Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final Coverage: Titrimetric Techniques, Gravimetric Analysis and Special Methods
Final Coverage: Titrimetric Techniques, Gravimetric Analysis and Special Methods
Uploaded by
Krisza LeiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- General Chemistry Laboratory ManualDocument46 pagesGeneral Chemistry Laboratory ManualmeriiNo ratings yet
- 7 Neutralization TitrationsDocument32 pages7 Neutralization TitrationsnidsNo ratings yet
- The Polyolefin IndustryDocument24 pagesThe Polyolefin IndustryJomari Magadan67% (3)
- Ssri Presentation - 674 - Final2Document52 pagesSsri Presentation - 674 - Final2api-289842236100% (1)
- KeumBoo Guide PDFDocument19 pagesKeumBoo Guide PDFDIANA CAROLINA GAMBOA RODRIGUEZ50% (2)
- 5.2 Neutralization and Precipitation TitrimetryDocument2 pages5.2 Neutralization and Precipitation TitrimetrySister RislyNo ratings yet
- Phan111lec FinalsDocument34 pagesPhan111lec FinalsANDREA ROSELLE FULLONANo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Analysis (Module 2)Document4 pagesPharmaceutical Analysis (Module 2)Bea TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Quim 5005Document2 pagesQuim 5005Yaiselle Feliciano CosmeNo ratings yet
- Marine Organic Geochemistry: Analytical Methods - I. Extraction and Separation MethodsDocument53 pagesMarine Organic Geochemistry: Analytical Methods - I. Extraction and Separation MethodsKamal AlmahdyNo ratings yet
- Aqueous and Non-Aqueous Titrimetric AnalysisDocument3 pagesAqueous and Non-Aqueous Titrimetric AnalysisBea TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Histopathologic TechniquesDocument11 pagesHistopathologic TechniquesGail SantanderNo ratings yet
- Tanning IndustryDocument23 pagesTanning IndustryVidisha JhaNo ratings yet
- DMA Chemical Analysis KODocument2 pagesDMA Chemical Analysis KOqwesghwqedfgNo ratings yet
- Chromatography: A) PrecautionsDocument2 pagesChromatography: A) PrecautionsAhmedA.SharafNo ratings yet
- Histopathologic TechniquesDocument10 pagesHistopathologic TechniquesM C0% (1)
- Chapter 5 Soil Polltuion TreatmentDocument24 pagesChapter 5 Soil Polltuion TreatmentChươngNo ratings yet
- 1 AdDocument39 pages1 AdPratik PradhanNo ratings yet
- Grease 1Document3 pagesGrease 1Sivakumar PNo ratings yet
- CC Colored Test SummaryDocument5 pagesCC Colored Test SummarymendoxastarNo ratings yet
- Protein Purification MLDocument25 pagesProtein Purification MLZorica MisimovićNo ratings yet
- Precipitation Titration by SiteshDocument17 pagesPrecipitation Titration by Siteshsanjeev khanalNo ratings yet
- Module 4 P.ADocument4 pagesModule 4 P.Aer dequilatoNo ratings yet
- DOC182.53.20103.Jan15 TitrationGuide - Web PDFDocument12 pagesDOC182.53.20103.Jan15 TitrationGuide - Web PDFAhmed RaNo ratings yet
- Volumetric AnalysisDocument3 pagesVolumetric AnalysisMohamed Babiker SulimanNo ratings yet
- Biological Treatrment 2Document15 pagesBiological Treatrment 2Minhaj UllahNo ratings yet
- 20 C N Bond Forming ReactionsDocument15 pages20 C N Bond Forming ReactionsAnonymous XHwkbC7No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Natural Biological Treatment ProcessDocument20 pagesChapter 7 Natural Biological Treatment ProcessShafayet UllahNo ratings yet
- CC1 - MtapDocument56 pagesCC1 - Mtapdriani1No ratings yet
- Ana Lec M 1Document3 pagesAna Lec M 1THEA KRIZIA ANGELESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Biological Nitrogen Removal Process: I. OverviewDocument26 pagesChapter 6 Biological Nitrogen Removal Process: I. OverviewJing ZeNo ratings yet
- AlbendazoleDocument13 pagesAlbendazoleShankar SoniNo ratings yet
- Micellar Liquid Chromatography: Lecture-7Document12 pagesMicellar Liquid Chromatography: Lecture-7raja dahar JanweryNo ratings yet
