Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03 Circular & WPE SC
03 Circular & WPE SC
Uploaded by
Deepak ThakurCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- IIT-JEE 2002 Screening Paper With Answer KeyDocument16 pagesIIT-JEE 2002 Screening Paper With Answer KeyNarmadha Ramesh100% (1)
- Power Distribution LossesDocument24 pagesPower Distribution LossesmuskanumeedNo ratings yet
- 03 Circular WPE QuestionsDocument7 pages03 Circular WPE Questions17swabhiNo ratings yet
- Kinematics QuizDocument5 pagesKinematics QuizShashi Shekhar Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- KM QuizDocument2 pagesKM Quiztgfkwwn2npNo ratings yet
- Two Yr CRP 224 - B-Lot - Ph-I - Mains - PhyDocument4 pagesTwo Yr CRP 224 - B-Lot - Ph-I - Mains - Phyjdhmyj2zchNo ratings yet
- DPP 1Document11 pagesDPP 1ADARSH KUMAR BEHERANo ratings yet
- NTSE Support Program: SESSION: 2019-20Document6 pagesNTSE Support Program: SESSION: 2019-20Anita SinhaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Growth Apex CT - 11 - (27-05-2024) - SCDocument6 pages11 - Growth Apex CT - 11 - (27-05-2024) - SCsangamkumar01010No ratings yet
- 1st Year Full Book Past Paper MCQS 100 With KeyDocument6 pages1st Year Full Book Past Paper MCQS 100 With KeyAbcdefNo ratings yet
- Most Selected 100 MCQs of Physics Part-1 - UnlockedDocument6 pagesMost Selected 100 MCQs of Physics Part-1 - Unlockedchmudassarimran2No ratings yet
- System of Particles and RotationDocument33 pagesSystem of Particles and RotationLet's work today For better tomorrowNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE TEST - (Vectors & KM) : Pattern-1 Part-A Single Correct Choice Type (1-6)Document3 pagesPRACTICE TEST - (Vectors & KM) : Pattern-1 Part-A Single Correct Choice Type (1-6)chaitanya goyalNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-21 12th (A4) CLASS TESTDocument3 pagesPHYSICS-21 12th (A4) CLASS TESTRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- DPP 1-13 Rotation JA Nurture LiveDocument118 pagesDPP 1-13 Rotation JA Nurture LivebqfhwdmdcyNo ratings yet
- PCCP Sample Paper PDFDocument9 pagesPCCP Sample Paper PDFtanyasharma_3010No ratings yet
- DPP - 01 _ Kinematics Of Circular MotionDocument4 pagesDPP - 01 _ Kinematics Of Circular MotionAnsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- MT Xi Physics 291020Document6 pagesMT Xi Physics 291020cutuNo ratings yet
- Allen Race Nurture Iit Jee AdvancedDocument2 pagesAllen Race Nurture Iit Jee AdvancedUma MandalNo ratings yet
- Class:XII Time: 40 Min. M.M.: 36 DPP. NO.-48: Discussion: 27-28/07/2015Document6 pagesClass:XII Time: 40 Min. M.M.: 36 DPP. NO.-48: Discussion: 27-28/07/2015RahulNo ratings yet
- W ID8 OL0 EEp 7 Ejg 08 A8 GJDocument3 pagesW ID8 OL0 EEp 7 Ejg 08 A8 GJROHIT ARYANo ratings yet
- Wa 6 Wep VCMDocument5 pagesWa 6 Wep VCMAvishkar JaiswalNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-29 12th (A1)Document3 pagesPHYSICS-29 12th (A1)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- CombinedELP 1to11studentDocument35 pagesCombinedELP 1to11studentsureshserious7226No ratings yet
- MathongoDocument40 pagesMathongosatya sandeepNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice Sheet 1-15Document24 pagesDaily Practice Sheet 1-15kraken monsterNo ratings yet
- Physics Chemistry Mathematics IITJEE TestDocument17 pagesPhysics Chemistry Mathematics IITJEE TestAbhay Kumar Nayak100% (5)
- Kinametics (Rectilinear+Motion) Exercise-5 (B) +Document2 pagesKinametics (Rectilinear+Motion) Exercise-5 (B) +Shivam RoyNo ratings yet
- Most Selected 100 MCQs of Physics Part-1-1Document6 pagesMost Selected 100 MCQs of Physics Part-1-1Amna ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Part - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 10 April - Morning Shift MathongoDocument37 pagesPart - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 10 April - Morning Shift Mathongorohit574No ratings yet
- 2023 - JEE-Main-7 - Paper (Gen 4A 4B 4C 4D 4E 6A and 6B)Document13 pages2023 - JEE-Main-7 - Paper (Gen 4A 4B 4C 4D 4E 6A and 6B)Archana SharmaNo ratings yet
- JEE MAINS PART TEST 4Document12 pagesJEE MAINS PART TEST 4Sparsh SinghNo ratings yet
- PCM-11-02 - (13th) Paper-1 Code-ADocument16 pagesPCM-11-02 - (13th) Paper-1 Code-ARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- BoSoN Sample Paper Class XIDocument11 pagesBoSoN Sample Paper Class XISKUL PARADOXNo ratings yet
