can see that all these of State and local importance,
features apply to the provisions such as police, trade, commerce,
of the Indian Constitution. The agriculture and irrigation. The State
Constitution originally provided Governments alone can make laws
for a two-tier system of government, relating to the subjects mentioned
the Union Government or what in the State List.
we call the Central Government, C o nc ur r ent List includes
representing the Union of India subjects of common interest to
and the State governments. Later, both the Union Government as
a third tier of federalism was added well as the State Governments, such
2024-25
16
Chapter 2.indd 16 08-04-2022 12:30:52
as education, forest, trade unions, There are some units of the
marriage, adoption and succession. Indian Union which enjoy very little
Both the Union as well as the State power. These are areas which are
Governments can make laws on too small to become an independent
the subjects mentioned in this list. State but which could not be merged
If their laws conflict with each with any of the existing States.
other, the law made by the Union These areas, like Chandigarh, or
If agriculture and
Government will prevail. Lakshadweep or the capital city of
commerce are
What about subjects that do not Delhi, are called Union Territories.
state subjects,
fall in any of the three lists? Or subjects These territories do not have the
why do we have
like computer software that came up powers of a State. The Central
ministers of
after the constitution was made? Government has special powers in
agriculture and
According to our constitution, the running these areas.
commerce in the
Union Government has the power to This sharing of power between Union cabinet?
legislate on these ‘residuary’ subjects. the Union Government and the State
We noted above that most Governments is basic to the structure
federations that are formed by of the Constitution. It is not easy to
‘holding together’ do not give equal make changes to this power sharing
power to its constituent units. Thus, arrangement. The Parliament cannot
all States in the Indian Union do not on its own change this arrangement.
have identical powers. Some States Any change to it has to be first passed
enjoy a special status. States such by both the Houses of Parliament
as Assam, Nagaland, Arunachal with at least two-thirds majority.
Pradesh and Mizoram enjoy special Then it has to be ratified by the
powers under certain provisions of legislatures of at least half of the
the Constitution of India (Article total States.
371) due to their peculiar social The judiciary plays an important
and historical circumstances. These role in overseeing the implementation
special powers are especially enjoyed of constitutional provisions and
in relation to the protection of procedures. In case of any dispute
land rights of indigenous peoples, about the division of powers, the
their culture and also preferential High Courts and the Supreme Court
employment in government services. make a decision. The Union and
Indians who are not permanent State Governments have the power
residents of this State cannot buy to raise resources by levying taxes in
land or house here. Similar special order to carry on the government
provisions exist for some other States and the responsibilities assigned to
of India as well. each of them.
Listen to one national and one regional news bulletin broadcast by All India
Federalism
Radio daily for one week. Make a list of news items related to government
policies or decisions by classifying these into the following categories:
News items that relate only to the Central Government,
News items that relate only to your or any other State Government,
News items about the relationship between the Central and State Governments.
2024-25 17
Chapter 2.indd 17 08-04-2022 12:30:53
Pokharan, the place where India conducted its nuclear tests, lies
in Rajasthan. Suppose the Government of Rajasthan was opposed to
the Central Government’s nuclear policy, could it prevent the Government
of India from conducting the nuclear tests?
Suppose the Government of Sikkim plans to introduce new textbooks in its
schools. But the Union Government does not like the style and content of the new
textbooks. In that case, does the state government need to take permission from
the Union Government before these textbooks can be launched?
Suppose the Chief Ministers of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Orissa have
different policies on how their state police should respond to the naxalites. Can the
Prime Minister of India intervene and pass an order that all the Chief Ministers will
have to obey?
D e m o c ra t i c Po l i t i c s
2024-25
18
Chapter 2.indd 18 08-04-2022 12:30:55
How is federalism practised?