- 1-Fundamentals of HPLC 2Document65 pages1-Fundamentals of HPLC 2Spinco InformaticsNo ratings yet
- HISTOPATH-MODULE-4 NotesDocument7 pagesHISTOPATH-MODULE-4 NotesKaycee AyoNo ratings yet
- B. Pharmacy 2nd Year Subjects Syllabus PDF B Pharm Second Year 3 4 Semester PDF DOWNLOADDocument25 pagesB. Pharmacy 2nd Year Subjects Syllabus PDF B Pharm Second Year 3 4 Semester PDF DOWNLOADarshad alamNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its CompoundsDocument9 pagesDetermination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its CompoundsTi MaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineDocument9 pagesDetermination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineTorkhani RachelNo ratings yet
- Ab-098 5 en PDFDocument9 pagesAb-098 5 en PDFAriana FraticelliNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineDocument9 pagesDetermination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineAriana FraticelliNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineDocument9 pagesDetermination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineMaria MosqueraNo ratings yet
- Ab-098 5 en PDFDocument9 pagesAb-098 5 en PDFAriana FraticelliNo ratings yet
- Questions:: Ceruloplasmin Transferrin Ferritin Hemosiderin Hemopexin Haptoglobin Albumin TibcDocument17 pagesQuestions:: Ceruloplasmin Transferrin Ferritin Hemosiderin Hemopexin Haptoglobin Albumin TibcLauter Manaloto FrancoNo ratings yet
- 15 DetermindatioOfTheSodium PDFDocument2 pages15 DetermindatioOfTheSodium PDFRogerio CannoniNo ratings yet
- Test For ProteinsDocument2 pagesTest For Proteinsdiamonddia145No ratings yet
- Principles of Neutralization TitrationDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Neutralization TitrationKeith Celine BaccayNo ratings yet
- Pharmcal Lab ReviewerDocument6 pagesPharmcal Lab ReviewerRaven Janica DeangNo ratings yet
- Title: 1) Preliminary TestsDocument5 pagesTitle: 1) Preliminary TestsAkash PawarNo ratings yet
- Chem 121 - Presentation - Acid-BaseDocument12 pagesChem 121 - Presentation - Acid-Basedramemariam590No ratings yet
- Lecture Note WWTSWM1Document114 pagesLecture Note WWTSWM1Amanueal Melkamu kassawNo ratings yet
- Inorg Med.1.1-1Document38 pagesInorg Med.1.1-1Kathleen Joy ArutaNo ratings yet
- Course Name:: Volumetric and Gravimetric Analytical Chemistry: 4022133-3Document43 pagesCourse Name:: Volumetric and Gravimetric Analytical Chemistry: 4022133-3faycalfaidiNo ratings yet
- DOC182.52.20103.Jan15 TitrationGuide - WebDocument12 pagesDOC182.52.20103.Jan15 TitrationGuide - Webসৌরভ পালNo ratings yet
- Chem 16 Gen Chem 1Document47 pagesChem 16 Gen Chem 1Rovie Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests BacteriaDocument30 pagesBiochemical Tests BacteriaScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument10 pagesChapter OneTesfayeNo ratings yet
- Title: 1) Preliminary TestsDocument6 pagesTitle: 1) Preliminary TestsAkash PawarNo ratings yet
- Chem (Final)Document17 pagesChem (Final)Jaynie Lee VillaranNo ratings yet
- Green Pharma Handout 10 - Abcfccb9 BBFC 4956 B11e 2ae51b69fdb8Document12 pagesGreen Pharma Handout 10 - Abcfccb9 BBFC 4956 B11e 2ae51b69fdb8sunnyraja2004No ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 1: Finals TLA No.3 - Nonprotein Nitrogen CompoundsDocument4 pagesClinical Chemistry 1: Finals TLA No.3 - Nonprotein Nitrogen CompoundsBRYAN M. MOLDENo ratings yet
- Ijca 30a (6) 531-535Document5 pagesIjca 30a (6) 531-535Zia KhanNo ratings yet
- New Frontiers in Asymmetric CatalysisFrom EverandNew Frontiers in Asymmetric CatalysisKoichi MikamiNo ratings yet
- Acroleina Agua AzeotropoDocument1 pageAcroleina Agua AzeotropoAnonymous ZAr1RKNo ratings yet