- SPP-1 Physics (JEE Advanced)Document6 pagesSPP-1 Physics (JEE Advanced)anilpurnimakothariNo ratings yet
- Ae 2012 PDFDocument11 pagesAe 2012 PDFSubhash KorumilliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Circular MotionDocument4 pagesChapter 04 Circular MotionMuhammad AtirNo ratings yet
- Revision Assignment (Adv Level) - 1Document7 pagesRevision Assignment (Adv Level) - 1Gandharv BhoiteNo ratings yet
- 4S Sample Medical Selection Test Paper Answer Key (2020 21)Document16 pages4S Sample Medical Selection Test Paper Answer Key (2020 21)Prem TewariNo ratings yet
- Mains Neet Class 3Document3 pagesMains Neet Class 3Swastik DasNo ratings yet
- 4 Jeem 2023 April 08 Second Shift PaperDocument38 pages4 Jeem 2023 April 08 Second Shift PaperSURAKSHA PATELNo ratings yet
- 2025-JEE Main-6 - GEN - 1 & 2 - PaperDocument22 pages2025-JEE Main-6 - GEN - 1 & 2 - PaperNavaya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Answer Correct Type) : IIT - JEE: 2022 Xii - TW Test DATE: 19/07/20 TIME: 1 Hr. Physics MARKS: 100Document8 pagesSection-I (Single Answer Correct Type) : IIT - JEE: 2022 Xii - TW Test DATE: 19/07/20 TIME: 1 Hr. Physics MARKS: 100pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- SPP 01Document6 pagesSPP 01Ryan MittalNo ratings yet
- Part - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 8 April - Evening Shift MathongoDocument41 pagesPart - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 8 April - Evening Shift MathongoAparaNo ratings yet
- Vector PDocument3 pagesVector PAshutoshNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-11 (12th & 13th) Paper 1Document7 pagesPHYSICS-11 (12th & 13th) Paper 1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment CH 04 ADocument2 pagesAssignment CH 04 AHK AbbasiNo ratings yet
- CIRCULAR MOTION JEE PracticeDocument21 pagesCIRCULAR MOTION JEE PracticeDev PatelNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: Class: XI General InstructionsDocument8 pagesSample Paper: Class: XI General InstructionsmadhavNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Plane DPP 02 (Of Lec 05) Arjuna JEE 2024Document3 pagesMotion in A Plane DPP 02 (Of Lec 05) Arjuna JEE 2024PriyanshuNo ratings yet
- Class XI Math Moving To Class XII Math Test Paper With Detailed SolutionDocument20 pagesClass XI Math Moving To Class XII Math Test Paper With Detailed Solutionghostrider828837No ratings yet
- Grade 11-VectorsDocument5 pagesGrade 11-VectorsChetanNo ratings yet
- 11th PhysicsDocument5 pages11th PhysicsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- JEE MAIN 2020 (02.09.2020 - 2nd Shift) 1Document12 pagesJEE MAIN 2020 (02.09.2020 - 2nd Shift) 1Arjun PanditaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 1 Paper (2022) Gen. 1Document11 pagesJEE Main 1 Paper (2022) Gen. 1Halfborn GundersonNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: Level - 01Document5 pagesElectrostatics: Level - 01Om PungleNo ratings yet
- 1ST Year 150 MCQDocument13 pages1ST Year 150 MCQUsman ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- 2 L SBYkb J3 ATsabyqsw 5 ZDocument14 pages2 L SBYkb J3 ATsabyqsw 5 ZÂshútösh KumarNo ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Answer Correct Type)Document6 pagesSection-I (Single Answer Correct Type)pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Dynamic MeasurementsDocument217 pagesHandbook of Dynamic MeasurementsronfrendNo ratings yet
- Laser Ion Source With Solenoid FieldDocument6 pagesLaser Ion Source With Solenoid FieldbhumijayaNo ratings yet
- S B P G S S R L A S: Technical Paper by A. Mcgown, I. Yogarajah, K.Z. Andrawes and M.A. SaadDocument15 pagesS B P G S S R L A S: Technical Paper by A. Mcgown, I. Yogarajah, K.Z. Andrawes and M.A. SaadRaluca IoanaNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument39 pagesElectrostaticsshreyas bulbule100% (1)
- Inductance of 3 Phase LineDocument50 pagesInductance of 3 Phase LineFemi PrinceNo ratings yet
- Motion Connect 500: 6FX5002-2DC10-1AF0Document2 pagesMotion Connect 500: 6FX5002-2DC10-1AF0Khizar AltafNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Chapter 01Document42 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers Chapter 01topwarmachineNo ratings yet