Constitutional provisions are If you look at the political map of
necessary for the success of federalism India when it began its journey as a
but these are not sufficient. If the democracy in 1947 and that of 2019,
federal experiment has succeeded you will be surprised by the extent
in India, it is not merely because of of the changes. Many old States have
the clearly laid out constitutional vanished and many new States have
provisions. The real success of been created. Areas, boundaries
federalism in India can be attributed and names of the States have been
to the nature of democratic politics changed.
in our country. This ensured that In 1947, the boundaries of several
the spirit of federalism, respect old States of India were changed in
for diversity and desire for living order to create new States. This was
together became shared ideals in our done to ensure that people who
country. Let us look at some of the spoke the same language lived in
major ways in which this happened. the same State. Some States were
created not on the basis of language
Linguistic States but to recognise differences based
The creation of linguistic States on culture, ethnicity or geography.
was the first and a major test for These include States like Nagaland,
democratic politics in our country. Uttarakhand and Jharkhand.
Has your village / town / city
remained under the same State
since Independence? If not,
what was the name of the earlier
Federalism
State?
Can you identify names of three
States in 1947 that have been
changed later?
Identify any three States which
have been carved out of bigger
States.
2024-25 19
Chapter 2.indd 19 08-04-2022 12:31:02
When the demand for the think that this solution favoured the
formation of States on the basis of English-speaking elite. Promotion
language was raised, some national of Hindi continues to be the official
leaders feared that it would lead to policy of the Government of India.
the disintegration of the country. Promotion does not mean that the
The Central Government resisted Central Government can impose
linguistic States for some time. Hindi on States where people speak
But the experience has shown that a different language. The flexibility
the formation of linguistic States shown by Indian political leaders
has actually made the country helped our country avoid the kind of
more united. It has also made situation that Sri Lanka finds itself in.
administration easier.
Centre-State relations
Language policy Restructuring the Centre-State
A second test for Indian federation is relations is one more way in which
the language policy. Our Constitution federalism has been strengthened
did not give the status of national in practice. How the constitutional
language to any one language. Hindi arrangements for sharing power
was identified as the official language. work in reality depends to a large
Why Hindi? But Hindi is the mother tongue of extent on how the ruling parties and
Why not only about 40 per cent of Indians. leaders follow these arrangements.
Bangla or Therefore, there were many safeguards For a long time, the same party
Telugu? to protect other languages. Besides ruled both at the Centre and in most
Hindi, there are 22 other languages of the States. This meant that the
recognised as Scheduled Languages State Governments did not exercise
by the Constitution. A candidate in their rights as autonomous federal
an examination conducted for the units. As and when the ruling party
Central Government positions may at the State level was different, the
opt to take the examination in any parties that ruled at the Centre tried
of these languages. States too have to undermine the power of the
their own official languages. Much States. In those days, the Central
of the government work takes Government would often misuse
place in the official language of the the Constitution to dismiss the State
concerned State. Governments that were controlled
Unlike Sri Lanka, the leaders by rival parties. This undermined
of our country adopted a very the spirit of federalism.
cautious attitude in spreading the All this changed significantly
use of Hindi. According to the after 1990. This period saw the
D e m o c ra t i c Po l i t i c s
Constitution, the use of English rise of regional political parties in
for official purposes was to stop in many States of the country. This
Coalition government: 1965. However, many non-Hindi was also the beginning of the era
A government formed
speaking States demanded that the of coalition governments at the
by the coming together
of at least two political use of English continue. In Tamil Centre. Since no single party got a
parties. Usually Nadu, this movement took a violent clear majority in the Lok Sabha, the
partners in a coalition form. The Central Government major national parties had to enter
form a political alliance responded by agreeing to continue into an alliance with many parties
and adopt a common the use of English along with Hindi including several regional parties to
programme.
for official purposes. Many critics form a government at the Centre.
2024-25
20
Chapter 2.indd 20 19/03/2024 10:40:43
The States Plead for More Powers
© Kutty - Laughing with Kutty
Perils of Running a Coalition Government
© Ajith Ninan - India Today Book of Cartoons
Here are two cartoons showing the relationship between Centre and States. Should the
State go to the Centre with a begging bowl? How can the leader of a coalition keep the
partners of government satisfied?
