Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Asm 97560
Asm 97560
Uploaded by
aarnachauhan.2008Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Calculation According To Euler: Piston Rod SelectionDocument2 pagesCalculation According To Euler: Piston Rod SelectionbalajimetturNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document3 pagesExperiment 7Atonimous 07No ratings yet
- Lifting Cargoes With An A-Symmetrical CoGDocument7 pagesLifting Cargoes With An A-Symmetrical CoGRaja GopalNo ratings yet
- Design of Beam Column (Compatibility Mode)Document64 pagesDesign of Beam Column (Compatibility Mode)Sérgio MoraesNo ratings yet
- Modal Analysis of A Small Ship Sea Keeping Trial: A. Metcalfe L. Maurits T. Svenson R. Thach G. E. HearnDocument19 pagesModal Analysis of A Small Ship Sea Keeping Trial: A. Metcalfe L. Maurits T. Svenson R. Thach G. E. Hearnricky.pigazziniNo ratings yet
- A Study On-" ": Buckling & It's TheoriesDocument34 pagesA Study On-" ": Buckling & It's TheoriesAghil BuddyNo ratings yet
- Spring Constant ExperimentDocument4 pagesSpring Constant ExperimentRacNo ratings yet
- Sections-Dev-Intersection of Solids-KsrDocument8 pagesSections-Dev-Intersection of Solids-KsrK S ChalapathiNo ratings yet
- 11 PHY - Term 2 - PracticalsDocument4 pages11 PHY - Term 2 - PracticalsLambò GhiniNo ratings yet
- Xi Practical Term 2Document11 pagesXi Practical Term 2Abhinav YadavNo ratings yet
- Mechanics QuestionsDocument8 pagesMechanics QuestionslloydNo ratings yet
- Experiment - Spring Ofa: ConstantDocument2 pagesExperiment - Spring Ofa: ConstantAsom BartaNo ratings yet
- Phy ProjectDocument5 pagesPhy ProjectSiddharthNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Manual Term2Document18 pagesPhysics Practical Manual Term2studies for sundarNo ratings yet
- ME - 244 Ex 4Document5 pagesME - 244 Ex 4Jubaer RabbyNo ratings yet
- Name: - Worksheet 3.1 - Translational EquilibriumDocument3 pagesName: - Worksheet 3.1 - Translational EquilibriumYehualashet BelaynehNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 - Engg Mech PDFDocument8 pagesAssignment-2 - Engg Mech PDFNiteshNo ratings yet
- Meriam - Dynamics - 8th Ed (2015) - 8Document8 pagesMeriam - Dynamics - 8th Ed (2015) - 8hoormohameed2019No ratings yet
- ObjectiveDocument19 pagesObjectiveAmmir JusohNo ratings yet
- Outline: Spring Functions & Types Helical SpringsDocument46 pagesOutline: Spring Functions & Types Helical SpringsMohammed AlnasharNo ratings yet
- Convex Hull and Voronoi Diagram of Additively Weighted PointsDocument16 pagesConvex Hull and Voronoi Diagram of Additively Weighted Pointsabhiraj1234No ratings yet
- Spring ConstantDocument2 pagesSpring ConstantugharshytNo ratings yet
- Basics of Spar Analysis (Tension Field Beams)Document39 pagesBasics of Spar Analysis (Tension Field Beams)kuracha jayasaikumarNo ratings yet
- A Simple Approach To Truss Deflections: N-Braced TypeDocument6 pagesA Simple Approach To Truss Deflections: N-Braced Typealbertoxina100% (1)
- EXP4 Bending and TorsionDocument2 pagesEXP4 Bending and Torsionaman chopraNo ratings yet
- 7 SuspensionDocument98 pages7 SuspensionRajkumar NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document6 pagesExperiment 4Majdy gamingNo ratings yet
- CE6501 Structural Analysis I 2 Marks Unit 3 PDFDocument14 pagesCE6501 Structural Analysis I 2 Marks Unit 3 PDFJuan WagnerNo ratings yet
- Lab 2: Fundamental Concepts: Beam BendingDocument21 pagesLab 2: Fundamental Concepts: Beam BendingudithaireshaNo ratings yet
- Work 2Document5 pagesWork 2David DanielNo ratings yet
- Lecture12 PDFDocument14 pagesLecture12 PDFTihomir MarkovicNo ratings yet
- Torsion: Torsion Is The Twisting of An Object Due To An AppliedDocument20 pagesTorsion: Torsion Is The Twisting of An Object Due To An Appliedirum,No ratings yet
