Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.3. Adaptations for transport QP
2.3. Adaptations for transport QP
Uploaded by
aakashsolomon3Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.3. Adaptations for transport QP
2.3. Adaptations for transport QP
Uploaded by
aakashsolomon3Copyright:
Available Formats
WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
2.3: Adaptations for Transport
Questions by Topic
<
1.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 1 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 2 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
2.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 3 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 4 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 5 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
3.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 6 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
4. (a) Plants carry out the process of transpiration. [2]
State what is meant by the term transpiration.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 7 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
(b) State two practical measures which should be taken when setting up the apparatus to ensure the
potometer functions correctly. Give reasons for your answers.
[4]
(c) Water passes through the xylem of the root and stem of a plant before reaching its leaves.
(i) Name the original source of energy that moves water through a plant
[1]
(ii) Explain how water moves up the xylem.
[2]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 8 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
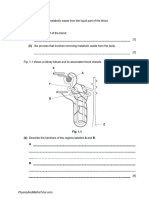
(d) The diagram below shows the cross section of a root.
(i) Name the two tissues labelled A and B on the diagram above.
[2]
A....................................................................................
B...................................................................................
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 9 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
(ii) Explain how it is possible to tell that the diagram above is of a root and not a stem.
[2]
5. The atrio-ventricular node (AVN), bundle of His and Purkyne (Purkinje) fibres are specialised cardiac
muscle tissues which are involved in the control of heartbeat.
(a) State the function of the following structures in the functioning of the heart.
(i) atrio-ventricular node (AVN);
[2]
(ii) bundle of His and Purkyne fibres.
[2]
The graph below shows the pressure changes in the left ventricle, left atrium and aorta during one cardiac
cycle.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 10 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
(b) The following statements list events or phases that occur during a cardiac cycle. State the numbers
indicated on the graph above that correspond to each of the following statements.
[8]
(i) ventricular diastole (ventricles are relaxing) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(ii) recoil of aorta . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(iii) atrial systole . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(iv) closing of semi-lunar valves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(v) opening of semi-lunar valves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(vi) atrio-ventricular valves close . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(vii) ventricular systole (ventricles are contracting) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
..
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 11 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
(viii) passive filling of atrium by venous return . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6. The diagram below shows a section of a human heart, cut just above the heart valves, as seen
from above.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 12 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
(a) Name valves A, B and C.
[3]
(b) Name blood vessels D which are found on the surface of the heart and explain their function.
[2]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 13 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
(c) (i) Explain why valve B often has to be replaced because it ceases to work effectively
and why valve A rarely needs replacing.
[1]
(ii) What would happen to the flow of blood if the valve is damaged?
[1]
(iii) Suggest one symptom a person with a failing valve B may have.
[1]
7. The photograph below shows a transverse section through the leaf of heather (Erica cinerea).
This heather lives in a dry, windy environment.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 14 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
(a) (i) State three features of the leaf shown above which indicate that it lives in a dry
environment.
[3]
Feature 1
Feature 2
Feature 3
(ii) Explain how any one of these features help Erica live in a dry environment.
[1]
(b) What name is given to plants that live in dry environments?
[1]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 15 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
(c) The diagram below shows a transverse section of a buttercup (Ranunculus sp.) root as
seen under high power with a light microscope.
(i) Name tissue A and explain its role in the plant.
[2]
(ii) Name tissue B and explain its role in the plant.
[2]
(iii) Name cells C.
(iv) Draw a simple longitudinal section of cell C clearly labelling the special feature of
this cell. [2]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 16 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 17 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
(v) Explain how cell C carries out its function in the uptake of water and minerals in the plant.
[4]
8. (a) The diagram below shows part of a plant stem with the tissue external to the xylem removed, a
technique known as ringing.
An accumulation of sucrose was found in the region shown.
(i) Explain why this accumulation of sucrose occurred.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 18 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
[3]
(ii) Name one other type of organic molecule that is likely to accumulate with the sucrose.
[1]
(b) If the growing points of the shoot of the plant are removed there is a greater accumulation of sucrose.