- Extreme Steel Wastage From WTC 1 or 2 and WTC 7Document11 pagesExtreme Steel Wastage From WTC 1 or 2 and WTC 7sirisfiNo ratings yet
- 0625 w18 QP 23Document16 pages0625 w18 QP 23saeed akhtarNo ratings yet
- Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand in WaterDocument9 pagesDetermination of Chemical Oxygen Demand in WaterHafiz Shahril100% (1)
- Elimination Reactions - KEY: CHEM 109A Clas 1. Predict The Products of The Following ReactionsDocument7 pagesElimination Reactions - KEY: CHEM 109A Clas 1. Predict The Products of The Following ReactionsAlyssa Thea Ablang TeofiloNo ratings yet
- Samsung Wd10k6410ox User ManualDocument64 pagesSamsung Wd10k6410ox User Manualafcpa70% (1)
- Le Chatelier LabDocument3 pagesLe Chatelier LabDeep ManNo ratings yet
- Water in Cracked Gas Dryer Vessel Outlets: Application NoteDocument2 pagesWater in Cracked Gas Dryer Vessel Outlets: Application Noteluciole60No ratings yet
- TIBCDocument2 pagesTIBCFatma Gemala100% (1)
- Crude OilDocument73 pagesCrude OilSachin HarriramNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question Bank 2017 NewDocument22 pagesChemistry Question Bank 2017 Newஅன்புடன் அஸ்வின்No ratings yet
- Crude Oil and Refined Product Fingerprinting: Principles: Flash PointDocument2 pagesCrude Oil and Refined Product Fingerprinting: Principles: Flash PointalokaNo ratings yet
- Method of Preparing S Nitrofurfural DiacetateDocument8 pagesMethod of Preparing S Nitrofurfural DiacetateKarla VTNo ratings yet
- StafloDocument2 pagesStaflomadcokelNo ratings yet
- IUPAC ExerciseDocument27 pagesIUPAC ExerciseDhritismita Kalita100% (1)
- Trisoxalatoaluminato PDFDocument1 pageTrisoxalatoaluminato PDFFelipe VilchesNo ratings yet
- Aparat PT Biodiesel METROHMDocument16 pagesAparat PT Biodiesel METROHMCorina StanculescuNo ratings yet
- Standard Test (Bubble Emission) PDFDocument3 pagesStandard Test (Bubble Emission) PDFAbdul SalamNo ratings yet
- R410A Non Inverter: High Static Ducted UnitDocument6 pagesR410A Non Inverter: High Static Ducted UnitAyda JohariNo ratings yet
- Hbi Use in FoundryDocument3 pagesHbi Use in Foundryravikataria02No ratings yet
- Principles and Procedures: Rev.4 - January 2004Document137 pagesPrinciples and Procedures: Rev.4 - January 2004mberoualNo ratings yet
- GED Chemistry Note2 (Compounds and Solutions)Document4 pagesGED Chemistry Note2 (Compounds and Solutions)Shahadat Hussain Parvez100% (1)
- Lab3a PDMS Polymer PreparationDocument5 pagesLab3a PDMS Polymer Preparationtaylorwilson120No ratings yet
- Preparation of Polyurethane PerpolymerDocument7 pagesPreparation of Polyurethane PerpolymertareeenNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Numericals SolutionsDocument41 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Numericals SolutionsNewage ScienceNo ratings yet
- RNA Structure and PropertyDocument64 pagesRNA Structure and Propertystevensb055No ratings yet
Final Coverage: Titrimetric Techniques, Gravimetric Analysis and Special Methods
Final Coverage: Titrimetric Techniques, Gravimetric Analysis and Special Methods
Uploaded by
Krisza LeiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Final Coverage: Titrimetric Techniques, Gravimetric Analysis and Special Methods
Final Coverage: Titrimetric Techniques, Gravimetric Analysis and Special Methods
Uploaded by
Krisza LeiCopyright:
Available Formats
MEDICAL COLLEGES OF NORTHERN PHILIPPINES
Alimannao Hills, Peñablanca, Cagayan
Telefax No.: (078) 304-1010
Website: www.mcnp.edu.phE-Mail Address: adminoffice@mcnp.edu.ph
COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
FINAL COVERAGE: TITRIMETRIC TECHNIQUES, GRAVIMETRIC ANALYSIS AND SPECIAL METHODS
o Titration of ____ with a standard _____
Overview:
