Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Central DOGMA of Molecular Biology
Central DOGMA of Molecular Biology
Uploaded by
Bea SimonCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Nucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidDocument60 pagesNucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidWillar Deanson Navarro100% (1)
- CRISPR-Cas Extraordinary Editing PostersDocument1 pageCRISPR-Cas Extraordinary Editing Postersk100% (1)
- Chapter 9 (Protein Synthesis)Document15 pagesChapter 9 (Protein Synthesis)dellavajames192000No ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Nucleic Acid and Synthesis ProteinDocument32 pagesChapter 6. Nucleic Acid and Synthesis ProteinratuadhwaNo ratings yet
- Discussion Questions Exam 4Document3 pagesDiscussion Questions Exam 4Subham BhandariNo ratings yet
- (SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and PhotosynthesisDocument2 pages(SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and Photosynthesisitz.jdv1694No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Genetic CodeDocument2 pagesNucleic Acid: Genetic CodeAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication, Protein Synthesis, and Gene RegulationDocument15 pagesDNA Replication, Protein Synthesis, and Gene RegulationKarl LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Genetic ControlDocument53 pagesChapter 3 Genetic ControlCor GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry FinalsDocument11 pagesBiochemistry FinalsKc CalderonNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument35 pagesProtein SynthesisDaryl GumacalNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Functions and Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument12 pagesNucleic Acid Functions and Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyJennifer MalunaoNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis (1)Document1 pageProtein-Synthesis (1)Juan Carlo SamsonNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument28 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologysannsannNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody DNA Ebook Oct2021Document14 pagesVisibleBody DNA Ebook Oct2021Anjarika TripathyNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid SynthesisDocument9 pagesNucleic Acid SynthesisrosalindaNo ratings yet
- Biochem ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiochem ReviewerKathleenNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTSDocument3 pagesHANDOUTScareeseta bongcawilNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Biotech 2Document3 pagesQuarter 3 Biotech 2Hezekiah GatesNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument35 pagesDNA Replication and Protein Synthesisryangela545No ratings yet
- BIOTECHNOLOGYDocument4 pagesBIOTECHNOLOGYheyyouNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Study MaterialDocument58 pagesMolecular Biology Study MaterialchitraNo ratings yet
- 00a Ch. 8 VocabDocument7 pages00a Ch. 8 VocabaubreymertNo ratings yet
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocument73 pagesDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five GeneticsDocument28 pagesChapter Five GeneticsYahya AbdiwahabNo ratings yet
- Heredity Inheritance and Variations PDFDocument56 pagesHeredity Inheritance and Variations PDFNoean LargoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument33 pagesLesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologySherwin YenogacioNo ratings yet
- BMD-3201 - Trans 2.2 - Cells and Tissue ContinuationDocument15 pagesBMD-3201 - Trans 2.2 - Cells and Tissue ContinuationOwen RoldanNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument5 pagesBio ReviewerFaye Lianne MaderoNo ratings yet
- Part 3Document18 pagesPart 3Ultima PhaseNo ratings yet
- Self Study Assignment On Marker Enzymes, Semiautonomous - PPTX 1740512Document20 pagesSelf Study Assignment On Marker Enzymes, Semiautonomous - PPTX 1740512aswinNo ratings yet
- HEREDITYDocument23 pagesHEREDITYvivas.kznne.9No ratings yet
- Protein Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesProtein Structure and FunctionCindy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules IIDocument20 pagesBiomolecules IIMark Vincent Rei VillacruzNo ratings yet
- Week 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Unit IV and VDocument60 pagesMolecular Biology Unit IV and VchitraNo ratings yet