- 1989 Hong Kong Advanced Level Examination AL Physics Multiple Choice QuestionDocument11 pages1989 Hong Kong Advanced Level Examination AL Physics Multiple Choice QuestionedisonNo ratings yet
- Buckling of Strut ReportDocument19 pagesBuckling of Strut ReportEsyad E-chad50% (2)
- PQM Supplementary Notes: Spin, Topology, SU (2) SO (3) Etc: 1 Rotations and Non-Contractible LoopsDocument8 pagesPQM Supplementary Notes: Spin, Topology, SU (2) SO (3) Etc: 1 Rotations and Non-Contractible LoopsJosé JiménezNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Lab Manual Work - Experiment 5.1Document1 pageClass 11 Physics Lab Manual Work - Experiment 5.11445800No ratings yet
- Strength of Materials EngineerdogDocument43 pagesStrength of Materials EngineerdogHormedo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Smith Charts r3Document31 pagesClass 8 Smith Charts r3Dan ClementiNo ratings yet
- Beam StressesDocument20 pagesBeam StresseshideoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Plate No. 1Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics Plate No. 1Charmaine NarvadezNo ratings yet
- 4.belt and PulleyDocument1 page4.belt and PulleyNimish Raman MitalNo ratings yet
- Simple PendulumDocument5 pagesSimple Pendulumpiyushdua01No ratings yet
- CE Characteristics: Up: PreviousDocument3 pagesCE Characteristics: Up: PrevioussNo ratings yet
- Shear ForceDocument5 pagesShear Forcea.h.alkamyaniNo ratings yet
- TorsionalformulaDocument24 pagesTorsionalformulaMuhammad MusaNo ratings yet
- Observations and CalculationsDocument2 pagesObservations and CalculationsHACKER CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Class 11Document9 pagesPhysics Practical Class 11Surbhi DwivediNo ratings yet
- L-12 CoulumnsDocument59 pagesL-12 CoulumnsBilal KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - NotesDocument29 pagesUnit 8 - NotesNico Dela RamaNo ratings yet
- CD2 - Lect12!17!12-2011 Zapata AislaDocument43 pagesCD2 - Lect12!17!12-2011 Zapata AislaDarlys Rodriguez VillarNo ratings yet
- 6 Experiment6 Torque 1Document5 pages6 Experiment6 Torque 1icecubexx02No ratings yet
- G2-Izham Bin Azhar-Combined Stresses-FrDocument20 pagesG2-Izham Bin Azhar-Combined Stresses-FrZainal PiutNo ratings yet
- Course Work O1Document4 pagesCourse Work O1zaianzNo ratings yet
- Chap 12Document74 pagesChap 12noscribdyoucantNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 14 PDFRui JiNo ratings yet
- Bending Moment (1) : Bending Moment at A Point Due To A Point Load Acting at A Specific Location ObjectiveDocument6 pagesBending Moment (1) : Bending Moment at A Point Due To A Point Load Acting at A Specific Location ObjectiveAltamashuddin KhanNo ratings yet
- Review Pneumatics HydraulicsDocument200 pagesReview Pneumatics Hydraulicshoan thanhNo ratings yet
- f M π /4) d S D /2) t P (D/2) : Southern Region Houston, TexasDocument4 pagesf M π /4) d S D /2) t P (D/2) : Southern Region Houston, Texasmohamed amine AtiaNo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisFrom EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNo ratings yet
- Structure and Di Ffusion Behavior of Trioctyl Trimellitate (TOTM) in PVC Film Studied by ATR-IR SpectrosDocument11 pagesStructure and Di Ffusion Behavior of Trioctyl Trimellitate (TOTM) in PVC Film Studied by ATR-IR SpectrosGanciarov MihaelaNo ratings yet
- 23.ray OpticsDocument50 pages23.ray OpticsRakesh Ranjan Mishra100% (1)
- Lubrication Solutions For Industrial Applications: Energizing Performance. Every DayDocument68 pagesLubrication Solutions For Industrial Applications: Energizing Performance. Every DayEid EeidNo ratings yet
- Overview of Rotating Disc Electrode (RDE) Optical Emission Spectroscopy For In-Service Oil AnalysisDocument6 pagesOverview of Rotating Disc Electrode (RDE) Optical Emission Spectroscopy For In-Service Oil AnalysisenioleaoNo ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - 3. Worksheet QP 3Document2 pagesHSSRPTR - 3. Worksheet QP 3AswithNo ratings yet