Are you
suggesting that
Federalism
This led to a new culture of Central Government to dismiss state
power sharing and respect for the governments in an arbitrary manner. regionalism is
autonomy of State Governments. Thus, federal power sharing is more good for our
This trend was supported by a effective today than it was in the democracy? Are
major judgement of the Supreme early years after the Constitution you serious?
Court that made it difficult for the came into force.
2024-25 21
Chapter 2.indd 21 08-04-2022 12:31:05
+
Linguistic diversity of India
How many languages do we have Make a bar or pie chart on
in India? The answer depends the basis of this information.
on how one counts it. The latest
Prepare a map of linguistic
information that we have is from diversity of India by shading
the Census of India held in 2011. the region where each of these
This census recorded more than languages is spoken on the map
1300 distinct languages which of India.
people mentioned as their mother
Find out about any three
tongues. These languages were
languages that are spoken in
grouped together under some
India but are not included in
major languages. For example,
this table.
languages like Bhojpuri, Magadhi,
Bundelkhandi, Chhattisgarhi,
Rajasthani and many others were
grouped together under ‘Hindi’. Scheduled Languages of India
Even after this grouping,
Language Proportion of
the Census found 121 major
speakers (%)
languages. Of these, 22
Assamese 1.26
languages are now included in
the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Bengali 8.03
Constitution and are therefore Bodo 0.12
called ‘Scheduled Languages’. Dogri 0.21
Others are called Gujarati 4.58
‘non-Scheduled Languages’. In Hindi 43.63
terms of languages, India is Kannada 3.61
perhaps the most diverse country Kashmiri 0.56
in the world. Konkani 0.19
A look at the enclosed table Maithili 1.12
makes it clear that no one Malayalam 2.88
language is the mother tongue of Manipuri 0.15
the majority of our population. Marathi 6.86
The largest language, Hindi, is the
Nepali 0.24
mother tongue of only about 44
per cent Indians. If we add to that Odia 3.10
all those who knew Hindi as their Punjabi 2.74
D e m o c ra t i c Po l i t i c s
second or third language, the total Sanskrit N
number was still less than 50 per Santali 0.61
cent in 2011. As for English, only
Sindhi 0.23
0.02 per cent Indians recorded it
as their mother tongue. Another
Tamil 5.70
11 per cent knew it as a second or Telugu 6.70
third language. Urdu 4.19
Read this table carefully, but
N — Stands for negligible.
you need not memorise it. Just do Source: http://www.censusindia.gov.in
the following:
2024-25
22
Chapter 2.indd 22 08-04-2022 12:31:05
‘
Read the following excerpts from an article by noted historian,
Ramachandra Guha, that appeared in the Times of India on November 1,
2006:
‘ Federalism
Take the example of your own state or any other state that was affected by
linguistic reorganisation. Write a short note for or against the argument given by
the author here on the basis of that example.
2024-25 23
Chapter 2.indd 23 08-04-2022 12:31:16
Decentralisation in India
We noted above that federal power to the level of villages and
governments have two or more towns. Panchayats in villages and
tiers of governments. We have municipalities in urban areas were
so far discussed the two-tiers of set up in all the States. But these
government in our country. But were directly under the control of
a vast country like India cannot state governments. Elections to these
be run only through these local governments were not held
So, we are like a two-tiers. States in India are as large as regularly. Local governments did
three-tier coach independent countries of Europe. In not have any powers or resources of
in a train! I terms of population, Uttar Pradesh their own. Thus, there was very little
always prefer the is bigger than Russia, Maharashtra decentralisation in effective terms.
lower berth! is about as big as Germany. Many A major step towards decentra-
of these States are internally very lisation was taken in 1992. The
diverse. There is thus a need for Constitution was amended to make
power sharing within these States. the third-tier of democracy more
Federal power sharing in India needs powerful and effective.
