Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewssch3u7-bornhaber
sch3u7-bornhaber
Uploaded by
priyaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chemical Energetics Notes PDFDocument7 pagesChemical Energetics Notes PDFNurul Farhana50% (2)
- Suggested Answer For STPM 2013 Paper 2 (U)Document4 pagesSuggested Answer For STPM 2013 Paper 2 (U)Jin Yee Tan100% (2)
- Worksheet - Chapter 12 - Acids and BasesDocument5 pagesWorksheet - Chapter 12 - Acids and BasesKatrina EstradaNo ratings yet
- Lattive EnergyDocument44 pagesLattive EnergyClarize Soo HooNo ratings yet
- CHEM1100F23 Ch5 Notes Pt2Document26 pagesCHEM1100F23 Ch5 Notes Pt2Adeyinka OluyoleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CBCS Bonding 2018-19 PDFDocument72 pagesChapter 2 CBCS Bonding 2018-19 PDFAlbert PaulNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Thermodynamics Born-Haber Cycles Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water Entropy ChangesDocument10 pagesTopic 10 Thermodynamics Born-Haber Cycles Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water Entropy ChangesHenry SupriNo ratings yet
- 15 2+Lattice+EnthalpyDocument14 pages15 2+Lattice+EnthalpyZara BrookesNo ratings yet
- Gce Chemistry: FactfileDocument12 pagesGce Chemistry: Factfilejules blancoNo ratings yet
- Lattice Enthalpy, Ionisation Energy, Born-Haber Cycles, Hydration EnthalpyDocument8 pagesLattice Enthalpy, Ionisation Energy, Born-Haber Cycles, Hydration Enthalpyzubair0% (1)
- H - X(S) M(S) S MX H MX(S) X(S) S M: Experimental Evaluation of The Lattice EnergyDocument31 pagesH - X(S) M(S) S MX H MX(S) X(S) S M: Experimental Evaluation of The Lattice Energysepti handayaniNo ratings yet
- Lattice EnergyDocument14 pagesLattice Energyvita iftitahiyahNo ratings yet
- Lattice EnergyDocument66 pagesLattice EnergyHuiru ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Energetics I (Multiple Choice) QPDocument16 pagesEnergetics I (Multiple Choice) QPsarahNo ratings yet
- Energetics - CN - STDT7Document2 pagesEnergetics - CN - STDT7NkemziNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.1Document5 pagesUnit 4.1Tilak K CNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics NotesDocument7 pagesChemical Energetics NotesSalwa Ag Akbar100% (1)
- Topic 6Document15 pagesTopic 6tonmaai007No ratings yet
- Chem 586 C 3Document15 pagesChem 586 C 3Mohammed AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- Born-Haber Cycles: AQA Chemistry A2 Stretch and Challenge © Nelson Thornes LTD 2009 1Document2 pagesBorn-Haber Cycles: AQA Chemistry A2 Stretch and Challenge © Nelson Thornes LTD 2009 1Paul MurrayNo ratings yet
- پیوند کوالانسی 2Document3 pagesپیوند کوالانسی 2api-3706290No ratings yet
- CHE201 Ch8b Skeletal Notes SP23Document12 pagesCHE201 Ch8b Skeletal Notes SP23Reade YTNo ratings yet
- Energetics I (Multiple Choice) QPDocument15 pagesEnergetics I (Multiple Choice) QPSalmantt SalmanlohussaNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Norganic HermodynamicsDocument8 pagesExercises: Norganic HermodynamicskjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Born Haber CycleDocument15 pagesBorn Haber CyclefayNo ratings yet
- Lattice Energy I Unit 4 New SpecificationsDocument12 pagesLattice Energy I Unit 4 New SpecificationsLoh Jun XianNo ratings yet
- 8oxidation Reduction ReactionsDocument50 pages8oxidation Reduction ReactionsMohamed AlQallafNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energeticsby Mohsina FatimaDocument3 pagesChemical Energeticsby Mohsina FatimaAnwar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- As Chemistry Unit 1 DefinitionDocument7 pagesAs Chemistry Unit 1 DefinitionRaymond ChanNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes PDFDocument13 pagesEnergy Changes PDFMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 19 Born-Haber CyclesDocument14 pagesLesson 19 Born-Haber Cyclesdela2No ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics: ChemistryDocument5 pagesChemical Energetics: ChemistryArda RahmainiNo ratings yet
