Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Theory summed up
Theory summed up
Uploaded by
a.dorodnyhhCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Theory summed up
Theory summed up
Uploaded by
a.dorodnyhhCopyright:
Available Formats
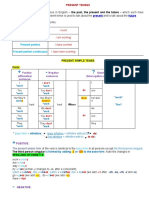
SPELLING RULES
Spelling rules for the third person Singular: Spelling rules
Verbs ending in –y : the third person Rule 1: For words that end in a silent (not
changes the –y to -ies: pronounced) -e, drop the -e and add -ing.
fly --> flies, cry --> cries Example: smile → smiling
Exception: if there is a vowel before the -
y: play --> plays, pray --> prays
Add –es ([-iz]) to verbs ending in:-ss, -x,
-sh, -ch, -z, - tch (sibilants): he passes, Rule 2: For one-syllable words that end in
she catches, he fixes, it pushes consonant-vowel-consonant (except x and w),
double the last letter and add -ing. Examples: sit
→ sitting run → running
Pronunciation
[iz] after sibilant [s], [z], [ʃ], [ʧ], [dʒ]
Rule 3: For most other words (including words
passes, judges, changes
that end in -y), add -ing with no changes.
[z] after voiced consonants and vowels Examples: rain → raining send → sending play
→ playing
sees, lives, reads
[s] after voiceless consonants
works, wants,
The Present Simple The Present Continuous (Progressive)
Customary, repeated action or habit. Action going on now, action in progress. The
(often, usually, always, never, frequently, precise time limits of the action are not known,
sometimes, rarely, a once a ______ (day, minute, its beginning and its end are not specified. The
hour, year, week, etc.), every _______ (day, night, indication of time is not necessary in this case
minute, year, week, seldom, occasionally, every though occasionally such adverbial modifiers as
year (week, month, day), once {twice, three now and at present are found. The process, not
the fact is important. (now, today, this year etc.
times) a year, daily, on Sundays (Mondays, etc.)
if we mean process) – You are working hard
today.
Action and state characterizing a given person. A state or a quality of the person at the
given moment. Compare!!!
I can't understand why he's being so
selfish. He isn't usually like that. (being
selfish = behaving selfishly at the
moment)
He never thinks about other people. He is
very selfish. (= He is selfish generally,
not only at the moment)
We use am/is/are being to say how somebody
is behaving. It is not usually possible in other
sentences: it's hot today. (not it is being hot)
Sarah is very tired. (not is being tired)
When no emotional colouring is implied, the Present
Indefinite is used to give an objective characteristic.
A continual process, going without intervals,
with adverbs always, constantly, ever. Often
expresses irritation, often contains an element of
exaggeration. Eg. She is constantly smiling. (and
it annoys me)
Universal truth, fact. Changes happening around now (to get, to
change, to rise, to fall, to increase, to grow, to
begin, to start). The population of the world is
increasing very fast.
We use it to speak about current tendencies
Action going on at the present moment with Some durative verbs, for example, verbs of
verbs that are not used in Continuous (see the bodily sensation (to ache, to feel, to hurt, to
section “Verbs not used in Continuous” ) itch, etc.) and such verbs as to wear, to look (=
to seem), to shine and some other can be used
either in the Present Indefinite or in the
Present Continuous with little difference in
meaning.
Eg. You're looking well, cousin Joan. You look quite
happy today. “I know what you are feeling, Roy," she
said. "We all feel exactly the same."
When there are two actions – one in progress,
the other is habitual. I never talk while I am
working.
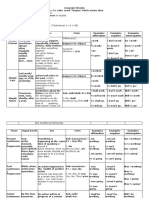
For future action For future action
In clause of time and condition, after
when, till, until, before, after, as soon as, To express actions which will take place in the near
as long as, if, unless, on condition that, future due to one's previous decision. (I cannot
provided that stay with you, Bilbo. I am leaving for Mordor
Compare! If Frodo takes the ring to Mordor tomorrow).
(clause of condition), I will go with him. When
Frodo goes to Mordor (clause of time), I will go
with him. But! I don’t know if Frodo will take
the ring to Mordor (object clause).
fixed action in the future, something
that happens according to a timetable,
programme, schedule, command or
arrangement worked out for a per- son or
persons officially. The sentence usually
contains an indication of time.