- Current TransformerDocument6 pagesCurrent TransformerSwinlife WinlifeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Problems For Momentum TransferDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Problems For Momentum TransferZiyad Al Abasie0% (1)
- Questions Type Wise PDFDocument26 pagesQuestions Type Wise PDFAyaan NaveedNo ratings yet
- C-16 Diploma ElectricalDocument39 pagesC-16 Diploma ElectricalSuryavamsiNo ratings yet
- DSS41A05Document7 pagesDSS41A05petrovi482No ratings yet
- Development of An Underactuated Exoskeleton For EfDocument19 pagesDevelopment of An Underactuated Exoskeleton For EftaylanNo ratings yet
- Notes Viscosity PDFDocument8 pagesNotes Viscosity PDFManjunath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Module 6 Edited 1Document10 pagesPhysical Science Module 6 Edited 1Alfa May BuracNo ratings yet
- AP1 Simple Harmonic Motion Presenter W AnswersDocument33 pagesAP1 Simple Harmonic Motion Presenter W AnswersDamion Mcdowell100% (1)
- On Mechanical Properties of Square and Rectangular Stainless Steel Wires Tested in Torsion PDFDocument11 pagesOn Mechanical Properties of Square and Rectangular Stainless Steel Wires Tested in Torsion PDFDiana Paola FontechaNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet PDFjoseph govadaNo ratings yet
- AP125 Designing Microcontroller Systems For Electrically Noisy EnvironmentsDocument26 pagesAP125 Designing Microcontroller Systems For Electrically Noisy EnvironmentsAdam CampbellNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Highway and Railroad EnggDocument21 pagesModule 1 Highway and Railroad EnggMarlo NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram S K GoyalDocument47 pagesSingle Line Diagram S K Goyalrakeshran100% (1)
- AN296065 Allegro Hall Effect Sensor ICs PDFDocument5 pagesAN296065 Allegro Hall Effect Sensor ICs PDFPhong DoNo ratings yet
- Ncac 2012 W 005 PDFDocument18 pagesNcac 2012 W 005 PDFNingu AmrutattiNo ratings yet
- Inter Part One Physics Old PaperDocument72 pagesInter Part One Physics Old PaperMian EjazNo ratings yet
- 18.0 Inches: LF DriversDocument2 pages18.0 Inches: LF DriversRafRouf SehiliNo ratings yet
- Spherical Wave Scattering by A Rigid SphereDocument3 pagesSpherical Wave Scattering by A Rigid Spheretimosp1973No ratings yet
- Substation DesignDocument764 pagesSubstation DesignNahidi100% (5)
- Chapter 1 States of Stress and Strain at A PointDocument25 pagesChapter 1 States of Stress and Strain at A PointRyan GinNo ratings yet
- MEC521 - Chapter 2Document27 pagesMEC521 - Chapter 2Hafizudin DaudNo ratings yet
03 Circular & WPE SC
03 Circular & WPE SC
Uploaded by
Deepak ThakurCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
03 Circular & WPE SC
03 Circular & WPE SC
Uploaded by
Deepak ThakurCopyright:
Available Formats
CIRCULAR & WPE (NSEP Questions Bank)
SECTION-I
• This section contains TWENTY (20) questions.
• Each question has Four options (A), (B), (C) and (D). ONLY ONE of these four options is correct.
• For each question, choose the option corresponding to the correct answer.
• Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +3 If ONLY the correct option is chosen.
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered)
Negative Marks : –1 In all other cases.
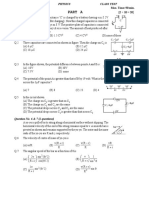
1. The kinetic energy K of a particle moving along a circle of radius R depends on the distance covered
s as K = as2 where a is a positive constant. The total force acting on the particle is:
1/2
s2 s2
(A) 2a (B) 2as 1 +
R R2
R2
(C) 2 as (D) 2a
s
2. Consider a case in which, the driver of a car travelling at a high speed suddenly sees a wall at a
distance r directly in front of him. To avoid collision,
(A) he should apply brakes sharply
(B) he should turn the car sharply
(C) he should apply brakes and then sharply turn
(D) None of these
3. A particle moves with deceleration along the circle of radius R so that at any moment of time its
tangential and normal accelerations are equal in magnitude. At the initial moment t = 0 the speed
of the particle equals v0, then :
(i) the speed of the particle as a function of the distance covered s will be
(A) v = v0 e–s/ R (B) v = v0 es/ R (C) v = v0 e–R/s (D) v = v0 eR/s
(ii) the total acceleration of the particle as function of velocity.
