Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Newton
Newton
Uploaded by
Nakkungu MarylnCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- L9 - Newtons Laws of MotionDocument17 pagesL9 - Newtons Laws of MotionMeeta DeviNo ratings yet
- OL Activity Science8Document2 pagesOL Activity Science8Yadnis Waters NaejNo ratings yet
- Ancy C Simon Physical Science Optional Register Number-13971004Document20 pagesAncy C Simon Physical Science Optional Register Number-13971004Mark Jay BongolanNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion 1Document9 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion 1grantstuartwNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument24 pagesLaws of MotionAna Marie Renton100% (1)
- Year 10 Physical Sciences Week 3 and 4 AnswersDocument12 pagesYear 10 Physical Sciences Week 3 and 4 AnswersDaniel XuNo ratings yet
- Newtons Second Law and WeightDocument1 pageNewtons Second Law and WeighttasnimNo ratings yet
- Force Equals Mass Times AccelerationDocument1 pageForce Equals Mass Times AccelerationDen EsicNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Grade 12 General PhysicsDocument3 pagesModule 4 Grade 12 General PhysicsLaarni Tolete100% (1)
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: ?N 20kg 10m/s2Document3 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: ?N 20kg 10m/s2Te_Ke_407No ratings yet
- ForceDocument26 pagesForceShinji100% (1)
- Laws of Motion 3 (C)Document4 pagesLaws of Motion 3 (C)Samrudh MysoreNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Newtons-1st-LawDocument52 pagesPHYSICS Newtons-1st-LawLago, Azel Chin L.No ratings yet
- Newtons Law of Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagesNewtons Law of Motion WorksheetAlyssa Mae DapadapNo ratings yet
- Newton's Secon Law of MotionDocument8 pagesNewton's Secon Law of MotionMerlyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Forces-1Document46 pagesLesson 6 Forces-1bloomNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument19 pagesProblem SolvingMary Mariette Escalante100% (1)
- Physical Science Chapter 2Document4 pagesPhysical Science Chapter 2Nurhanifa MustafaNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Physics: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Syllabus: Chapter 2.07, 2.08 and 2.10Document2 pagesClass 6 Physics: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Syllabus: Chapter 2.07, 2.08 and 2.10tasnimNo ratings yet
- AP B Chapter 4 Newtons Laws PDFDocument19 pagesAP B Chapter 4 Newtons Laws PDFAbcNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Newton's 2nd and 3rd LawDocument18 pages3.4 Newton's 2nd and 3rd LawIDKNo ratings yet
- Physics (CETs)Document9 pagesPhysics (CETs)AkiNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument18 pagesMomentumpalicpicantorearichNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws F MaDocument12 pagesNewtons Laws F MaMaruli AmbaritaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 NotesDocument14 pagesChapter 8 NotesDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Fie's Newton LawDocument26 pagesFie's Newton LawNida'ul KhasanahNo ratings yet
- Second Law-Law of AccelerationDocument13 pagesSecond Law-Law of AccelerationArcela Heloise T. CalanganNo ratings yet
- Third Law of Motion: LAW OF Acceleration Third Law of Motion: LAW OF AccelerationDocument15 pagesThird Law of Motion: LAW OF Acceleration Third Law of Motion: LAW OF AccelerationDiana BagayNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 Scalars and Vectors: 1 Law of Motion (Law of Inertia)Document4 pagesLecture-1 Scalars and Vectors: 1 Law of Motion (Law of Inertia)Raef AhmedNo ratings yet
- According To NewtonDocument4 pagesAccording To NewtonBaltazar MarcosNo ratings yet
- Solid Snappy Jelly Presentation G8 Science 2nd QuarterDocument26 pagesSolid Snappy Jelly Presentation G8 Science 2nd Quarterftv397900No ratings yet
- Newtons 2nd Law CalcsDocument4 pagesNewtons 2nd Law CalcscaitlyntreacyNo ratings yet