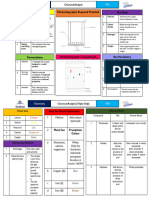
I. Types of Titrations based on the Chemical Reaction Aqueous Non-Aqueous
Involved
VS Naoh Na Methoxide
A. Neutralization Methods
KOH Li Methoxide
• Based on the media used
• Based on Titrant Primary Standard K Biphthalate Benzoic Acid In
B. Reduction – Oxidation Dimethylformamide
• Permanganometry
Direct Hcl Phenytoin
• Iodine Methods: Iodimetry andIodometry
H3PO4
• Diazotization Assay Boric Acid
C. Reactions involving Combination of Ions Tartaric Acid
• Complexation
D. Volumetric Precipitation Residual ASA (HPLC)
• Volhard Method Indicators Methyl Orange Azo-Violet
• Mohr Methyl Red Thymol Blue
• Fajans Phenolphthalein O-Nitroaniline
• Gay – Lussac
II. Gravimetric Method B. Reduction – Oxidation
III. Special Method ➢ Methods of analysis involving a ________ in __________ of
A. Ash Content Determination the reacting substances.
➢ Reduction (LEORA)
B. Water Content Determination
C. Assay of Fatty substances, waxes, balsams and resins
D. Assay of Volatile oils ➢ Oxidation (GEROA)
E. Assay of Nitrogen
I. • OF TITRATIONS BASED ON THE CHEMICAL REACTION
TYPES a. Permanganometry
INVOLVED: Volumetric solution KMnO4
A. Neutralization Reaction Primary standard Na oxalate
➢ Chemical reactions or chemical processed in which an
________ reacts with a _______ Direct titration H2O2
➢ Product:
Indirect Titration Malic acid in Cherry juice
a. Based on the Media Used
1. Aqueous Titration Residual titration Na and K nitrite
Indicator Permanganate solution
2. Non-aqueous Titration
b. Iodimetry
o Analysis of REDUCING AGENTS with standard
b. Based on Titrant
solution of iodine
1. Acidimetry
o EP:
o Titration of ____ with standard _____
o Indicator:
AQUEOUS NON-AQUEOUS
Volumetric Solution Iodine Solution
VOLUMETRIC Hcl, H2SO4 Perchloric Acid In
Primary Standard Arsenic trioxide
STANDARD Glacial Acetic Acid
Direct titration Antimony potassium tartrate
PRIMARY Anhydrous Sodium
Ascorbic acid
STANDARD Carbonate
Sodium ascorbate
SECONDARY Naoh, KOH Sodium thiosulfate
STANDARD
Indirect titration Calomel, antipyrine, NaHSO,
Direct Titration Naoh, Naco3, NAHCO3, Metacholine NaSO
Na Salicylate
c. Iodometry
Residual Zno Phenytoin
o Indirect analysis of OXIDIZING AGENTS
Titration Nak Tartrate
o EP:
Milk Of Magnesia
o Indicator:
Indicators Methyl Orange Crystal Violet Volumetric Solution Iodine Solution
Methyl Red Malachite Green Sodium Thiosulfate
Phenolphthalein Methyl Rosaniline
Chloride Primary Standard IS: Arsenic trioxide
ST: Potassium dichromate
2. Alkalimetry
RICA CARMELA STA. INES, RPH 1
MEDICAL COLLEGES OF NORTHERN PHILIPPINES
Alimannao Hills, Peñablanca, Cagayan
Telefax No.: (078) 304-1010
Website: www.mcnp.edu.phE-Mail Address: adminoffice@mcnp.edu.ph
COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
Direct titration CuSO4, NaOCl Primary Std Silver Nitrate
Residual Titration Phenol, resorcinol, PbO Manifestation Colored Precipitate
Assay Aminophylline Sodium
d. Diazotization Assay with Nitrile Chloride
o Assay of the ___________ and other compounds
containing _________ group.
o VS: b. Mohr Method
o Reference Std: o Conducted in the presence of _________
o EP o Type of titration:
e. Cerimetry o Used for:
Volumetric solution Cerric sulfate
Volumetric Solution Silver Nitrate
Primary standard Arsenic trioxide
Indicator Potassium chromate
Direct titration Menadione, Ferrous sulfate
Primary Std Sodium chloride
Indicator Orthophenanthroline
Manifestation Formation of secondary
precipitate
C. Reactions involving Combination of Ions
a. Complexation Assay Sodium Lauryl Sulfate
o Ligand:
c. Fajans Method
o Monodentate Ligand
Volumetric Solution Silver Nitrate solution
o Multidentate Ligand Indicator Adsorption indicator
Primary Std Sodium chloride
o Masking – Metal detection in the presence of Manifestation Change in the color of
another metal precipitate
▪ Protects other components form
reacting with EDTA Assay Phenylephrine
2.3 dimercapto-1-propanol Bi, Cd, Cu, Hg, Pb Tubocurarine
Meperidine
o Fajans Indicator
Triethanolamine Al, Fe, Mn ▪ AKA:
▪ D
o Demasking Agent – Releases the metal ion form ▪ E
the masking agent ▪ T
o Auxiliary complexing agent – used to permit
metals to be titrated in alkaline solution for EDTA. d. Gay – lussac Method
Volumetric Solution Disodium EDTA Volumetric Solution Silver Nitrate
Primary standard Ca carbonate Indicator None
Direct titration Ca carbonate Primary Std Sodium chloride
Ca gluconate
ZnO Manifestation Cessation of precipitate
Residual titration Alum Example NaCl
Aluminum hydroxide
o Metal Ion INDICATORS (CHEMP) II. GRAVIMETRIC METHODS
C ➢ Analysis by __________
H ➢ Process of __________ and _______ the compound of
E known composition
M ➢ Equation:
𝒈𝒓𝒆𝒔𝒊𝒅𝒖𝒆 𝒙 𝑴𝑾𝒔𝒂𝒎𝒑𝒍𝒆
P %𝑷 = 𝒙 𝟏𝟎𝟎
𝒈𝒔𝒂𝒎𝒑𝒍𝒆 𝒙 𝑴𝑾𝒓𝒆𝒔𝒊𝒅𝒖𝒆
D. Volumetric Precipitation o Problem 1: If a 0.46 g sample of KI yielded 0.7215
a. Volhard Method g of AgI precipitate by gravimetric assay. What
o ___________ titration method would be the percentage purity of KI?
