Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsCOVID-19 - Guidance for Paediatrics
COVID-19 - Guidance for Paediatrics
Uploaded by
Awais ArshadCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Final PPT - EincDocument75 pagesFinal PPT - EincJia Smith100% (3)
- Golden Hours Management of High Risk Newborns - 2019Document10 pagesGolden Hours Management of High Risk Newborns - 2019Suryadi LimardiNo ratings yet
- Induction and Augmentation of LaborDocument22 pagesInduction and Augmentation of LaborDagnachew kasaye100% (1)
- Anatomy of Breast, Milk Production, and Milk-EjectionDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Breast, Milk Production, and Milk-EjectionDeepak Ghimire100% (2)
- Newborn Life Support: Delivery AreaDocument5 pagesNewborn Life Support: Delivery AreaRizalMarubobSilalahiNo ratings yet
- Saudi Guideline For NeonatennnnnnnDocument11 pagesSaudi Guideline For NeonatennnnnnnAhmed ElshewiNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 - Guidance For Paediatric ServicesDocument16 pagesCOVID 19 - Guidance For Paediatric ServicesKomite Medik RSUD BangilNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Guideline: Perinatal-Neonatal Management of COVID-19Document6 pagesClinical Practice Guideline: Perinatal-Neonatal Management of COVID-19Sughosh MitraNo ratings yet
- If Ppih Covid 19 Neonatal Management PathwayDocument5 pagesIf Ppih Covid 19 Neonatal Management PathwayAbdul SamadNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Neonates of Mothers - 1301-NewDocument5 pagesGuidelines For Neonates of Mothers - 1301-NewadeNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Management of Pregnant Women and Nursing MothersDocument8 pagesGuidelines For The Management of Pregnant Women and Nursing MothersGbadeyanka O WuraolaNo ratings yet
- Labor Room Managementduring Covid19-5Document78 pagesLabor Room Managementduring Covid19-5Kalyani RathNo ratings yet
- MOH Rapid Repspons Guideline For Corona Infection in Pregnancy With Addition of Breast Feeding Protective MeasuresDocument5 pagesMOH Rapid Repspons Guideline For Corona Infection in Pregnancy With Addition of Breast Feeding Protective Measuresrazan alamriNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - NCM 119 Case Scenario - Bartolata-4ADocument6 pagesGroup 3 - NCM 119 Case Scenario - Bartolata-4AKeisha BartolataNo ratings yet
- 2019 Child Care GuidanceDocument6 pages2019 Child Care GuidanceadjcdaughtNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Covid 19 Guidance On Use of Personal Protective Equipment Ppe in Non Inpatient Health Care Settings During The Covid 19 OutbreakDocument6 pagesCoronavirus Covid 19 Guidance On Use of Personal Protective Equipment Ppe in Non Inpatient Health Care Settings During The Covid 19 OutbreakGerlan Madrid MingoNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Infection Prevention and ControlDocument70 pagesCovid19 Infection Prevention and ControlAdeuga ADEKUOYENo ratings yet
- POGS-PSMFM Interim Guidelines On Labor and Delivery For COVID EditedDocument20 pagesPOGS-PSMFM Interim Guidelines On Labor and Delivery For COVID EditedMacky YongcoNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Infection in Pregnancy: Dr. Asmita Pantha 3 Year Resident Department of OBGYN KusmsDocument61 pagesCovid-19 Infection in Pregnancy: Dr. Asmita Pantha 3 Year Resident Department of OBGYN Kusmsshrinkhala bhattaraiNo ratings yet
- IPC in HD ServicesDocument28 pagesIPC in HD ServicesseptianyganescyaNo ratings yet
- ANNEX 23a - Guidelines of COVID-19 in Obstetrics 30122021Document23 pagesANNEX 23a - Guidelines of COVID-19 in Obstetrics 30122021raul sinatoNo ratings yet
- Maternity Guidelines During The COVID-19 PandemicDocument2 pagesMaternity Guidelines During The COVID-19 PandemicBernewsAdminNo ratings yet
- IUD InsertionDocument4 pagesIUD InsertionToP Clutches PUBGMNo ratings yet
- Care For Breastfeeding Women - CDCDocument6 pagesCare For Breastfeeding Women - CDCLus FerreiraNo ratings yet
- 02a - PPE - Summary and Rationale For RecommendationsDocument2 pages02a - PPE - Summary and Rationale For RecommendationsMohammedNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding FAQsDocument7 pagesBreastfeeding FAQstam meiNo ratings yet
- Management of COVID-19 in PregnancyDocument13 pagesManagement of COVID-19 in PregnancyShazwani KKTSNo ratings yet
- C CCCCCCCCCCCC C C C CDocument20 pagesC CCCCCCCCCCCC C C C CZandra Kiamco MillezaNo ratings yet
