Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TATA Steel v1
TATA Steel v1
Uploaded by
prv261294Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 144A Vs RegSDocument1 page144A Vs RegSshrutias1989No ratings yet
- 2018 Level II Mock Exam PMDocument26 pages2018 Level II Mock Exam PMHui GuoNo ratings yet
- Sunsuria BHD (Written Report)Document6 pagesSunsuria BHD (Written Report)Monoliza PhilipsNo ratings yet
- Result GJwZP5hborGD5FkSshEUDocument22 pagesResult GJwZP5hborGD5FkSshEUurbansmileindiaNo ratings yet
- EasyJet PLC YEar 2022Document12 pagesEasyJet PLC YEar 2022Bharat LalNo ratings yet
- Comparative and Common Size FindingsDocument4 pagesComparative and Common Size FindingsHarsh KothariNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis - GVK TAJDocument11 pagesRatio Analysis - GVK TAJdeep guptaNo ratings yet
- Acid Test ROA InterpretationsDocument2 pagesAcid Test ROA InterpretationsMary Mia CenizaNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors AnalysisDocument9 pagesTata Motors AnalysisrastehertaNo ratings yet
- RatiosDocument3 pagesRatiosaadhilamjad2004No ratings yet
- Term Paper Assignment PPT FinalDocument26 pagesTerm Paper Assignment PPT FinalUday tejaNo ratings yet
- Hori Anal & RecoDocument8 pagesHori Anal & RecoMicha ArqueroNo ratings yet
- JK Accounts ResearchDocument7 pagesJK Accounts ResearchkrunalNo ratings yet
- Individual AssignmentDocument11 pagesIndividual AssignmentMohd Shahrul Naim ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- D - 05 Berger PaintsDocument7 pagesD - 05 Berger PaintstanyaNo ratings yet
- ACCY121 - REPORT - TND SquadDocument17 pagesACCY121 - REPORT - TND SquadToànNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Assignment Mini Case StudyDocument8 pages3.5 Assignment Mini Case StudyStudy BuddiesNo ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument6 pagesWorking Capital ManagementAnkur BahetiNo ratings yet
- assignment akuntansiDocument6 pagesassignment akuntansiIvannanda FalahandhikaNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors ReportDocument5 pagesTata Motors ReportrastehertaNo ratings yet
- CF Final ReportDocument11 pagesCF Final Reporteshmalsheikh703No ratings yet
- Accounting & Finance Major For College by SlidesgoDocument6 pagesAccounting & Finance Major For College by Slidesgomatthewbrandon0831No ratings yet
- Tata Motors ReportDocument5 pagesTata Motors ReportrastehertaNo ratings yet
- Accounting ProjectDocument3 pagesAccounting ProjectAbeer PervaizNo ratings yet
- Ompanies Rofile: Ucky EmentDocument14 pagesOmpanies Rofile: Ucky EmentAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Ma Cs 1Document5 pagesMa Cs 1shreya vermaNo ratings yet
- Fsa F8Document7 pagesFsa F8Sujit Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Working Capital of Dabur India - VinayDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Working Capital of Dabur India - VinayPratap Kshitish RajNo ratings yet
- Af210 - Major Assignment Essay 2023Document17 pagesAf210 - Major Assignment Essay 2023Avashnita ElakshiNo ratings yet
- Pinhome CaseDocument3 pagesPinhome CaseDean ErlanggaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management and ControlDocument18 pagesFinancial Management and ControlcrystalNo ratings yet
- Short-Term AnalysisDocument24 pagesShort-Term AnalysisJhaycob Lance Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis - Marks & SpencerDocument8 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis - Marks & Spencermuhammad.salmankhanofficial01No ratings yet
- Case Study 1 Muhammad JanjuaDocument6 pagesCase Study 1 Muhammad JanjuaAmeer Hamza JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratios FinaaaaaaalDocument8 pagesFinancial Ratios FinaaaaaaalHeidi Estuye MarceloNo ratings yet
- SNGPLDocument25 pagesSNGPLMimi mariyamNo ratings yet
- Code (K Uk)Document11 pagesCode (K Uk)jeet.researchquoNo ratings yet
- Tenda 4T23Document33 pagesTenda 4T23Flavya PereiraNo ratings yet
- BBF201 041220233 Ca1Document9 pagesBBF201 041220233 Ca1SO CreativeNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument17 pagesRatio Analysisgamerfleet211No ratings yet
- SRC Infra Developers PVT LTDDocument7 pagesSRC Infra Developers PVT LTDVijay DosapatiNo ratings yet
