Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Second Written Test
Second Written Test
Uploaded by
cristoblsepulvedaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Second Written Test
Second Written Test
Uploaded by
cristoblsepulvedaCopyright:
Available Formats
Present perfect and Present perfect continuous
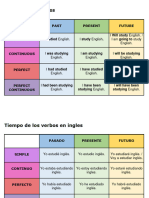
The present perfect simple describes actions or states that occurred at an unspecified time in the past and are relevant
to the present. SUBJECT + HAVE/HAS + PAST PARTICIPLE
Actions completed at an unspecified time. Actions that started in the past and continue to the present. Life
experiences. Recent events with relevance to the present.
The present perfect continuous describes actions that started in the past and may continue to the present or recently
finished, focusing on the duration of the action. SUBJECT + HAVE/HAS BEEN + VERB-ING
Actions that began in the past and continue into the present. Actions that recently stopped, emphazing the
duration.
P.P. SIMPLE P.P. CONTINUOUS
TYPICAL CONTEXTS Present perfect simple is used for life Present perfect continuous is used
experiences and completed actions. for ongoing actions or those that
recently ended.
FOCUS Present perfect simple emphasizes the Present perfect continuous
result or completion. emphasizes the duration.
Comparative and Superlatives
Comparative adjectives Superlative adjectives
RULE 1 If an adjective has 1 syllable we add the ending If an adjective has 1 syllable we add the ending -est
-er to the adjective. to the adjective.
RULE 2 If an adjective ends with a consonant + vowel + If an adjective ends with a consonant + vowel +
consonant you must double the last consonant consonant you must double the last consonant and
and add -er. add -est.
RULE 3 If an adjective ends with a “y” remove the “y” If an adjective ends with a “y” remove the “y” and
and add -ier. add -iest.
RULE 4 If an adjective has 2 syllables or more then we If an adjective has 2 syllables or more then we add
add the word “more” to the adjective. the word “most” to the adjective.
RULE 5 Better (Good); Worse (Bad); Farther (Far). Best (Good); Worst (Bad); Farthest (Far).
The comparative adjectives are used to show the difference between two objects. Meanwhile, the superlative
adjectives are used to show the difference between more than two objects.
Modal verbs of deduction and speculation
We use the modal verbs before the infinitive of other verbs to speculate and guess if something is true from the
information we have. SUBJECT + MODAL VERB + BASE FORM
Must Strong belief or certainty. Is used when the speaker is almost sure something is true.
(100%)
Can’t Indicates strong is belief or impossibility. Used when the speaker thinks something I possible but not
(100%) true.
Could Indicates possibility but not certainty. Used when the speaker thinks something is possible but not sure.
(50%)
May Indicates a more tentative possibility. Used when the speaker is less certain about the situation.
(25%)
You might also like
- TOEFL Grammar Guide: 23 Grammar Rules You Must Know To Guarantee Your Success On The TOEFL Exam!From EverandTOEFL Grammar Guide: 23 Grammar Rules You Must Know To Guarantee Your Success On The TOEFL Exam!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (41)
- Part A: Scenario 1: RileyDocument10 pagesPart A: Scenario 1: Rileythunguyenhoang0303No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - People - General English 1Document20 pagesUnit 1 - People - General English 1Hoàng KhangNo ratings yet
- Discourse and Context in Language Teaching - A Guide For Language Teachers (2001)Document292 pagesDiscourse and Context in Language Teaching - A Guide For Language Teachers (2001)HUỲNH YẾN NHINo ratings yet
- Aspect in English GrammarDocument6 pagesAspect in English GrammarDelma Andrade100% (1)
- Michel Thomas - German - Foundation and Advanced Course TranscriptsDocument62 pagesMichel Thomas - German - Foundation and Advanced Course Transcriptsroggeman100% (2)
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense - by Diffit (Printable)Document5 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous Tense - by Diffit (Printable)juliejuice3No ratings yet
- Proyecto Ingles PDFDocument27 pagesProyecto Ingles PDFDolman GonzalezNo ratings yet
- GRAMMARREVIEWDocument31 pagesGRAMMARREVIEWpaulinaveraNo ratings yet
- Verbs & AdverbDocument33 pagesVerbs & AdverbAli Ali AneesNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document23 pagesPresentation 2Renaldy MamarasiNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect SimpleDocument3 pagesPast Perfect Simplemayinovoa2610No ratings yet
- Week 3 PPT 12 Tenses OverviewDocument78 pagesWeek 3 PPT 12 Tenses OverviewdewxoNo ratings yet
- B2 Content ReviewDocument12 pagesB2 Content Reviewnina1317calleNo ratings yet
- 5th. Class - Adverbs - Already, Just, Still and Yet - June 19th, 2024Document6 pages5th. Class - Adverbs - Already, Just, Still and Yet - June 19th, 2024Abner Rafael Rodriguez valleNo ratings yet
- صفوت محمد رضا شعيب. قواعد اللغة الانجليزيةDocument79 pagesصفوت محمد رضا شعيب. قواعد اللغة الانجليزيةbewarkootcher100% (1)
- ProgressiveDocument5 pagesProgressiveDaisylineCaleonCruzNo ratings yet
- Homework PresentationDocument29 pagesHomework PresentationEmmanuel HrNo ratings yet
- VerbsDocument39 pagesVerbsPhương LinhNo ratings yet
- Easy EnglishDocument12 pagesEasy Englishbryan zavaleta benitesNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TenseDocument30 pagesPresent Perfect TenseMuthiah Nadiyah PutriNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris (Softskill) "Tenses"Document14 pagesBahasa Inggris (Softskill) "Tenses"Syairoh MunawarohNo ratings yet
- Verb TenseDocument4 pagesVerb TenseFlorencia Rita Leonor MolinaNo ratings yet
- Verbs, Tense, Aspect, and Mood: By: Acmad Yani, S.SDocument19 pagesVerbs, Tense, Aspect, and Mood: By: Acmad Yani, S.SametgembulNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Relative ClausesDocument5 pagesUnit 6 Relative ClausesJorge LunaNo ratings yet
- English GuideDocument4 pagesEnglish GuideMichelle YepezNo ratings yet
- Tenses and Verbs (Group 3)Document62 pagesTenses and Verbs (Group 3)Ghea LuthfiaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Sentence 2Document2 pagesParts of A Sentence 2Meryem GomezNo ratings yet
- Modals Are Auxiliary or Helping Verbs. They May Be Used in Expressing Permission, Obligation and ProhibitionDocument9 pagesModals Are Auxiliary or Helping Verbs. They May Be Used in Expressing Permission, Obligation and ProhibitionJurelyn Victoria VeranNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument20 pagesInglesJesús RamsésNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Vs Past PERFECTDocument2 pagesPast Simple Vs Past PERFECTDaniela BlagojevicNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 3 EnglishDocument21 pagesKelompok 3 EnglishIka putriNo ratings yet
- Aspects of VerbsDocument5 pagesAspects of VerbsCharmange Faye BlancaNo ratings yet
- Present TenseDocument24 pagesPresent Tensearyasaputra7333No ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument8 pagesPresent ContinuousDolores EscobedoNo ratings yet
- English ClassDocument40 pagesEnglish ClassDiego Coba BravoNo ratings yet
- CCS PPT!Document25 pagesCCS PPT!Dhien KinilitanNo ratings yet
- 11 Le2Document4 pages11 Le2amaterasu.sendaiNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument9 pagesInglesDaniela Brunal VilaróNo ratings yet
- English Grammar For A2 Level Students: OutlineDocument12 pagesEnglish Grammar For A2 Level Students: OutlineJuan Carlos Martinez ReynaNo ratings yet
- Unit 05 - Grammar C 2Document16 pagesUnit 05 - Grammar C 2RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Formato de Guía Actividad 1 Nivel VDocument5 pagesFormato de Guía Actividad 1 Nivel Vsilvia sanchez barretoNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument20 pagesConditional SentencesBelinha FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument2 pagesVerb TensesSiska WidyawatiNo ratings yet
- Present Vs Past PerfectDocument9 pagesPresent Vs Past PerfectyopruebapremiereNo ratings yet
- We Use of Verbs To Refer To, Actions or Situations in The Present in The Past and in The FutureDocument78 pagesWe Use of Verbs To Refer To, Actions or Situations in The Present in The Past and in The FutureHaryatmo TriNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Progressive TenseDocument15 pagesPresent Perfect Progressive TenseJustine Jhon AdolfoNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Progressive Tense: Bye: Zella Fran Sisca Resty Madeha Ilahi Ira VeronikaDocument14 pagesSimple Present Progressive Tense: Bye: Zella Fran Sisca Resty Madeha Ilahi Ira VeronikaRafatar RaffiNo ratings yet
- Planeacion InglesDocument16 pagesPlaneacion InglesRicardo VillegasNo ratings yet
- Universidad Yacambú Vice-Rectorado Académico Facultad de Ciencias Jurídicas Y PolíticasDocument7 pagesUniversidad Yacambú Vice-Rectorado Académico Facultad de Ciencias Jurídicas Y PolíticasKristian DíazNo ratings yet
- Presentaciningls Presenteperfecto 130226121227 Phpapp02 PDFDocument7 pagesPresentaciningls Presenteperfecto 130226121227 Phpapp02 PDFKristian DíazNo ratings yet
- Grammar Guide 1: Katherine González EsquivelDocument9 pagesGrammar Guide 1: Katherine González Esquiveljesus sentiesNo ratings yet
- Perfect TensesDocument7 pagesPerfect TensesNaobi Porras MillánNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple and Present Perfect Continuous - Test-EnglishDocument1 pagePresent Perfect Simple and Present Perfect Continuous - Test-EnglishMoldir TolbassyNo ratings yet
- Trabalho de InglesDocument18 pagesTrabalho de InglesSabio Maria JulioNo ratings yet
- What Is The Present Perfect TenseDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Present Perfect TenseGareth JoseNo ratings yet
- What Is A Verb TenseDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Verb TenseDavie Jane PascuaNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument20 pagesTensesMoh FaisolNo ratings yet
- Grammar Review - English Preparatory School - Paragon International UniversityDocument1 pageGrammar Review - English Preparatory School - Paragon International Universitygechan168No ratings yet
- English PPT Group 4 MJKBDocument16 pagesEnglish PPT Group 4 MJKBAnanda MaylaffaizaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past X Pres PerfectDocument28 pagesSimple Past X Pres PerfectAdriano Santos100% (1)
- Introduction To Tenses: by Oxtapianus TawarikDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Tenses: by Oxtapianus Tawariko.tawarikNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument1 pagePresent PerfectAracely TurrizaNo ratings yet
- Eng 150 Case StudyDocument8 pagesEng 150 Case Studyella.sinontao.cocNo ratings yet
- JPSP - 2022 - 102Document5 pagesJPSP - 2022 - 102Sean TayleNo ratings yet
- Phrasal Verbs - 25Document6 pagesPhrasal Verbs - 25Nguyễn Khánh ChiNo ratings yet
- Object Pronouns - Lesson Plan FinalDocument2 pagesObject Pronouns - Lesson Plan Finalmariamjaramillo6No ratings yet
- 2022-03-15 Reference ListDocument2 pages2022-03-15 Reference ListLa TaNo ratings yet
- BHSEC - English Paper 1Document6 pagesBHSEC - English Paper 1laguman GurungNo ratings yet
- General English Scope and Sequence OutlinesDocument85 pagesGeneral English Scope and Sequence OutlinesGavin BrazierNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology Chapter 8 9 - Group 3Document64 pagesPhonetics and Phonology Chapter 8 9 - Group 3Phương Thảo PhạmNo ratings yet
- Tools, Verbs, Nouns, AdjectivesDocument2 pagesTools, Verbs, Nouns, Adjectiveslei dyluNo ratings yet
- .................. Smaller.................. : Use The Prompts Below To Make Sentences, As in The ExampleDocument4 pages.................. Smaller.................. : Use The Prompts Below To Make Sentences, As in The ExamplePhạm Khắc Trung100% (1)
- Unit 4 Business Communication: A. Warming Up ActivitiesDocument7 pagesUnit 4 Business Communication: A. Warming Up ActivitiesAlfatihahNo ratings yet
- Grammar Dilemma - Teaching Grammar As A Resource For Making MeaningDocument20 pagesGrammar Dilemma - Teaching Grammar As A Resource For Making MeaningTram Nguyen TrinhNo ratings yet
- New Headway - Elementary WorkbookDocument96 pagesNew Headway - Elementary WorkbookAndrés Potes100% (2)
- Ticket 1 Bac LP Comp2 U.8 Grammar Phrasal Verbs Lesson PlanDocument1 pageTicket 1 Bac LP Comp2 U.8 Grammar Phrasal Verbs Lesson PlanSamir AmraniNo ratings yet
- Adverb and Its TypesDocument9 pagesAdverb and Its TypesNOELNo ratings yet
- Pretérito IrregularDocument2 pagesPretérito IrregularJacob ToutNo ratings yet
- Possessive Adjective ExercisesDocument2 pagesPossessive Adjective Exercisesmaxgospel1983No ratings yet
- CAE Students HandbookDocument12 pagesCAE Students HandbookDavid CastroNo ratings yet
- Interrogative Question Sentences Learn English Grammar RajeeveltDocument9 pagesInterrogative Question Sentences Learn English Grammar RajeeveltmarikaNo ratings yet
- Improving Students Speaking Ability Through Repetition DrillDocument10 pagesImproving Students Speaking Ability Through Repetition DrillRoyana Joy FuentesNo ratings yet
- CS 305 Compiler DesignDocument7 pagesCS 305 Compiler DesignKumar shivamNo ratings yet
- English File 3rd Edition Beginners Teacher S ManualDocument234 pagesEnglish File 3rd Edition Beginners Teacher S ManualSiu YauNo ratings yet
- Karya Harris Nizam: Sebuah Tinjauan Pragmatik Dan Implikasinya Terhadap Pembelajaran Bahasa Julia IsmailDocument12 pagesKarya Harris Nizam: Sebuah Tinjauan Pragmatik Dan Implikasinya Terhadap Pembelajaran Bahasa Julia IsmailarfNo ratings yet
- Bhaashika: Telugu Tts System: Dr. K.V.N.SunithaDocument9 pagesBhaashika: Telugu Tts System: Dr. K.V.N.Sunithakanak73No ratings yet
- A2 Study PlanDocument2 pagesA2 Study Plan雅妲យ់ា់ដាNo ratings yet
- Engleza Cls A 10 A A BarDocument3 pagesEngleza Cls A 10 A A BarAna MariaNo ratings yet