- Care of The NewbornDocument3 pagesCare of The NewbornJohn Wendell BuñagNo ratings yet
- 4 - Healthscope COVID-19 - Swabbing For COVID-19 v3Document10 pages4 - Healthscope COVID-19 - Swabbing For COVID-19 v3Rad KingNo ratings yet
- RevisedGuidelinesforDialysisofCOVID19Patients PDFDocument8 pagesRevisedGuidelinesforDialysisofCOVID19Patients PDFAmjadali ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- 2021 08 25 Coronavirus Covid 19 Infection in Pregnancy v14Document122 pages2021 08 25 Coronavirus Covid 19 Infection in Pregnancy v14zidni fatayanNo ratings yet
- RevisedGuidelinesforDialysisofCOVID19Patients PDFDocument8 pagesRevisedGuidelinesforDialysisofCOVID19Patients PDFSaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Infection and Abortion CareDocument27 pagesCoronavirus (COVID-19) Infection and Abortion CareShaliniMargamNo ratings yet
- dm2020 0202 PDFDocument6 pagesdm2020 0202 PDFcode4saleNo ratings yet
- Nicu ReportDocument66 pagesNicu ReportEr Shah Rukh QadriNo ratings yet
- Ortigas Hospital and Healthcare Center Process Flow in The Management of Covid 19 in The NewbornDocument2 pagesOrtigas Hospital and Healthcare Center Process Flow in The Management of Covid 19 in The NewbornLucian CaelumNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Sinopharm Vaccine - 5705Document5 pagesGuidelines For Sinopharm Vaccine - 5705Wpress PressNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Moderna Vaccine - 7401Document6 pagesGuidelines For Moderna Vaccine - 7401Maria MunirNo ratings yet
- KEAMANAN PRAKTEK ERA PANDEMI, Ari UIDocument37 pagesKEAMANAN PRAKTEK ERA PANDEMI, Ari UIlidya kurniawanNo ratings yet
- 9 NicuDocument8 pages9 NicuMohamed Mahmoud saadNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 Tasks and QuestionsDocument8 pagesPhase 1 Tasks and QuestionsEmmanuel RumbaoaNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 PPE Training Presentation - Without Video - 6 MayDocument29 pagesCOVID-19 PPE Training Presentation - Without Video - 6 Maymeherul hasanNo ratings yet
- 04august2021 20210804 Guidelines For Moderna Vaccine 7404Document6 pages04august2021 20210804 Guidelines For Moderna Vaccine 7404UsmanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Covid-19Document4 pagesGuidelines For Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Covid-19Gbadeyanka O WuraolaNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 BreastfeedingDocument1 pageCOVID 19 BreastfeedingRyan SNo ratings yet
- Jurding Manangement Pregnant Women in Time of Covid 19Document29 pagesJurding Manangement Pregnant Women in Time of Covid 19Wiwit AsariNo ratings yet
- COVID 19: Infection Prevention and ControlDocument29 pagesCOVID 19: Infection Prevention and ControlJp Rizal IPCCNo ratings yet
- Maternity Care For Mothers and Babies During The COVID-19 PandemicDocument33 pagesMaternity Care For Mothers and Babies During The COVID-19 PandemicAllyssa Joy Orajay PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For AstraZeneca Vaccine - 7106Document5 pagesGuidelines For AstraZeneca Vaccine - 7106A MahNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For AstraZeneca Vaccine - 7102Document5 pagesGuidelines For AstraZeneca Vaccine - 7102Muhammad Izhar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Needs of New-Born CareDocument27 pagesNeeds of New-Born CarePruthviNo ratings yet
- Guidance For Routine Immunization Services During COVID-19: - PageDocument14 pagesGuidance For Routine Immunization Services During COVID-19: - PagePrisma CahyaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Cansino Bio Vaccine 5901Document4 pagesGuidelines For Cansino Bio Vaccine 5901Muhammad Usman parvezNo ratings yet
- PCB BF KKS 31072020 V 1Document40 pagesPCB BF KKS 31072020 V 1ew1 rNo ratings yet
- Final Camp Guidelines Operating During COVID-19Document2 pagesFinal Camp Guidelines Operating During COVID-19MarloNo ratings yet
- Family-Centered-Care-of-the-newborn-Newborn-ppts-2023 Chapter 4Document55 pagesFamily-Centered-Care-of-the-newborn-Newborn-ppts-2023 Chapter 4Ahmed - SawalhaNo ratings yet
- AstraZeneca Vaccine GuidelineDocument5 pagesAstraZeneca Vaccine GuidelinePM-II-Alpha1-001 Fatima-tuz-ZahraNo ratings yet
- Monkeypox in Pregnancy - Dr. Lingga, SP - OGDocument20 pagesMonkeypox in Pregnancy - Dr. Lingga, SP - OGIndah KaDeNo ratings yet
- G Covid 19Document19 pagesG Covid 19Nabilla Sophia SofyanNo ratings yet