- Article - Newtons 3 Laws - Intro To DynamicsDocument6 pagesArticle - Newtons 3 Laws - Intro To DynamicsRegina Mae Narciso NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Ch.3 Dynamics (Q &ans) - 1Document5 pagesCh.3 Dynamics (Q &ans) - 1boltplayz2009No ratings yet
- NddvjiyfgnkDocument7 pagesNddvjiyfgnkClyde QuitorasNo ratings yet
- Sample AMS Questions-Exam 1617-FM32 (Chapter3 Section2 - Newton's 2 Law of Motion)Document3 pagesSample AMS Questions-Exam 1617-FM32 (Chapter3 Section2 - Newton's 2 Law of Motion)api-270387817No ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of Motion - UnlockedDocument11 pagesNewtons Laws of Motion - UnlockedmadjerkmemesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document68 pagesChapter 2api-19824406No ratings yet
- Law of Motion Final PDFDocument32 pagesLaw of Motion Final PDFMark RosalesNo ratings yet
- 9 Science NcertSolutions Chapter 9 Intext Page 126 127Document2 pages9 Science NcertSolutions Chapter 9 Intext Page 126 127ShivanshNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law of MotionDocument9 pagesNewton's Second Law of Motionlekshmikrishnan224No ratings yet
- Chapter Two - Newtons Law-FDocument67 pagesChapter Two - Newtons Law-Fnajjar119No ratings yet
- PHYSICS - Newton's Law of MotionDocument5 pagesPHYSICS - Newton's Law of MotionClaire OndesNo ratings yet
- Physics Ss2 2nd Term e NotesDocument73 pagesPhysics Ss2 2nd Term e NotesAdio Babatunde Abiodun CabaxNo ratings yet
- Week 2.newtons Second Law of Motion ComputationDocument29 pagesWeek 2.newtons Second Law of Motion ComputationKylle AtencioNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of MotionDocument17 pagesNewtons Laws of MotionlouserafaelNo ratings yet
- Science Group 2: Newton's Second LawDocument2 pagesScience Group 2: Newton's Second LawJohn Philip PatuñganNo ratings yet
- Lab 14 Study of Newton's 2nd Law of MotionDocument5 pagesLab 14 Study of Newton's 2nd Law of MotionWaqas Muneer KhanNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion: Physics 1Document61 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion: Physics 1rajaNo ratings yet
- AS LEVEL PHYSICS NOTES Newton's LawsDocument2 pagesAS LEVEL PHYSICS NOTES Newton's LawsKartika PrajogoNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To Gravity ForcesDocument28 pagesAcceleration Due To Gravity Forcesfelipee20No ratings yet
- Law of AccelerationDocument22 pagesLaw of AccelerationArceusNo ratings yet
- Quarter1 Week5 Module5 GENERAL-PHYSICS1 Second-Law-of-Motion SecondEditionDocument10 pagesQuarter1 Week5 Module5 GENERAL-PHYSICS1 Second-Law-of-Motion SecondEditionelyzadelapena123No ratings yet
- Topic 4 Linear Kinetic of Human MovementDocument14 pagesTopic 4 Linear Kinetic of Human Movementilostmya44No ratings yet
- Classical MechanicsDocument5 pagesClassical MechanicsFarjana KabirNo ratings yet
- National Christian Life College Science 8 - Worksheet Newton's Laws of Motion - CDocument3 pagesNational Christian Life College Science 8 - Worksheet Newton's Laws of Motion - CLannayah coNo ratings yet
- Newton's LawsDocument56 pagesNewton's Lawskoromamoses235No ratings yet
- Power, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPower, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
Newton
Newton
Uploaded by
Nakkungu MarylnCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Newton
Newton
Uploaded by
Nakkungu MarylnCopyright:
Available Formats
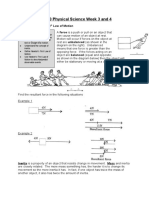
Newton’s second law of motion:
Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly related to
the net force and inversely related to its mass. Acceleration of an object depends on
two things, force and mass. This shows that the bowling experiences a much
greater force. But because of the big mass, it resists acceleration more.
The law is often expressed with the formula: F = m𝑎, where F is the net force, m is
the mass and 𝑎 is the acceleration.
1. A ball develops a certain amount of acceleration after being hit. The
acceleration with which the ball moves is directly proportional to the force
applied to it. This means that the harder you hit the ball, the faster it will
move, thereby demonstrating Newton's second law of motion in daily life.