Explain why there is a greater accumulation of sucrose.
[2]
(c) Explain fully the likely effect of the removal of the ring of tissue on the concentration of sucrose below
the ring.
[3]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 19 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
9. The diagram shows two different types of vessel found in the tissues of the human body.
(a) Name the type of blood vessel labelled X in the diagram
[1]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 20 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
(b) Name the fluid found in vessel Y.
[1]
(c) The movement of water out of the blood vessels into the tissue fluid is caused by high hydrostatic
pressure at the arterial end. The reabsorption of most of the water back into the blood at the venous end
is due to osmotic pressure.
(i) Name a substance found in the plasma that helps to maintain this osmotic pressure
[1]
(ii) What name is given to the medical condition caused by a low level of this substance in the blood?
[1]
10. Answer one of the following questions.
Any diagrams included in your answers must be fully annotated.
Either, (a) (i) Describe how carbon dioxide is transported from respiring tissues to the lungs.
[6]
(ii) Explain how changes in carbon dioxide concentrations in the blood can lead to an increased oxygen
supply for respiring tissues.
[4]
Or (b) Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and functioning of arteries and xylem
vessels.
[10]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 21 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 22 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
11. (a) The graph below shows the oxygen dissociation curve for three mammals.
Graph A is the curve for a llama which is a mammal that lives at high altitudes. Graph B is the curve for a
domestic cat and graph C is the curve for a mouse which is a small mammal with a high metabolic rate.
Key:
A = llama
B = domestic cat
C = mouse
(i) What is the percentage saturation of the cat's haemoglobin with oxygen when the partial pressure of
oxygen in the muscle tissue of a cat is 3.0kPa.?
[1]
(ii) Explain the circumstances under which the partial pressure of oxygen may fall to 3.0kPa in muscle
tissues.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 23 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
[2]
(b) State which of the three curves represents the haemoglobin with the lowest affinity for oxygen at
3.0kPa.
[1]
(c) If the pH of the blood became more acidic, the position of curve C for the mouse would change.
(i) Draw on the graph opposite the new position of curve C when the blood becomes more acidic.
[1]
(ii) Explain the benefits to the mouse of this change in position of curve C.
[3]
(d) Explain how curve A for the llama shows that its haemoglobin is well adapted for its environment.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 24 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
[3]
(e) State which of the three curves could represent the oxygen dissociation curve of a lugworm.
[1]
12. (a) (i) State what is meant by the term transpiration.
[2]
(ii) Give one benefit of transpiration to a plant.
[1]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 25 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
(b) The diagram below shows a piece of apparatus called a potometer which is used to measure the rate
of transpiration
(i) Suggest why the end of the shoot should be cut under water before being inserted into the potometer.
[2]
(ii) State what measurements would have to be made, in order to determine the rate of transpiration.
[2]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 26 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
(i) State the general name for plants that live in, and are adapted for, dry conditions.
[1]
(ii) With reference to the diagram, explain how a sunken stoma is able to reduce transpiration.
[3]
(iii) Describe and explain two other adaptations which reduce the rate of transpiration in plants that live in
very dry conditions.
[2]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 27 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
13. The diagram below shows two types of cell that are found in phloem tissue.
(a) Name two other types of cell that are found in phloem.
[2]
1.
2.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 28 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
(b) The function of phloem is to transport organic molecules, such as sucrose, in a plant.
Using the diagram only, explain how two features of the sieve tube element enable the phloem to carry
out its function.
[4]
(c) The mass flow theory is one explanation to account for the movement of solutes in the phloem.
Suggest why the presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the companion cells does not support this
theory.
[3]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 29 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
14.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 30 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 31 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 32 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 33 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
15.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 34 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 35 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
16.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 36 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
17.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 37 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 38 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
18.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 39 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 40 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
19.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 41 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
21.
20.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 42 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
22.
21.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 43 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 44 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
23.
22.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 45 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 46 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
24.
23.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 47 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
25.
