Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment in Trading
Assignment in Trading
Uploaded by
Floriemae MercadoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment in Trading
Assignment in Trading
Uploaded by
Floriemae MercadoCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment in Trading
1. Define what is trading? Differentiate Local Trading from International Trading.
Trading refers to the process of buying, selling, or exchanging goods, services, or financial instruments. Local
trading occurs within a specific geographical area, typically a single country, and is governed by local laws and
regulations, involving domestic currencies and benefiting from reduced transportation costs and fewer
regulatory barriers. In contrast, international trading involves the exchange of goods and services between
countries, governed by international trade agreements, global standards, and multiple currencies. This type of
trading allows countries to access a broader range of goods and services and tap into global markets, but it also
involves higher transportation costs, tariffs, and more complex regulatory compliance.
2. Who are the winners and losers of local and international trading?
In both local and international trading, there are distinct winners and losers. Consumers generally benefit from a
greater variety of goods and services and potentially lower prices due to increased competition. Exporters gain
access to larger markets, leading to increased sales and economies of scale, while efficient producers in
countries with comparative or absolute advantages can maximize production efficiency and profitability.
However, domestic industries that struggle to compete with foreign producers may face job losses and business
closures. Workers in non-competitive sectors could experience unemployment or reduced wages as production
shifts to more competitive or efficient markets. Additionally, countries with weaker economies might suffer
from trade deficits, currency devaluation, and economic instability due to unequal trading conditions.
3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of local and international trading
Local and international trading each come with their own sets of advantages and disadvantages. Local trading
offers lower transportation and transaction costs, simpler regulatory compliance, and supports local businesses
and economies. However, it also has a limited market size, which can restrict business growth, offer less variety
and availability of goods and services, and potentially result in higher prices due to less competition. On the
other hand, international trading provides access to a wider range of goods and services, economies of scale,
and encourages innovation and technological advancements through competition. The disadvantages include
higher transportation costs, exposure to global economic fluctuations and trade policies, and complex regulatory
compliance, with potential for trade disputes.
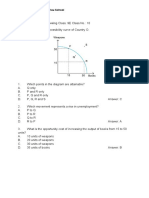
4. Explain the Production Possibility Frontier.
The Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) is a curve illustrating the maximum feasible quantity of two goods
that an economy can produce given its resources and technology. Points on the PPF represent efficient
production levels, while points inside the curve indicate underutilization of resources, and points outside the
curve are unattainable with current resources and technology. The PPF demonstrates trade-offs between
different goods, showing that producing more of one good requires sacrificing some of another due to limited
resources. It highlights the concepts of opportunity cost and economic efficiency, indicating the most efficient
allocation of resources.
5. Differentiate comparative vs absolute advantage and how does it work?
6. Enumerate and explain what are the common barriers to international trading
You might also like
- PPC Question & Answer For IGCSE StudentsDocument4 pagesPPC Question & Answer For IGCSE Studentsemonimtiaz100% (4)
- PPC Revision Worksheet.Document3 pagesPPC Revision Worksheet.Isaac HoNo ratings yet
- Section 3.1 International Trade 6Document82 pagesSection 3.1 International Trade 6swssNo ratings yet
- MGT 9Document12 pagesMGT 9Anjelika ViescaNo ratings yet
- Business ManagementDocument6 pagesBusiness ManagementBechaida, Princess Aila A.No ratings yet
- International Trade and Agreement Summary Reviewer Chapter 1 To 3Document4 pagesInternational Trade and Agreement Summary Reviewer Chapter 1 To 3Ralph AbutinNo ratings yet