- Pledge CampsDocument7 pagesPledge CampsAnonymous GF8PPILW5No ratings yet
- Real Issues for COVID-19 Vaccine Immunization & Pregnancy, Breastfeeding MothersFrom EverandReal Issues for COVID-19 Vaccine Immunization & Pregnancy, Breastfeeding MothersNo ratings yet
- Pro Choice SpeechDocument2 pagesPro Choice Speechme_el_st100% (1)
- 225-Medication Abortion Up To 70 Days of Gestation, 2020Document17 pages225-Medication Abortion Up To 70 Days of Gestation, 2020waleedaliNo ratings yet
- Nihms 1804691Document25 pagesNihms 1804691Annisa Zaskia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Letter Symposium Resource SpeakerDocument3 pagesLetter Symposium Resource SpeakerCRISTOPHER GONZAGANo ratings yet
- Pengetahuan Dan Sikap Ibu Menyusui Dengan Pemberian Asi Secara On Demand Di Rsb. Restu MakassarDocument5 pagesPengetahuan Dan Sikap Ibu Menyusui Dengan Pemberian Asi Secara On Demand Di Rsb. Restu MakassarMuhammad Halil GibranNo ratings yet
- The Nayars and The Definition o - Gough, KathleenDocument13 pagesThe Nayars and The Definition o - Gough, KathleenataripNo ratings yet
- 2022 Ob2 s1t17 Fetal Growth DisordersDocument10 pages2022 Ob2 s1t17 Fetal Growth DisordersmedicoNo ratings yet
- MCU GTD SQ - Achondo, CarlosDocument2 pagesMCU GTD SQ - Achondo, CarlosDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- 2017 JULIO - Frases de Sheila Jeffreys Sobre Hegemonia Patriarcal PDFDocument1 page2017 JULIO - Frases de Sheila Jeffreys Sobre Hegemonia Patriarcal PDFAdanMartinezNo ratings yet
- Physiology of OvulationDocument7 pagesPhysiology of OvulationAza Patullah ZaiNo ratings yet
- Developing SMART Objectives Case StudyDocument3 pagesDeveloping SMART Objectives Case StudyVarun AchrejaNo ratings yet
- Grounds of Divorce Under Christian LawDocument2 pagesGrounds of Divorce Under Christian LawNasma Abidi100% (1)
- Jules Sexy PaperDocument3 pagesJules Sexy PaperStephen FletcherNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics in Obstetrics and Gynaecology NursingDocument6 pagesDissertation Topics in Obstetrics and Gynaecology NursingCollegePaperHelpSouthBendNo ratings yet
- Moot AssignmentDocument5 pagesMoot AssignmentAkhil SainiNo ratings yet
- Star Super Surplus Floater BrochureDocument2 pagesStar Super Surplus Floater BrochureqcselvaNo ratings yet
- PRE - NATAL PERIOD by GROUP 1Document27 pagesPRE - NATAL PERIOD by GROUP 1marjorie gervacioNo ratings yet
- Family IntroDocument23 pagesFamily IntroSADIA SOHAILNo ratings yet
- Chapter 015Document9 pagesChapter 015Christopher EndicottNo ratings yet
- Endoscopy in Obstetric & GynaecologyDocument19 pagesEndoscopy in Obstetric & GynaecologyChrist PhanerooNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes of Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes Before ViabilityDocument10 pagesMaternal and Neonatal Outcomes of Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes Before ViabilitymudeyNo ratings yet
- Newborn Mothers The Ultimate Guide To Postpartum Work PDFDocument22 pagesNewborn Mothers The Ultimate Guide To Postpartum Work PDFSinziana Anghel Vizinteanu100% (1)
- Antepartum HemorrhageDocument36 pagesAntepartum HemorrhageGregorius Andrew BillyanthoNo ratings yet
- High Risk Pregnancy and Medical Decisions Case Study PDFDocument2 pagesHigh Risk Pregnancy and Medical Decisions Case Study PDFEimyel Laman Oxcho BarroNo ratings yet
- Molar PregnancyDocument1 pageMolar Pregnancymawel100% (1)
- Recent Advancements in Infertility Techniques AloneDocument111 pagesRecent Advancements in Infertility Techniques AlonesanthanalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 2 For StudentsDocument8 pagesCase Scenario 2 For StudentsPrince DetallaNo ratings yet
- The Evaluation of Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument16 pagesThe Evaluation of Abnormal Uterine BleedingEstefania gonzalez torresNo ratings yet
COVID-19 - Guidance for Paediatrics
COVID-19 - Guidance for Paediatrics
Uploaded by
Awais Arshad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views27 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views27 pagesCOVID-19 - Guidance for Paediatrics
COVID-19 - Guidance for Paediatrics
Uploaded by
Awais ArshadCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 27
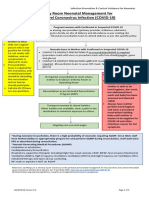
COVID-19 - Guidance for
Newborn infants
AFAF KORRAA
afaf korraa 2020 1
Clinical presentation
• At present, expert opinion is that the fetus is
unlikely to be exposed during pregnancy.