24.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 48 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 49 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
25.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 50 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 51 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 52 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
26.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 53 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 54 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
27.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 55 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 56 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 57 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
28.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 58 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 59 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
29.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 60 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
30.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 61 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 62 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 63 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
31.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 64 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 65 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 66 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
<
32.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Page 67 WJEC (Eduqas) Biology A-level
You might also like
- Kcse 2023 Biology Replica ExamsDocument120 pagesKcse 2023 Biology Replica Examsmicah isaboke100% (3)
- Success in BiologyDocument97 pagesSuccess in BiologyJoan Banda85% (26)
- Mcdonalds Corporation Case StudyDocument19 pagesMcdonalds Corporation Case StudyAnas Mahmood100% (1)
- Payslip - March, 2020: Total Earnings Total Deductions Net PayDocument2 pagesPayslip - March, 2020: Total Earnings Total Deductions Net PayJoyxfulNo ratings yet
- Century PlyboardsDocument24 pagesCentury PlyboardsHarsh BansalNo ratings yet
- Biology 2001 - 2016 Paper 2 DJ PrincipleDocument186 pagesBiology 2001 - 2016 Paper 2 DJ PrincipleStanleyNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 2 QDocument13 pagesBiology Form 2 QEazi X AnzigareNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and The Kidney QuestionsDocument40 pagesHomeostasis and The Kidney Questionsdiyoraabduvaliyeva06No ratings yet
- 10th ICSE Biology (QP) 2023Document6 pages10th ICSE Biology (QP) 2023Anshmaan DwivediNo ratings yet
- Revision 2023Document10 pagesRevision 2023Zain AliNo ratings yet
- Revision 2023Document10 pagesRevision 2023Zain AliNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Exam Questions With MarkschemeDocument21 pagesOsmosis Exam Questions With MarkschemeMay Lay NgeNo ratings yet
- Biology: Paper - I (Theory)Document4 pagesBiology: Paper - I (Theory)Arnab BoseNo ratings yet
- Kcse F2 Biology TopicalsDocument21 pagesKcse F2 Biology TopicalsligawacalvinceNo ratings yet
- Mass TransportDocument7 pagesMass TransportAs6870No ratings yet
- Form Ii Biology End Term of Term IiDocument7 pagesForm Ii Biology End Term of Term IioyooNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Form 3 Holiday Assignment QuestionsDocument9 pagesBIOLOGY Form 3 Holiday Assignment QuestionsgurlavatarNo ratings yet
- 3.B. Human Musculoskeletal Anatomy QPDocument40 pages3.B. Human Musculoskeletal Anatomy QPNonuNo ratings yet
- Ans 2022 PT1 F4 BioDocument6 pagesAns 2022 PT1 F4 BiomsgreenhwangNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 9 Final Exam RevisionDocument19 pagesBiology Class 9 Final Exam RevisionPearl SamuelNo ratings yet
- BIO-PP2-Teacher Co KeDocument8 pagesBIO-PP2-Teacher Co KeraymurigiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Life Processes - 2022-23 PYQsDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Life Processes - 2022-23 PYQsrmsadhviNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2011 Biology p1Document4 pagesKcse 2011 Biology p1Urex ZNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Humans 3 QPDocument9 pagesExcretion in Humans 3 QPKimNo ratings yet