- Internationaltrade 11Document5 pagesInternationaltrade 11Bisrat MekonenNo ratings yet
- Finals ModuleDocument11 pagesFinals ModulenilmajeanjasminNo ratings yet
- Elements of International BusinessDocument7 pagesElements of International Businesstania leonelaNo ratings yet
- Motives For Protectionism and Motives For TradeDocument4 pagesMotives For Protectionism and Motives For Tradecharlotte frances bagaoisanNo ratings yet
- Module 8Document4 pagesModule 8Chin Keanna BuizonNo ratings yet
- International Trade: by Group 6 - LS 403 (SY 2010-2011)Document47 pagesInternational Trade: by Group 6 - LS 403 (SY 2010-2011)Shefey IbrahimNo ratings yet
- (Finals) International Trade Practices and PoliciesDocument4 pages(Finals) International Trade Practices and PoliciesJUDE VINCENT MACALOSNo ratings yet
- GBM Unit 1 NotesDocument13 pagesGBM Unit 1 NotesGracyNo ratings yet
- COMMERCIAL CONSIDERATIONs AND ORGANIZATIONS - TOPIC 5Document23 pagesCOMMERCIAL CONSIDERATIONs AND ORGANIZATIONS - TOPIC 5Money CafeNo ratings yet
- Transport, TheDocument23 pagesTransport, TheRujjiNo ratings yet
- Economics Theme 4Document8 pagesEconomics Theme 4hwriggles2002No ratings yet
- TradeDocument14 pagesTradeMae Rachel Muyuela LacsonNo ratings yet
- Impediments and Barriers To EducationDocument2 pagesImpediments and Barriers To EducationMonalisa Vargas Laron67% (3)
- Trade RestrictionsDocument23 pagesTrade RestrictionsNamita patilNo ratings yet
- AveryB CS2Document2 pagesAveryB CS2Avery BrooksNo ratings yet
- CartelDocument4 pagesCartelFRANCIS EDWIN MOJADONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Global Issues Lecture No, 2 (Autosaved)Document17 pagesChapter 1 Global Issues Lecture No, 2 (Autosaved)رضا صابر علىNo ratings yet
- International Marketing: MK0018 - AssignmentDocument7 pagesInternational Marketing: MK0018 - Assignmentar009baNo ratings yet
- Trade Barriers, Dumping Anti DumpingDocument30 pagesTrade Barriers, Dumping Anti Dumpingqwertyuiop_6421100% (3)
- Velammal Engineering College, CHENNAI - 600 066: Department of Management Sciences Questions & AnswersDocument50 pagesVelammal Engineering College, CHENNAI - 600 066: Department of Management Sciences Questions & AnswerscowgaNo ratings yet
- Int Trade A LevelDocument6 pagesInt Trade A LevelLeo RajNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of International TradeDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of International TradeAaNo ratings yet
- MK0018Document8 pagesMK0018Sny Kumar DeepakNo ratings yet
- Intenational TradeDocument30 pagesIntenational TradeDA YenNo ratings yet
- Assingnment 3Document3 pagesAssingnment 3Aung Kaung MyatNo ratings yet
- Liberalisation of Import-Export SystemDocument4 pagesLiberalisation of Import-Export SystemMimi LaurentNo ratings yet
- Trade Restrictions in RussiaDocument15 pagesTrade Restrictions in Russiasayalipatil1196No ratings yet
- Comparative Advantage and Gains From TradeDocument27 pagesComparative Advantage and Gains From TradeMikylla Rodriguez VequisoNo ratings yet
- TradeDocument6 pagesTradeLouise CruzNo ratings yet
- MK0018Document8 pagesMK0018Ganesh ShindeNo ratings yet
- Global Business Environment FINALDocument41 pagesGlobal Business Environment FINALSanthosh KrishnaNo ratings yet
- understanding ibDocument13 pagesunderstanding ibgarvmahajan3410No ratings yet
- Assignment 10 International Trade Theory and Development StrategyDocument2 pagesAssignment 10 International Trade Theory and Development StrategyAlyssa BerangberangNo ratings yet
- International TradeDocument7 pagesInternational Tradeluis philipNo ratings yet
- Angol Szakmai Szobeli TetelekDocument19 pagesAngol Szakmai Szobeli Tetelekgiranzoltan100% (1)
- DGVHGFXDocument2 pagesDGVHGFXAntonio HerguetaNo ratings yet
- International Trade-Written ReportDocument18 pagesInternational Trade-Written ReportKyotNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - International Trade - Part 1 - To Sts-Đã G PDocument113 pagesUnit 1 - International Trade - Part 1 - To Sts-Đã G PMinh Huyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- 27 - International TradeDocument5 pages27 - International Tradehoangduylong.iccNo ratings yet
- SDFSDFSDocument2 pagesSDFSDFSAntonio HerguetaNo ratings yet
- International Trade - Theory Practice WWDocument99 pagesInternational Trade - Theory Practice WWthenxtbigbucksNo ratings yet
- Enm PT2Document11 pagesEnm PT2handi2k4No ratings yet
- IBT Assignment EditedDocument8 pagesIBT Assignment EditedLysss EpssssNo ratings yet
- The Task EnvironmentDocument8 pagesThe Task EnvironmentStoryKingNo ratings yet
- International Trade 2 - Week 3Document15 pagesInternational Trade 2 - Week 3Ahmad Dwi Syaiful AmriIB102No ratings yet