- DR - Sachin: Lovely Professional UniversityDocument9 pagesDR - Sachin: Lovely Professional UniversityJayesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Current RatioDocument10 pagesCurrent RatioAnugya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Finance Assignment Sainsbury's Ratio AnalysisDocument7 pagesAccounting and Finance Assignment Sainsbury's Ratio AnalysisAngela NixxNo ratings yet
- Liquidity PositionDocument16 pagesLiquidity PositionNuqman AmranNo ratings yet
- Abi Far AssignmentDocument11 pagesAbi Far AssignmentAbinayaNo ratings yet
- MJ PLCDocument16 pagesMJ PLCRichard Osahon EseleNo ratings yet
- Fsa Final InterpretationDocument42 pagesFsa Final InterpretationTakibul HasanNo ratings yet
- Radware Reports Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2022 Financial ResultsDocument9 pagesRadware Reports Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2022 Financial ResultsJeremy LambertNo ratings yet
- Anjalirawat - MB 104Document10 pagesAnjalirawat - MB 104AnjaliNo ratings yet
- 9711 SOLUTIONS UpdatedDocument20 pages9711 SOLUTIONS Updatedhaseeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- Accounts-Annual Report PPT-Group 7 - 20231105 - 104024 - 0000Document38 pagesAccounts-Annual Report PPT-Group 7 - 20231105 - 104024 - 0000Akshar VekariyaNo ratings yet
- Rajendra Singh Bhamboo Infra Private LimitedDocument5 pagesRajendra Singh Bhamboo Infra Private LimitedBABU LAL CHOUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio GSKDocument3 pagesFinancial Ratio GSKNirajan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Asset ManagementDocument4 pagesAsset ManagementNur Jihad AntaoNo ratings yet
- Megaworld Corp.Document11 pagesMegaworld Corp.Louise Merinelle Amores PosoNo ratings yet
- Ap A2. NTLDocument24 pagesAp A2. NTLLinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Onshore Construction Company Private LimitedDocument7 pagesOnshore Construction Company Private Limitedhesham zakiNo ratings yet
- Thatta Cement Company LimitedDocument24 pagesThatta Cement Company LimitedyoqimkNo ratings yet
- Profitability RatiosDocument6 pagesProfitability RatiosMERVZ TYSONNo ratings yet
- Financial Management and Control - AssignmentDocument7 pagesFinancial Management and Control - AssignmentSabahat BashirNo ratings yet
- Report On Ratio AnalysisDocument31 pagesReport On Ratio AnalysisSayeed Rahmatullah0% (1)
- Ap104 Inventories PDFDocument6 pagesAp104 Inventories PDFMicaela Betis100% (1)
- MAS Lecture Variable CostingDocument8 pagesMAS Lecture Variable CostingLhoel Delremedios100% (1)
- Buletin BVB OCT2018Document61 pagesBuletin BVB OCT2018Bogdan Marian CroitorNo ratings yet
- Strategy Overview: Private Equity FundDocument2 pagesStrategy Overview: Private Equity FundleminhptnkNo ratings yet
- MERGE - Letter of Intent - REYESDocument14 pagesMERGE - Letter of Intent - REYESAileen ReyesNo ratings yet
- Fixed Assets and Depreciation: ChapterfiveDocument12 pagesFixed Assets and Depreciation: ChapterfivecantalicoNo ratings yet
- 1.MFRS 112Document46 pages1.MFRS 112Yau Xiang Ying100% (1)
- Disinformation Index Foundation (An Foundation) 2021 990Document20 pagesDisinformation Index Foundation (An Foundation) 2021 990Gabe KaminskyNo ratings yet
- 1.160 ATP 2023-24 GR 11 Acc FinalDocument4 pages1.160 ATP 2023-24 GR 11 Acc FinalsiyabongaNo ratings yet
- FM 2016 Week 3 - Chapter 3Document86 pagesFM 2016 Week 3 - Chapter 3Wira MokiNo ratings yet
- Ia1 - Chapter 13 - Gross Profit MethodDocument17 pagesIa1 - Chapter 13 - Gross Profit MethodKhezia Mae U. GarlandoNo ratings yet
- HLB Receipt-2023-03-02 PDFDocument3 pagesHLB Receipt-2023-03-02 PDFNabilla HudaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Adjusting EntriesDocument7 pagesMCQ Adjusting EntriesMara Clara100% (1)
- Accounting For CorporationDocument11 pagesAccounting For CorporationMaricar D. VillarazaNo ratings yet
- Mac Trading Company Comparative Balance Sheet For The Year Ended December 20CY 20CY 20PYDocument8 pagesMac Trading Company Comparative Balance Sheet For The Year Ended December 20CY 20CY 20PYJoymee BigorniaNo ratings yet
