Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 4 - Birefringence (DontWorry - NoLec3)
Lecture 4 - Birefringence (DontWorry - NoLec3)
Uploaded by
Junaid Kaleem0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views12 pagesBirefringence Optical Fibres
Original Title
Lecture 4_Birefringence (DontWorry_NoLec3)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBirefringence Optical Fibres
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views12 pagesLecture 4 - Birefringence (DontWorry - NoLec3)
Lecture 4 - Birefringence (DontWorry - NoLec3)
Uploaded by
Junaid KaleemBirefringence Optical Fibres
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 12
Birefringence
Lecture 3
Attiq Ahmed Optical Communication
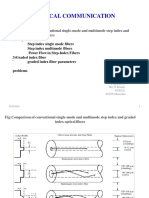
Single Mode Fibers
The core size of single mode fibers is small. The core size (diameter) is typically
around 8 to 10 micrometers.
A fiber core of this size allows only the fundamental or lowest order mode to
propagate.
Single mode fibers propagate only one mode, because the core size approaches the
operational wavelength (λ).
The normalized frequency V is a dimensionless parameter that relates in a very
useful manner the core radius a, the numerical aperture and the operating
wavelength.
In single mode fibers, V is less than or equal to 2.405. When V ≤ 2.405, single
mode fibers propagate the fundamental mode down the fiber core.
For low V values (≤ 1.0), most of the power is propagated in the cladding material.
Power transmitted by the cladding is easily lost at fiber bends. The value of V should
remain near 2.405.
It is advantageous to use SMF.
Attiq Ahmed Optical Communication
Mode Index
p2 2 n n2
b = 1- 2 1- 2 .
V V n1 n2
2 a 2 (n12 k02 2 ) ; γ 2 a 2 ( 2 n22 k02 )
1
V k0 a ( n n )
2
1
2
2
2
n = n2+b(n1−n2) ≈ n2(1+b∆)
An analytic approximation for b is;
b(V) ≈ (1.1428−0.9960/V)2 Fig: 2.5
Attiq Ahmed Optical Communication
Birefringence
Fibers exhibit considerable variation in the shape of
their core along the fiber length i.e. the core is not
perfectly cylindrical and core diameter is not uniform, so
the cylindrical symmetry of the fiber is broken.
Ideal fiber: cylindrical core
Uniform diameter
Degenerate modes
Real fiber variation in shape
non uniform stress
Degeneracy between the orthogonally polarized fiber
modes is removed – thus fiber acquires birefringence.
Attiq Ahmed Optical Communication
Cont.
Thus the modes have different propagation constants. The
degree of modal birefringence is defined by
where nx and ny are the mode indices for the orthogonally
polarized fiber modes.
Birefringence leads to a periodic power exchange between the
two polarization components. The period, referred to as the
beat length, is given by
Typically, Bm ~ 10−7, and LB ~ 10 m for λ ~ 1µm.
Attiq Ahmed Optical Communication
Polarization – Linear to Elliptical
If polarized along one of the principal axes, Linear to Linear
Otherwise, its state of polarization changes along the fiber length from linear to
elliptical, and then back to linear, in a periodic manner over the length LB.
Fast axis - Low refractive index.
Slow axis - High refractive index.
Birefringence is not constant in SMF -
changes randomly, both in magnitude and
direction.
Different frequency components of a pulse
acquire different polarization states,
resulting in pulse broadening.
This phenomenon is called polarization-
mode dispersion (PMD).
Attiq Ahmed Optical Communication
Attiq Ahmed Optical Communication
Polarization Mode Dispersion
Polarization mode dispersion (PMD) is caused by asymmetric distortions to the
fiber from a perfect cylindrical geometry.
The fiber is not truly a cylindrical waveguide, but it can be best described as an
imperfect cylinder with physical dimensions that are not perfectly constant.
The mechanical stress exerted upon the fiber due to extrinsically induced bends
and stresses caused during cabling, deployment, and splicing as well as the
imperfections resulting from the manufacturing process are the reasons for the
variations in the cylindrical geometry.
The asymmetry introduces small refractive index differences for the two
polarization states.
This characteristic is known as birefringence. Birefringence causes one
polarization mode to travel faster than the other, resulting in a difference in the
propagation time, which is called the differential group delay (DGD).
Attiq Ahmed Optical Communication
Cont..
Pulse broadening can be estimated from the time delay ∆T
between the two polarization components during propagation
of the pulse. For a fiber of length L, ∆T is given by
x and y identify the two orthogonally polarized modes .
and ∆ β1 is related to the Fiber birefringence .
Attiq Ahmed Optical Communication
Cont..
The PMD-induced pulse broadening is characterized by the
value of ∆T/L.