- Chemguide - Answers: Lattice EnthalpiesDocument3 pagesChemguide - Answers: Lattice EnthalpiesAlexander HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Thermo ChemistryDocument13 pagesThermo ChemistryGalib FidaNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Hess - S LawDocument8 pagesThermochemistry Hess - S LawsumathiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 STPMDocument5 pagesChemistry Form 6 STPMChong Yin PingNo ratings yet
- DL Assignment - Energetic I Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesDL Assignment - Energetic I Review QuestionsShahnaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- CHEM1612 Worksheet 2 - Answers To Critical Thinking QuestionsDocument4 pagesCHEM1612 Worksheet 2 - Answers To Critical Thinking QuestionsKeNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 WSDocument13 pagesChap 6 WSSaif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ch09 (Ikatan Kimia) (Compatibility Mode)Document12 pagesCh09 (Ikatan Kimia) (Compatibility Mode)IvanNo ratings yet
- Topic 15 Born Haber CyclesDocument2 pagesTopic 15 Born Haber CyclesMind NiramindNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes ChemDocument48 pagesRevision Notes ChemUmer Sayeed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Inorg 2 - Tut 1 - 2018 - MemoDocument4 pagesInorg 2 - Tut 1 - 2018 - MemoStolo SbaeNo ratings yet
- KMTK Thermo 2013 Stud (D)Document22 pagesKMTK Thermo 2013 Stud (D)kjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Lattice Enthalpy PDFDocument8 pagesLattice Enthalpy PDFLisa DentonNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergeticsDocument7 pagesChemical EnergeticsRaiyan RahmanNo ratings yet
- STPM 2019 Sem 2uDocument7 pagesSTPM 2019 Sem 2uAprillia ChanNo ratings yet
- 13 Energetics II PDFDocument11 pages13 Energetics II PDFSamson AmosNo ratings yet
- Transferred: Electrons AreDocument7 pagesTransferred: Electrons Aremonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Ch07 2 LatticeEnergyDocument9 pagesCh07 2 LatticeEnergyBRUNO RAMOS DE LIMANo ratings yet
- Answers To End of Chapter Questions: A Q M × C × B Number of Moles Ethanol Used 0.02Document4 pagesAnswers To End of Chapter Questions: A Q M × C × B Number of Moles Ethanol Used 0.02Fernando PalokaNo ratings yet
- Iconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistDocument12 pagesIconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistKingson_786No ratings yet
- Ionic Model Lecture 3Document32 pagesIonic Model Lecture 3espanholdNo ratings yet
- Born Haber Cycles: + - Latt - 1 + - Latt - 1Document5 pagesBorn Haber Cycles: + - Latt - 1 + - Latt - 1Pedro Moreno de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Periodicity HL: Ib DP ChemistryDocument61 pagesPeriodicity HL: Ib DP ChemistryLaura Estefania MoraNo ratings yet
- 7.2. Thermo 2 Born - Haber CycleDocument12 pages7.2. Thermo 2 Born - Haber CycleHayley MclearyNo ratings yet
- 1.8 Revision Guide Thermodynamics AqaDocument8 pages1.8 Revision Guide Thermodynamics AqaRabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Amal 6 Born Haber - EditDocument4 pagesAmal 6 Born Haber - EditkjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- LS2A03 F2023 IntroToResearchPeerReview Siddiqui STDocument32 pagesLS2A03 F2023 IntroToResearchPeerReview Siddiqui STpriyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Statistical PhysicsDocument6 pagesAssignment 2 Statistical PhysicspriyaNo ratings yet
- Bioknowledgy Quick Quiz On Dna Structure and Replication (7.1)Document3 pagesBioknowledgy Quick Quiz On Dna Structure and Replication (7.1)priyaNo ratings yet