- The Replication of DNA in ProkaryotesDocument6 pagesThe Replication of DNA in ProkaryotesAditya KukretiNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument41 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular Biologyanmbeltran31No ratings yet
- Assignment # 8 Genes & Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pagesAssignment # 8 Genes & Nucleic Acidskyle james duclanNo ratings yet
- 2021 Protein-Synthesis-And-Genetic-CodeDocument5 pages2021 Protein-Synthesis-And-Genetic-CodeLucila OriveNo ratings yet
- 5.2 - DNA Replication During The S PhaseDocument23 pages5.2 - DNA Replication During The S PhaseAna JuatasNo ratings yet
- Asam Nukleat Dan Protein With SoundDocument18 pagesAsam Nukleat Dan Protein With SoundFika Nurul HafidzohNo ratings yet
- Heredity Protein SynthesisDocument23 pagesHeredity Protein SynthesispaulangelomicoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Genetic Control of Protein Synthesis, Cell Function, and Cell ReproductionDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 3: Genetic Control of Protein Synthesis, Cell Function, and Cell ReproductionMan DejeloNo ratings yet
- Biotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 5 Role of DNA RNA and Protein in The Transmission of Hereditary Traits 3Document14 pagesBiotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 5 Role of DNA RNA and Protein in The Transmission of Hereditary Traits 3Aileen Ocampo100% (1)
- 2.3. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pages2.3. Nucleotides and Nucleic Acidsstu.suman-iftikharNo ratings yet
- Activity 09Document2 pagesActivity 09Shella Mie JamisonNo ratings yet
- Week 4 NotesDocument13 pagesWeek 4 NotesGHEIST INC.No ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument88 pagesNucleic AcidJoyce Jimenez100% (1)
- Bnbi Oral PresentationDocument17 pagesBnbi Oral PresentationAshria Sonali PrakashNo ratings yet
- Nuceic Acid ProjectDocument2 pagesNuceic Acid ProjectCaryl Alvarado SilangNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNucleic AcidsAntonette SolaresNo ratings yet
- Chapt 7 DNA Replication NotesDocument8 pagesChapt 7 DNA Replication Notesmalenya1100% (1)
- Ensayo-Ácidos Nucléiocs.Document18 pagesEnsayo-Ácidos Nucléiocs.Jampier BritoNo ratings yet
- Codon ChartDocument3 pagesCodon ChartMymy SalgadoNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDocument12 pagesDNA Replication in ProkaryotesSumit MandalNo ratings yet
- THE Geneticists: Grade 11 St. John BoscoDocument24 pagesTHE Geneticists: Grade 11 St. John Boscojason balmasNo ratings yet
- 1.central DogmaDocument2 pages1.central DogmaShantel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- U5 Study GuideDocument6 pagesU5 Study GuideJuan CastellanosNo ratings yet
- 13.5 DNA Structure and Protein Synthesis (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsDocument55 pages13.5 DNA Structure and Protein Synthesis (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 6 Common Factors Contributed To Pathogenic Mechanism of Repeat Expansion DiseasesDocument3 pages6 Common Factors Contributed To Pathogenic Mechanism of Repeat Expansion DiseasesGia HoàngNo ratings yet
- Aeromonas Salmonicida Aeromonas Bestiarum: Phenotypic, Genotypic, and Phylogenetic Discrepancies To Differentiate FromDocument11 pagesAeromonas Salmonicida Aeromonas Bestiarum: Phenotypic, Genotypic, and Phylogenetic Discrepancies To Differentiate FromIon MacreaNo ratings yet
- DNA RepilicationDocument57 pagesDNA RepilicationJeevikaGoyalNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Genetic EngineeringDocument11 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Genetic EngineeringHazel AbitriaNo ratings yet
- Hi Scribe T7 ARCAm RNAmanual E2060Document11 pagesHi Scribe T7 ARCAm RNAmanual E2060starkonly7No ratings yet
- tRNA-derived Small RNAs Target Transposable Element TranscriptsDocument11 pagestRNA-derived Small RNAs Target Transposable Element TranscriptsMan Ba SotzNo ratings yet
- Purines, Pyrimidine MetabolismDocument22 pagesPurines, Pyrimidine Metabolism202210034No ratings yet
- BasicsDocument18 pagesBasicsBiraj KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Replication, Transcription, Translation, Mutation HWDocument20 pagesReplication, Transcription, Translation, Mutation HWtahamidNo ratings yet
- Linkers and AdaptersDocument11 pagesLinkers and AdaptersYogesh Pawar0% (1)