v2 v2
(A) a = 2 (B) a =
R R
2v2 2 2 v2
(C) a = (D) a =
R R
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 1
CIRCULAR & WPE (NSEP Questions Bank)
4. A particle A moves along a circle of radius R = 50 cm so that its radius vector r relative to the
fixed point O (Figure) rotates with the constant angular velocity = 0.40 rad/s. Then modulus v of
the velocity of the particle, and the modulus a of its total acceleration will be
(A) v = 0.4 m/s, a = 0.4 m/s2 (B) v = 0.32 m/s, a = 0.32 m/s2
(C) v = 0.32 m/s, a = 0.4 m/s2 (D) v = 0.4 m/s, a = 0.32 m/s2
5. A small frictionless block slides with velocity 0.5 gr on the horizontal surface as shown in the
Figure. The block leaves the surface at point C. The angle in the Figure is :
−1 −1 −1
(A) cos (4/9) (B) cos (3/4) (C) cos (1/2) (D) none of the above
6. The figure shows the velocity and acceleration of a point like body at the initial moment of its
motion. The acceleration vector of the body remains constant. The minimum radius of curvature
of trajectory of the body is
(A) 2 meter (B) 4 meter (C) 8 meter (D) 16 meter.
7. A racing car moves along circular track of radius b. The car starts from rest and its speed increases
at a constant rate . Let the angle between the velocity and the acceleration be at time t. Then
(cos ) is :
b b
(A) 0 (B) t2/b (C) (D)
(b + t )
2
( b2 + 2t4 )
1
2
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 2
CIRCULAR & WPE (NSEP Questions Bank)
8. As shown in figure a body of mass 1 kg is shifted from A to D slowly on inclined planes by applying
a force parallel to incline plane, such that the block is always in contact with the plane surfaces.
Neglecting the jerk experienced at points C and B, total work done by the force is :
(A) 90 J (B) 56 J (C) 180 J (D) 0 J
9. A small block of mass m is kept on a rough inclined surface of inclination fixed in a elevator. The
elevator goes down with a uniform velocity v and the block does not slide on the wedge. The work
done by the force of friction on the block with respect to ground in time t will be:
(A) zero (B) –mgvt cos2 (C) –mgvt sin2 (D) mgvt sin2
10. A block of mass 50 kg is projected horizontally on a rough horizontal floor. The coefficient of
friction between the block and the floor is 0.1. The block strikes a light spring of stiffness
k = 100 N/m with a velocity 2m/s. The maximum compression of the spring is :
(A) 1 m (B) 2 m (C) 3 m (D) 4 m
11. A block of mass 2 kg drops vertically from a height of 0.4 m onto a spring whose force constant K
is 1960 N/m. Therefore, the maximum compression of the spring is
(A) 0.40 m (B) 0.25 m (C) 0.80 m (D) 0.1 m
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 3
CIRCULAR & WPE (NSEP Questions Bank)
12. A particle is moving in anticlockwise sense as seen from positive z-axis in a circle under the
( )
influence of a force F = x2 − y ˆi + (x + 5y − z)ˆj + (3x − 4y + z)kˆ N where x, y and z are in meter. The
circle lies in the xy plane with its centre at the origin and has radius of 2m. The work done by the
force as the particle completes one revolution is (in Joule)
(A) 4 (B) 8 (C) 2 (D) 16
13. If the force acting on a body is inversely proportional to its speed, the kinetic energy of the body
varies with time t as
(A) t0 (B) t1 (C) t2 (D) t–1
14. The resistive force on an aeroplane flying in a horizontal plane is given by Ff = kv2, where k is
constant and v is the speed of the aeroplane. When the power output from the engine is P0, the
plane flies at a speed v0. If the power output of the engine is doubled the aeroplane will fly at a
speed of
(A) 1.12 v0 (B) 1.26 v0 (C) 1.41 v0 (D) 2.82 v0
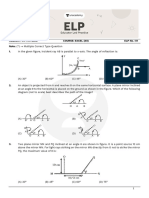
15. The potential energy (U) of a particle moving in a potential field varies with its displacement (x) as
shown below-
The variation of force F(x) acting on the particle as a function of x can be represented by
(A) Fig (i) (B) Fig (ii) (C) Fig (iii) (D) Fig (iv)
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 4
CIRCULAR & WPE (NSEP Questions Bank)
16. ( ) ( )
A force F = 3 t ˆi + 5 ˆj N acts on a body due to which its position varies as s = 2t2 ˆi − 5 ˆj . Work
done by this force in first two seconds is:
(A) 23 J (B) 32 J (C) zero (D) can't be obtained
17. In the figure shown below masses of blocks A and B are 3 kg and 6 kg respectively. The force
constants of springs S1 and S2 are 160 N/m and 40 N/m respectively. Length of the light string
connecting the blocks is 8 m. The system is released from rest with the springs at their natural
lengths. The maximum elongation of spring S1 will be :
B
A
S2
S1
(A) 0.294 m (B) 0.490 m (C) 0.588 m (D) 0.882 m
18. Force acting on a particle moving in a straight line varies with the velocity v of the particle as
K
F = , where K is a constant. The work done by this force in time t is
v
K 2Kt
(A) t (B) 2Kt (C) Kt (D)
2
v v2
19. A 10 kg small block is pulled in the vertical plane along a frictionless surface
in the form of an arc of a circle of radius 10 m. The applied force is of 200 N
as shown in the figure. If the block started from rest at A, the speed at B
would be: (g = 10 m/s2)
(A) 3 m/s (B) 10 3 m/s (C) 100 3 m/s (D) None of these
20. A car of mass m starts moving so that its velocity varies according to the law v = s , where is
a constant, and s is the distance covered. The total work performed by all the forces which are
acting on the car during the first t seconds after the beginning of motion is
(A) m4 t2/8 (B) m2 t4/8 (C) m4 t2/4 (D) m2 t4/4
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 5
CIRCULAR & WPE (NSEP Questions Bank)
SECTION-II
• This section contains TEN (10) questions.
• Each question has FOUR options. ONE OR MORE THAN ONE of these four option(s) is (are) correct
answer(s).
• For each question, choose the option(s) corresponding to (all) the correct answer(s)
• Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +4 If only (all) the correct option(s) is (are) chosen.
Partial Marks : +3 If all the four options are correct but ONLY three options are chosen.
Partial Marks : +2 If three or more options are correct but ONLY two options are chosen
and both of which are correct.
Partial Marks : +1 If two or more options are correct but ONLY one option is chosen and it
is a correct option.
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered).
Negative Marks : –2 In all other cases.
For Example: If first, third and fourth are the ONLY three correct options for a question with second
option being an incorrect option; selecting only all the three correct options will result in +4 marks.
Selecting only two of the three correct options (e.g. the first and fourth options), without selecting any
incorrect option (second option in this case), will result in +2 marks. Selecting only one of the three
correct options (either first or third or fourth option), without selecting any incorrect option (second
option in this case), will result in +1 marks. Selecting any incorrect option(s) (second option in this case),
with or without selection of any correct option(s) will result in –2 marks.
21. A car of mass m attempts to go on the circular road of radius r, which is banked for a speed of
36 km/hr. The friction coefficient between the tyre and the road is negligible.
(A) The car cannot make a turn without skidding.
(B) If the car turns at a speed less than 36 km/hr, it will slip down
mv2
(C) If the car turns at the constant speed of 36 km/hr, the force by the road on the car is equal to
r
(D) If the car turns at the correct speed of 36 km/hr, the force by the road on the car is greater
than mg as well as greater than
22. A particle is attached to an end of a rigid rod. The other end of the rod is hinged and the rod
rotates always remaining horizontal. It’s angular speed is increasing at constant rate. The mass of
the particle is 'm'. The force exerted by the rod on the particle is F , then :
(A) F mg
(B) F is constant
(C) The angle between F and horizontal plane decreases.
(D) The angle between F and the rod decreases.
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 6
CIRCULAR & WPE (NSEP Questions Bank)
23. A particle starting form rest at the highest point slides down the outside of a smooth vertical
circular track of radius 0.3 m. When it leaves the track its vertical fall is h and the linear velocity
is v. The angle made by the radius at that position of the particle with the vertical is . Now
consider the following observation : (g = 10 m/s2)
() h = 0.1 m and cos = 2/3. () h = 0.2 m and cos = 1/3 () v = 2 m/s–1. (V) After leaving the
circular track the particle will describe a parabolic path. Therefore,
(A) () and () both are correct (B) only () is incorrect
(C) only () is correct (D) (V) is correct
2
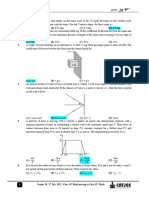
24. In the figure shown, there is no friction between B and ground and = between A and B.
3
A M
B 2M F = Mg
(A) The net work done on block A with respect to B is zero
MgS
(B) The net work done on block A with respect to ground for a displacement ‘S’ is
3
2MgS
(C) The net work done on block B with respect to ground for a displacement ‘S’ is
3
(D) The work done by friction with respect to ground on A and B is equal and opposite in sign.
25. A body of constant mass m = 1 kg moves under variable force F as shown. If at t = 0, S = 0 and
velocity of the body is 20 m/s and the force is always along direction of velocity, then choose
the incorrect options
(A) velocity of the particle will increase upto S = 2m and then decrease.
(B) the final velocity at S = 6 m is 10 m/s
(C) the final velocity at S = 6 m is 4 5 m/s
(D) the acceleration is constant up to S = 2m and then it is negative.
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 7
CIRCULAR & WPE (NSEP Questions Bank)
26. A block of mass m = 10 kg is hanging over a frictionless light fixed pulley by an inextensible light
rope. Initially the block is held at rest. The other end of the rope is now pulled by a constant force
F in the vertically downward direction. The linear momentum of the block is seen to increase by
2 kgm/s in 1s (in the first second). Therefore,
(A) the tension in the rope is F
(B) the tension in the rope is 3N
(C) the work done by the tension on the block, in first second, is = 19.8 J
(D) the work done against the force of gravity, in first second, is = 9.8 J
27. A block of mass ' m ' is attached to one end of a massless spring of spring constant ' k '. The other
end of the spring is fixed to a wall. The block can move on a horizontal rough surface. The
coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is . The block is released when the
2 mg
spring has a compression of. then choose the incorrect option(s):
k
m
(A) The maximum speed of the block is g
k
m
(B) The maximum speed of the block is g
k
(C) The block will have velocity towards left during its motion.