another tier of government, below Now it is constitutionally
that of the State governments. This mandatory to hold regular elections
is the rationale for decentralisation to local government bodies.
of power. Thus, resulted a third-
tier of government, called local Seats are reserved in the elected
bodies and the executive heads of
government.
these institutions for the Scheduled
When power is taken away from Castes, Scheduled Tribes and Other
Central and State governments and Backward Classes.
given to local government, it is called
decentralisation. The basic idea behind At least one-third of all positions
are reserved for women.
decentralisation is that there are a large
number of problems and issues which An independent institution
are best settled at the local level. People called the State Election Commission
have better knowledge of problems has been created in each State to
in their localities. They also have conduct panchayat and municipal
better ideas on where to spend money elections.
and how to manage things more The State governments are
efficiently. Besides, at the local level required to share some powers and
it is possible for the people to directly revenue with local government
D e m o c ra t i c Po l i t i c s
participate in decision making. This bodies. The nature of sharing varies
helps to inculcate a habit of democratic from State to State.
participation. Local government is the Rural local government is
best way to realise one important popularly known by the name
principle of democracy, namely local panchayati raj. Each village, or a
self-government. group of villages in some States, has
The need for decentralisation a gram panchayat. This is a council
was recognised in our Constitution. consisting of several ward members,
Since then, there have been often called panch, and a president
several attempts to decentralise or sarpanch. They are directly
2024-25
24
Chapter 2.indd 24 08-04-2022 12:31:16
elected by all the adult population the zilla (district) parishad. Most
living in that ward or village. It is members of the zilla parishad are
the decision-making body for the elected. Members of the Lok Sabha
entire village. The panchayat works and MLAs of that district and some
under the overall supervision of the other officials of other district level
gram sabha. All the voters in the bodies are also its members. Zilla
village are its members. It has to parishad chairperson is the political
meet at least twice or thrice in a year head of the zilla parishad.
to approve the annual budget of the Prime Minister
Similarly, local government
gram panchayat and to review the runs the country.
bodies exist for urban areas as
performance of the gram panchayat. Chief Minister
well. Municipalities are set up in
runs the state.
The local government structure towns. Big cities are constituted
Logically, then, the
goes right up to the district level. A into municipal corporations. Both
chairperson of Zilla
few gram panchayats are grouped municipalities and municipal
Parishad should
together to form what is usually corporations are controlled
run the district.
called a panchayat samiti or block by elected bodies consisting of
Why does the
or mandal. The members of this people’s representatives. Municipal
D.M. or Collector
representative body are elected by all chairperson is the political head of
administer the
the panchyat members in that area. the municipality. In a municipal
district?
All the panchayat samitis or mandals corporation, such an officer is called
in a district together constitute the mayor.
Federalism
What do these newspaper clippings have to say about efforts of decentralisation in India?
2024-25 25
Chapter 2.indd 25 08-04-2022 12:31:18
+ An experiment in Brazil
A city called Porto Alegre in Brazil has carried out an extraordinary experiment
in combining decentralisation with participative democracy. The city has set up
a parallel organisation operating alongside the municipal council, enabling local
inhabitants to take real decisions for their city. The nearly 13 lakh people in this
city get to participate in making the budget for their own city. The city is divided
into many sectors or what we call wards. Each sector has a meeting, like that of
the gram sabha, in which anyone living in that area can participate. There are
some meetings to discuss issues that affect the entire city. Any citizen of the city
can participate in those meetings. The budget of the city is discussed in these
meetings. The proposals are put to the municipality that takes a final decision
about it.
About 20,000 people participate in this decision making exercise every year.
This method has ensured that the money cannot be spent only for the benefit
of the colonies where rich people live. Buses now run to the poor colonies and
builders cannot evict slum-dwellers without resettling them.
In our own country, a similar experiment has taken place in some areas in
Kerala. Ordinary people have participated in making a plan for the development
of their locality.