Clauses of concession are introduced by the
conjunctions even if, even though, no matter
how, whenever, whatever, however, etc. e.g.
Even if he hates me (concession) I shall never
do him any harm. I'll have dinner whenever
it's ready (concession).
In object clauses after to see (to), to take care
and to make (be) sure. e.g. I'll see that the
lady is properly looked after. Her husband will
look after her, and make sure no harm comes
to her. He will take care that no one
interferes with them.
With reference to the immediate future is
structurally dependent in some special
questions. e.g. What do we do next? ('Что
будем сейчас делать?') Where do we go
now? ('Куда сейчас пойдем?') What
happens next? ('Что сейчас будет?')
Stylistically restricted use of the Present Simple Stylistically restricted use of the Present
Continuous
* For an ongoing action.
a) to express a succession of point actions The Present Continuous is used to
taking place at the time of speaking. Used in describe pictures. Eg. Our head of our
stage directions or by radio and TV department is the one who is standing
commentators in describing sports events, slightly behind in the college photo.
public functions. We can use the Present Continues with
b) For an instantaneous action which takes the Present Simple to give more
place at the moment of speaking but it is not immediacy. In an anecdote we use the
viewed in its progress. The speaker just names continuous for actions which form a
the occurrence itself, the action as such. You background and the simple for the
leave me no choice. I swear it to you! I refuse to actions that make up the narrative. Eg.
listen to you. You talk such nonsense. This use of There is an old woman with thick glasses
the Present Indefinite is also often found in who is serving the hot drinks, so I go up
exclamatory and interrogative sentences. e.g. She to her and ask ( = she started serving
said: "How swiftly the years fly!" before the action of the narrative).
This is often the way that we described
7. In literary style to describe a succession of the beginning of books films or plays.
actions in the past, usually to make a vivid Eg. At the start of the play Hamlet is
narrative of past events. This application of the walking along the castle walls when he
Present Indefinite is often called in grammars the hears a strange voice.
historic or dramatic present.
e.g. She arrives full of life and spirit. And about a
quarter of an hour later she sits down in a chair,
says she doesn't feel well, gasps a bit and dies.
a) In stage directions:
REV. S. Good night. (They shake hands. As he passes
Vivie he shakes hands with her also and bids her good-
night. Then, in booming command, to Frank) Come
along, Sir, at onc
b) In comments (here on a TV film about Chi-Chi, the
giant panda, who returns home after her stay in the
Moscow Zoo): "Chi-Chi is in the pen. She walks over
to the travelling box. Chi-Chi climbs on the rock. The
crowd moves closer to Chi-Chi."
c) In demonstrations: Now I peel the apples, slice
them and put into the dish. Then I whip the cream
until thick and pour it over the apples.
In newspaper headlines we often use the
Present Simple to express a past event which
again gives more immediacy to the event. Eg.
UK jobless total climbs to 2.4 million
Verbs not used in Continuous
Non-continuous verbs are verbs that we do not normally use with continuous
tenses. These "stative" verbs are about state, not action, and they cannot express
the continuous or progressive aspect. Here are some of the most common non-
continuous verbs:
feeling: hate, like, love, prefer, want, wish
senses: appear, feel, hear, see, seem, smell, sound, taste
communication: agree, deny, disagree, mean, promise, satisfy, surprise
thinking: believe, imagine, know, mean, realize, recognize, remember,
understand
other states: be, belong, concern, depend, involve, matter, need, owe, own,
possess
Remember!!!!!
Think
When think means 'believe' or 'have an opinion', we do not use the continuous:
I think Mary is Canadian, but I'm not sure. (not I'm thinking)
What do you think of my plan? (=What is your opinion?)
When think means 'consider', the continuous is possible:
I'm thinking about what happened. I often think about it.
Nicky is thinking of giving up her job. (=she is considering it)
Look and feel
You can use the present simple or continuous to say how somebody looks or feels
now:
You look well today. or You're looking well today.