- Ingles Preguntas 12Document3 pagesIngles Preguntas 12Dennis CanaviriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 4Document9 pagesChapter 3 4molinatherabbit20No ratings yet
- International Trade and InvestmentDocument19 pagesInternational Trade and InvestmentJasmine MaghirangNo ratings yet
- Globalization, Trade and Business PDFDocument13 pagesGlobalization, Trade and Business PDFEconomics LabNo ratings yet
- Trade Theory and Economic DevelopmentDocument44 pagesTrade Theory and Economic DevelopmentwajagewNo ratings yet
- Sbaa 5301Document143 pagesSbaa 5301samayasanjeeviNo ratings yet
- Sbaa 5301Document143 pagesSbaa 5301samayasanjeeviNo ratings yet
- Assignment Subject Code & Name MB0053 - International Business ManagementDocument6 pagesAssignment Subject Code & Name MB0053 - International Business ManagementNIKHILPATNINo ratings yet
- EsgdfcDocument2 pagesEsgdfcAntonio HerguetaNo ratings yet
- EoG Extra NotesDocument20 pagesEoG Extra NotesVrishank JhunjhunwalaNo ratings yet
- Smooth Sailing: A Quick Guide to Effective Cargo Import and Export: Logistics, #1From EverandSmooth Sailing: A Quick Guide to Effective Cargo Import and Export: Logistics, #1No ratings yet
- MAC 1E Study Guide CompleteDocument225 pagesMAC 1E Study Guide Completealicia1990No ratings yet
- International Economics 14th Edition Carbaugh Solution ManualDocument7 pagesInternational Economics 14th Edition Carbaugh Solution Manualraymond100% (29)
- Tutorial 1 With AnswersDocument6 pagesTutorial 1 With AnswersYejiNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Template: Author InformationDocument9 pagesUnit Plan Template: Author InformationSandra MaclangNo ratings yet
- MR Moyo - Economics Revision Basic Economic Problem, Resource Allocating, PPC, Money Citrusperibus, Assignment 1 AsDocument14 pagesMR Moyo - Economics Revision Basic Economic Problem, Resource Allocating, PPC, Money Citrusperibus, Assignment 1 AsFaryalNo ratings yet
- Exam Success in Economics For Cambridge IGCSE AnswersDocument30 pagesExam Success in Economics For Cambridge IGCSE AnswersAKARESH JOSE EBOOKS100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - DDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - DSujani MaarasingheNo ratings yet
- Economics: Principles in Action NOTES For Chapter 1Document1 pageEconomics: Principles in Action NOTES For Chapter 1Sebastian RamirezNo ratings yet
- Applied-Economics SHS Q1 LP-2Document17 pagesApplied-Economics SHS Q1 LP-2UnknownNo ratings yet
- Scarcity, Choice, and Opportunity Costs: T OutlineDocument11 pagesScarcity, Choice, and Opportunity Costs: T OutlineFurqan ArifNo ratings yet
- Under What Conditions Will Opportunity Cost Be Equal To Zero, One or More?Document4 pagesUnder What Conditions Will Opportunity Cost Be Equal To Zero, One or More?VeronicaNo ratings yet
- sg27 Parte8Document7 pagessg27 Parte8Carlos CerezoNo ratings yet
- Production Possibility FrontierDocument22 pagesProduction Possibility FrontierFetty Ptek100% (2)
- 1.1 The Economizing ProblemDocument28 pages1.1 The Economizing ProblemahsakahNo ratings yet
- Basic Economic ProblemDocument12 pagesBasic Economic ProblemDhrutik KamaniNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics 7th Edition Hubbard Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesMacroeconomics 7th Edition Hubbard Solutions ManualJoshuaAndersonwpdr100% (50)
- PPC QuestionsDocument4 pagesPPC Questionssumedhasajeewani100% (1)
- EconomicsDocument287 pagesEconomicskkNo ratings yet
- C05 Krugman 11eDocument82 pagesC05 Krugman 11eKumar Ak100% (2)
- Introduction To Economics PDFDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Economics PDFNakijwa MndemeNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Economics 6th Edition Mankiw Solutions ManualDocument19 pagesEssentials of Economics 6th Edition Mankiw Solutions Manualnancycarrollaocprizwen100% (10)
- Eco162 2024 01 SGDocument114 pagesEco162 2024 01 SGgfdqewdfujnycajutnNo ratings yet
- ECO 222 Exam 1Document26 pagesECO 222 Exam 1Ty-Shana MaximeaNo ratings yet
- Eco402 Final Term Quiz FileDocument30 pagesEco402 Final Term Quiz FileYounas MujahidNo ratings yet
- Eco401 Highlighted Handouts by Sir Bilal KahlonDocument124 pagesEco401 Highlighted Handouts by Sir Bilal Kahlonlaraib tariqNo ratings yet
- CAPE Economics Syllabus 2010 PDFDocument11 pagesCAPE Economics Syllabus 2010 PDFSarah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Actuarial Economics IDocument278 pagesActuarial Economics IKritika VermaNo ratings yet
- RybczynskiDocument9 pagesRybczynskiManeeshaNo ratings yet