This new system of local increased women’s representation
government is the largest experiment and voice in our democracy. At
in democracy conducted anywhere the same time, there are many
in the world. There are now about difficulties. While elections are
36 lakh elected representatives in held regularly and enthusiastically,
the panchayats and municipalities gram sabhas are not held regularly.
etc., all over the country. This Most state governments have not
number is bigger than the population transferred significant powers to the
of many countries in the world. local governments. Nor have they
Constitutional status for local given adequate resources. We are
government has helped to deepen thus still a long way from realising
democracy in our country. It has also the ideal of self-government.
D e m o c ra t i c Po l i t i c s
Find out about the local government in the village or town you live in.
If you live in a village, find out the names of the following: your panch or
ward member, your sarpanch, your panchayat samiti, the chairperson of your zilla
parishad. Also find out when did the last meeting of the gram sabha take place and
how many people took part in that.
If you live in urban areas, find out the name of your municipal councillor, and the
municipal chairperson or mayor. Also find out about the budget of your municipal
corporation, municipality and the major items on which money was spent.
2024-25
26
Chapter 2.indd 26 08-04-2022 12:31:19
1. Locate the following States on a blank outline political map of India:
Manipur, Sikkim, Chhattisgarh and Goa.
2. Identify and shade three federal countries (other than India) on a
blank outline political map of the world.
3. Point out one feature in the practice of federalism in India that is
similar to and one feature that is different from that of Belgium.
4. What is the main difference between a federal form of government
and a unitary one? Explain with an example.
5. State any two differences between the local government before and
after the Constitutional amendment in 1992.
6. Fill in the blanks:
Since the United States is a ___________________ type of
Exercises
federation, all the constituent States have equal powers and States
are ______________vis-à-vis the federal government. But India is a
_____________________ type of federation and some States have
more power than others. In India, the ____________ government
has more powers.
7. Here are three reactions to the language policy followed in India.
Give an argument and an example to support any of these positions.
Sangeeta: The policy of accommodation has strengthened
national unity.
Arman: Language-based States have divided us by making
everyone conscious of their language.
Harish: This policy has only helped to consolidate the
dominance of English over all other languages.
8. The distinguishing feature of a federal government is:
(a) National government gives some powers to the provincial
governments.
(b) Power is distributed among the legislature, executive and
judiciary.
(c) Elected officials exercise supreme power in the government.
(d) Governmental power is divided between different levels of
government.
9. A few subjects in various Lists of the Indian Constitution are given
here. Group them under the Union, State and Concurrent Lists as
provided in the table below.
A. Defence; B. Police; C. Agriculture; D. Education;
E. Banking; F. Forests; G. Communications; H. Trade; I. Marriages
Federalism
Union List
State List
Concurrent List
2024-25 27
Chapter 2.indd 27 08-04-2022 12:31:20
10. Examine the following pairs that give the level of government in India
and the powers of the government at that level to make laws on the
subjects mentioned against each. Which of the following pairs is not
correctly matched?
(a) State government State List
(b) Central government Union List
(c) Central and State governments Concurrent List
(d) Local governments Residuary powers
11. Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using
the codes given below the lists:
List I List II
Exercises
1. Union of India A. Prime Minister
2. State B. Sarpanch
3. Municipal Corporation C. Governor
4. Gram Panchayat D. Mayor
1 2 3 4
(a) D A B C
(b) B C D A
(c) A C D B
(d) C D A B
12. Consider the following two statements.
A. In a federation, the powers of the federal and provincial
governments are clearly demarcated.
B. India is a federation because the powers of the Union and State
Governments are specified in the Constitution and they have
exclusive jurisdiction on their respective subjects.
C. Sri Lanka is a federation because the country is divided into
provinces.