PMD is not an issue at low bit rates but becomes an issue at bit
rates in excess of 5 Gbps.
PMD is noticeable at high bit rates and is a significant source of
impairment for ultra-long-haul systems.
PMD induced pulse broadening is relatively small compared
with the GVD effects.
PMD compensation can be achieved by using PMD
compensators that contain dispersion-maintaining fibers with
degrees of birefringence in them.
Attiq Ahmed Optical Communication
SPM
Attiq Ahmed Optical Communication
Attiq Ahmed Optical Communication
You might also like
- Fiber CadDocument266 pagesFiber CadDavid RogerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - BirefringenceDocument12 pagesLecture 4 - BirefringenceInam ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Lecture 4 BirefringenceDocument24 pagesWeek 4 Lecture 4 BirefringenceZain ShabbirNo ratings yet
- EC2402 Optical Communication and Networks 12Document21 pagesEC2402 Optical Communication and Networks 12vinothiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - TTQ 2022ADocument73 pagesChapter 02 - TTQ 2022Ahai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Fiber Dispersion, Which Leads To Broadening of Individual OpticalDocument17 pagesFiber Dispersion, Which Leads To Broadening of Individual OpticalAnnas TunggalNo ratings yet
- 2 YjhyDocument20 pages2 YjhyNithindev GuttikondaNo ratings yet
- WDM Concepts and Components: Wavelength-Division Multiplexing or WDM. The Key System Features of WDMDocument114 pagesWDM Concepts and Components: Wavelength-Division Multiplexing or WDM. The Key System Features of WDMTPO BVCOEKNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 StudentDocument15 pagesLecture 4 StudentJanine NaluzNo ratings yet
- Optical NotesDocument71 pagesOptical NoteslosliyaNo ratings yet
- Optical CommunicationDocument19 pagesOptical Communicationanon_118391344No ratings yet
- Introduction To Fiber Optics: Presented by R.Hemalatha M.ParthibanDocument90 pagesIntroduction To Fiber Optics: Presented by R.Hemalatha M.ParthibanHemalatha R 19PHD0343No ratings yet
- OFC Module 1Document85 pagesOFC Module 1VargheseMartinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Optical FibersDocument60 pagesChapter 2 - Optical Fiberseyohamehari235No ratings yet
- Optical Communication Question BankDocument24 pagesOptical Communication Question BankdhivyakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 1Document57 pagesOptical Fiber Communication Lecture 1Achala DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication 2mark PDFDocument20 pagesOptical Communication 2mark PDFAnant ShankarNo ratings yet
- Lecture #1 Optical FibersDocument59 pagesLecture #1 Optical Fibersjeddo2005No ratings yet
- EE493 - Second Set of Lecture Slides-Spring 2021Document78 pagesEE493 - Second Set of Lecture Slides-Spring 2021احمد الديريNo ratings yet
- Optical CommunicationDocument64 pagesOptical CommunicationAmit Samrat MauryaNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibers: Structures: Unit-2Document15 pagesOptical Fibers: Structures: Unit-2Mithun KumarNo ratings yet
- Oc Question BankDocument50 pagesOc Question BankAmit SivaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Chapter 2: Optical Fibers Structures, Waveguiding, and FabricationDocument16 pagesLecture Notes For Chapter 2: Optical Fibers Structures, Waveguiding, and Fabricationsohaib100% (1)
- Lecture 5Document43 pagesLecture 5Mjj VegaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Optical FibreDocument195 pagesFundamentals of Optical Fibrebinarystars100% (1)
- Ec8751-Optical Communication-534191069-Ec8751 Optical Communication Question BankDocument60 pagesEc8751-Optical Communication-534191069-Ec8751 Optical Communication Question Bankaajdufkf0% (1)
- Models - Woptics.step Index Fiber BendDocument24 pagesModels - Woptics.step Index Fiber BendMoti Ben LaishNo ratings yet
- 1 Optical Fiber Profiles Modes Materials FabriactionDocument18 pages1 Optical Fiber Profiles Modes Materials FabriactionCharles WilliamNo ratings yet
- Fibers From The View of Geometrical Optics: EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 2Document21 pagesFibers From The View of Geometrical Optics: EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 2gautamckumarNo ratings yet
- Etop 2015 Tpe22Document6 pagesEtop 2015 Tpe22Deepesh JainNo ratings yet
- Optical CommunicationDocument16 pagesOptical CommunicationElma RaymondNo ratings yet
- Numerical With AnswerDocument19 pagesNumerical With AnswerRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Optelec2 PDFDocument114 pagesOptelec2 PDFafifeh ghaemniaNo ratings yet