- Keerthi ProjectDocument78 pagesKeerthi ProjectAnu GraphicsNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2023 Corporate ValuationDocument5 pagesFinal Exam 2023 Corporate ValuationShivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- THE Complete Beginner'S Guide: Simple StockmarketDocument37 pagesTHE Complete Beginner'S Guide: Simple StockmarketDharshiniNo ratings yet
- cc78b4a013a1ea0106599cd465d99893Document8 pagescc78b4a013a1ea0106599cd465d99893Liyana AzizulNo ratings yet
- BUS 438 (Durham) - HW 8 - Capital Budgeting 3Document5 pagesBUS 438 (Durham) - HW 8 - Capital Budgeting 3sum pradhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction Genting Malaysia BerhadDocument55 pagesIntroduction Genting Malaysia BerhadSharonz MuthuveeranNo ratings yet
- Corporate FinanceDocument142 pagesCorporate FinancetagashiiNo ratings yet
- Harrison 5ce ISM Ch03Document105 pagesHarrison 5ce ISM Ch03PmNo ratings yet
- 1.3) Accounting StandardsDocument15 pages1.3) Accounting StandardsF93 SHIFA KHANNo ratings yet
- Acct Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesAcct Cheat SheetAllen LiouNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument18 pagesUntitledjake ruthNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Statement of Changes in Equity PDFDocument7 pagesModule 5 - Statement of Changes in Equity PDFSandyNo ratings yet
TATA Steel v1
TATA Steel v1
Uploaded by
prv261294Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TATA Steel v1
TATA Steel v1
Uploaded by
prv261294Copyright:
Available Formats
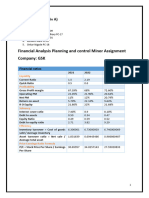
Tata Steel
Analysis of financial ratios and assessment of financial health
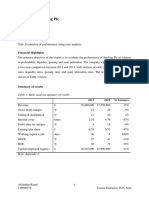
1. Profitability analysis
The company saw a significant decline in profitability, with Return on Equity (ROE) plummeting from 26.32% in
2022 to 11.5% in 2023.
Similarly, both Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) and Return on Total Assets (ROTA) experienced significant
drops, declining from 28.03% to 13.91% and 21.23% to 10.95%, respectively.
These declines suggest that the company's ability to generate profits from its investments and assets decreased notably
over the one-year period.
2. Asset and inventory management
In addition to the profitability dip in 2023, Total Asset Turnover Ratio also worsened, Specifically, there was a
notable decrease in the Current Asset Turnover Ratio from 4.12 to 3.8, indicating a reduction in the efficiency of
utilizing current assets to generate revenue.
However, the Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio experienced a slight improvement, increasing from 1.37 to 1.41, suggesting
a marginal enhancement in the utilization of fixed assets to generate sales.
Overall, these changes suggest challenges in efficiently deploying current assets while showing a modest
improvement in leveraging fixed assets for revenue generation during the specified period.
In 2023, there was a notable improvement in the Inventory Turnover Ratio, which increased from 3.91 to 4.87. This
suggests that the company managed its inventory more efficiently, with goods being sold and replaced more
frequently during the year.
Furthermore, the decrease in Inventory Days from 93 days in 2022 to 75 days in 2023 indicates that the company
reduced the average number of days it held inventory before selling it. This reduction suggests improved inventory
management efficiency and a quicker turnover of goods.
However, the Receivables Turnover Ratio experienced a slight decline from 39.33 to 38.49, indicating a small
decrease in the speed at which receivables were collected.
Receivables Days remained consistent at 9 days in both 2022 and 2023, indicating that the company maintained a
stable average collection period for receivables over the two years.
3. Solvency and Liquidity ratios
In 2023, the Current Ratio improved significantly from 0.58 to 0.73, indicating a healthier liquidity position compared
to the previous year.
Similarly, the Quick Ratio also showed improvement, increasing from 0.21 to 0.28. These increases suggest that the
company had a better ability to cover its short-term liabilities with its most liquid assets in 2023 compared to 2022.