- Continuous Modification Treatment of Polyester Fabric by Dielectric Barrier DischargeDocument5 pagesContinuous Modification Treatment of Polyester Fabric by Dielectric Barrier DischargeKasra GolbanNo ratings yet
- Turbine Protection SystemDocument47 pagesTurbine Protection SystemArup MondalNo ratings yet
- The Free High School Science Texts - A Textbook For Highschool Students Studying Physics (Team Nanban) (TPB) PDFDocument397 pagesThe Free High School Science Texts - A Textbook For Highschool Students Studying Physics (Team Nanban) (TPB) PDFAnonymous hYHGFMBJmNo ratings yet
- Lab Practice 1-Use of The MicroscopeDocument4 pagesLab Practice 1-Use of The MicroscopeANANo ratings yet
- Kiln Mechanics - (1.3) - ''Design''.ppsDocument110 pagesKiln Mechanics - (1.3) - ''Design''.ppsDiego AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Electrochemical Power Sources Fundamentals Systems and Applications Hydrogen Production by Water Electrolysis PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Electrochemical Power Sources Fundamentals Systems and Applications Hydrogen Production by Water Electrolysis PDFdennis.wallace581100% (22)
- Chapter 3 Diffusion Osmosis Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Diffusion Osmosis Lecture Notesshammah2rashadNo ratings yet
- Beam StructuralDocument2 pagesBeam StructuraldhantoroNo ratings yet
- Gasdynamics AE4140 Chapter 1: IntroductionDocument60 pagesGasdynamics AE4140 Chapter 1: IntroductionPythonraptorNo ratings yet
- CH 14 ThermodynamicsDocument46 pagesCH 14 ThermodynamicsHarshad MehtaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: (7th Edition)Document8 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: (7th Edition)Shanice CabrilesNo ratings yet
- SapVerification PDFDocument103 pagesSapVerification PDFedgardNo ratings yet
- Csa G40 21Document6 pagesCsa G40 21Andi SuntoroNo ratings yet
- Critical State Soil Mechanics - by Jishnu R BDocument265 pagesCritical State Soil Mechanics - by Jishnu R BJishnu Ramabhadran100% (1)
- E BJSFMDocument4 pagesE BJSFMAnonymous 1rLNlqUNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Scheme of Work 4.2Document55 pagesA Level Chemistry Scheme of Work 4.2Tiras NgugiNo ratings yet
- Physics MCQs For Class 12 With Answers Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction-1Document6 pagesPhysics MCQs For Class 12 With Answers Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction-1unknwn2009No ratings yet
- Ultipor GF Plus Series Filter Elements: DescriptionDocument2 pagesUltipor GF Plus Series Filter Elements: Descriptionвлад камрNo ratings yet
- General Information 500MW BoilerDocument4 pagesGeneral Information 500MW BoilerSaurabh BarangeNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument35 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsLOLA PATRICIA MORALES DE LA CUBANo ratings yet
- Vapor Absorption SystemsDocument17 pagesVapor Absorption SystemsTalibHussainNo ratings yet
- Extended Elastic Impedance EEI Inversion PDFDocument37 pagesExtended Elastic Impedance EEI Inversion PDFsonu420No ratings yet
- Fluid 9ed Solution Manual PDFDocument919 pagesFluid 9ed Solution Manual PDFDermz GayosoNo ratings yet
- ACI 435.5R-73 R1989 Deflections of Continuous Concrete BeamsDocument7 pagesACI 435.5R-73 R1989 Deflections of Continuous Concrete BeamsMohamed alhaj EmadNo ratings yet
- Weather Insturments and MeasurementsDocument35 pagesWeather Insturments and MeasurementsRemigio Rabel HuamaniNo ratings yet
Asm 97560
Asm 97560
Uploaded by
aarnachauhan.2008Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Asm 97560
Asm 97560
Uploaded by
aarnachauhan.2008Copyright:
Available Formats
NAME: _____________ EXPERIMENT - 5
DATE: 10/12/2023 CLASS: XI
PHYSICS
Aim
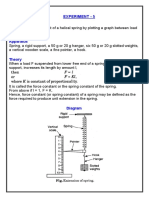
To nd the force constant of a helical spring by plotting a graph between load and extension.