o Complete precipitation of insoluble silver salts ▪ MW of AgI : 234. 7745
from nitric acid solution by the addition of excess ▪ MW of KI: 166.0045
standard silver nitrate solution to a soluble salt.
o ____________ titration with standard
__________________________.
Volumetric Solution Ammonium thiocyanate
Indicator Ferric ammonium sulfate
RICA CARMELA STA. INES, RPH 2
MEDICAL COLLEGES OF NORTHERN PHILIPPINES
Alimannao Hills, Peñablanca, Cagayan
Telefax No.: (078) 304-1010
Website: www.mcnp.edu.phE-Mail Address: adminoffice@mcnp.edu.ph
COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
III. SPECIAL METHOD
A. Ash Content Determination c. Method III
o Gravimetric
Importance Methods
o For vegetable drugs
Inorganic salts (naturally- Total Ash C. Assay of fatty substances, waxes, balsams and resins
occurring or as Acid-Insoluble ash a. Acid value
adulterants) Sulfated ash o Acid number or acidity index
o No. of mg of KOH necessary to _______ the
___________ in 1 g of substance.
o Equation:
➢ Total Ash 𝑵 𝒙 𝑽 𝒙 𝟓𝟔. 𝟏𝟏
𝑨𝒄𝒊𝒅 𝒗𝒂𝒍𝒖𝒆 =
𝒘𝒕 𝒊𝒏 𝒈
➢ Acid Insoluble Ash
b. Ester value
o Part of the total ash which is insoluble in diluted
o Ester number
HCl
o No of mg of KOH required to ______ the _______
o Represents the ________ content of the sample
contained in 1 g of oil, fat, wax, resin or balsam.
o Equation:
c. Saponification Value
𝒂𝒄𝒊𝒅 𝒊𝒏𝒔𝒐𝒍𝒖𝒃𝒍𝒆 𝒂𝒔𝒉
%𝑨𝑰𝑨 = 𝒙 𝟏𝟎𝟎 o Saponification number or _____________ number
𝒘𝒕 𝒐𝒇 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝒕𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 𝒂𝒔𝒉
o No of mg of KOH necessary to ________ the
➢ Sulfurated ash
________ and _____ the _______ in 1 g of
o Ash treated with _________
substance
➢ Approximate Temperature Equivalent
o Equation:
𝑺𝑽 = 𝑨𝑽 + 𝑬𝑽
d. Iodine Value
Very dull red heat 500C- 550C
o Iodine number
Dull red heat 550C-700C o Number of mg of ______ absorbed by 100 g of oil,
fat, wax or other substance
Bright red heat 800C-1000C o Measure degree of __________
o Method I :
Yellow Heat 1000C-1200C o Method II:
o Method III:
White Heat 1200C-1600C
o Equation:
[(𝑵𝒙𝑽)𝒃𝒍𝒂𝒏𝒌 − (𝑵𝒙𝑽)𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒖𝒂𝒍 ] 𝒙 𝟎. 𝟏𝟐𝟔𝟗
B. Water Content Determination 𝑰𝑽 = 𝒙 𝟏𝟎𝟎
𝒘𝒕 𝒊𝒏 𝒈
a. Method I
o Titrimetric or _____________
o Reagent is freshly prepared Type IV Examples
▪ Pyridine, methanol, SO2, iodine Drying oils >120 Linseed oil
o Primary standard: Fish oil
o Equation: Cod liver oil
𝑽𝑲𝑭𝑹 𝒊𝒏 𝒎𝑳 𝒙 𝑬𝑭
%𝑯𝟐 𝑶 = 𝒙 𝟏𝟎𝟎
𝒘𝒕 𝒐𝒇 𝒔𝒙 𝒊𝒏 𝒎𝒈 Non-Drying oils <100 Olive oil
o Sample problem: Calculate the water content of Almond oil
streptomycin powder using 3.50 g sample. The
water equivalence factor is 4.6 and the volume Semi-drying oils 100-120 Cottonseed oil
consumed was 9.2 mL. the water content was: Sesame seed oil
D. Assay of Volatile Oils
a. Acetylization Flask
o Assay of __________ volatile oils: (LiBoG Me)
▪ Li
o Karl fischer reagents: ▪ Bo
▪ Anhydrous methanol ▪ G
▪ Me
b. Cassia Flask – bisulfite method
▪ Iodine o Assay of _______ volatile oils
▪ Cinnamaldehyde, citral
o Assay of _______ volatile oils
▪ Sulfuric Acid ▪ Camphor, carvone
c. Cassia flask – KOH method
o Assay of ________ volatile oil
▪ Pyridine ▪ Anethol, eugenol, thymol
o Equation:
𝑽𝒔𝒂𝒎𝒑𝒍𝒆 − 𝑽𝒓𝒆𝒔𝒊𝒅𝒖𝒂𝒍
b. Method II %𝑷𝒉𝒆𝒏𝒐𝒍 = 𝒙 𝟏𝟎𝟎
𝑽𝒔𝒂𝒎𝒑𝒍𝒆
o ________ Distillation or _________ method
o Sample Problem: In phenol content determination of
o Toluene Moisture apparatus
volatile oil, the insoluble layer in the graduated neck
o For samples containing 2-4 ml moisture
of the Cassia flask reached 3.1 mL which is contained
o Also used in ________ content determination
from a sample of 10 mL after treatment with KOH.