The slight increase in the Debt to Equity Ratio from 0.34 to 0.36 suggests that the company relied more on debt
financing relative to equity in 2023 compared to 2022, indicating heightened leverage.
Additionally, the significant decline in the Interest Coverage Ratio from 16.88 to 6.75 reflects increased difficulty in
covering interest expenses with operating earnings in 2023, indicating potentially strained financial health and an
increased risk of default.
4. Cost Structure
The significant increase in the Raw Materials to Sales ratio from 30.5% in 2022 to 47.66% in 2023 indicates a higher
proportion of sales revenue being consumed by raw material costs, possibly due to increased material prices or
inefficient procurement practices.
While the Employee Cost to Sales ratio increased slightly from 4.93% to 5.13%, suggesting a minor rise in the portion
of sales revenue allocated to employee expenses, the stability of Other Expenses to Sales around 26% and
Depreciation to Sales around 4.2% indicates consistency in these cost components relative to sales revenue between
the two years.
5. Tax and Leverage Impact
The Impact of Leverage decreased notably from 7.3% in 2022 to 2.26% in 2023, suggesting a reduced influence of
financial leverage on the company's returns.
Similarly, the Impact of Tax Planning declined from 1.16% to 0.62%, indicating a decrease in the effectiveness of tax
planning strategies in enhancing returns after accounting for the applicable tax rate.
Additional Ratios and Effects
Payable Days: Decreased from 196 to 107 days, implying quicker settlement of payables.
Long-term Debt to Total Capital: Increased from 19.32% to 22.48%, indicating an increase in reliance on long-term
debt financing.
Interest Bearing Liabilities: Increased from INR 42,636 crores to INR 49,172crores, reflecting higher borrowing
levels.
Non-Interest Bearing Liabilities: Decreased from INR 53,915 crores to INR 49,820 crores, indicating improved
financial stability.
ROCE (PBIT/Non-interest bearing liabilities): Declined from 28.03% to 13.91%, indicating lower efficiency in
generating profits from non-interest bearing liabilities.
Debt/Equity (Interest Bearing Liabilities/Equity): Increased from 0.3399 to 0.3648, reflecting increased financial
leverage.
Impact of Leverage (ROCE - Cost of Debt) * (D/E): Dropped from 7.30% to 2.26%, indicating reduced benefits
from leveraging.
Summary: In summary, Tata Steel's financial performance in 2023 reflects a company grappling with a more challenging
economic landscape, characterized by reduced profitability, heightened costs, and increased leverage. While some
improvements in asset management were observed, the overall financial health and capacity to meet financial obligations have
weakened compared to 2022. Stakeholders should closely monitor these trends for potential future implications on the
company's financial viability.
You might also like
- 144A Vs RegSDocument1 page144A Vs RegSshrutias1989No ratings yet
- 2018 Level II Mock Exam PMDocument26 pages2018 Level II Mock Exam PMHui GuoNo ratings yet
- Sunsuria BHD (Written Report)Document6 pagesSunsuria BHD (Written Report)Monoliza PhilipsNo ratings yet
- Result GJwZP5hborGD5FkSshEUDocument22 pagesResult GJwZP5hborGD5FkSshEUurbansmileindiaNo ratings yet
- EasyJet PLC YEar 2022Document12 pagesEasyJet PLC YEar 2022Bharat LalNo ratings yet
- Comparative and Common Size FindingsDocument4 pagesComparative and Common Size FindingsHarsh KothariNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis - GVK TAJDocument11 pagesRatio Analysis - GVK TAJdeep guptaNo ratings yet
- Acid Test ROA InterpretationsDocument2 pagesAcid Test ROA InterpretationsMary Mia CenizaNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors AnalysisDocument9 pagesTata Motors AnalysisrastehertaNo ratings yet
- RatiosDocument3 pagesRatiosaadhilamjad2004No ratings yet
- Term Paper Assignment PPT FinalDocument26 pagesTerm Paper Assignment PPT FinalUday tejaNo ratings yet
- Hori Anal & RecoDocument8 pagesHori Anal & RecoMicha ArqueroNo ratings yet
- JK Accounts ResearchDocument7 pagesJK Accounts ResearchkrunalNo ratings yet