How do you feel now? or How are you feeling now?
but
I usually feel tired in the morning. (not I'm usually feeling)
You might also like
- Super Minds cls.3 PlanificareDocument2 pagesSuper Minds cls.3 PlanificareAnina Mariana Mihai100% (1)
- Tablolarla Bütün Ingiliz GrameriDocument23 pagesTablolarla Bütün Ingiliz Grameritkesil100% (4)
- Dynamic and Stative Verbs PDFDocument7 pagesDynamic and Stative Verbs PDFDiego TrejoNo ratings yet
- Developing Language SkillsDocument15 pagesDeveloping Language SkillswilliamNo ratings yet
- Coffee Break German Lesson 16Document10 pagesCoffee Break German Lesson 16asfNo ratings yet
- IELTS Grammar GuideDocument29 pagesIELTS Grammar GuidePradeep PaudelNo ratings yet
- On Screen B The Grammar Rules of Unit 1 (En - LT)Document15 pagesOn Screen B The Grammar Rules of Unit 1 (En - LT)Daiva SnipaitieneNo ratings yet
- Resumen de Tiempos. Inglés Tiempo Estructura Usos: Present ContinuosDocument3 pagesResumen de Tiempos. Inglés Tiempo Estructura Usos: Present ContinuosEnalys García MenaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple and Continuous - IntermediateDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect Simple and Continuous - IntermediateALEJANDRA2605No ratings yet
- Handout 1Document3 pagesHandout 1edenamiriambutNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Affirmative NegativeDocument15 pagesPresent Simple: Affirmative NegativeJosé Miguel SerraNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument4 pagesPresent ContinuousMarcos CachuloNo ratings yet
- VERB TENSES ExplanationsDocument8 pagesVERB TENSES ExplanationsMihaela GradinaruNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument6 pagesPresent ContinuousAyy SykesNo ratings yet
- Verbal Tenses EnglishDocument15 pagesVerbal Tenses EnglishXoel Carracedo PardoNo ratings yet
- Actionality and Situation Types: Shinta Putri Prihanto Reni OktarinaDocument12 pagesActionality and Situation Types: Shinta Putri Prihanto Reni OktarinaAulia Rahma Sastrosudjono100% (2)
- Class 02 (30 10 23)Document4 pagesClass 02 (30 10 23)Liza JaneNo ratings yet
- Present TensesDocument7 pagesPresent TensesDamjan LakićNo ratings yet
- State Verbs Are Not Used in Any Continuous Form!!!: Form V1/Vs/Es Form V2/Ved He Spoke/WaitedDocument5 pagesState Verbs Are Not Used in Any Continuous Form!!!: Form V1/Vs/Es Form V2/Ved He Spoke/WaitedKsenia KostirkinaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense, Past Tense, Conditional Sentence Type 1, Conditional Sentence Type 2Document8 pagesSimple Present Tense, Past Tense, Conditional Sentence Type 1, Conditional Sentence Type 2Aby'sNo ratings yet
- The Present Simple Tense (Affirmative) : She On Her Basket After Dinner Every DayDocument28 pagesThe Present Simple Tense (Affirmative) : She On Her Basket After Dinner Every DayNini TskhakaiaNo ratings yet
- Present Tenses - UsagesDocument8 pagesPresent Tenses - UsagesГабриела ГеоргиеваNo ratings yet
- Focus-BrE5 StudentsBook Unit1-GrammarFocus PDFDocument3 pagesFocus-BrE5 StudentsBook Unit1-GrammarFocus PDFJulio Emmanuel MezaNo ratings yet
- Kompendium GramatyczneDocument20 pagesKompendium GramatyczneArek KozakNo ratings yet
- Stative VerbsDocument4 pagesStative VerbsKAROL MARIANA ADAME DIAZNo ratings yet
- SYKES - in TransitDocument5 pagesSYKES - in TransitJorge BulaNo ratings yet
- English Tenses TableDocument5 pagesEnglish Tenses TableRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Secion 6 InglesDocument12 pagesSecion 6 InglesWalter Atao SalazarNo ratings yet
- English - TensesDocument11 pagesEnglish - TensesteodoraniculaitaNo ratings yet