o Equation:
What is the percentage phenol sample?
𝒎𝑳 𝒓𝒆𝒂𝒅𝒊𝒏𝒈
%𝒘𝒂𝒕𝒆𝒓 = 𝒙 𝟏𝟎𝟎
𝒘𝒕 𝒐𝒇 𝒔𝒂𝒎𝒑𝒍𝒆
RICA CARMELA STA. INES, RPH 3
MEDICAL COLLEGES OF NORTHERN PHILIPPINES
Alimannao Hills, Peñablanca, Cagayan
Telefax No.: (078) 304-1010
Website: www.mcnp.edu.phE-Mail Address: adminoffice@mcnp.edu.ph
COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
E. Assay of Nitrogen
➢ _____________ method
➢ Used in determining nitrogen content of substances.
•conversion of organic nitrogen into ______ by adding
______
Digestion
•Conversion of ______ into ______
Distillation
•Titrating with ________
Titration
RICA CARMELA STA. INES, RPH 4
You might also like
- General Chemistry Laboratory ManualDocument46 pagesGeneral Chemistry Laboratory ManualmeriiNo ratings yet
- 7 Neutralization TitrationsDocument32 pages7 Neutralization TitrationsnidsNo ratings yet
- The Polyolefin IndustryDocument24 pagesThe Polyolefin IndustryJomari Magadan67% (3)
- Ssri Presentation - 674 - Final2Document52 pagesSsri Presentation - 674 - Final2api-289842236100% (1)
- KeumBoo Guide PDFDocument19 pagesKeumBoo Guide PDFDIANA CAROLINA GAMBOA RODRIGUEZ50% (2)
- 5.2 Neutralization and Precipitation TitrimetryDocument2 pages5.2 Neutralization and Precipitation TitrimetrySister RislyNo ratings yet
- Phan111lec FinalsDocument34 pagesPhan111lec FinalsANDREA ROSELLE FULLONANo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Analysis (Module 2)Document4 pagesPharmaceutical Analysis (Module 2)Bea TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Quim 5005Document2 pagesQuim 5005Yaiselle Feliciano CosmeNo ratings yet
- Marine Organic Geochemistry: Analytical Methods - I. Extraction and Separation MethodsDocument53 pagesMarine Organic Geochemistry: Analytical Methods - I. Extraction and Separation MethodsKamal AlmahdyNo ratings yet
- Aqueous and Non-Aqueous Titrimetric AnalysisDocument3 pagesAqueous and Non-Aqueous Titrimetric AnalysisBea TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Histopathologic TechniquesDocument11 pagesHistopathologic TechniquesGail SantanderNo ratings yet
- Tanning IndustryDocument23 pagesTanning IndustryVidisha JhaNo ratings yet
- DMA Chemical Analysis KODocument2 pagesDMA Chemical Analysis KOqwesghwqedfgNo ratings yet
- Chromatography: A) PrecautionsDocument2 pagesChromatography: A) PrecautionsAhmedA.SharafNo ratings yet
- Histopathologic TechniquesDocument10 pagesHistopathologic TechniquesM C0% (1)
- Chapter 5 Soil Polltuion TreatmentDocument24 pagesChapter 5 Soil Polltuion TreatmentChươngNo ratings yet
- 1 AdDocument39 pages1 AdPratik PradhanNo ratings yet
- Grease 1Document3 pagesGrease 1Sivakumar PNo ratings yet
- CC Colored Test SummaryDocument5 pagesCC Colored Test SummarymendoxastarNo ratings yet
- Protein Purification MLDocument25 pagesProtein Purification MLZorica MisimovićNo ratings yet
- Precipitation Titration by SiteshDocument17 pagesPrecipitation Titration by Siteshsanjeev khanalNo ratings yet
- Module 4 P.ADocument4 pagesModule 4 P.Aer dequilatoNo ratings yet
- DOC182.53.20103.Jan15 TitrationGuide - Web PDFDocument12 pagesDOC182.53.20103.Jan15 TitrationGuide - Web PDFAhmed RaNo ratings yet
- Volumetric AnalysisDocument3 pagesVolumetric AnalysisMohamed Babiker SulimanNo ratings yet
- Biological Treatrment 2Document15 pagesBiological Treatrment 2Minhaj UllahNo ratings yet
- 20 C N Bond Forming ReactionsDocument15 pages20 C N Bond Forming ReactionsAnonymous XHwkbC7No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Natural Biological Treatment ProcessDocument20 pagesChapter 7 Natural Biological Treatment ProcessShafayet UllahNo ratings yet