• Only one case of possible vertical transmission
caused by intrauterine infection has been
identified.
afaf korraa 2020 2
Transmission of the virus is therefore most
likely to occur post birth
• We are strongly encouraged to conduct a
risk/benefit discussion with families to
individualise care in babies that may be more
susceptible to COVID-19 infection.
afaf korraa 2020 3
Antenatal
• Mode of birth should be individualized based
on obstetric indications and the woman’s
preferences.
• WHO recommends that caesarean section
should ideally be undertaken only when
medically justified
• Steroids should be given to mothers
anticipating preterm delivery where
indicated and urgent delivery should not be
delayedfor their administration (as normal
practice).
• MgSO4 should be given for neuroprotection of
infants < 30 weeks’ gestation as per current
guidance
afaf korraa 2020 4
Antenatal
• All women with confirmed or
suspected COVID-19 should have
continuous cardiotocography
monitoring in labour.
• The appropriate Personal Protective
Equipment determined locally must
be worn by any person entering the
room.
• Only essential staff should be
present in the delivery
room/theatre.
RCPCH 2020
afaf korraa 2020 5
MANAGEMENT AT THE
DELIVERY ROOM
• Delivery shall take place in a dedicated isolation room .
• All Infant Resuscitation/ Assessment will occur in the
location where the infant is born – AVOID TRANSFER
• Resuscitation will be carried out as per NRP protocol.
• Clinical staff should use Droplet and Contact Precautions.
• N95, and eye proteciton goggle is needed when
performing newborn resuscitation that can generate
aerosols:
– bag-mask ventilation, intubation, suctioning, oxygen at a flow >2
LPM/kg, continuous positive airway pressure and/or positive
pressure ventilation.
afaf korraa 2020 6
MANAGEMENT AT THE
DELIVERY ROOM
• Once baby is stable ,should be
bathed by water and soap after
birth before transfere to NICU.
• Delayed cord clamping is not
recommended
• Queensland 2020
afaf korraa 2020 7
• Mother –infant contact is not ADVISABLE
• In preterm baby, standard thermoregulatory
measures including the use of a plastic bag.
AAP 2020
afaf korraa 2020 8
MANAGEMENT POST DELIVERY
1- Assessment
High index of suspicion for signs of sepsis/unwell baby
1-Both stable and unstable infants should be moved immediately after
resuscitation to a dedicated Isolation Room in the NICU.
2- Babies born to suspected/confirmed mothers with COVID-19 should have a
throat or nasopharyngeal pharyngeal swab for COVID-19 PCR at 12/ or 24
Hr of age. and repeat at around 48 hours by special procedure (*)
AAP 2020
afaf korraa 2020 9
Rooming-in for mothers and well
newborns
• Temporary separation minimizes the risk of postnatal
infant infection from maternal respiratory secretions. If
possible, admit the infant to an area separate from
unaffected infants, and wear gowns, gloves, eye
protection goggles and standard procedural masks for
newborn care.
• If the center cannot place the infant in a separate area
— or the mother chooses rooming-in despite
recommendations
• — ensure the infant is at least 6 feet from the mother.
A curtain or an isolette can help facilitate separation
AAP2020
afaf korraa 2020 10
Feeding
Mother should be assisted to initiate breast milk feeding
OR / expression after delivery if her condition allows.
This should be done after proper hand hygiene and while
wearing a face mask.