Apparatus/ Materials Required
L
OO
• A rigid support
• Spring
• A 10 g or 20 g hanger
CH
• Six 10 g or 20 g slotted weight
• A ne pointer
S
• A vertical wooden scale
AL
• A hook
Diagram
I ON
AT
RN
TE
IN
M
TA
OT
Theory
RV
When a load F suspended from the lower free end of the spring hanging from rigid support increases its length
SA
by l, then
Where K is the proportionality constant
K, the proportionality constant, is also known as the force constant or the spring constant of the spring
From the above equation, it is clear that if l =1, F = K.
Sarvo am Interna onal School/2023-24 Page-1
fi
fi
tt
ti
Hence, spring constant can be de ned as the force required to produce a unit extension in the spring.
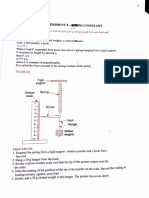
Procedure
1. Suspend the spring from a rigid support and attach the pointer and the hook from its lower free end.
2. Hang a 10 g hanger from the hook
3. Arrange the vertical wooden scale such that the tip of the pointer comes over the divisions on the scale
but does not touch the scale.
4. Note the reading on the scale and record it in the loading column against the zero loads.
L
5. Gently add a suitable load of 10 g or 20 g of slotted weight to the hanger. The tip of the pointer moves
OO
down.
6. Wait for some time till the pointer comes to rest. Repeat step 4.
7. Repeat steps 5 and 6 till six slots have been added.
CH
8. Remove one slotted weight. The pointer moves up. Repeat step 6 and record the reading in the
unloading column.
S
9. Repeat step 8 till the only hanger is left.
AL
10. Record your observation as given below in the table.
Observations
ON
The least count of vernier scale is 0.1 cm.
Observation Table for extension and load
I
AT
RN
Load on Reading of position of pointer tip Extension K
Serial hanger(W) =
No. of Applied force
Loading Unloading Mean = x+y/2
TE
obs. (F) L(cm) (gwt/cm)
x(cm) your(cm) =L
(gwt)
IN
M
TA
OT
RV
SA
Mean k =
Graph : From this given data, the spring constant can be calculated as follows:
Spring constant, k from load extension graph
Sarvo am Interna onal School/2023-24 Page-2
tt
ti
fi
L
OO
CH
AB=---------g wt
BC=---------cm
Slope = 1/k
S
AL
= ---------gwt/cm
ON
Result
By calculation, the force constant of the given spring = .............
I
From load-extension graph, the force constant of the given spring =………Result
AT
PRECAUTIONS
RN
1. The spring should be suspended from a rigid support and it should hang freely so that it remains vertical.
TE
2. Slotted weights should be chosen according to elastic limit of the spring.
3. After adding or removing the slotted weight on the hanger, wait for sometime before noting the position of
IN
the pointer on the scale because the spring takes time to attain equilibrium position.