- Individual AssignmentDocument11 pagesIndividual AssignmentMohd Shahrul Naim ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- D - 05 Berger PaintsDocument7 pagesD - 05 Berger PaintstanyaNo ratings yet
- ACCY121 - REPORT - TND SquadDocument17 pagesACCY121 - REPORT - TND SquadToànNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Assignment Mini Case StudyDocument8 pages3.5 Assignment Mini Case StudyStudy BuddiesNo ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument6 pagesWorking Capital ManagementAnkur BahetiNo ratings yet
- assignment akuntansiDocument6 pagesassignment akuntansiIvannanda FalahandhikaNo ratings yet
- Tata Motors ReportDocument5 pagesTata Motors ReportrastehertaNo ratings yet
- CF Final ReportDocument11 pagesCF Final Reporteshmalsheikh703No ratings yet
- Accounting & Finance Major For College by SlidesgoDocument6 pagesAccounting & Finance Major For College by Slidesgomatthewbrandon0831No ratings yet
- Tata Motors ReportDocument5 pagesTata Motors ReportrastehertaNo ratings yet
- Accounting ProjectDocument3 pagesAccounting ProjectAbeer PervaizNo ratings yet
- Ompanies Rofile: Ucky EmentDocument14 pagesOmpanies Rofile: Ucky EmentAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Ma Cs 1Document5 pagesMa Cs 1shreya vermaNo ratings yet
- Fsa F8Document7 pagesFsa F8Sujit Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Working Capital of Dabur India - VinayDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Working Capital of Dabur India - VinayPratap Kshitish RajNo ratings yet
- Af210 - Major Assignment Essay 2023Document17 pagesAf210 - Major Assignment Essay 2023Avashnita ElakshiNo ratings yet
- Pinhome CaseDocument3 pagesPinhome CaseDean ErlanggaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management and ControlDocument18 pagesFinancial Management and ControlcrystalNo ratings yet
- Short-Term AnalysisDocument24 pagesShort-Term AnalysisJhaycob Lance Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis - Marks & SpencerDocument8 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis - Marks & Spencermuhammad.salmankhanofficial01No ratings yet
- Case Study 1 Muhammad JanjuaDocument6 pagesCase Study 1 Muhammad JanjuaAmeer Hamza JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratios FinaaaaaaalDocument8 pagesFinancial Ratios FinaaaaaaalHeidi Estuye MarceloNo ratings yet
- SNGPLDocument25 pagesSNGPLMimi mariyamNo ratings yet
- Code (K Uk)Document11 pagesCode (K Uk)jeet.researchquoNo ratings yet
- Tenda 4T23Document33 pagesTenda 4T23Flavya PereiraNo ratings yet
- BBF201 041220233 Ca1Document9 pagesBBF201 041220233 Ca1SO CreativeNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument17 pagesRatio Analysisgamerfleet211No ratings yet
- SRC Infra Developers PVT LTDDocument7 pagesSRC Infra Developers PVT LTDVijay DosapatiNo ratings yet
- DR - Sachin: Lovely Professional UniversityDocument9 pagesDR - Sachin: Lovely Professional UniversityJayesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Current RatioDocument10 pagesCurrent RatioAnugya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Finance Assignment Sainsbury's Ratio AnalysisDocument7 pagesAccounting and Finance Assignment Sainsbury's Ratio AnalysisAngela NixxNo ratings yet
- Liquidity PositionDocument16 pagesLiquidity PositionNuqman AmranNo ratings yet
- Abi Far AssignmentDocument11 pagesAbi Far AssignmentAbinayaNo ratings yet
- MJ PLCDocument16 pagesMJ PLCRichard Osahon EseleNo ratings yet
- Fsa Final InterpretationDocument42 pagesFsa Final InterpretationTakibul HasanNo ratings yet
- Radware Reports Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2022 Financial ResultsDocument9 pagesRadware Reports Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2022 Financial ResultsJeremy LambertNo ratings yet
- Anjalirawat - MB 104Document10 pagesAnjalirawat - MB 104AnjaliNo ratings yet
- 9711 SOLUTIONS UpdatedDocument20 pages9711 SOLUTIONS Updatedhaseeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- Accounts-Annual Report PPT-Group 7 - 20231105 - 104024 - 0000Document38 pagesAccounts-Annual Report PPT-Group 7 - 20231105 - 104024 - 0000Akshar VekariyaNo ratings yet