AAP 2020
afaf korraa 2020 11
Well near-term or term rooming with
their mothers
afaf korraa 2020 12
Mother should:
• wear a long-sleeved gown and surgical mask
• Clean her hands properly and often with soap
and water or alcohol rub - before and after
interacting with your baby.
afaf korraa 2020 13
Neonatal Nursery
• COVID-19 positive mother alone (i.e. no other
neonatal criteria), is not itself an indication for
admission to a neonatal nursery
• Perform clinical assessment after birth as per
usual protocols
• Assess if required care can safely be provided
during co-location with mother.
afaf korraa 2020 14
In-hospital neonatal transport
• Guidance is available on safe transfers
between departments, but neonates should
be transferred in a closed incubator.
• Where possible, all procedures and
investigations should be carried out in the
single room with a minimal number of staff
present.
afaf korraa 2020 15
In-hospital neonatal transport
• There Must be a pathways for transport to the
post-partum wards and the NICU if an infant born
to a COVID-positive mother is symptomatic.
• An infant on respiratory support should be
transported to the NICU using a designated
route in a closed isolette to minimize the
possibility of unfiltered expiratory gases exposing
anyone not wearing airborne precautions.
afaf korraa 2020 16
Outborn transport of infant born to
COVID-positive mother
• There is currently no data to guide the
practice of outborn transport of an infant born
to a COVID-positive mother.
• In centers where staff who perform aerosol
generating medical procedures (AGMP) use
N95 respirators regardless of time after birth,
to be consistent, all transport team members
should have access to the same precautions
afaf korraa 2020 17
NICU
• Infants requiring neonatal intensive care ideally should be
admitted to a single-patient room with the potential for
negative room pressure or other air filtration system.
• If unavailable, or if the center must cohort multiple COVID-
exposed infants, there should be at least 6 feet between
infants.
• Consider ways to reduce unnecessary investigations
Intubation/LISA are particularly high risk and must involve
use of appropriate PPE, even in an emergency.
afaf korraa 2020 18
NICU
• In-line suction with endotracheal tubes should
be used if possible.
• Where possible use of a video-laryngoscope
should be considered for intubation (if
available), and the baby kept within the
incubator.
• AAP 2020
afaf korraa 2020 19
NICU
• CPAP and high flow therapies are associated
with significant aerolisation and must
therefore be also be considered high risk.
afaf korraa 2020 20
Testing and discharge
Infants who cannot be tested should be treated
as if they are positive for the virus for the 14-
day observation period.
Infants Positive test results:
• If an infant tests positive for COVID-19 but
does not display symptoms, plan for frequent
outpatient follow-up (phone, telemedicine or
in-office) through 14 days after birth.
• Follow precautions (including stools) to
prevent household spread from infant to
caregivers
afaf korraa 2020 21
Testing and discharge
Negative test results:
• Discharge the infant, ideally, to the care of a designated healthy
caregiver.
• The mother should maintain a 6-foot distance when possible and
use a mask and hand hygiene when directly caring for the infant
until either a) she meets the criteria for non-infectivity ***.
***.
(a) she has been afebrile for 72 hours without use of antipyretics, and
(b) at least 7 days have passed since her symptoms first appeared;
OR she has negative results of a SARS-CoV-2 test from at least two
consecutive specimens collected ≥24 hours apart
afaf korraa 2020 22
Visit Protocol if the baby is in
the NICU?
• Mothers with COVID-19 should not visit infants requiring
neonatal intensive care until she met the criteria of non-
infectivity***
• COVID-19 positive parents should not be able to visit their
baby on the NNU.
• No other visitors (including siblings) should be allowed to
visit infants in NNUs (all areas), except under exceptional
circumstances, to be discussed with local infection control.
afaf korraa 2020 23
Parents and visitors
• COVID-19 positive parents should not be able to visit their
baby on the NNU.
• Parents who have been screened for COVID-19, for
whatever reason, should not be permitted to visit their
baby until they have been confirmed negative .
• No other visitors (including siblings) should be allowed to
visit infants in NNUs (all areas), except under exceptional
circumstances, to be discussed with local infection control.
• Visits from other NHS staff and personnel to the NNU
should be kept to a minimum – consider opportunities for
remote meetings.