D. India is no longer a federation because some powers of the States
have been devolved to the local government bodies.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) A, B and C (b) A, C and D (c) A and B only (d) B and C only
D e m o c ra t i c Po l i t i c s
2024-25
28
Chapter 2.indd 28 08-04-2022 12:31:21
You might also like
- Elements of Success 2 With AnswersDocument626 pagesElements of Success 2 With AnswersChi Nguyễn75% (4)
- Lesson Plan On Verb TensesDocument5 pagesLesson Plan On Verb TensesPurisima D. Bagsawan100% (1)
- Law On Public Corporation (Largo) ReviewerDocument23 pagesLaw On Public Corporation (Largo) ReviewerMia Alba100% (6)
- English: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Recognizing The Use of A/An + NounDocument27 pagesEnglish: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Recognizing The Use of A/An + NounJABP18100% (2)
- Jess 402Document16 pagesJess 402Sharad MusaleNo ratings yet
- 02 FederalismDocument16 pages02 FederalismsankarNo ratings yet
- FedaralizmDocument23 pagesFedaralizmsatheesh17981No ratings yet
- Jess 402Document16 pagesJess 402K GOVINDIENNo ratings yet
- Dubai2021 - P1C1 - Lecture FéderalismDocument8 pagesDubai2021 - P1C1 - Lecture FéderalismsamaristoocoolNo ratings yet
- Federalism Shobhit NirwanDocument13 pagesFederalism Shobhit Nirwansarvesh manav100% (3)
- Federalism NotesDocument28 pagesFederalism Notesangel / joysvoid100% (1)
- CH 2 Federalism by Swati AroraDocument10 pagesCH 2 Federalism by Swati AroraAsh JainNo ratings yet
- FEDERALISMDocument66 pagesFEDERALISMAnushka RoutNo ratings yet
- Federalism YTDocument66 pagesFederalism YTdark aaasNo ratings yet
- Baps3a Abel, Rejay M. Module2lesson1 Venn DiagramDocument1 pageBaps3a Abel, Rejay M. Module2lesson1 Venn DiagramSIBAYAN, WINSON OLIVERNo ratings yet
- Federalism Basics English Student BookDocument54 pagesFederalism Basics English Student BookarNo ratings yet
- Federalism - NotesDocument8 pagesFederalism - Notespratikshaarya97No ratings yet
- Federalism in IndiaDocument5 pagesFederalism in IndiaBasavaraj JNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 30 Apr 2024Document4 pagesAdobe Scan 30 Apr 2024prernasharma9253No ratings yet
- Federalism: CH 2 Civics - Class 10Document23 pagesFederalism: CH 2 Civics - Class 10ArshadNo ratings yet
- X - POL. SC - CH-2 - Federalism - SCANNERDocument13 pagesX - POL. SC - CH-2 - Federalism - SCANNERseex adviceNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Federalism in IndiaDocument5 pagesCooperative Federalism in IndiaBasavaraj JNo ratings yet
- FederalismDocument11 pagesFederalismsimoneNo ratings yet
- Confederalism, Cetralism, Federalism TableDocument3 pagesConfederalism, Cetralism, Federalism TableAlejandra SigüenzaNo ratings yet
- FederalismDocument36 pagesFederalismanyastudysNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Civics Federalism: Question Answers K.SindhuDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Civics Federalism: Question Answers K.SindhusiaNo ratings yet
- FederalismDocument16 pagesFederalismRiya Kumari100% (1)
- Federal, Unitary and Local Government: FederalismDocument16 pagesFederal, Unitary and Local Government: Federalismkila prisNo ratings yet
- UNITARY Vs FederalDocument6 pagesUNITARY Vs FederalvkNo ratings yet
- Class 10th - Civics - Federalism - Full Chapter Explanation Connect With The Previous ChapterDocument38 pagesClass 10th - Civics - Federalism - Full Chapter Explanation Connect With The Previous ChapterBajarangi BhaiyaNo ratings yet