M
SOURCES OF ERROR
TA
1. If support is not perfectly rigid, some error may creep in due to the yielding of the support.
OT
2. The slotted weights may not be standard weights.
RV
SA
Sarvo am Interna onal School/2023-24 Page-3
tt
ti
You might also like
- Calculation According To Euler: Piston Rod SelectionDocument2 pagesCalculation According To Euler: Piston Rod SelectionbalajimetturNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document3 pagesExperiment 7Atonimous 07No ratings yet
- Lifting Cargoes With An A-Symmetrical CoGDocument7 pagesLifting Cargoes With An A-Symmetrical CoGRaja GopalNo ratings yet
- Design of Beam Column (Compatibility Mode)Document64 pagesDesign of Beam Column (Compatibility Mode)Sérgio MoraesNo ratings yet
- Modal Analysis of A Small Ship Sea Keeping Trial: A. Metcalfe L. Maurits T. Svenson R. Thach G. E. HearnDocument19 pagesModal Analysis of A Small Ship Sea Keeping Trial: A. Metcalfe L. Maurits T. Svenson R. Thach G. E. Hearnricky.pigazziniNo ratings yet
- A Study On-" ": Buckling & It's TheoriesDocument34 pagesA Study On-" ": Buckling & It's TheoriesAghil BuddyNo ratings yet
- Spring Constant ExperimentDocument4 pagesSpring Constant ExperimentRacNo ratings yet
- Sections-Dev-Intersection of Solids-KsrDocument8 pagesSections-Dev-Intersection of Solids-KsrK S ChalapathiNo ratings yet
- 11 PHY - Term 2 - PracticalsDocument4 pages11 PHY - Term 2 - PracticalsLambò GhiniNo ratings yet
- Xi Practical Term 2Document11 pagesXi Practical Term 2Abhinav YadavNo ratings yet
- Mechanics QuestionsDocument8 pagesMechanics QuestionslloydNo ratings yet
- Experiment - Spring Ofa: ConstantDocument2 pagesExperiment - Spring Ofa: ConstantAsom BartaNo ratings yet
- Phy ProjectDocument5 pagesPhy ProjectSiddharthNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Manual Term2Document18 pagesPhysics Practical Manual Term2studies for sundarNo ratings yet
- ME - 244 Ex 4Document5 pagesME - 244 Ex 4Jubaer RabbyNo ratings yet
- Name: - Worksheet 3.1 - Translational EquilibriumDocument3 pagesName: - Worksheet 3.1 - Translational EquilibriumYehualashet BelaynehNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 - Engg Mech PDFDocument8 pagesAssignment-2 - Engg Mech PDFNiteshNo ratings yet
- Meriam - Dynamics - 8th Ed (2015) - 8Document8 pagesMeriam - Dynamics - 8th Ed (2015) - 8hoormohameed2019No ratings yet
- ObjectiveDocument19 pagesObjectiveAmmir JusohNo ratings yet
- Outline: Spring Functions & Types Helical SpringsDocument46 pagesOutline: Spring Functions & Types Helical SpringsMohammed AlnasharNo ratings yet
- Convex Hull and Voronoi Diagram of Additively Weighted PointsDocument16 pagesConvex Hull and Voronoi Diagram of Additively Weighted Pointsabhiraj1234No ratings yet
- Spring ConstantDocument2 pagesSpring ConstantugharshytNo ratings yet
- Basics of Spar Analysis (Tension Field Beams)Document39 pagesBasics of Spar Analysis (Tension Field Beams)kuracha jayasaikumarNo ratings yet
- A Simple Approach To Truss Deflections: N-Braced TypeDocument6 pagesA Simple Approach To Truss Deflections: N-Braced Typealbertoxina100% (1)
- EXP4 Bending and TorsionDocument2 pagesEXP4 Bending and Torsionaman chopraNo ratings yet
- 7 SuspensionDocument98 pages7 SuspensionRajkumar NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document6 pagesExperiment 4Majdy gamingNo ratings yet
- CE6501 Structural Analysis I 2 Marks Unit 3 PDFDocument14 pagesCE6501 Structural Analysis I 2 Marks Unit 3 PDFJuan WagnerNo ratings yet
- Lab 2: Fundamental Concepts: Beam BendingDocument21 pagesLab 2: Fundamental Concepts: Beam BendingudithaireshaNo ratings yet
- Work 2Document5 pagesWork 2David DanielNo ratings yet
- Lecture12 PDFDocument14 pagesLecture12 PDFTihomir MarkovicNo ratings yet