- Presente Continuo - InglesDocument14 pagesPresente Continuo - InglesMiyouba CarriganNo ratings yet
- Eng GrammarDocument9 pagesEng GrammarSeba Tube HDNo ratings yet
- Simple Continuous TenseDocument13 pagesSimple Continuous TenseNaila HikmahNo ratings yet
- Stative and Dynamic VerbsDocument5 pagesStative and Dynamic VerbsViviane SantosNo ratings yet
- Present Tenses (Simple - Continuous)Document11 pagesPresent Tenses (Simple - Continuous)Ольга Ігорівна ШкарупаNo ratings yet
- TYPES OF TensesDocument19 pagesTYPES OF Tensesariesyue100% (2)
- Simple P VS P ProgressiveDocument15 pagesSimple P VS P ProgressiveAaly MoretthNo ratings yet
- Simple PresentDocument31 pagesSimple PresentJuni DzibNo ratings yet
- For The Third Person Singular (He/she/it) and For The Others (I/ You/ We /they)Document13 pagesFor The Third Person Singular (He/she/it) and For The Others (I/ You/ We /they)Samu PrietoNo ratings yet
- Expressing The PresentDocument5 pagesExpressing The PresentflorianhNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous and FamilyDocument13 pagesPresent Continuous and FamilyErica SoaresNo ratings yet
- Te3 Int Entcheck 01Document2 pagesTe3 Int Entcheck 01Dasha MoskalenkoNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument12 pagesSimple Present Tenselilis ayuNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument12 pagesSimple Present TenseDenna Refnaldi SatryaNo ratings yet
- Exceptions in Spelling: Affirmative NegativeDocument6 pagesExceptions in Spelling: Affirmative NegativeEnGiNo ratings yet
- The Group of Continuous TensesDocument2 pagesThe Group of Continuous TensesJuliaNo ratings yet
- Subjunctive MoodDocument21 pagesSubjunctive MoodЭльнара ДемидоваNo ratings yet
- Tenses Summary PDFDocument2 pagesTenses Summary PDFمحمد اسحمNo ratings yet
- Present ContinousDocument6 pagesPresent ContinousFernando HernándezNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument4 pagesEnglish TensesNassim DjellaliNo ratings yet
- Present Simple and Present ContinuousDocument3 pagesPresent Simple and Present ContinuousMel LoNo ratings yet
- Roadmap A2 Grammar ResourcesDocument20 pagesRoadmap A2 Grammar ResourcesЯна Сизоненко100% (1)
- Past Simple TenseDocument4 pagesPast Simple TenseDr. Amr AboelmagdNo ratings yet
- Cuando El Infinitivo Del Verbo Acaba en ¿Qué Se Añade A La 3 Persona SG? ExampleDocument4 pagesCuando El Infinitivo Del Verbo Acaba en ¿Qué Se Añade A La 3 Persona SG? ExampleItsNotMeNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Grammar Exercise Present PerfectDocument3 pagesIntermediate Grammar Exercise Present PerfectEsther León JorgeNo ratings yet
- English Verb TensesDocument5 pagesEnglish Verb TensesNabil El makoudyNo ratings yet
- Infografia Presente ContinuoDocument1 pageInfografia Presente ContinuoDavid Ureña100% (1)
- Tiempos Simples: AfirmativaDocument8 pagesTiempos Simples: AfirmativaMarcos SanchesNo ratings yet
- Tenses GradeDocument56 pagesTenses Gradelevin39919No ratings yet
- Intermediate Grammar Exercise Present PerfectDocument3 pagesIntermediate Grammar Exercise Present PerfectAndreeaNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument53 pagesEnglish TensesJenya IvanovaNo ratings yet
- A"rmative, Negative, Questions: Present Simple Present ContinuousDocument1 pageA"rmative, Negative, Questions: Present Simple Present ContinuousFilipa SousaNo ratings yet
- Italian Irregular Verbs Fully Conjugated in all Tenses (Learn Italian Verbs Book 2)From EverandItalian Irregular Verbs Fully Conjugated in all Tenses (Learn Italian Verbs Book 2)No ratings yet
- More About French ExamsDocument10 pagesMore About French Examsskr skrtNo ratings yet