- Rajendra Singh Bhamboo Infra Private LimitedDocument5 pagesRajendra Singh Bhamboo Infra Private LimitedBABU LAL CHOUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio GSKDocument3 pagesFinancial Ratio GSKNirajan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Asset ManagementDocument4 pagesAsset ManagementNur Jihad AntaoNo ratings yet
- Megaworld Corp.Document11 pagesMegaworld Corp.Louise Merinelle Amores PosoNo ratings yet
- Ap A2. NTLDocument24 pagesAp A2. NTLLinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Onshore Construction Company Private LimitedDocument7 pagesOnshore Construction Company Private Limitedhesham zakiNo ratings yet
- Thatta Cement Company LimitedDocument24 pagesThatta Cement Company LimitedyoqimkNo ratings yet
- Profitability RatiosDocument6 pagesProfitability RatiosMERVZ TYSONNo ratings yet
- Financial Management and Control - AssignmentDocument7 pagesFinancial Management and Control - AssignmentSabahat BashirNo ratings yet
- Report On Ratio AnalysisDocument31 pagesReport On Ratio AnalysisSayeed Rahmatullah0% (1)
- Ap104 Inventories PDFDocument6 pagesAp104 Inventories PDFMicaela Betis100% (1)
- MAS Lecture Variable CostingDocument8 pagesMAS Lecture Variable CostingLhoel Delremedios100% (1)
- Buletin BVB OCT2018Document61 pagesBuletin BVB OCT2018Bogdan Marian CroitorNo ratings yet
- Strategy Overview: Private Equity FundDocument2 pagesStrategy Overview: Private Equity FundleminhptnkNo ratings yet
- MERGE - Letter of Intent - REYESDocument14 pagesMERGE - Letter of Intent - REYESAileen ReyesNo ratings yet
- Fixed Assets and Depreciation: ChapterfiveDocument12 pagesFixed Assets and Depreciation: ChapterfivecantalicoNo ratings yet
- 1.MFRS 112Document46 pages1.MFRS 112Yau Xiang Ying100% (1)
- Disinformation Index Foundation (An Foundation) 2021 990Document20 pagesDisinformation Index Foundation (An Foundation) 2021 990Gabe KaminskyNo ratings yet
- 1.160 ATP 2023-24 GR 11 Acc FinalDocument4 pages1.160 ATP 2023-24 GR 11 Acc FinalsiyabongaNo ratings yet
- FM 2016 Week 3 - Chapter 3Document86 pagesFM 2016 Week 3 - Chapter 3Wira MokiNo ratings yet
- Ia1 - Chapter 13 - Gross Profit MethodDocument17 pagesIa1 - Chapter 13 - Gross Profit MethodKhezia Mae U. GarlandoNo ratings yet
- HLB Receipt-2023-03-02 PDFDocument3 pagesHLB Receipt-2023-03-02 PDFNabilla HudaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Adjusting EntriesDocument7 pagesMCQ Adjusting EntriesMara Clara100% (1)
- Accounting For CorporationDocument11 pagesAccounting For CorporationMaricar D. VillarazaNo ratings yet
- Mac Trading Company Comparative Balance Sheet For The Year Ended December 20CY 20CY 20PYDocument8 pagesMac Trading Company Comparative Balance Sheet For The Year Ended December 20CY 20CY 20PYJoymee BigorniaNo ratings yet
- Keerthi ProjectDocument78 pagesKeerthi ProjectAnu GraphicsNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2023 Corporate ValuationDocument5 pagesFinal Exam 2023 Corporate ValuationShivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- THE Complete Beginner'S Guide: Simple StockmarketDocument37 pagesTHE Complete Beginner'S Guide: Simple StockmarketDharshiniNo ratings yet
- cc78b4a013a1ea0106599cd465d99893Document8 pagescc78b4a013a1ea0106599cd465d99893Liyana AzizulNo ratings yet
- BUS 438 (Durham) - HW 8 - Capital Budgeting 3Document5 pagesBUS 438 (Durham) - HW 8 - Capital Budgeting 3sum pradhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction Genting Malaysia BerhadDocument55 pagesIntroduction Genting Malaysia BerhadSharonz MuthuveeranNo ratings yet
- Corporate FinanceDocument142 pagesCorporate FinancetagashiiNo ratings yet
- Harrison 5ce ISM Ch03Document105 pagesHarrison 5ce ISM Ch03PmNo ratings yet
- 1.3) Accounting StandardsDocument15 pages1.3) Accounting StandardsF93 SHIFA KHANNo ratings yet
- Acct Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesAcct Cheat SheetAllen LiouNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument18 pagesUntitledjake ruthNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Statement of Changes in Equity PDFDocument7 pagesModule 5 - Statement of Changes in Equity PDFSandyNo ratings yet