- Bioknowledgy Quick Quiz On Transcription & Gene Expression (7.2)Document2 pagesBioknowledgy Quick Quiz On Transcription & Gene Expression (7.2)priyaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 EcologyDocument40 pagesCH 4 EcologypriyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Metals and NonmetalsDocument37 pagesChapter 3 Metals and NonmetalsVibi VibesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Corrosion, Inspection & ProtectionDocument2 pagesChapter 6. Corrosion, Inspection & ProtectionblackhawkNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Series-2024Document6 pagesPeriodic Table Series-2024KINGSCOMPUTERS CYBERNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Mocks Set 1Document167 pagesChemistry Mocks Set 1Citron AkhalaNo ratings yet
- G10-2nd-Q-review Sheets-Chem-Chap7, 8.1, 8.2Document8 pagesG10-2nd-Q-review Sheets-Chem-Chap7, 8.1, 8.2Karim Ahmed100% (1)
- Igcse 72 Radiation&HalflifeDocument32 pagesIgcse 72 Radiation&HalflifeHany ElGezawy50% (2)
- A Review of Rare Earth Mineral Processing TechnoloDocument17 pagesA Review of Rare Earth Mineral Processing TechnoloAlejandro Sulbaran100% (1)
- Fluorides IN Dentistry: Meghna VermaDocument20 pagesFluorides IN Dentistry: Meghna Vermanew bieeNo ratings yet
- General Concepts of The Chemistry of ChelationDocument11 pagesGeneral Concepts of The Chemistry of ChelationBatuhan ElçinNo ratings yet
- MODULE 7 General Chemistry1 Quarter3 Module7 Week2revalidated Converted 1Document23 pagesMODULE 7 General Chemistry1 Quarter3 Module7 Week2revalidated Converted 1Jolina Imbuido ValdezNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chapter 1 Paper 2Document2 pagesForm 4 Chapter 1 Paper 2FakhriahNo ratings yet
- Thermocouple Colour CodesDocument2 pagesThermocouple Colour CodesmgkvprNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 8 CURRICULUM MAP 3rd QDocument3 pagesSCIENCE 8 CURRICULUM MAP 3rd QAntonyNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts For Grade 7Document36 pagesAcids Bases and Salts For Grade 7raynjeremay100% (1)
- Atomic Structure 1Document27 pagesAtomic Structure 1Mamdooh AlqathamiNo ratings yet
- Module I Seminar Skor A Chemistry SPM 2010Document9 pagesModule I Seminar Skor A Chemistry SPM 2010Suriati Bt A RashidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure WS1Document3 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure WS1Ananthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- 11th Grade ChemistryDocument98 pages11th Grade ChemistryRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Vidya Jyothi Chem Mock TestDocument6 pagesVidya Jyothi Chem Mock TestArko SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formula Sheet Class 9: Matter in Our SurroundingDocument4 pagesChemical Formula Sheet Class 9: Matter in Our SurroundingMadan JhaNo ratings yet
- TC 5628Document16 pagesTC 5628ARINDAM SETTNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Analysis: Scrooby'S Laboratory Service CCDocument1 pageCertificate of Analysis: Scrooby'S Laboratory Service CCmusaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Moles To Grams PDFDocument6 pagesCalculating Moles To Grams PDFjaymarmandiaNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of The Electronic Properties of SolidsDocument6 pagesBand Theory of The Electronic Properties of SolidsSrinivas SaiNo ratings yet
- Element Poster Project: MY ELEMENT IS - MY POSTER Is DUE ONDocument6 pagesElement Poster Project: MY ELEMENT IS - MY POSTER Is DUE ONReluktantNo ratings yet
- Dangerous GoodsDocument1 pageDangerous GoodsSachin Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Terraflex PIS 2015Document2 pagesTerraflex PIS 2015Andrian SergheevNo ratings yet
- Ce 480 - IoxDocument22 pagesCe 480 - IoxNTEYE CHITONGENo ratings yet
- PUC II Chemistry Passing PackageDocument28 pagesPUC II Chemistry Passing PackageVaishnavi Vaishu100% (1)
sch3u7-bornhaber
sch3u7-bornhaber
Uploaded by
priya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views15 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views15 pagessch3u7-bornhaber
sch3u7-bornhaber
Uploaded by
priyaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 15
Topic 5: Energetics
Born Haber Cycles & Lattice Enthalpy
Thursday, May 16, 2013
Born-Haber Cycle
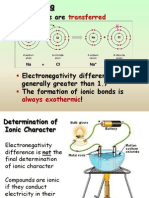
• Why are NF3 and PCl3 stable while NCl3 is
dangerously explosive?