- Biology 2Document15 pagesBiology 2PHANG QI ZHI MoeNo ratings yet
- Bio 22072021 012 pp1Document13 pagesBio 22072021 012 pp1MARK SIMIYUNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Biological Compounds QPDocument18 pages1.1. Biological Compounds QPufaqnavid29No ratings yet
- General InstructionsDocument4 pagesGeneral InstructionsMehak ShireenNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Humans 2 QPDocument11 pagesExcretion in Humans 2 QPMikiko Fujiwara SamaNo ratings yet
- Class Test 1Document6 pagesClass Test 1Sayma AkterNo ratings yet
- Plant QDocument4 pagesPlant QKaran PrabaNo ratings yet
- Gaseous ExchangeDocument4 pagesGaseous ExchangeArvin DiNozzoNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 2 May 6th 12thDocument8 pagesBiology Form 2 May 6th 12thEliud BrianNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Humans 3 QP-merged PDFDocument43 pagesExcretion in Humans 3 QP-merged PDFrachit100% (1)
- CH 10Document12 pagesCH 10Olivia LinNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument368 pagesBiologydamariskituku97No ratings yet
- 13.3 Excretion - in - Humans - Igcse Cie Biology - Ext Theory QPDocument10 pages13.3 Excretion - in - Humans - Igcse Cie Biology - Ext Theory QPTaelo MasuNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Human & Social Biology Paper 1 June 1997Document10 pagesCambridge International Examinations Human & Social Biology Paper 1 June 1997Jerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- Cl-11 Biology UT3 2021-22Document2 pagesCl-11 Biology UT3 2021-22aroxx johnsonNo ratings yet
- G Transport - Plants: The Leaves Can Cause The Water To Move Upwards.Document6 pagesG Transport - Plants: The Leaves Can Cause The Water To Move Upwards.Arvin DiNozzoNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Previous Year Question Paper 2011 PDFDocument9 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Previous Year Question Paper 2011 PDFmohammedNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition and Transport CIE iGCSE 0610 PPQDocument14 pagesPlant Nutrition and Transport CIE iGCSE 0610 PPQdinakempho3No ratings yet
- Blood Vessels QuestionsDocument7 pagesBlood Vessels QuestionsT-Jay Ellis-DaleNo ratings yet
- Section A: Time Allowed: 3 Hours Marks: 70Document4 pagesSection A: Time Allowed: 3 Hours Marks: 70Dhiraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Revision 1Document5 pagesRevision 1nevankurainneeliyaraNo ratings yet
- HL BIOLOGY PAST QUESTIONS PAPER PrintingDocument192 pagesHL BIOLOGY PAST QUESTIONS PAPER PrintingFaizaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Diagram Questions - 0e127ec1 04bd 44df 8218 B21116a7baa0Document11 pagesReproductive System Diagram Questions - 0e127ec1 04bd 44df 8218 B21116a7baa0radhikadaksh1983No ratings yet
- Mbbs Paper - 8Document2 pagesMbbs Paper - 8Monika ReddyNo ratings yet
- S3 Biology End of Term2 District Exam, 2023-2024Document4 pagesS3 Biology End of Term2 District Exam, 2023-2024NSABIMANA JANVIERNo ratings yet
- S5 BIOLOGY TEST I TERM II 2024 and MARKING GUIDEDocument16 pagesS5 BIOLOGY TEST I TERM II 2024 and MARKING GUIDEmunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- Life Process Complete Board Questions and AnswersDocument18 pagesLife Process Complete Board Questions and AnswersPavan JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 CellsDocument2 pagesExercise 3 CellsMolan JenaNo ratings yet
- Biology IGCSE - June Test Series Structured Questions Paper1Document14 pagesBiology IGCSE - June Test Series Structured Questions Paper1qhlwjuvrvqygwglzegNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 2Document9 pagesForm 3 Chapter 2naza9775100% (17)