- Lect5-Optical Fibers 2Document134 pagesLect5-Optical Fibers 2trlp1712100% (1)
- OCN Unit 1,2Document23 pagesOCN Unit 1,2M Madhu MaliniNo ratings yet
- Ofc TheoryDocument69 pagesOfc TheorynainaNo ratings yet
- TC-315 Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 6aDocument28 pagesTC-315 Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 6aTahreem FatimaNo ratings yet
- Fibers and Its Properties: Chapter ThreeDocument67 pagesFibers and Its Properties: Chapter ThreeErmias WasihunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Optical W.GDocument42 pagesChapter 3 Optical W.G歐育成No ratings yet
- Soham PECEC801A f1681907921052 PDFDocument6 pagesSoham PECEC801A f1681907921052 PDFAshish OjhaNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communications - Unit 1 - ASRaoDocument28 pagesOptical Fiber Communications - Unit 1 - ASRaoAllanki Sanyasi RaoNo ratings yet
- Foli Unit 1 - 2 Mark Question and AnswerDocument4 pagesFoli Unit 1 - 2 Mark Question and AnswerJayakumar ThangavelNo ratings yet
- Rohini 24928786475Document12 pagesRohini 24928786475aswinvirat84No ratings yet
- EEE 404 - Lecture 3-7 (Optical Fiber)Document64 pagesEEE 404 - Lecture 3-7 (Optical Fiber)md.saiful islamNo ratings yet
- OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION Basic and CharactersticsDocument36 pagesOPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION Basic and CharactersticsabidNo ratings yet
- Compare Single Mode and Multimode Step Index and Graded Index Optical Fibers PDFDocument24 pagesCompare Single Mode and Multimode Step Index and Graded Index Optical Fibers PDFbeaulajenishNo ratings yet
- Day 4Document41 pagesDay 4Abhiram SwarnaNo ratings yet
- Prof. Suren's Notes On Optical FibresDocument11 pagesProf. Suren's Notes On Optical FibresYo azharNo ratings yet
- Ofc 1 1Document16 pagesOfc 1 1Wasimul HaqNo ratings yet
- Signal Degradation in Optical FibersDocument75 pagesSignal Degradation in Optical FibersBasud Mohammed RasoolNo ratings yet
- OCN Unit I KeyDocument11 pagesOCN Unit I KeyChandra MathiNo ratings yet
- 2-Fibers and Transmission CharacteristicsDocument80 pages2-Fibers and Transmission CharacteristicsIsmat JahanNo ratings yet
- Mode TheoryDocument24 pagesMode Theoryaslakshmi153No ratings yet
- Loss in Fiber OpticsDocument23 pagesLoss in Fiber OpticsCeline Dian SitorusNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Modes and ConfigurationsDocument37 pagesOptical Fiber Modes and ConfigurationsDhivya GunasekarNo ratings yet
- Source of Information Electrical Transmit Optical SourceDocument37 pagesSource of Information Electrical Transmit Optical SourcesubashNo ratings yet
- PH1001T Lec11Document12 pagesPH1001T Lec11Tejashree VNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document18 pagesChapter 3mohammed emadNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Optical SourcesDocument31 pagesUnit Iii Optical SourcesPavani MandapatiNo ratings yet
- FYP Thesis - Template-1Document50 pagesFYP Thesis - Template-1Junaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Signals ClassificationDocument5 pagesSignals ClassificationJunaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Code of EthicsDocument2 pagesCode of EthicsJunaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- DSP - Classification of DT SignalsDocument5 pagesDSP - Classification of DT SignalsJunaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - Application Layer - IDocument16 pagesLec 2 - Application Layer - IJunaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - Application Layer - V - P2PDocument19 pagesLec 2 - Application Layer - V - P2PJunaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- DSP - Classification of CT SignalsDocument8 pagesDSP - Classification of CT SignalsJunaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - Application Layer - IV - Electronic MailDocument17 pagesLec 2 - Application Layer - IV - Electronic MailJunaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - Application Layer - II - WEB HTTPDocument29 pagesLec 2 - Application Layer - II - WEB HTTPJunaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- DR Kifayat Ullah EPM 2Document32 pagesDR Kifayat Ullah EPM 2Junaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Engineering Project Management Lecture 5Document37 pagesEngineering Project Management Lecture 5Junaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Lec 10,11Document24 pagesLec 10,11Junaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Lec #9 (Newton Divided Difference)Document20 pagesLec #9 (Newton Divided Difference)Junaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Lec # 10 (LAGRANGES INTERPOLATION) PDFDocument20 pagesLec # 10 (LAGRANGES INTERPOLATION) PDFJunaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Lec #2 (Bisection Method & False Position) PDFDocument41 pagesLec #2 (Bisection Method & False Position) PDFJunaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Proferssinoal Ethics 2 PDFDocument14 pagesProferssinoal Ethics 2 PDFJunaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Lec # 11 (Eulers Method) PDFDocument14 pagesLec # 11 (Eulers Method) PDFJunaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Lec #3 (Successive App & Newton Raphson) PDFDocument34 pagesLec #3 (Successive App & Newton Raphson) PDFJunaid KaleemNo ratings yet
- Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD), Its Limits, Compensation and Effect On Optical Fiber NetworksDocument6 pagesPolarization Mode Dispersion (PMD), Its Limits, Compensation and Effect On Optical Fiber NetworksJournal of ComputingNo ratings yet
- Tender 2013-B-OVS - Yangon Pathein Fiber Link (UG Cable) - 48 Core UG Fiber Spec PDFDocument6 pagesTender 2013-B-OVS - Yangon Pathein Fiber Link (UG Cable) - 48 Core UG Fiber Spec PDFTechne PhobosNo ratings yet
- Polarization Mode DispersionDocument2 pagesPolarization Mode DispersionUsman M. NooruddinNo ratings yet
- MD40 Patch Panel Data SheetDocument6 pagesMD40 Patch Panel Data SheetMohamed YousufNo ratings yet
- Oc Module 1-6 PDFDocument162 pagesOc Module 1-6 PDFTintu TrmNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument29 pagesPPTMahendra MandalapuNo ratings yet
- Agilent N3900A - 3910AL DatasheetDocument28 pagesAgilent N3900A - 3910AL DatasheetAmir GoodarziNo ratings yet
- Polarization Mode Dispersion - FibreOptoDocument17 pagesPolarization Mode Dispersion - FibreOptoclaudia khansa'No ratings yet
- IEMS5705 Part1 PDFDocument55 pagesIEMS5705 Part1 PDFsmsekarNo ratings yet
- Lec13 ES475 2023 UploadDocument38 pagesLec13 ES475 2023 UploadUmar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Transmission Characteristic of Optical FibersDocument64 pagesTransmission Characteristic of Optical FibersVargheseMartinNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibers: Presented by Asst. Prof. Hamidullah RiazDocument24 pagesOptical Fibers: Presented by Asst. Prof. Hamidullah RiazMohammad Yasin QuraishiNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber-Dispersion SP 2014Document19 pagesOptical Fiber-Dispersion SP 2014Ajay DillikarNo ratings yet
- Power Point Presentation On Analysis and Reduction of Polarization Mode DispersionDocument12 pagesPower Point Presentation On Analysis and Reduction of Polarization Mode Dispersiongvr11100% (1)
- 7 - Fiber Attenuation and DispersionDocument74 pages7 - Fiber Attenuation and DispersionSalim KhanNo ratings yet
- DROP CABLE-1 G.657A2: Cable Cross-Section and DimensionsDocument5 pagesDROP CABLE-1 G.657A2: Cable Cross-Section and DimensionsJairoARojasNo ratings yet
- Fiber DesignDocument42 pagesFiber DesignAFS AssociatesNo ratings yet
- Resume Abstrak Artikel Internasional 2020Document371 pagesResume Abstrak Artikel Internasional 2020Irwina eka derayaNo ratings yet
- Transmissioin Charecteristics of Optical FibresDocument33 pagesTransmissioin Charecteristics of Optical FibresNagaraj HegdeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6. Transmission Characteristics of Optical Fibers - Fiber PDFDocument92 pagesLecture 6. Transmission Characteristics of Optical Fibers - Fiber PDFVijay JanyaniNo ratings yet
- Advanced DWDM TrainingDocument144 pagesAdvanced DWDM TrainingShaytaanNo ratings yet
- Attenuation and DispersionDocument92 pagesAttenuation and Dispersionscribd01No ratings yet
- Programmable PMD Emulator Solution: FBERPRO's PMD (Polarization ModeDocument4 pagesProgrammable PMD Emulator Solution: FBERPRO's PMD (Polarization ModeNguyễn Thành TrungNo ratings yet
- WDM FundamentalsDocument52 pagesWDM FundamentalsArshiya Bhatti100% (1)
- Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Fourth EditionDocument67 pagesFiber-Optic Communication Systems Fourth Editionnina7896No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Gaussian Pulse Inside Optical Fiber With Particular Consideration of Pulse BroadeningDocument6 pagesDynamics of Gaussian Pulse Inside Optical Fiber With Particular Consideration of Pulse BroadeningJournal of TelecommunicationsNo ratings yet
- Dispersion Compensation ModuleDocument19 pagesDispersion Compensation ModuleRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- 5-OTC000601 OptiX WDM Network Design Basics ISSUE1.01Document51 pages5-OTC000601 OptiX WDM Network Design Basics ISSUE1.01HachidSofianeNo ratings yet