- Torsion: Torsion Is The Twisting of An Object Due To An AppliedDocument20 pagesTorsion: Torsion Is The Twisting of An Object Due To An Appliedirum,No ratings yet
- 1989 Hong Kong Advanced Level Examination AL Physics Multiple Choice QuestionDocument11 pages1989 Hong Kong Advanced Level Examination AL Physics Multiple Choice QuestionedisonNo ratings yet
- Buckling of Strut ReportDocument19 pagesBuckling of Strut ReportEsyad E-chad50% (2)
- PQM Supplementary Notes: Spin, Topology, SU (2) SO (3) Etc: 1 Rotations and Non-Contractible LoopsDocument8 pagesPQM Supplementary Notes: Spin, Topology, SU (2) SO (3) Etc: 1 Rotations and Non-Contractible LoopsJosé JiménezNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Lab Manual Work - Experiment 5.1Document1 pageClass 11 Physics Lab Manual Work - Experiment 5.11445800No ratings yet
- Strength of Materials EngineerdogDocument43 pagesStrength of Materials EngineerdogHormedo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Smith Charts r3Document31 pagesClass 8 Smith Charts r3Dan ClementiNo ratings yet
- Beam StressesDocument20 pagesBeam StresseshideoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Plate No. 1Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics Plate No. 1Charmaine NarvadezNo ratings yet
- 4.belt and PulleyDocument1 page4.belt and PulleyNimish Raman MitalNo ratings yet
- Simple PendulumDocument5 pagesSimple Pendulumpiyushdua01No ratings yet
- CE Characteristics: Up: PreviousDocument3 pagesCE Characteristics: Up: PrevioussNo ratings yet
- Shear ForceDocument5 pagesShear Forcea.h.alkamyaniNo ratings yet
- TorsionalformulaDocument24 pagesTorsionalformulaMuhammad MusaNo ratings yet
- Observations and CalculationsDocument2 pagesObservations and CalculationsHACKER CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Class 11Document9 pagesPhysics Practical Class 11Surbhi DwivediNo ratings yet
- L-12 CoulumnsDocument59 pagesL-12 CoulumnsBilal KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - NotesDocument29 pagesUnit 8 - NotesNico Dela RamaNo ratings yet
- CD2 - Lect12!17!12-2011 Zapata AislaDocument43 pagesCD2 - Lect12!17!12-2011 Zapata AislaDarlys Rodriguez VillarNo ratings yet
- 6 Experiment6 Torque 1Document5 pages6 Experiment6 Torque 1icecubexx02No ratings yet
- G2-Izham Bin Azhar-Combined Stresses-FrDocument20 pagesG2-Izham Bin Azhar-Combined Stresses-FrZainal PiutNo ratings yet
- Course Work O1Document4 pagesCourse Work O1zaianzNo ratings yet
- Chap 12Document74 pagesChap 12noscribdyoucantNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 14 PDFRui JiNo ratings yet
- Bending Moment (1) : Bending Moment at A Point Due To A Point Load Acting at A Specific Location ObjectiveDocument6 pagesBending Moment (1) : Bending Moment at A Point Due To A Point Load Acting at A Specific Location ObjectiveAltamashuddin KhanNo ratings yet
- Review Pneumatics HydraulicsDocument200 pagesReview Pneumatics Hydraulicshoan thanhNo ratings yet
- f M π /4) d S D /2) t P (D/2) : Southern Region Houston, TexasDocument4 pagesf M π /4) d S D /2) t P (D/2) : Southern Region Houston, Texasmohamed amine AtiaNo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisFrom EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNo ratings yet
- Structure and Di Ffusion Behavior of Trioctyl Trimellitate (TOTM) in PVC Film Studied by ATR-IR SpectrosDocument11 pagesStructure and Di Ffusion Behavior of Trioctyl Trimellitate (TOTM) in PVC Film Studied by ATR-IR SpectrosGanciarov MihaelaNo ratings yet
- 23.ray OpticsDocument50 pages23.ray OpticsRakesh Ranjan Mishra100% (1)
- Lubrication Solutions For Industrial Applications: Energizing Performance. Every DayDocument68 pagesLubrication Solutions For Industrial Applications: Energizing Performance. Every DayEid EeidNo ratings yet