(D) The extension in the spring at the instant the velocity of block become zero for the first time
mg
after being released is
k
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 8
CIRCULAR & WPE (NSEP Questions Bank)
28. A force F (power of F is p = constant) is applied on block A of mass m as shown in figure, F is
parallel to the inclined plane. Then :
P
(A) The maximum speed of block A is
mg sin
P
(B) The maximum speed of block A is
mg cos
(C) The speed of block A first increases and then becomes constant
(D) Speed of block A continuously increases
29. The given plot shows the variation of U, the potential energy of interaction between two particles
with the distance separating them is r. Then which of the following statements is / are correct. :
(A) B and D are equilibrium points
(B) C is a point of stable equilibrium
(C) The force of interaction between the two particles is attractive between points C and D and
repulsive between points D and E on the curve.
(D) The force of interaction between the particles is repulsive between points E and F on the
curve.
30. A body of mass 1.0 kg moves in X-Y plane under the influence of a conservative force. Its potential
energy is given by U = 2x + 3y where (x, y) denote the coordinates of the body. The body is at rest
at (2, –4) initially. All the quantities have SI units. Therefore, the body
(A) moves along a parabolic path (B) moves with a constant acceleration
(C) never crosses the X axis (D) has a speed of 2 13 m/s at time t = 2s.
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 9
CIRCULAR & WPE (NSEP Questions Bank)
ANSWER KEY
1. (B) 2. (A) 3. (i)-(A), (ii)-(A) 4. (D) 5. (B)
6. (C) 7. (D) 8. (A) 9. (C) 10. (A)
11. (D) 12. (B) 13. (B) 14. (B) 15. (D)
16. (B) 17. (A) 18. (C) 19. (B) 20. (A)
21. (B) 22. (A,C,D) 23. (A,B,D) 24. (A,B,C,D) 25. (A,C,D)
26. (A, D) 27. (B,C,D) 28. (A,C) 29. (B,D) 30. (B,C,D)
Space for Rough Work
For more study material visit - https://unacademy.com/content/jee2024/ 10
You might also like
- IIT-JEE 2002 Screening Paper With Answer KeyDocument16 pagesIIT-JEE 2002 Screening Paper With Answer KeyNarmadha Ramesh100% (1)
- Power Distribution LossesDocument24 pagesPower Distribution LossesmuskanumeedNo ratings yet
- 03 Circular WPE QuestionsDocument7 pages03 Circular WPE Questions17swabhiNo ratings yet
- Kinematics QuizDocument5 pagesKinematics QuizShashi Shekhar Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- KM QuizDocument2 pagesKM Quiztgfkwwn2npNo ratings yet
- Two Yr CRP 224 - B-Lot - Ph-I - Mains - PhyDocument4 pagesTwo Yr CRP 224 - B-Lot - Ph-I - Mains - Phyjdhmyj2zchNo ratings yet
- DPP 1Document11 pagesDPP 1ADARSH KUMAR BEHERANo ratings yet
- NTSE Support Program: SESSION: 2019-20Document6 pagesNTSE Support Program: SESSION: 2019-20Anita SinhaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Growth Apex CT - 11 - (27-05-2024) - SCDocument6 pages11 - Growth Apex CT - 11 - (27-05-2024) - SCsangamkumar01010No ratings yet
- 1st Year Full Book Past Paper MCQS 100 With KeyDocument6 pages1st Year Full Book Past Paper MCQS 100 With KeyAbcdefNo ratings yet
- Most Selected 100 MCQs of Physics Part-1 - UnlockedDocument6 pagesMost Selected 100 MCQs of Physics Part-1 - Unlockedchmudassarimran2No ratings yet
- System of Particles and RotationDocument33 pagesSystem of Particles and RotationLet's work today For better tomorrowNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE TEST - (Vectors & KM) : Pattern-1 Part-A Single Correct Choice Type (1-6)Document3 pagesPRACTICE TEST - (Vectors & KM) : Pattern-1 Part-A Single Correct Choice Type (1-6)chaitanya goyalNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-21 12th (A4) CLASS TESTDocument3 pagesPHYSICS-21 12th (A4) CLASS TESTRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- DPP 1-13 Rotation JA Nurture LiveDocument118 pagesDPP 1-13 Rotation JA Nurture LivebqfhwdmdcyNo ratings yet
- PCCP Sample Paper PDFDocument9 pagesPCCP Sample Paper PDFtanyasharma_3010No ratings yet
- DPP - 01 _ Kinematics Of Circular MotionDocument4 pagesDPP - 01 _ Kinematics Of Circular MotionAnsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- MT Xi Physics 291020Document6 pagesMT Xi Physics 291020cutuNo ratings yet
- Allen Race Nurture Iit Jee AdvancedDocument2 pagesAllen Race Nurture Iit Jee AdvancedUma MandalNo ratings yet