• Units should seek to mitigate loss of family contact with
video techniques
afaf korraa 2020 24
afaf korraa 2020 25
afaf korraa 2020 26
Thank you
afaf korraa 2020 27
You might also like
- Final PPT - EincDocument75 pagesFinal PPT - EincJia Smith100% (3)
- Golden Hours Management of High Risk Newborns - 2019Document10 pagesGolden Hours Management of High Risk Newborns - 2019Suryadi LimardiNo ratings yet
- Induction and Augmentation of LaborDocument22 pagesInduction and Augmentation of LaborDagnachew kasaye100% (1)
- Anatomy of Breast, Milk Production, and Milk-EjectionDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Breast, Milk Production, and Milk-EjectionDeepak Ghimire100% (2)
- Newborn Life Support: Delivery AreaDocument5 pagesNewborn Life Support: Delivery AreaRizalMarubobSilalahiNo ratings yet
- Saudi Guideline For NeonatennnnnnnDocument11 pagesSaudi Guideline For NeonatennnnnnnAhmed ElshewiNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 - Guidance For Paediatric ServicesDocument16 pagesCOVID 19 - Guidance For Paediatric ServicesKomite Medik RSUD BangilNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Guideline: Perinatal-Neonatal Management of COVID-19Document6 pagesClinical Practice Guideline: Perinatal-Neonatal Management of COVID-19Sughosh MitraNo ratings yet
- If Ppih Covid 19 Neonatal Management PathwayDocument5 pagesIf Ppih Covid 19 Neonatal Management PathwayAbdul SamadNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Neonates of Mothers - 1301-NewDocument5 pagesGuidelines For Neonates of Mothers - 1301-NewadeNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Management of Pregnant Women and Nursing MothersDocument8 pagesGuidelines For The Management of Pregnant Women and Nursing MothersGbadeyanka O WuraolaNo ratings yet
- Labor Room Managementduring Covid19-5Document78 pagesLabor Room Managementduring Covid19-5Kalyani RathNo ratings yet
- MOH Rapid Repspons Guideline For Corona Infection in Pregnancy With Addition of Breast Feeding Protective MeasuresDocument5 pagesMOH Rapid Repspons Guideline For Corona Infection in Pregnancy With Addition of Breast Feeding Protective Measuresrazan alamriNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - NCM 119 Case Scenario - Bartolata-4ADocument6 pagesGroup 3 - NCM 119 Case Scenario - Bartolata-4AKeisha BartolataNo ratings yet
- 2019 Child Care GuidanceDocument6 pages2019 Child Care GuidanceadjcdaughtNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Covid 19 Guidance On Use of Personal Protective Equipment Ppe in Non Inpatient Health Care Settings During The Covid 19 OutbreakDocument6 pagesCoronavirus Covid 19 Guidance On Use of Personal Protective Equipment Ppe in Non Inpatient Health Care Settings During The Covid 19 OutbreakGerlan Madrid MingoNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Infection Prevention and ControlDocument70 pagesCovid19 Infection Prevention and ControlAdeuga ADEKUOYENo ratings yet
- POGS-PSMFM Interim Guidelines On Labor and Delivery For COVID EditedDocument20 pagesPOGS-PSMFM Interim Guidelines On Labor and Delivery For COVID EditedMacky YongcoNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Infection in Pregnancy: Dr. Asmita Pantha 3 Year Resident Department of OBGYN KusmsDocument61 pagesCovid-19 Infection in Pregnancy: Dr. Asmita Pantha 3 Year Resident Department of OBGYN Kusmsshrinkhala bhattaraiNo ratings yet
- IPC in HD ServicesDocument28 pagesIPC in HD ServicesseptianyganescyaNo ratings yet
- ANNEX 23a - Guidelines of COVID-19 in Obstetrics 30122021Document23 pagesANNEX 23a - Guidelines of COVID-19 in Obstetrics 30122021raul sinatoNo ratings yet
- Maternity Guidelines During The COVID-19 PandemicDocument2 pagesMaternity Guidelines During The COVID-19 PandemicBernewsAdminNo ratings yet
- IUD InsertionDocument4 pagesIUD InsertionToP Clutches PUBGMNo ratings yet
- Care For Breastfeeding Women - CDCDocument6 pagesCare For Breastfeeding Women - CDCLus FerreiraNo ratings yet
- 02a - PPE - Summary and Rationale For RecommendationsDocument2 pages02a - PPE - Summary and Rationale For RecommendationsMohammedNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding FAQsDocument7 pagesBreastfeeding FAQstam meiNo ratings yet