- CC1 - MtapDocument56 pagesCC1 - Mtapdriani1No ratings yet
- Ana Lec M 1Document3 pagesAna Lec M 1THEA KRIZIA ANGELESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Biological Nitrogen Removal Process: I. OverviewDocument26 pagesChapter 6 Biological Nitrogen Removal Process: I. OverviewJing ZeNo ratings yet
- AlbendazoleDocument13 pagesAlbendazoleShankar SoniNo ratings yet
- Micellar Liquid Chromatography: Lecture-7Document12 pagesMicellar Liquid Chromatography: Lecture-7raja dahar JanweryNo ratings yet
- 1-Fundamentals of HPLC 2Document65 pages1-Fundamentals of HPLC 2Spinco InformaticsNo ratings yet
- HISTOPATH-MODULE-4 NotesDocument7 pagesHISTOPATH-MODULE-4 NotesKaycee AyoNo ratings yet
- B. Pharmacy 2nd Year Subjects Syllabus PDF B Pharm Second Year 3 4 Semester PDF DOWNLOADDocument25 pagesB. Pharmacy 2nd Year Subjects Syllabus PDF B Pharm Second Year 3 4 Semester PDF DOWNLOADarshad alamNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its CompoundsDocument9 pagesDetermination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its CompoundsTi MaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineDocument9 pagesDetermination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineTorkhani RachelNo ratings yet
- Ab-098 5 en PDFDocument9 pagesAb-098 5 en PDFAriana FraticelliNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineDocument9 pagesDetermination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineAriana FraticelliNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineDocument9 pagesDetermination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineMaria MosqueraNo ratings yet
- Ab-098 5 en PDFDocument9 pagesAb-098 5 en PDFAriana FraticelliNo ratings yet
- Questions:: Ceruloplasmin Transferrin Ferritin Hemosiderin Hemopexin Haptoglobin Albumin TibcDocument17 pagesQuestions:: Ceruloplasmin Transferrin Ferritin Hemosiderin Hemopexin Haptoglobin Albumin TibcLauter Manaloto FrancoNo ratings yet
- 15 DetermindatioOfTheSodium PDFDocument2 pages15 DetermindatioOfTheSodium PDFRogerio CannoniNo ratings yet
- Test For ProteinsDocument2 pagesTest For Proteinsdiamonddia145No ratings yet
- Principles of Neutralization TitrationDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Neutralization TitrationKeith Celine BaccayNo ratings yet
- Pharmcal Lab ReviewerDocument6 pagesPharmcal Lab ReviewerRaven Janica DeangNo ratings yet
- Title: 1) Preliminary TestsDocument5 pagesTitle: 1) Preliminary TestsAkash PawarNo ratings yet
- Chem 121 - Presentation - Acid-BaseDocument12 pagesChem 121 - Presentation - Acid-Basedramemariam590No ratings yet
- Lecture Note WWTSWM1Document114 pagesLecture Note WWTSWM1Amanueal Melkamu kassawNo ratings yet
- Inorg Med.1.1-1Document38 pagesInorg Med.1.1-1Kathleen Joy ArutaNo ratings yet
- Course Name:: Volumetric and Gravimetric Analytical Chemistry: 4022133-3Document43 pagesCourse Name:: Volumetric and Gravimetric Analytical Chemistry: 4022133-3faycalfaidiNo ratings yet
- DOC182.52.20103.Jan15 TitrationGuide - WebDocument12 pagesDOC182.52.20103.Jan15 TitrationGuide - Webসৌরভ পালNo ratings yet
- Chem 16 Gen Chem 1Document47 pagesChem 16 Gen Chem 1Rovie Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests BacteriaDocument30 pagesBiochemical Tests BacteriaScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument10 pagesChapter OneTesfayeNo ratings yet
- Title: 1) Preliminary TestsDocument6 pagesTitle: 1) Preliminary TestsAkash PawarNo ratings yet
- Chem (Final)Document17 pagesChem (Final)Jaynie Lee VillaranNo ratings yet