- NEW Khairul AzmiDocument27 pagesNEW Khairul Azmiaramis_crosnierNo ratings yet
- Political Science ProjectDocument13 pagesPolitical Science Projectniyati1171No ratings yet
- Unit For Course Plan First Federalism and CooperaDocument8 pagesUnit For Course Plan First Federalism and Coopera03fl22bcl033No ratings yet
- UNITRAY and FEDERAL SYSTEMDocument4 pagesUNITRAY and FEDERAL SYSTEMshruti singhNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Recall From Previous ChapterDocument2 pagesIntroduction and Recall From Previous Chapterparamveersandhu2009No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 QuestionsDocument1 pageChapter 2 QuestionsAlbert BrayfieldNo ratings yet
- Citizenship Lesson Note For Grade 10Document46 pagesCitizenship Lesson Note For Grade 10biniam.abiyNo ratings yet
- X02 enDocument16 pagesX02 enMansi GuravNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Design For Territorially Divided SocietiesDocument9 pagesConstitutional Design For Territorially Divided SocietiesMin Khant LwinNo ratings yet
- Government FinalDocument6 pagesGovernment FinalEvelyn ArjonaNo ratings yet
- FederalismDocument10 pagesFederalismSahil TiwariNo ratings yet
- Class 10 DP Ho - Federalism 2022-2023Document12 pagesClass 10 DP Ho - Federalism 2022-2023GOURAV RAMANINo ratings yet
- Grade X Chapter 2 FederalismDocument6 pagesGrade X Chapter 2 Federalismupadhyay.goodboyNo ratings yet
- Comaparitive ConstitutionDocument22 pagesComaparitive Constitutionpriyakankaria77No ratings yet
- Co IndiaDocument17 pagesCo Indiariddhi pareekNo ratings yet
- The Theory, Practice and Current Trends in Federalism: Corresponding AuthorDocument11 pagesThe Theory, Practice and Current Trends in Federalism: Corresponding AuthorAnthony ObiNo ratings yet
- Concept of FederalismDocument1 pageConcept of FederalismPAWANNo ratings yet
- AISV6 - X - Political Science - Federalism - RRDocument4 pagesAISV6 - X - Political Science - Federalism - RRHridi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Unitary & FedaralDocument4 pagesUnitary & FedaralDarshil RathodNo ratings yet
- Federalism by Himanshu SirDocument6 pagesFederalism by Himanshu SirHimanshu DixitNo ratings yet
- G-X-Pol Sc. CH - 2 notes-FEDERALISMDocument6 pagesG-X-Pol Sc. CH - 2 notes-FEDERALISMPartha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Federalism Q & ADocument2 pagesChapter 2-Federalism Q & AAravind Santhosh Kumar40% (5)
- Federal Form of GovernmentDocument4 pagesFederal Form of GovernmentAnoushka KeswaniNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Civics Chater 1Document5 pagesClass 10th Civics Chater 1rao sahabNo ratings yet
- Pol SC Ch-2 FederalismDocument3 pagesPol SC Ch-2 FederalismBlack ScratchNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 FEDERAL FORM OF GOVERNMENTDocument17 pagesUnit - 2 FEDERAL FORM OF GOVERNMENTsunny.verma613No ratings yet
- FEDERALISM Notes Class 10Document4 pagesFEDERALISM Notes Class 10PARDEEP0% (1)
- Federal RepublicDocument5 pagesFederal RepublicRashmiNo ratings yet
- Diaz-Federal and Unitary Government-12 People SmartDocument1 pageDiaz-Federal and Unitary Government-12 People SmartGj Emmanuel DiazNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Jurisdiction Battle Between the States and the Federal GovernmentFrom EverandUnderstanding the Jurisdiction Battle Between the States and the Federal GovernmentNo ratings yet
- A Democratic Government: Understanding the System and Its Interconnected PartsFrom EverandA Democratic Government: Understanding the System and Its Interconnected PartsNo ratings yet