- Class:XII Time: 40 Min. M.M.: 36 DPP. NO.-48: Discussion: 27-28/07/2015Document6 pagesClass:XII Time: 40 Min. M.M.: 36 DPP. NO.-48: Discussion: 27-28/07/2015RahulNo ratings yet
- W ID8 OL0 EEp 7 Ejg 08 A8 GJDocument3 pagesW ID8 OL0 EEp 7 Ejg 08 A8 GJROHIT ARYANo ratings yet
- Wa 6 Wep VCMDocument5 pagesWa 6 Wep VCMAvishkar JaiswalNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-29 12th (A1)Document3 pagesPHYSICS-29 12th (A1)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- CombinedELP 1to11studentDocument35 pagesCombinedELP 1to11studentsureshserious7226No ratings yet
- MathongoDocument40 pagesMathongosatya sandeepNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice Sheet 1-15Document24 pagesDaily Practice Sheet 1-15kraken monsterNo ratings yet
- Physics Chemistry Mathematics IITJEE TestDocument17 pagesPhysics Chemistry Mathematics IITJEE TestAbhay Kumar Nayak100% (5)
- Kinametics (Rectilinear+Motion) Exercise-5 (B) +Document2 pagesKinametics (Rectilinear+Motion) Exercise-5 (B) +Shivam RoyNo ratings yet
- Most Selected 100 MCQs of Physics Part-1-1Document6 pagesMost Selected 100 MCQs of Physics Part-1-1Amna ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Part - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 10 April - Morning Shift MathongoDocument37 pagesPart - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 10 April - Morning Shift Mathongorohit574No ratings yet
- 2023 - JEE-Main-7 - Paper (Gen 4A 4B 4C 4D 4E 6A and 6B)Document13 pages2023 - JEE-Main-7 - Paper (Gen 4A 4B 4C 4D 4E 6A and 6B)Archana SharmaNo ratings yet
- JEE MAINS PART TEST 4Document12 pagesJEE MAINS PART TEST 4Sparsh SinghNo ratings yet
- PCM-11-02 - (13th) Paper-1 Code-ADocument16 pagesPCM-11-02 - (13th) Paper-1 Code-ARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- BoSoN Sample Paper Class XIDocument11 pagesBoSoN Sample Paper Class XISKUL PARADOXNo ratings yet
- SPP-1 Physics (JEE Advanced)Document6 pagesSPP-1 Physics (JEE Advanced)anilpurnimakothariNo ratings yet
- Ae 2012 PDFDocument11 pagesAe 2012 PDFSubhash KorumilliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Circular MotionDocument4 pagesChapter 04 Circular MotionMuhammad AtirNo ratings yet
- Revision Assignment (Adv Level) - 1Document7 pagesRevision Assignment (Adv Level) - 1Gandharv BhoiteNo ratings yet
- 4S Sample Medical Selection Test Paper Answer Key (2020 21)Document16 pages4S Sample Medical Selection Test Paper Answer Key (2020 21)Prem TewariNo ratings yet
- Mains Neet Class 3Document3 pagesMains Neet Class 3Swastik DasNo ratings yet
- 4 Jeem 2023 April 08 Second Shift PaperDocument38 pages4 Jeem 2023 April 08 Second Shift PaperSURAKSHA PATELNo ratings yet
- 2025-JEE Main-6 - GEN - 1 & 2 - PaperDocument22 pages2025-JEE Main-6 - GEN - 1 & 2 - PaperNavaya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Answer Correct Type) : IIT - JEE: 2022 Xii - TW Test DATE: 19/07/20 TIME: 1 Hr. Physics MARKS: 100Document8 pagesSection-I (Single Answer Correct Type) : IIT - JEE: 2022 Xii - TW Test DATE: 19/07/20 TIME: 1 Hr. Physics MARKS: 100pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- SPP 01Document6 pagesSPP 01Ryan MittalNo ratings yet
- Part - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 8 April - Evening Shift MathongoDocument41 pagesPart - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 8 April - Evening Shift MathongoAparaNo ratings yet
- Vector PDocument3 pagesVector PAshutoshNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-11 (12th & 13th) Paper 1Document7 pagesPHYSICS-11 (12th & 13th) Paper 1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment CH 04 ADocument2 pagesAssignment CH 04 AHK AbbasiNo ratings yet
- CIRCULAR MOTION JEE PracticeDocument21 pagesCIRCULAR MOTION JEE PracticeDev PatelNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: Class: XI General InstructionsDocument8 pagesSample Paper: Class: XI General InstructionsmadhavNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Plane DPP 02 (Of Lec 05) Arjuna JEE 2024Document3 pagesMotion in A Plane DPP 02 (Of Lec 05) Arjuna JEE 2024PriyanshuNo ratings yet
- Class XI Math Moving To Class XII Math Test Paper With Detailed SolutionDocument20 pagesClass XI Math Moving To Class XII Math Test Paper With Detailed Solutionghostrider828837No ratings yet
- Grade 11-VectorsDocument5 pagesGrade 11-VectorsChetanNo ratings yet