- Overview of Rotating Disc Electrode (RDE) Optical Emission Spectroscopy For In-Service Oil AnalysisDocument6 pagesOverview of Rotating Disc Electrode (RDE) Optical Emission Spectroscopy For In-Service Oil AnalysisenioleaoNo ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - 3. Worksheet QP 3Document2 pagesHSSRPTR - 3. Worksheet QP 3AswithNo ratings yet
- Continuous Modification Treatment of Polyester Fabric by Dielectric Barrier DischargeDocument5 pagesContinuous Modification Treatment of Polyester Fabric by Dielectric Barrier DischargeKasra GolbanNo ratings yet
- Turbine Protection SystemDocument47 pagesTurbine Protection SystemArup MondalNo ratings yet
- The Free High School Science Texts - A Textbook For Highschool Students Studying Physics (Team Nanban) (TPB) PDFDocument397 pagesThe Free High School Science Texts - A Textbook For Highschool Students Studying Physics (Team Nanban) (TPB) PDFAnonymous hYHGFMBJmNo ratings yet
- Lab Practice 1-Use of The MicroscopeDocument4 pagesLab Practice 1-Use of The MicroscopeANANo ratings yet
- Kiln Mechanics - (1.3) - ''Design''.ppsDocument110 pagesKiln Mechanics - (1.3) - ''Design''.ppsDiego AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Electrochemical Power Sources Fundamentals Systems and Applications Hydrogen Production by Water Electrolysis PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Electrochemical Power Sources Fundamentals Systems and Applications Hydrogen Production by Water Electrolysis PDFdennis.wallace581100% (22)
- Chapter 3 Diffusion Osmosis Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Diffusion Osmosis Lecture Notesshammah2rashadNo ratings yet
- Beam StructuralDocument2 pagesBeam StructuraldhantoroNo ratings yet
- Gasdynamics AE4140 Chapter 1: IntroductionDocument60 pagesGasdynamics AE4140 Chapter 1: IntroductionPythonraptorNo ratings yet
- CH 14 ThermodynamicsDocument46 pagesCH 14 ThermodynamicsHarshad MehtaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: (7th Edition)Document8 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: (7th Edition)Shanice CabrilesNo ratings yet
- SapVerification PDFDocument103 pagesSapVerification PDFedgardNo ratings yet
- Csa G40 21Document6 pagesCsa G40 21Andi SuntoroNo ratings yet
- Critical State Soil Mechanics - by Jishnu R BDocument265 pagesCritical State Soil Mechanics - by Jishnu R BJishnu Ramabhadran100% (1)
- E BJSFMDocument4 pagesE BJSFMAnonymous 1rLNlqUNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Scheme of Work 4.2Document55 pagesA Level Chemistry Scheme of Work 4.2Tiras NgugiNo ratings yet
- Physics MCQs For Class 12 With Answers Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction-1Document6 pagesPhysics MCQs For Class 12 With Answers Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction-1unknwn2009No ratings yet
- Ultipor GF Plus Series Filter Elements: DescriptionDocument2 pagesUltipor GF Plus Series Filter Elements: Descriptionвлад камрNo ratings yet
- General Information 500MW BoilerDocument4 pagesGeneral Information 500MW BoilerSaurabh BarangeNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument35 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsLOLA PATRICIA MORALES DE LA CUBANo ratings yet
- Vapor Absorption SystemsDocument17 pagesVapor Absorption SystemsTalibHussainNo ratings yet
- Extended Elastic Impedance EEI Inversion PDFDocument37 pagesExtended Elastic Impedance EEI Inversion PDFsonu420No ratings yet
- Fluid 9ed Solution Manual PDFDocument919 pagesFluid 9ed Solution Manual PDFDermz GayosoNo ratings yet
- ACI 435.5R-73 R1989 Deflections of Continuous Concrete BeamsDocument7 pagesACI 435.5R-73 R1989 Deflections of Continuous Concrete BeamsMohamed alhaj EmadNo ratings yet
- Weather Insturments and MeasurementsDocument35 pagesWeather Insturments and MeasurementsRemigio Rabel HuamaniNo ratings yet