- The Chaos Word Bank: (Poem)Document4 pagesThe Chaos Word Bank: (Poem)Nichole DequitoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Least Mastered Skills 2019-2020Document3 pagesDiagnostic Least Mastered Skills 2019-2020Mabelle Mengote NardoNo ratings yet
- Grammar Worksheet 1: Possessive Adjectives Possessive 'S and S'Document1 pageGrammar Worksheet 1: Possessive Adjectives Possessive 'S and S'Viviana GalanNo ratings yet
- Making Type 1 Fonts For VietnameseDocument6 pagesMaking Type 1 Fonts For VietnameseRommel PagaraNo ratings yet
- وشه - سازی زمانی كوردی 2Document138 pagesوشه - سازی زمانی كوردی 2Birwalla FanNo ratings yet
- YCT 2 Word ListDocument6 pagesYCT 2 Word ListМайя ЗаяцьNo ratings yet
- Thank You: A. Match The Greetings With The Correct PictureDocument8 pagesThank You: A. Match The Greetings With The Correct PictureHIDAYAHNo ratings yet
- 2008-06 Gardner HumorDocument6 pages2008-06 Gardner HumorScott GardnerNo ratings yet
- Illustrated American IdiomsDocument3 pagesIllustrated American Idiomscute20060% (1)
- Kumpulan Soal B. Inggris Akpol, Akmil, SBMPTNDocument8 pagesKumpulan Soal B. Inggris Akpol, Akmil, SBMPTNVivi ArdianiNo ratings yet
- Haiku PowerpointDocument9 pagesHaiku PowerpointAnemona PatrulescuNo ratings yet
- 3 SHoRTDocument12 pages3 SHoRTSigrid TecaNo ratings yet
- Summary SlaDocument36 pagesSummary SlaNatalia OliveraNo ratings yet
- Unit 6B-GrammarDocument11 pagesUnit 6B-GrammarNguyễn Ngọc Tâm NhưNo ratings yet
- Student - Group - Date - Usos Del Do Y DoesDocument3 pagesStudent - Group - Date - Usos Del Do Y DoesHectorNo ratings yet
- Ballb-unit-2-Question Tags & Sharot ResponsesDocument11 pagesBallb-unit-2-Question Tags & Sharot ResponsesArchana Sharma Learning AcademyNo ratings yet
- Proficiency In: Examination For The Certificate of EnglishDocument7 pagesProficiency In: Examination For The Certificate of EnglishhaldcitoNo ratings yet
- Linkers and ConnectorsDocument8 pagesLinkers and ConnectorsselvaNo ratings yet
- Unit-I - 4 StringDocument23 pagesUnit-I - 4 StringMochiNo ratings yet
- A Model Lesson For Using Songs As Esl Audio Listening MaterialsDocument5 pagesA Model Lesson For Using Songs As Esl Audio Listening MaterialsMnky VINo ratings yet
- C Programming - Question Bank PDFDocument21 pagesC Programming - Question Bank PDFSambit Patra90% (10)
- ENGL115 Grammar 10-2 - Making Comparisons 1.2Document4 pagesENGL115 Grammar 10-2 - Making Comparisons 1.2Ivonne PerezNo ratings yet
- American and British EnglishDocument35 pagesAmerican and British EnglishRyan HoganNo ratings yet
- A Thesis Error Analysis of Sentences in Writing Poster by 6 Semester Students of Elt in UmmatDocument53 pagesA Thesis Error Analysis of Sentences in Writing Poster by 6 Semester Students of Elt in UmmatMuhammad AqibNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Poets - Harold BloomDocument218 pagesContemporary Poets - Harold BloomUSHNISH15728100% (11)
- GRADE 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Plan SCHOOL Cabayabasan Elem. School Grade Level Four TEACHER Florante C. Alconcel Quarter Subject Date 4Document6 pagesGRADE 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Plan SCHOOL Cabayabasan Elem. School Grade Level Four TEACHER Florante C. Alconcel Quarter Subject Date 4Karmela VeluzNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Rohit KumarDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Rohit KumarNirlipta SwainNo ratings yet