2. Scenario: An elevator with a mass of 1000 kg is being pulled upward with a
force of 12000 N. What is the acceleration of the elevator?
Explanation: To find the acceleration, subtract the force due to gravity from the
total force applied.
The force due to gravity (weight) is:
Fg = mg = 1000kg x 9.8 m/s^2 = 9800N
1200N – 9800N = 2200N
Fa = ma
2200N = 1000kg x a
a=2200N/ 1000kg = 2.2m/s^2
The elevator will accelerate upwards at 2.2 meters per second squared.
3. Pushing a cart. It is easier to push an empty cart in a supermarket than a
loaded one, and more mass requires more acceleration.
You might also like
- L9 - Newtons Laws of MotionDocument17 pagesL9 - Newtons Laws of MotionMeeta DeviNo ratings yet
- OL Activity Science8Document2 pagesOL Activity Science8Yadnis Waters NaejNo ratings yet
- Ancy C Simon Physical Science Optional Register Number-13971004Document20 pagesAncy C Simon Physical Science Optional Register Number-13971004Mark Jay BongolanNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion 1Document9 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion 1grantstuartwNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument24 pagesLaws of MotionAna Marie Renton100% (1)
- Year 10 Physical Sciences Week 3 and 4 AnswersDocument12 pagesYear 10 Physical Sciences Week 3 and 4 AnswersDaniel XuNo ratings yet
- Newtons Second Law and WeightDocument1 pageNewtons Second Law and WeighttasnimNo ratings yet
- Force Equals Mass Times AccelerationDocument1 pageForce Equals Mass Times AccelerationDen EsicNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Grade 12 General PhysicsDocument3 pagesModule 4 Grade 12 General PhysicsLaarni Tolete100% (1)
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: ?N 20kg 10m/s2Document3 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: ?N 20kg 10m/s2Te_Ke_407No ratings yet
- ForceDocument26 pagesForceShinji100% (1)
- Laws of Motion 3 (C)Document4 pagesLaws of Motion 3 (C)Samrudh MysoreNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Newtons-1st-LawDocument52 pagesPHYSICS Newtons-1st-LawLago, Azel Chin L.No ratings yet
- Newtons Law of Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagesNewtons Law of Motion WorksheetAlyssa Mae DapadapNo ratings yet
- Newton's Secon Law of MotionDocument8 pagesNewton's Secon Law of MotionMerlyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Forces-1Document46 pagesLesson 6 Forces-1bloomNo ratings yet
- Problem SolvingDocument19 pagesProblem SolvingMary Mariette Escalante100% (1)
- Physical Science Chapter 2Document4 pagesPhysical Science Chapter 2Nurhanifa MustafaNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Physics: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Syllabus: Chapter 2.07, 2.08 and 2.10Document2 pagesClass 6 Physics: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Syllabus: Chapter 2.07, 2.08 and 2.10tasnimNo ratings yet
- AP B Chapter 4 Newtons Laws PDFDocument19 pagesAP B Chapter 4 Newtons Laws PDFAbcNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Newton's 2nd and 3rd LawDocument18 pages3.4 Newton's 2nd and 3rd LawIDKNo ratings yet
- Physics (CETs)Document9 pagesPhysics (CETs)AkiNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument18 pagesMomentumpalicpicantorearichNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws F MaDocument12 pagesNewtons Laws F MaMaruli AmbaritaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 NotesDocument14 pagesChapter 8 NotesDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Fie's Newton LawDocument26 pagesFie's Newton LawNida'ul KhasanahNo ratings yet
- Second Law-Law of AccelerationDocument13 pagesSecond Law-Law of AccelerationArcela Heloise T. CalanganNo ratings yet