• Born-Haber cycle provides a useful way
to account for the relative stabilities of
chemical compounds
• Relative stability of the compound is
determined by the lattice enthalpy of a
compound
Thursday, May 16, 2013
Born-Haber Cycle
• How can we determine the lattice enthalpy of
an ionic compound?
• We can break up the formation of an ionic
compound into a series of steps
• Then take all those steps and add them up so
it is really a Hess’ Law problem!
• Recall that the enthalpy of formation for an
uncombined element is therefore = 0
Thursday, May 16, 2013
Some Definitions
• The enthalpy of atomization is the enthalpy change that
occurs when one mole of gaseous atoms is formed
from the element in the standard state under standard
conditions
Example: ½ Cl2 (g) Cl (g) ΔHoat = 121 kJ mol-1
• The electron affinity is the enthalpy change that occurs
when an electron is added to an isolated atom in the
gaseous state:
O (g) + e- O- (g) ΔHo = -142 kJ mol-1
O- (g) + e- O2- (g) ΔHo = +844 kJ mol-1
• The lattice enthalpy is the enthalpy change that occurs
from the conversion of an ionic compound in the
gaseous state into its gaseous ions
LiCl (g) Li+ (g) + Cl- (g) ΔHo = +846 kJ mol-1
Thursday, May 16, 2013
Born Haber Cycle for NaCl
The formation of NaCl can be considered as a five
step process
Na (s) + 1/2 Cl2 (g) NaCl (s)
1. The vaporization of sodium metal to form the gaseous
element. Na(s) Na(g)
2. The dissociation of chlorine gas to gaseous chlorine
atoms is equal to one half of the bond energy for a Cl-Cl
covalent bond 1/2 Cl2(g) Cl(g)
3. The ionization of gaseous sodium atoms to
Na(g) Na+(g) + e-
4. The ionization of chlorine atoms. (This quantity is the
negative electron affinity for the element chlorine.)
Cl(g) + e- Cl-(g)
5. The lattice energy on the formation of sodium chloride
from the gaseous ions Na+(g) + Cl-(g) NaCl(s)
Thursday, May 16, 2013
Born Haber Cycle Diagram
The stepwise energy changes for the formation of NaCl
Thursday, May 16, 2013
Born-Haber Cycle for NaCl
The stepwise energy changes for the formation of NaCl:
The vaporization of sodium metal to form the gaseous
element.
Na (s) Na (g) ∆H°sublimation = + 109 kJ mol-1
The dissociation of chlorine gas to gaseous chlorine
atoms is equal to one half of the bond energy for a Cl-Cl
covalent bond
1/2 Cl2 (g) Cl (g) ∆H°diss = + 122 kJ mol-1
The ionization of gaseous sodium atoms to:
Na (g) Na+ (g) + e- ∆H°ionization = + 496 kJ mol-1
The ionization of chlorine atoms. (This quantity is the
negative electron affinity for the element chlorine.)
Cl (g) + e- Cl- (g) ∆H°elect.affinity = - 368 kJ mol-1
Thursday, May 16, 2013
Thursday, May 16, 2013
Try it for MgCl2
Thursday, May 16, 2013
10
Thursday, May 16, 2013
Try it!
• 1. Calculate the energy released (in kJ mol-1 ) in the reaction
K (s) + 1/2 Br2 (l) --------> KBr (s)
The energy of vaporization of potassium is +89 kJ mol-1. The first ionization enthalpy of
potassium is +419 kJ mol-1.
The sum of the dissociation energy and vaporization energy for Br2 (l) is 223 kJ mol-1,
the negative electron affinity of bromine is -324 kJ mol-1, and the lattice energy of
KBr is -688 kJ mol-1.
2. Calculate the energy released (in kJ mol-1 ) in the reaction
Na (s) + 1/2 I2 (l) --------> NaI (s)
The energy of vaporization of sodium is +109 kJ mol-1. The first ionization energy of
sodium is +496 kJ mol-1.
The sum of the dissociation energy and vaporization energy for I2 (s) is 214 kJ mol-1,
the negative electron affinity of iodine is -295 kJ mol-1, and the lattice energy of NaI
is - 704 kJ mol-1.