- Green Pharma Handout 10 - Abcfccb9 BBFC 4956 B11e 2ae51b69fdb8Document12 pagesGreen Pharma Handout 10 - Abcfccb9 BBFC 4956 B11e 2ae51b69fdb8sunnyraja2004No ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 1: Finals TLA No.3 - Nonprotein Nitrogen CompoundsDocument4 pagesClinical Chemistry 1: Finals TLA No.3 - Nonprotein Nitrogen CompoundsBRYAN M. MOLDENo ratings yet
- Ijca 30a (6) 531-535Document5 pagesIjca 30a (6) 531-535Zia KhanNo ratings yet
- New Frontiers in Asymmetric CatalysisFrom EverandNew Frontiers in Asymmetric CatalysisKoichi MikamiNo ratings yet
- Acroleina Agua AzeotropoDocument1 pageAcroleina Agua AzeotropoAnonymous ZAr1RKNo ratings yet
- Extreme Steel Wastage From WTC 1 or 2 and WTC 7Document11 pagesExtreme Steel Wastage From WTC 1 or 2 and WTC 7sirisfiNo ratings yet
- 0625 w18 QP 23Document16 pages0625 w18 QP 23saeed akhtarNo ratings yet
- Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand in WaterDocument9 pagesDetermination of Chemical Oxygen Demand in WaterHafiz Shahril100% (1)
- Elimination Reactions - KEY: CHEM 109A Clas 1. Predict The Products of The Following ReactionsDocument7 pagesElimination Reactions - KEY: CHEM 109A Clas 1. Predict The Products of The Following ReactionsAlyssa Thea Ablang TeofiloNo ratings yet
- Samsung Wd10k6410ox User ManualDocument64 pagesSamsung Wd10k6410ox User Manualafcpa70% (1)
- Le Chatelier LabDocument3 pagesLe Chatelier LabDeep ManNo ratings yet
- Water in Cracked Gas Dryer Vessel Outlets: Application NoteDocument2 pagesWater in Cracked Gas Dryer Vessel Outlets: Application Noteluciole60No ratings yet
- TIBCDocument2 pagesTIBCFatma Gemala100% (1)
- Crude OilDocument73 pagesCrude OilSachin HarriramNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question Bank 2017 NewDocument22 pagesChemistry Question Bank 2017 Newஅன்புடன் அஸ்வின்No ratings yet
- Crude Oil and Refined Product Fingerprinting: Principles: Flash PointDocument2 pagesCrude Oil and Refined Product Fingerprinting: Principles: Flash PointalokaNo ratings yet
- Method of Preparing S Nitrofurfural DiacetateDocument8 pagesMethod of Preparing S Nitrofurfural DiacetateKarla VTNo ratings yet
- StafloDocument2 pagesStaflomadcokelNo ratings yet
- IUPAC ExerciseDocument27 pagesIUPAC ExerciseDhritismita Kalita100% (1)
- Trisoxalatoaluminato PDFDocument1 pageTrisoxalatoaluminato PDFFelipe VilchesNo ratings yet
- Aparat PT Biodiesel METROHMDocument16 pagesAparat PT Biodiesel METROHMCorina StanculescuNo ratings yet
- Standard Test (Bubble Emission) PDFDocument3 pagesStandard Test (Bubble Emission) PDFAbdul SalamNo ratings yet
- R410A Non Inverter: High Static Ducted UnitDocument6 pagesR410A Non Inverter: High Static Ducted UnitAyda JohariNo ratings yet
- Hbi Use in FoundryDocument3 pagesHbi Use in Foundryravikataria02No ratings yet
- Principles and Procedures: Rev.4 - January 2004Document137 pagesPrinciples and Procedures: Rev.4 - January 2004mberoualNo ratings yet
- GED Chemistry Note2 (Compounds and Solutions)Document4 pagesGED Chemistry Note2 (Compounds and Solutions)Shahadat Hussain Parvez100% (1)
- Lab3a PDMS Polymer PreparationDocument5 pagesLab3a PDMS Polymer Preparationtaylorwilson120No ratings yet
- Preparation of Polyurethane PerpolymerDocument7 pagesPreparation of Polyurethane PerpolymertareeenNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Numericals SolutionsDocument41 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Numericals SolutionsNewage ScienceNo ratings yet
- RNA Structure and PropertyDocument64 pagesRNA Structure and Propertystevensb055No ratings yet