- Management of COVID-19 in PregnancyDocument13 pagesManagement of COVID-19 in PregnancyShazwani KKTSNo ratings yet
- C CCCCCCCCCCCC C C C CDocument20 pagesC CCCCCCCCCCCC C C C CZandra Kiamco MillezaNo ratings yet
- Care of The NewbornDocument3 pagesCare of The NewbornJohn Wendell BuñagNo ratings yet
- 4 - Healthscope COVID-19 - Swabbing For COVID-19 v3Document10 pages4 - Healthscope COVID-19 - Swabbing For COVID-19 v3Rad KingNo ratings yet
- RevisedGuidelinesforDialysisofCOVID19Patients PDFDocument8 pagesRevisedGuidelinesforDialysisofCOVID19Patients PDFAmjadali ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- 2021 08 25 Coronavirus Covid 19 Infection in Pregnancy v14Document122 pages2021 08 25 Coronavirus Covid 19 Infection in Pregnancy v14zidni fatayanNo ratings yet
- RevisedGuidelinesforDialysisofCOVID19Patients PDFDocument8 pagesRevisedGuidelinesforDialysisofCOVID19Patients PDFSaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Infection and Abortion CareDocument27 pagesCoronavirus (COVID-19) Infection and Abortion CareShaliniMargamNo ratings yet
- dm2020 0202 PDFDocument6 pagesdm2020 0202 PDFcode4saleNo ratings yet
- Nicu ReportDocument66 pagesNicu ReportEr Shah Rukh QadriNo ratings yet
- Ortigas Hospital and Healthcare Center Process Flow in The Management of Covid 19 in The NewbornDocument2 pagesOrtigas Hospital and Healthcare Center Process Flow in The Management of Covid 19 in The NewbornLucian CaelumNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Sinopharm Vaccine - 5705Document5 pagesGuidelines For Sinopharm Vaccine - 5705Wpress PressNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Moderna Vaccine - 7401Document6 pagesGuidelines For Moderna Vaccine - 7401Maria MunirNo ratings yet
- KEAMANAN PRAKTEK ERA PANDEMI, Ari UIDocument37 pagesKEAMANAN PRAKTEK ERA PANDEMI, Ari UIlidya kurniawanNo ratings yet
- 9 NicuDocument8 pages9 NicuMohamed Mahmoud saadNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 Tasks and QuestionsDocument8 pagesPhase 1 Tasks and QuestionsEmmanuel RumbaoaNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 PPE Training Presentation - Without Video - 6 MayDocument29 pagesCOVID-19 PPE Training Presentation - Without Video - 6 Maymeherul hasanNo ratings yet
- 04august2021 20210804 Guidelines For Moderna Vaccine 7404Document6 pages04august2021 20210804 Guidelines For Moderna Vaccine 7404UsmanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Covid-19Document4 pagesGuidelines For Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Covid-19Gbadeyanka O WuraolaNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 BreastfeedingDocument1 pageCOVID 19 BreastfeedingRyan SNo ratings yet
- Jurding Manangement Pregnant Women in Time of Covid 19Document29 pagesJurding Manangement Pregnant Women in Time of Covid 19Wiwit AsariNo ratings yet
- COVID 19: Infection Prevention and ControlDocument29 pagesCOVID 19: Infection Prevention and ControlJp Rizal IPCCNo ratings yet
- Maternity Care For Mothers and Babies During The COVID-19 PandemicDocument33 pagesMaternity Care For Mothers and Babies During The COVID-19 PandemicAllyssa Joy Orajay PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For AstraZeneca Vaccine - 7106Document5 pagesGuidelines For AstraZeneca Vaccine - 7106A MahNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For AstraZeneca Vaccine - 7102Document5 pagesGuidelines For AstraZeneca Vaccine - 7102Muhammad Izhar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Needs of New-Born CareDocument27 pagesNeeds of New-Born CarePruthviNo ratings yet
- Guidance For Routine Immunization Services During COVID-19: - PageDocument14 pagesGuidance For Routine Immunization Services During COVID-19: - PagePrisma CahyaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Cansino Bio Vaccine 5901Document4 pagesGuidelines For Cansino Bio Vaccine 5901Muhammad Usman parvezNo ratings yet
- PCB BF KKS 31072020 V 1Document40 pagesPCB BF KKS 31072020 V 1ew1 rNo ratings yet
- Final Camp Guidelines Operating During COVID-19Document2 pagesFinal Camp Guidelines Operating During COVID-19MarloNo ratings yet
- Family-Centered-Care-of-the-newborn-Newborn-ppts-2023 Chapter 4Document55 pagesFamily-Centered-Care-of-the-newborn-Newborn-ppts-2023 Chapter 4Ahmed - SawalhaNo ratings yet