Thursday, May 16, 2013
Size & Charge
• How does size and charge effect the lattice
enthalpy?
12
Thursday, May 16, 2013
Which has larger lattice
enthalpy?
KCl 701 kJ mol-1, NaCl 777 kJ mol -1
K is larger
The cation remains the same, the anion gets bigge
The larger the anion, the smaller the enthalpy
MgF2 2957 kJ mol-1
NaF 902 kJ mol-1
13
Thursday, May 16, 2013
Why the difference?
14
Thursday, May 16, 2013
15
Thursday, May 16, 2013
You might also like
- Chemical Energetics Notes PDFDocument7 pagesChemical Energetics Notes PDFNurul Farhana50% (2)
- Suggested Answer For STPM 2013 Paper 2 (U)Document4 pagesSuggested Answer For STPM 2013 Paper 2 (U)Jin Yee Tan100% (2)
- Worksheet - Chapter 12 - Acids and BasesDocument5 pagesWorksheet - Chapter 12 - Acids and BasesKatrina EstradaNo ratings yet
- Lattive EnergyDocument44 pagesLattive EnergyClarize Soo HooNo ratings yet
- CHEM1100F23 Ch5 Notes Pt2Document26 pagesCHEM1100F23 Ch5 Notes Pt2Adeyinka OluyoleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CBCS Bonding 2018-19 PDFDocument72 pagesChapter 2 CBCS Bonding 2018-19 PDFAlbert PaulNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Thermodynamics Born-Haber Cycles Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water Entropy ChangesDocument10 pagesTopic 10 Thermodynamics Born-Haber Cycles Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water Entropy ChangesHenry SupriNo ratings yet
- 15 2+Lattice+EnthalpyDocument14 pages15 2+Lattice+EnthalpyZara BrookesNo ratings yet
- Gce Chemistry: FactfileDocument12 pagesGce Chemistry: Factfilejules blancoNo ratings yet
- Lattice Enthalpy, Ionisation Energy, Born-Haber Cycles, Hydration EnthalpyDocument8 pagesLattice Enthalpy, Ionisation Energy, Born-Haber Cycles, Hydration Enthalpyzubair0% (1)
- H - X(S) M(S) S MX H MX(S) X(S) S M: Experimental Evaluation of The Lattice EnergyDocument31 pagesH - X(S) M(S) S MX H MX(S) X(S) S M: Experimental Evaluation of The Lattice Energysepti handayaniNo ratings yet
- Lattice EnergyDocument14 pagesLattice Energyvita iftitahiyahNo ratings yet
- Lattice EnergyDocument66 pagesLattice EnergyHuiru ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Energetics I (Multiple Choice) QPDocument16 pagesEnergetics I (Multiple Choice) QPsarahNo ratings yet
- Energetics - CN - STDT7Document2 pagesEnergetics - CN - STDT7NkemziNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.1Document5 pagesUnit 4.1Tilak K CNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics NotesDocument7 pagesChemical Energetics NotesSalwa Ag Akbar100% (1)
- Topic 6Document15 pagesTopic 6tonmaai007No ratings yet
- Chem 586 C 3Document15 pagesChem 586 C 3Mohammed AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- Born-Haber Cycles: AQA Chemistry A2 Stretch and Challenge © Nelson Thornes LTD 2009 1Document2 pagesBorn-Haber Cycles: AQA Chemistry A2 Stretch and Challenge © Nelson Thornes LTD 2009 1Paul MurrayNo ratings yet
- پیوند کوالانسی 2Document3 pagesپیوند کوالانسی 2api-3706290No ratings yet
- CHE201 Ch8b Skeletal Notes SP23Document12 pagesCHE201 Ch8b Skeletal Notes SP23Reade YTNo ratings yet
- Energetics I (Multiple Choice) QPDocument15 pagesEnergetics I (Multiple Choice) QPSalmantt SalmanlohussaNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Norganic HermodynamicsDocument8 pagesExercises: Norganic HermodynamicskjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Born Haber CycleDocument15 pagesBorn Haber CyclefayNo ratings yet
- Lattice Energy I Unit 4 New SpecificationsDocument12 pagesLattice Energy I Unit 4 New SpecificationsLoh Jun XianNo ratings yet