- Third Law of Motion: LAW OF Acceleration Third Law of Motion: LAW OF AccelerationDocument15 pagesThird Law of Motion: LAW OF Acceleration Third Law of Motion: LAW OF AccelerationDiana BagayNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 Scalars and Vectors: 1 Law of Motion (Law of Inertia)Document4 pagesLecture-1 Scalars and Vectors: 1 Law of Motion (Law of Inertia)Raef AhmedNo ratings yet
- According To NewtonDocument4 pagesAccording To NewtonBaltazar MarcosNo ratings yet
- Solid Snappy Jelly Presentation G8 Science 2nd QuarterDocument26 pagesSolid Snappy Jelly Presentation G8 Science 2nd Quarterftv397900No ratings yet
- Newtons 2nd Law CalcsDocument4 pagesNewtons 2nd Law CalcscaitlyntreacyNo ratings yet
- Article - Newtons 3 Laws - Intro To DynamicsDocument6 pagesArticle - Newtons 3 Laws - Intro To DynamicsRegina Mae Narciso NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Ch.3 Dynamics (Q &ans) - 1Document5 pagesCh.3 Dynamics (Q &ans) - 1boltplayz2009No ratings yet
- NddvjiyfgnkDocument7 pagesNddvjiyfgnkClyde QuitorasNo ratings yet
- Sample AMS Questions-Exam 1617-FM32 (Chapter3 Section2 - Newton's 2 Law of Motion)Document3 pagesSample AMS Questions-Exam 1617-FM32 (Chapter3 Section2 - Newton's 2 Law of Motion)api-270387817No ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of Motion - UnlockedDocument11 pagesNewtons Laws of Motion - UnlockedmadjerkmemesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document68 pagesChapter 2api-19824406No ratings yet
- Law of Motion Final PDFDocument32 pagesLaw of Motion Final PDFMark RosalesNo ratings yet
- 9 Science NcertSolutions Chapter 9 Intext Page 126 127Document2 pages9 Science NcertSolutions Chapter 9 Intext Page 126 127ShivanshNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law of MotionDocument9 pagesNewton's Second Law of Motionlekshmikrishnan224No ratings yet
- Chapter Two - Newtons Law-FDocument67 pagesChapter Two - Newtons Law-Fnajjar119No ratings yet
- PHYSICS - Newton's Law of MotionDocument5 pagesPHYSICS - Newton's Law of MotionClaire OndesNo ratings yet
- Physics Ss2 2nd Term e NotesDocument73 pagesPhysics Ss2 2nd Term e NotesAdio Babatunde Abiodun CabaxNo ratings yet
- Week 2.newtons Second Law of Motion ComputationDocument29 pagesWeek 2.newtons Second Law of Motion ComputationKylle AtencioNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of MotionDocument17 pagesNewtons Laws of MotionlouserafaelNo ratings yet
- Science Group 2: Newton's Second LawDocument2 pagesScience Group 2: Newton's Second LawJohn Philip PatuñganNo ratings yet
- Lab 14 Study of Newton's 2nd Law of MotionDocument5 pagesLab 14 Study of Newton's 2nd Law of MotionWaqas Muneer KhanNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion: Physics 1Document61 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion: Physics 1rajaNo ratings yet
- AS LEVEL PHYSICS NOTES Newton's LawsDocument2 pagesAS LEVEL PHYSICS NOTES Newton's LawsKartika PrajogoNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To Gravity ForcesDocument28 pagesAcceleration Due To Gravity Forcesfelipee20No ratings yet
- Law of AccelerationDocument22 pagesLaw of AccelerationArceusNo ratings yet
- Quarter1 Week5 Module5 GENERAL-PHYSICS1 Second-Law-of-Motion SecondEditionDocument10 pagesQuarter1 Week5 Module5 GENERAL-PHYSICS1 Second-Law-of-Motion SecondEditionelyzadelapena123No ratings yet
- Topic 4 Linear Kinetic of Human MovementDocument14 pagesTopic 4 Linear Kinetic of Human Movementilostmya44No ratings yet
- Classical MechanicsDocument5 pagesClassical MechanicsFarjana KabirNo ratings yet
- National Christian Life College Science 8 - Worksheet Newton's Laws of Motion - CDocument3 pagesNational Christian Life College Science 8 - Worksheet Newton's Laws of Motion - CLannayah coNo ratings yet
- Newton's LawsDocument56 pagesNewton's Lawskoromamoses235No ratings yet
- Power, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPower, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet