Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BEE Electrical Installations Notes
BEE Electrical Installations Notes
Uploaded by
vainavi.ankamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BEE Electrical Installations Notes
BEE Electrical Installations Notes
Uploaded by
vainavi.ankamCopyright:
Available Formats
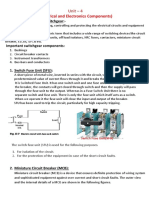
Switch fuse unit
Fuse
A short piece of metal wire, inserted in series with the circuit which melts when predetermined value
of current flows thru it and breaks the circuit.
Under normal conditions, it carriers current without over-heating itself but when an
excessive current flows, its temp. raises and it melts.
Excessive current flows under 2 conditions- overloads/short circuit
Acc. to i2Rt, as temp. increases, heat is produced
Time required to blow a fuse is dependent on the magnitude of the excessive current.
A fuse has inverse time-current characteristic.
Fuse is connected in phase wire -> current enter from phase->neutral wire so, to protect the
load/appliance
Advantages:
Cost of the device is low
Requires no maintenance
Interrupts heavy current without smoke/noise
Min. time of operation can be predetermined by selecting proper material for the
fuse wire
Its inverse time-current characteristic makes it suitable for protection
Disadvantages:
Time lost in re-wirinf or replacing the fuse after every operation
On short-circuit, differentiation between fuses in series can be done only if there is a
size difference between them.
The SFU consists of various porcelain rewireable fuses or HRC fuse fittings with their conductin
Miniature Circuit Breaker
An automatic operated switch under overload/short-circuit conditions
Ensures protection of wiring system, equipment/appliances.
Construction:
Working:
Overload condition: detection is achieved by the thermal expansion of a bimetallic
strip which deflects in response to the current passing thru it. The strip moves
against the trip lever releasing the trip mech.
Short circuit condition: when the current flowing thru the MCB reaches a
predetermined value, it pushes the solenoid plunger which releases the trip mech.
This action is achieved via electromagnetic mechanism.
Applications:
Available in different current ratings and have very smol breaking time so are used to
protect commercial and domestic appliances like computers, acs, refrigerators
Earth leakage circuit breaker (ELCB)
Principle of operation :
Under normal conditions, current flowing thru the phase and neutral wires is
same but when earth leakage (flux leakage) occurs, current in neutral will be
less than phase. This sets up a flux in the core of the core balanced
transformer which in turn induces an emf in the coil. Hence, the relay is
energised and the plunger disconnects the load from the supply
Thus, it protects the system from leakage.
Use of test knob
For the periodic checking of the mech. and function of ELCB
Moulded case circuit breaker (MCCB)
Used when the load current exceeds the capabilities of MCB
The 3 major functions of the MCCB:
Protection against overload
Protection against electrical faults
Switching the circuit on and off
Mechanism:
Overload protection: occurs by means of thermal mechanism. They have a bimetallic
which expands/contracts in response to changes in temp. As soon as temp. exceeds
the adjusted trip value, the contact will heat and expand until the circuit is
interrupted.
Fault protection: whenever a fault occurs, extremely high current induces a magnetic
field in the solenoid coil and this magnetic induction trips a contact and the current
is interruputed.
Manual operation: has disconnection switch which is used to trip the breaker
manually.
Types of wires and cables
Cable
A solid or stranded conductor covered with insulation is a cable
You might also like
- The Relay Testing Handbook-Generator Relay Protection Testing TOC-ToF-BibDocument36 pagesThe Relay Testing Handbook-Generator Relay Protection Testing TOC-ToF-BibMartin Goodnough100% (1)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- PROSPER CompleteDocument1,471 pagesPROSPER Completehamidahaku100% (1)
- Your Work Style in ColorDocument20 pagesYour Work Style in ColorNiraj Ram Shrestha50% (2)
- Crack Tip Opening Displacement CTODDocument11 pagesCrack Tip Opening Displacement CTODAnonymous dvrhf5100% (1)
- Protective DevicesDocument7 pagesProtective Devicesbolt sparkNo ratings yet
- Module 5 UpdatedDocument23 pagesModule 5 UpdatedSaksham (Games and More)No ratings yet
- Study of Power Supply & Safety DevicesDocument27 pagesStudy of Power Supply & Safety DevicesMueen FaisalNo ratings yet
- Protection Circuits: by Murtuza Bohari Sanket Patil Ankit KhandekarDocument21 pagesProtection Circuits: by Murtuza Bohari Sanket Patil Ankit KhandekarSanket PatilNo ratings yet
- I e S 24 QDocument23 pagesI e S 24 Qmdwahidali566No ratings yet
- Earthing System Fuse MCB MCCB Elcb Lightning ProtectionDocument28 pagesEarthing System Fuse MCB MCCB Elcb Lightning Protectionmelvinmathewp044No ratings yet
- Lastactivity NapiliDocument10 pagesLastactivity NapiliMArk BarenoNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Current ProtectionDocument20 pagesTopic 3 - Current ProtectionVictorNo ratings yet
- Installing Electrical Protective Devices For Distribution, Power, Lightning Protection and Grounding SystemsDocument23 pagesInstalling Electrical Protective Devices For Distribution, Power, Lightning Protection and Grounding SystemsYamut Si ako67% (6)
- Switches and BreakersDocument32 pagesSwitches and BreakersJely Taburnal BermundoNo ratings yet
- Mcbs or Miniature Circuit Breakers Are Electromechanical Devices Which ProtectDocument9 pagesMcbs or Miniature Circuit Breakers Are Electromechanical Devices Which ProtectDivyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 5th UnitDocument6 pages5th UnitAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- SUN ReportDocument10 pagesSUN Reportpratham sutharNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Manager Guide Circuit ProtectionDocument16 pagesMaintenance Manager Guide Circuit ProtectionPak Ngah SaniNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 Part 2Document16 pagesMod 1 Part 2Bikash SarrafNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installation: The Most Common Types of Faults in Domestic Systems AreDocument23 pagesElectrical Installation: The Most Common Types of Faults in Domestic Systems Arekrishnareddy_chintala100% (1)
- Topic: Electrical Protective EquipmentDocument17 pagesTopic: Electrical Protective EquipmentAnanjay ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Lightning ProtectionDocument15 pagesLightning ProtectionEnglish words BY Utkarsh johriNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Circuit BreakersDocument13 pagesUnit-I Circuit Breakerspurushg62No ratings yet
- What Is A Circuit BreakerDocument18 pagesWhat Is A Circuit Breakersrinu247No ratings yet
- Miniature Circuit Breakers Seminar NotesDocument6 pagesMiniature Circuit Breakers Seminar NotesAbinaya SriNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document13 pagesAssignment 3Ifeoluwa VictoriaNo ratings yet
- BEE Assignment Unit 4Document13 pagesBEE Assignment Unit 4Abhishek RaoNo ratings yet
- Electrical System Design NotesDocument15 pagesElectrical System Design Notesdilja aravindan100% (1)
- Unit IIDocument24 pagesUnit IIVIJAY BHATANENo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Protection DeviceDocument9 pagesOvercurrent Protection DeviceUmi YumiNo ratings yet
- MCB-Miniature Circuit BreakerDocument6 pagesMCB-Miniature Circuit BreakerVannak CHenNo ratings yet
- InstallationDocument45 pagesInstallationshaadi220622No ratings yet
- Protection Devices1Document45 pagesProtection Devices1sivaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Protective Devices-EcDocument19 pagesElectrical Protective Devices-EcZunaib AliNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 NoteDocument21 pagesUnit-3 NoteSankara nathNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breakers TypesDocument39 pagesCircuit Breakers TypesHeinrich EselaNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 BeeDocument37 pagesUnit-5 BeeAliNo ratings yet
- BEE Unit-5 Notes Basic Electrical InstallationDocument22 pagesBEE Unit-5 Notes Basic Electrical InstallationTapendra Tailor100% (10)
- Ircuit Reakers: (Theory, Classification, & Applications)Document28 pagesIrcuit Reakers: (Theory, Classification, & Applications)Syed Muhammad Munavvar Hussain100% (5)
- Electric Circuit Breaker & IsolatorDocument6 pagesElectric Circuit Breaker & IsolatorRik RkNo ratings yet
- 1 Three Phase Power Measurement, Electrical Safety - Fuses and Earthing, Residential WiringDocument49 pages1 Three Phase Power Measurement, Electrical Safety - Fuses and Earthing, Residential WiringUtkarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Protective Device A SwtichgearDocument24 pagesProtective Device A SwtichgearVarun Ghagare 03No ratings yet
- Slide 1 HistoryDocument2 pagesSlide 1 HistoryNurul ChofifahNo ratings yet
- Switchgear and ProtectionDocument17 pagesSwitchgear and Protection002Pradeep002No ratings yet
- SGP 5Document7 pagesSGP 5Soumajit PoddarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Circuit Breakers: Difference Between An Isolator and Circuit BreakerDocument18 pagesPrinciples of Circuit Breakers: Difference Between An Isolator and Circuit BreakerdemokykNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Basic Protection EquipmentDocument57 pagesChapter 2-Basic Protection EquipmentAkmal GaffarNo ratings yet
- Shakir Seminar Report On Ultra ConductorsDocument18 pagesShakir Seminar Report On Ultra ConductorsMeer ShakirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document15 pagesChapter 7Khaled RabeaNo ratings yet
- Protection Against Overload CurrentDocument21 pagesProtection Against Overload CurrentAzzhariff AHNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Switchgear and ProtectionDocument20 pagesLecture Notes: Switchgear and ProtectionAkula VeerrajuNo ratings yet
- House Wiring MCB MAVDocument7 pagesHouse Wiring MCB MAVP. ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker SGPDocument34 pagesCircuit Breaker SGPSamuel BhukyaNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit and Overload Protection Circuits and DevicesDocument2 pagesShort Circuit and Overload Protection Circuits and DevicesCODE0303456No ratings yet
- Electrical Distribution SystemDocument30 pagesElectrical Distribution SystemMahira NarwariNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument96 pagesLab ManualASWANI RAJAN50% (2)
- Protective Device Used in Electrical InstallationDocument21 pagesProtective Device Used in Electrical Installation622 MANSI TANJILANo ratings yet
- UNIT-VII Electrical Protection: RelayDocument17 pagesUNIT-VII Electrical Protection: RelayMonte CarloNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document17 pagesModule 3Vishal Anand ReddyNo ratings yet
- Empowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearFrom EverandEmpowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearNo ratings yet
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Impedance SpectrosDocument31 pagesElectrochemical Impedance SpectrosDanielPetreNo ratings yet
- Cd4538 Pin DiagramDocument8 pagesCd4538 Pin DiagramPrateek NailwalNo ratings yet
- Radiation: AccelerateDocument37 pagesRadiation: Accelerate張恩睿 CHANG,EN-RUEI C24101147No ratings yet
- Tajinder Singh: BSBSUS401 Implement and Monitor Environmentally Sustainable Work PracticesDocument4 pagesTajinder Singh: BSBSUS401 Implement and Monitor Environmentally Sustainable Work PracticesHarkamal singhNo ratings yet
- Solar Powered Water PumpsDocument6 pagesSolar Powered Water Pumpssandeepbabu28No ratings yet
- Equivariant Morse Theory And Closed Geodesics: (Cross'S) S/ Cp/ Yίp/ CapDocument32 pagesEquivariant Morse Theory And Closed Geodesics: (Cross'S) S/ Cp/ Yίp/ CapJhon Edison Bravo BuitragoNo ratings yet
- Ar Deependra Prashad - DPAPDocument10 pagesAr Deependra Prashad - DPAPAnonymous 1uGSx8bNo ratings yet
- Flacs ManualDocument547 pagesFlacs ManualSANGRAM POWAR100% (2)
- FAQ Wind&Solar MindscapeDocument27 pagesFAQ Wind&Solar MindscapeyacirNo ratings yet
- What To Consider When Welding Dissimilar MaterialsDocument8 pagesWhat To Consider When Welding Dissimilar MaterialsWeldPulse100% (2)
- Paper 9 PDFDocument10 pagesPaper 9 PDFLimuel EspirituNo ratings yet
- Waters of HopeDocument560 pagesWaters of HopePramod MalikNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Study Guide - Exam 1 - Chapters 1-3Document2 pagesInorganic Chemistry Study Guide - Exam 1 - Chapters 1-3Maddy AbdulNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy & Power Questions With Answers AU Special SchoolDocument8 pagesWork, Energy & Power Questions With Answers AU Special Schoolbesufekadmaregu981No ratings yet
- BS09 0875 882Document8 pagesBS09 0875 882Atanas StoykovNo ratings yet
- What Is Pollution:: Contaminants Chemical Substances Energy Pollutants Point SourceDocument7 pagesWhat Is Pollution:: Contaminants Chemical Substances Energy Pollutants Point SourceSameer Al Hossain100% (1)
- Sensitive Earth Fault ProtectionDocument2 pagesSensitive Earth Fault ProtectionWilson PavãoNo ratings yet
- Sample Solar Permit Plan - 1 Line Drawing PDFDocument1 pageSample Solar Permit Plan - 1 Line Drawing PDFSAEL SOLARNo ratings yet
- Low Cost HousingDocument42 pagesLow Cost Housingsai kiran100% (1)
- Solar PV Market in India - March 2024Document2 pagesSolar PV Market in India - March 2024Kirtan Ramesh JethvaNo ratings yet
- Planta Electrica de 152kva 120kw Motor Fawde Tipo Stamford Cabinada Abierta GSFX 120 PDFDocument6 pagesPlanta Electrica de 152kva 120kw Motor Fawde Tipo Stamford Cabinada Abierta GSFX 120 PDFSebastián Fernández LópezNo ratings yet
- Part 4Document6 pagesPart 4Romain DanielNo ratings yet
- CG41C - CH41C - S13 CiacDocument1 pageCG41C - CH41C - S13 CiacYadhira Dominguez ZuritaNo ratings yet
- MIT8 04S16 ps7 2016Document3 pagesMIT8 04S16 ps7 2016Ahmed0% (1)
- Urea CycleDocument8 pagesUrea CycleManohar PattarNo ratings yet
- S Type Load CellDocument2 pagesS Type Load CellAbhimanyu MamNo ratings yet