- 8oxidation Reduction ReactionsDocument50 pages8oxidation Reduction ReactionsMohamed AlQallafNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energeticsby Mohsina FatimaDocument3 pagesChemical Energeticsby Mohsina FatimaAnwar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- As Chemistry Unit 1 DefinitionDocument7 pagesAs Chemistry Unit 1 DefinitionRaymond ChanNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes PDFDocument13 pagesEnergy Changes PDFMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 19 Born-Haber CyclesDocument14 pagesLesson 19 Born-Haber Cyclesdela2No ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics: ChemistryDocument5 pagesChemical Energetics: ChemistryArda RahmainiNo ratings yet
- Chemguide - Answers: Lattice EnthalpiesDocument3 pagesChemguide - Answers: Lattice EnthalpiesAlexander HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Thermo ChemistryDocument13 pagesThermo ChemistryGalib FidaNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Hess - S LawDocument8 pagesThermochemistry Hess - S LawsumathiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 STPMDocument5 pagesChemistry Form 6 STPMChong Yin PingNo ratings yet
- DL Assignment - Energetic I Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesDL Assignment - Energetic I Review QuestionsShahnaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- CHEM1612 Worksheet 2 - Answers To Critical Thinking QuestionsDocument4 pagesCHEM1612 Worksheet 2 - Answers To Critical Thinking QuestionsKeNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 WSDocument13 pagesChap 6 WSSaif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ch09 (Ikatan Kimia) (Compatibility Mode)Document12 pagesCh09 (Ikatan Kimia) (Compatibility Mode)IvanNo ratings yet
- Topic 15 Born Haber CyclesDocument2 pagesTopic 15 Born Haber CyclesMind NiramindNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes ChemDocument48 pagesRevision Notes ChemUmer Sayeed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Inorg 2 - Tut 1 - 2018 - MemoDocument4 pagesInorg 2 - Tut 1 - 2018 - MemoStolo SbaeNo ratings yet
- KMTK Thermo 2013 Stud (D)Document22 pagesKMTK Thermo 2013 Stud (D)kjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Lattice Enthalpy PDFDocument8 pagesLattice Enthalpy PDFLisa DentonNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergeticsDocument7 pagesChemical EnergeticsRaiyan RahmanNo ratings yet
- STPM 2019 Sem 2uDocument7 pagesSTPM 2019 Sem 2uAprillia ChanNo ratings yet
- 13 Energetics II PDFDocument11 pages13 Energetics II PDFSamson AmosNo ratings yet
- Transferred: Electrons AreDocument7 pagesTransferred: Electrons Aremonster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Ch07 2 LatticeEnergyDocument9 pagesCh07 2 LatticeEnergyBRUNO RAMOS DE LIMANo ratings yet
- Answers To End of Chapter Questions: A Q M × C × B Number of Moles Ethanol Used 0.02Document4 pagesAnswers To End of Chapter Questions: A Q M × C × B Number of Moles Ethanol Used 0.02Fernando PalokaNo ratings yet
- Iconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistDocument12 pagesIconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistKingson_786No ratings yet
- Ionic Model Lecture 3Document32 pagesIonic Model Lecture 3espanholdNo ratings yet
- Born Haber Cycles: + - Latt - 1 + - Latt - 1Document5 pagesBorn Haber Cycles: + - Latt - 1 + - Latt - 1Pedro Moreno de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Periodicity HL: Ib DP ChemistryDocument61 pagesPeriodicity HL: Ib DP ChemistryLaura Estefania MoraNo ratings yet
- 7.2. Thermo 2 Born - Haber CycleDocument12 pages7.2. Thermo 2 Born - Haber CycleHayley MclearyNo ratings yet
- 1.8 Revision Guide Thermodynamics AqaDocument8 pages1.8 Revision Guide Thermodynamics AqaRabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Amal 6 Born Haber - EditDocument4 pagesAmal 6 Born Haber - EditkjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- LS2A03 F2023 IntroToResearchPeerReview Siddiqui STDocument32 pagesLS2A03 F2023 IntroToResearchPeerReview Siddiqui STpriyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Statistical PhysicsDocument6 pagesAssignment 2 Statistical PhysicspriyaNo ratings yet
- Bioknowledgy Quick Quiz On Dna Structure and Replication (7.1)Document3 pagesBioknowledgy Quick Quiz On Dna Structure and Replication (7.1)priyaNo ratings yet