- AstraZeneca Vaccine GuidelineDocument5 pagesAstraZeneca Vaccine GuidelinePM-II-Alpha1-001 Fatima-tuz-ZahraNo ratings yet
- Monkeypox in Pregnancy - Dr. Lingga, SP - OGDocument20 pagesMonkeypox in Pregnancy - Dr. Lingga, SP - OGIndah KaDeNo ratings yet
- G Covid 19Document19 pagesG Covid 19Nabilla Sophia SofyanNo ratings yet
- Pledge CampsDocument7 pagesPledge CampsAnonymous GF8PPILW5No ratings yet
- Real Issues for COVID-19 Vaccine Immunization & Pregnancy, Breastfeeding MothersFrom EverandReal Issues for COVID-19 Vaccine Immunization & Pregnancy, Breastfeeding MothersNo ratings yet
- Pro Choice SpeechDocument2 pagesPro Choice Speechme_el_st100% (1)
- 225-Medication Abortion Up To 70 Days of Gestation, 2020Document17 pages225-Medication Abortion Up To 70 Days of Gestation, 2020waleedaliNo ratings yet
- Nihms 1804691Document25 pagesNihms 1804691Annisa Zaskia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Letter Symposium Resource SpeakerDocument3 pagesLetter Symposium Resource SpeakerCRISTOPHER GONZAGANo ratings yet
- Pengetahuan Dan Sikap Ibu Menyusui Dengan Pemberian Asi Secara On Demand Di Rsb. Restu MakassarDocument5 pagesPengetahuan Dan Sikap Ibu Menyusui Dengan Pemberian Asi Secara On Demand Di Rsb. Restu MakassarMuhammad Halil GibranNo ratings yet
- The Nayars and The Definition o - Gough, KathleenDocument13 pagesThe Nayars and The Definition o - Gough, KathleenataripNo ratings yet
- 2022 Ob2 s1t17 Fetal Growth DisordersDocument10 pages2022 Ob2 s1t17 Fetal Growth DisordersmedicoNo ratings yet
- MCU GTD SQ - Achondo, CarlosDocument2 pagesMCU GTD SQ - Achondo, CarlosDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- 2017 JULIO - Frases de Sheila Jeffreys Sobre Hegemonia Patriarcal PDFDocument1 page2017 JULIO - Frases de Sheila Jeffreys Sobre Hegemonia Patriarcal PDFAdanMartinezNo ratings yet
- Physiology of OvulationDocument7 pagesPhysiology of OvulationAza Patullah ZaiNo ratings yet
- Developing SMART Objectives Case StudyDocument3 pagesDeveloping SMART Objectives Case StudyVarun AchrejaNo ratings yet
- Grounds of Divorce Under Christian LawDocument2 pagesGrounds of Divorce Under Christian LawNasma Abidi100% (1)
- Jules Sexy PaperDocument3 pagesJules Sexy PaperStephen FletcherNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics in Obstetrics and Gynaecology NursingDocument6 pagesDissertation Topics in Obstetrics and Gynaecology NursingCollegePaperHelpSouthBendNo ratings yet
- Moot AssignmentDocument5 pagesMoot AssignmentAkhil SainiNo ratings yet
- Star Super Surplus Floater BrochureDocument2 pagesStar Super Surplus Floater BrochureqcselvaNo ratings yet
- PRE - NATAL PERIOD by GROUP 1Document27 pagesPRE - NATAL PERIOD by GROUP 1marjorie gervacioNo ratings yet
- Family IntroDocument23 pagesFamily IntroSADIA SOHAILNo ratings yet
- Chapter 015Document9 pagesChapter 015Christopher EndicottNo ratings yet
- Endoscopy in Obstetric & GynaecologyDocument19 pagesEndoscopy in Obstetric & GynaecologyChrist PhanerooNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes of Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes Before ViabilityDocument10 pagesMaternal and Neonatal Outcomes of Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes Before ViabilitymudeyNo ratings yet
- Newborn Mothers The Ultimate Guide To Postpartum Work PDFDocument22 pagesNewborn Mothers The Ultimate Guide To Postpartum Work PDFSinziana Anghel Vizinteanu100% (1)
- Antepartum HemorrhageDocument36 pagesAntepartum HemorrhageGregorius Andrew BillyanthoNo ratings yet
- High Risk Pregnancy and Medical Decisions Case Study PDFDocument2 pagesHigh Risk Pregnancy and Medical Decisions Case Study PDFEimyel Laman Oxcho BarroNo ratings yet
- Molar PregnancyDocument1 pageMolar Pregnancymawel100% (1)
- Recent Advancements in Infertility Techniques AloneDocument111 pagesRecent Advancements in Infertility Techniques AlonesanthanalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 2 For StudentsDocument8 pagesCase Scenario 2 For StudentsPrince DetallaNo ratings yet
- The Evaluation of Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument16 pagesThe Evaluation of Abnormal Uterine BleedingEstefania gonzalez torresNo ratings yet