- A - Group 1 - Prescriptive Vs Descriptive GrammarDocument12 pagesA - Group 1 - Prescriptive Vs Descriptive GrammarFebby AnasyahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Past SimpleDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Past SimpleAlexandra SabauNo ratings yet
- Ghomara Berber A Brief Grammatical Survey by J El HannoucheDocument249 pagesGhomara Berber A Brief Grammatical Survey by J El HannoucheAzurag Arrif100% (3)
- The Influence of Social Classes On Language Variations: A Study On The People of Dhaka CityDocument58 pagesThe Influence of Social Classes On Language Variations: A Study On The People of Dhaka CityMuhammad sazzadul karimNo ratings yet
- MKDU Materials 4 Make Questions, Impersonal ItDocument3 pagesMKDU Materials 4 Make Questions, Impersonal ItHafizhRNo ratings yet
- The Latvian Language,: Languages in LatviaDocument18 pagesThe Latvian Language,: Languages in Latviaankara271828No ratings yet
- Proyecto de Aula InglesDocument7 pagesProyecto de Aula Inglesedith suarezNo ratings yet
- Grammar and Vocabulary For Cambridge Advanced and ProficiencyDocument244 pagesGrammar and Vocabulary For Cambridge Advanced and Proficiencyaformika0% (4)
- How To Write Letter or Email. FCEDocument14 pagesHow To Write Letter or Email. FCEDenis Davydow100% (1)
- Maroon 5 para o 3ano PDFDocument2 pagesMaroon 5 para o 3ano PDFAnonymous 6baDBV6No ratings yet
- Language Teaching Beliefs QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesLanguage Teaching Beliefs QuestionnaireG. RezaieNo ratings yet
- Collocations s3Document18 pagesCollocations s3Isferra RezanaNo ratings yet
- Basic and Optional Parts of A Business Letter Business Letter Punctuation and StylesDocument25 pagesBasic and Optional Parts of A Business Letter Business Letter Punctuation and StylesMary Linlyn Galera YacoNo ratings yet
- Ell ToolboxDocument2 pagesEll Toolboxapi-263996400No ratings yet
- You Are Requested To... : VoiceDocument1 pageYou Are Requested To... : VoiceAnonymous lqsJIe6l5No ratings yet
- CCE - Teachers Manual English STD 7Document33 pagesCCE - Teachers Manual English STD 7edwin_prakash75No ratings yet
- What Is A Preposition in EnglishDocument74 pagesWhat Is A Preposition in EnglishKamalakkannan Muniappan100% (1)
- Chuyên đề bồi dưỡng HSG Anh 8 Chuyên đề Adverb clause of resultDocument15 pagesChuyên đề bồi dưỡng HSG Anh 8 Chuyên đề Adverb clause of resultlam trầnNo ratings yet
- INGLES II - FUTURE SIMPLE Semana 14 PDFDocument6 pagesINGLES II - FUTURE SIMPLE Semana 14 PDFShamira Geydi Mamani AucapinoNo ratings yet
- C Users Eri Desktop ALL TOEFL Sentence Correction Pract5Document8 pagesC Users Eri Desktop ALL TOEFL Sentence Correction Pract5fatbardhaNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and Superlatives: Comparatives Are Used To Show The Difference Between Two ObjectsDocument4 pagesComparatives and Superlatives: Comparatives Are Used To Show The Difference Between Two ObjectsClaraNo ratings yet
- EP 1A Module 1.1Document7 pagesEP 1A Module 1.1Tine Vasiana DuermeNo ratings yet
- Together Starter 4A Two-StarDocument2 pagesTogether Starter 4A Two-StarCarla Morales MazzochiNo ratings yet
- VII - Limba Engleza, Nivelul A2.3 (A.2020) .PDF - Google DriveDocument1 pageVII - Limba Engleza, Nivelul A2.3 (A.2020) .PDF - Google DrivePascaru MarianaNo ratings yet
- Learning English March 2011 Lower Intermediate Classroom MaterialsDocument2 pagesLearning English March 2011 Lower Intermediate Classroom MaterialsThe GuardianNo ratings yet
- On PunctuationDocument15 pagesOn Punctuationall in one with vivaanNo ratings yet