- 11th PhysicsDocument5 pages11th PhysicsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- JEE MAIN 2020 (02.09.2020 - 2nd Shift) 1Document12 pagesJEE MAIN 2020 (02.09.2020 - 2nd Shift) 1Arjun PanditaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 1 Paper (2022) Gen. 1Document11 pagesJEE Main 1 Paper (2022) Gen. 1Halfborn GundersonNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: Level - 01Document5 pagesElectrostatics: Level - 01Om PungleNo ratings yet
- 1ST Year 150 MCQDocument13 pages1ST Year 150 MCQUsman ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- 2 L SBYkb J3 ATsabyqsw 5 ZDocument14 pages2 L SBYkb J3 ATsabyqsw 5 ZÂshútösh KumarNo ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Answer Correct Type)Document6 pagesSection-I (Single Answer Correct Type)pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Dynamic MeasurementsDocument217 pagesHandbook of Dynamic MeasurementsronfrendNo ratings yet
- Laser Ion Source With Solenoid FieldDocument6 pagesLaser Ion Source With Solenoid FieldbhumijayaNo ratings yet
- S B P G S S R L A S: Technical Paper by A. Mcgown, I. Yogarajah, K.Z. Andrawes and M.A. SaadDocument15 pagesS B P G S S R L A S: Technical Paper by A. Mcgown, I. Yogarajah, K.Z. Andrawes and M.A. SaadRaluca IoanaNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument39 pagesElectrostaticsshreyas bulbule100% (1)
- Inductance of 3 Phase LineDocument50 pagesInductance of 3 Phase LineFemi PrinceNo ratings yet
- Motion Connect 500: 6FX5002-2DC10-1AF0Document2 pagesMotion Connect 500: 6FX5002-2DC10-1AF0Khizar AltafNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Chapter 01Document42 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers Chapter 01topwarmachineNo ratings yet
- Current TransformerDocument6 pagesCurrent TransformerSwinlife WinlifeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Problems For Momentum TransferDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Problems For Momentum TransferZiyad Al Abasie0% (1)
- Questions Type Wise PDFDocument26 pagesQuestions Type Wise PDFAyaan NaveedNo ratings yet
- C-16 Diploma ElectricalDocument39 pagesC-16 Diploma ElectricalSuryavamsiNo ratings yet
- DSS41A05Document7 pagesDSS41A05petrovi482No ratings yet
- Development of An Underactuated Exoskeleton For EfDocument19 pagesDevelopment of An Underactuated Exoskeleton For EftaylanNo ratings yet
- Notes Viscosity PDFDocument8 pagesNotes Viscosity PDFManjunath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Module 6 Edited 1Document10 pagesPhysical Science Module 6 Edited 1Alfa May BuracNo ratings yet
- AP1 Simple Harmonic Motion Presenter W AnswersDocument33 pagesAP1 Simple Harmonic Motion Presenter W AnswersDamion Mcdowell100% (1)
- On Mechanical Properties of Square and Rectangular Stainless Steel Wires Tested in Torsion PDFDocument11 pagesOn Mechanical Properties of Square and Rectangular Stainless Steel Wires Tested in Torsion PDFDiana Paola FontechaNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet PDFjoseph govadaNo ratings yet
- AP125 Designing Microcontroller Systems For Electrically Noisy EnvironmentsDocument26 pagesAP125 Designing Microcontroller Systems For Electrically Noisy EnvironmentsAdam CampbellNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Highway and Railroad EnggDocument21 pagesModule 1 Highway and Railroad EnggMarlo NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram S K GoyalDocument47 pagesSingle Line Diagram S K Goyalrakeshran100% (1)
- AN296065 Allegro Hall Effect Sensor ICs PDFDocument5 pagesAN296065 Allegro Hall Effect Sensor ICs PDFPhong DoNo ratings yet
- Ncac 2012 W 005 PDFDocument18 pagesNcac 2012 W 005 PDFNingu AmrutattiNo ratings yet
- Inter Part One Physics Old PaperDocument72 pagesInter Part One Physics Old PaperMian EjazNo ratings yet
- 18.0 Inches: LF DriversDocument2 pages18.0 Inches: LF DriversRafRouf SehiliNo ratings yet
- Spherical Wave Scattering by A Rigid SphereDocument3 pagesSpherical Wave Scattering by A Rigid Spheretimosp1973No ratings yet
- Substation DesignDocument764 pagesSubstation DesignNahidi100% (5)
- Chapter 1 States of Stress and Strain at A PointDocument25 pagesChapter 1 States of Stress and Strain at A PointRyan GinNo ratings yet
- MEC521 - Chapter 2Document27 pagesMEC521 - Chapter 2Hafizudin DaudNo ratings yet