- Topic 2 - Principles of OrganisationDocument6 pagesTopic 2 - Principles of OrganisationMartina ColeNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 1 001Document111 pagesBiology Paper 1 001Makembu Wa Mwangi0% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Cell StructuresDocument63 pagesChapter 1 - Cell StructuresThanos GamingNo ratings yet
- Transport of Substances in Humans (LQ)Document13 pagesTransport of Substances in Humans (LQ)Wan Ching ChanNo ratings yet
- 1.topical Biology Booklet-1Document275 pages1.topical Biology Booklet-1euginemwakhaNo ratings yet
- Biomimetic Principles and Design of Advanced Engineering MaterialsFrom EverandBiomimetic Principles and Design of Advanced Engineering MaterialsNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Answers to Exam-style questionsDocument1 page5.3 Answers to Exam-style questionsaakashsolomon3No ratings yet
- 2.2.2 Bonding And StructureDocument6 pages2.2.2 Bonding And Structureaakashsolomon3No ratings yet
- 2.5_inheritance_worksheet_1Document3 pages2.5_inheritance_worksheet_1aakashsolomon3No ratings yet
- 2.3. TransportDocument9 pages2.3. Transportaakashsolomon3No ratings yet
- 2.1. Biodiversity and Classification MSDocument6 pages2.1. Biodiversity and Classification MSaakashsolomon3No ratings yet
- Sikafiber® Novocon® He-1050 HT: Product Data SheetDocument3 pagesSikafiber® Novocon® He-1050 HT: Product Data SheetCsillag JanosNo ratings yet
- Rabobank Environment AnalysisDocument4 pagesRabobank Environment AnalysistamtitNo ratings yet
- Excise Duty in IndiaDocument3 pagesExcise Duty in IndiaKomma RameshNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Foreign AidDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Foreign Aidsjner2056No ratings yet
- SP Indices Tickers ETFDocument41 pagesSP Indices Tickers ETFBrian ClarkNo ratings yet
- What Is CapitalismDocument4 pagesWhat Is Capitalismjunebohnandreu montante100% (1)
- Mcom - 04Document8 pagesMcom - 04GeetikaNo ratings yet
- BPM Main Brochure 13286 001 (Updated 12062008)Document16 pagesBPM Main Brochure 13286 001 (Updated 12062008)CharitynNo ratings yet
- Manual Invoice FormatDocument6 pagesManual Invoice FormatJunaid UsmanNo ratings yet
- ACIA - Final - Text - 26 Feb 2009 PDFDocument56 pagesACIA - Final - Text - 26 Feb 2009 PDFDe El Eurey ShineNo ratings yet
- Honda Pilot 2015SE Owners Manual PDFDocument488 pagesHonda Pilot 2015SE Owners Manual PDFRick JacobsonNo ratings yet
- HDB Resale Transactions - Dec 08Document4 pagesHDB Resale Transactions - Dec 08pinkcoralNo ratings yet
- Basic Energy Information Questionnaire-EnDocument2 pagesBasic Energy Information Questionnaire-Enmaykee01No ratings yet
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationNeha SinghalNo ratings yet
- List of MobilisersDocument9 pagesList of MobilisersPriyanka RawatNo ratings yet
- Krispy KremeDocument5 pagesKrispy Kremeraza73735No ratings yet
- Marshall Plan - HISTORYDocument4 pagesMarshall Plan - HISTORYNatacha Ariana RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Broken Hill Prospecting IGR FINAL1Document49 pagesBroken Hill Prospecting IGR FINAL1Mauricio ASNo ratings yet
- The 12 Pillars of CompetitivenessDocument6 pagesThe 12 Pillars of Competitivenessmalinici1No ratings yet
- Faktur Packing System Baradatu/F (Bdtu) : Halaman: 1 Dari 21Document21 pagesFaktur Packing System Baradatu/F (Bdtu) : Halaman: 1 Dari 21Yunias yuniasNo ratings yet
- Business Cycles and InflationDocument23 pagesBusiness Cycles and InflationBuen Caloy LlavoreNo ratings yet
- 01 Overview of Accounting PDFDocument18 pages01 Overview of Accounting PDFEdogawa SherlockNo ratings yet
- Incoterms 2011Document1 pageIncoterms 2011barath1986No ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy of Maruti Suzuki - Deepankti SenDocument93 pagesMarketing Strategy of Maruti Suzuki - Deepankti SenTahir HussainNo ratings yet
- Dirrectory of Appropriate Tech InstitutionsDocument40 pagesDirrectory of Appropriate Tech InstitutionspitufitoNo ratings yet
- Acid Hydrolysis of Bagasse For Ethanol ProductionDocument6 pagesAcid Hydrolysis of Bagasse For Ethanol ProductionRommelGalvanNo ratings yet
- Ibm 530Document6 pagesIbm 530Muhamad NasirNo ratings yet