- Bioknowledgy Quick Quiz On Transcription & Gene Expression (7.2)Document2 pagesBioknowledgy Quick Quiz On Transcription & Gene Expression (7.2)priyaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 EcologyDocument40 pagesCH 4 EcologypriyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Metals and NonmetalsDocument37 pagesChapter 3 Metals and NonmetalsVibi VibesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Corrosion, Inspection & ProtectionDocument2 pagesChapter 6. Corrosion, Inspection & ProtectionblackhawkNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Series-2024Document6 pagesPeriodic Table Series-2024KINGSCOMPUTERS CYBERNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Mocks Set 1Document167 pagesChemistry Mocks Set 1Citron AkhalaNo ratings yet
- G10-2nd-Q-review Sheets-Chem-Chap7, 8.1, 8.2Document8 pagesG10-2nd-Q-review Sheets-Chem-Chap7, 8.1, 8.2Karim Ahmed100% (1)
- Igcse 72 Radiation&HalflifeDocument32 pagesIgcse 72 Radiation&HalflifeHany ElGezawy50% (2)
- A Review of Rare Earth Mineral Processing TechnoloDocument17 pagesA Review of Rare Earth Mineral Processing TechnoloAlejandro Sulbaran100% (1)
- Fluorides IN Dentistry: Meghna VermaDocument20 pagesFluorides IN Dentistry: Meghna Vermanew bieeNo ratings yet
- General Concepts of The Chemistry of ChelationDocument11 pagesGeneral Concepts of The Chemistry of ChelationBatuhan ElçinNo ratings yet
- MODULE 7 General Chemistry1 Quarter3 Module7 Week2revalidated Converted 1Document23 pagesMODULE 7 General Chemistry1 Quarter3 Module7 Week2revalidated Converted 1Jolina Imbuido ValdezNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chapter 1 Paper 2Document2 pagesForm 4 Chapter 1 Paper 2FakhriahNo ratings yet
- Thermocouple Colour CodesDocument2 pagesThermocouple Colour CodesmgkvprNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 8 CURRICULUM MAP 3rd QDocument3 pagesSCIENCE 8 CURRICULUM MAP 3rd QAntonyNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts For Grade 7Document36 pagesAcids Bases and Salts For Grade 7raynjeremay100% (1)
- Atomic Structure 1Document27 pagesAtomic Structure 1Mamdooh AlqathamiNo ratings yet
- Module I Seminar Skor A Chemistry SPM 2010Document9 pagesModule I Seminar Skor A Chemistry SPM 2010Suriati Bt A RashidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure WS1Document3 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure WS1Ananthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- 11th Grade ChemistryDocument98 pages11th Grade ChemistryRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Vidya Jyothi Chem Mock TestDocument6 pagesVidya Jyothi Chem Mock TestArko SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formula Sheet Class 9: Matter in Our SurroundingDocument4 pagesChemical Formula Sheet Class 9: Matter in Our SurroundingMadan JhaNo ratings yet
- TC 5628Document16 pagesTC 5628ARINDAM SETTNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Analysis: Scrooby'S Laboratory Service CCDocument1 pageCertificate of Analysis: Scrooby'S Laboratory Service CCmusaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Moles To Grams PDFDocument6 pagesCalculating Moles To Grams PDFjaymarmandiaNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of The Electronic Properties of SolidsDocument6 pagesBand Theory of The Electronic Properties of SolidsSrinivas SaiNo ratings yet
- Element Poster Project: MY ELEMENT IS - MY POSTER Is DUE ONDocument6 pagesElement Poster Project: MY ELEMENT IS - MY POSTER Is DUE ONReluktantNo ratings yet
- Dangerous GoodsDocument1 pageDangerous GoodsSachin Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Terraflex PIS 2015Document2 pagesTerraflex PIS 2015Andrian SergheevNo ratings yet
- Ce 480 - IoxDocument22 pagesCe 480 - IoxNTEYE CHITONGENo ratings yet
- PUC II Chemistry Passing PackageDocument28 pagesPUC II Chemistry Passing PackageVaishnavi Vaishu100% (1)