- Midi-And Mini-Primer Sets For Mtdna Control Region Sequence Analysis From Highly Degraded Forensic SamplesDocument1 pageMidi-And Mini-Primer Sets For Mtdna Control Region Sequence Analysis From Highly Degraded Forensic Samplesoday_ada76No ratings yet
- Metabolizam SeceraDocument52 pagesMetabolizam SeceraAnel RedzepiNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument35 pagesDNA and RNAalchristian tomatomNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDocument24 pagesDNA Replication in ProkaryotesAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- RNAProtein Synthesis SEDocument7 pagesRNAProtein Synthesis SEAmbrielle WhiteNo ratings yet
- Genetic Information and Protein SynthesisDocument22 pagesGenetic Information and Protein Synthesisjason balmasNo ratings yet
- Dna Transcription NotesDocument3 pagesDna Transcription NotesviennaNo ratings yet
- Hair PresentationDocument7 pagesHair PresentationxMiracleNo ratings yet
- 12 Fire Letters - 1 DNA Strand Template (1 Fire Letter Sequence 144 Vector Codes)Document1 page12 Fire Letters - 1 DNA Strand Template (1 Fire Letter Sequence 144 Vector Codes)RobertNo ratings yet
- Equipe1 - A Tale of Three Next Generation Sequencing Platforms - Comparison of Ion Torrent, Pacific Biosciences and Illumina MiSeq SequencersDocument13 pagesEquipe1 - A Tale of Three Next Generation Sequencing Platforms - Comparison of Ion Torrent, Pacific Biosciences and Illumina MiSeq SequencersFagnerOliveiraNo ratings yet
- En QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR HandbookDocument32 pagesEn QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR Handbooknaini21No ratings yet
- Real Time PCR Handbook PDFDocument73 pagesReal Time PCR Handbook PDFRodney SalazarNo ratings yet
- Cloning MethodsDocument24 pagesCloning MethodsRam Nivas Ahirwar100% (7)
- BioCentralDogmaWorksheet 1Document3 pagesBioCentralDogmaWorksheet 1jaelajeanine326No ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance PDFDocument19 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance PDFBiju Mylachal94% (16)
- MA 7.2 DNA Replication Lab Answer KeyDocument5 pagesMA 7.2 DNA Replication Lab Answer KeyddNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - MBDocument31 pagesChapter 3 - MBMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- CORONA-SARS Detection BASED ON SPOT-CHECK PCR - PSA-PASTEUR TEST - V.0120Document22 pagesCORONA-SARS Detection BASED ON SPOT-CHECK PCR - PSA-PASTEUR TEST - V.0120Thanh DoNo ratings yet
Central DOGMA of Molecular Biology
Central DOGMA of Molecular Biology
Uploaded by
Bea SimonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Central DOGMA of Molecular Biology
Central DOGMA of Molecular Biology
Uploaded by
Bea SimonCopyright:
Available Formats
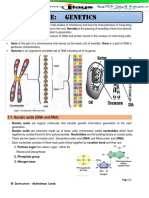
"Central DOGMA of
Molecular Biology"
-Is the process by which the instructions in DNA are
converted into a functional product. It was first proposed
in 1958 by Francis Crick, discoverer of the structure of
DNA. The central dogma of molecular biology explains
the flow of genetic information, from DNA to RNA, to
make a functional product, a protein.
DNA REPLICATION
Enzymes:
- DNA replication occurs through the help Helicase: unwinds parental double helix.
of several enzymes. These enzymes Binding Proteins: stabilize separate strands.
Primase: adds short primer to template strand.
“unzip” DNA molecules by breaking the DNA Polymerase: binds nucleotides to form new
hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands strands.
together. Each strand then serves as a DNA Polymerase I(Exonuclease): removes RNA
primer and inserts the correct bases.
template for a new complementary strand Ligase: joins Okazaki fragments and seals other
to be created. nicks in sugar-phosphate backbone.
- DNA replication is a
much-needed
process in the growth
and renewal of the
cells. The cells
cannot grow without
DNA replication.
RNA SYNTHESIS
- Transcription or RNA synthesis is the
process of synthesizing ribonucleic acid
(RNA). Synthesis takes place within the
nucleus of eukaryotic cells or in the
cytoplasm of prokaryotes and converts
the genetic code from a gene in
deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA ) to a strand
- RNA synthesis consists of four of RNA that then directs protein synthesis.
stages: Binding of RNA
polymerase enzyme to the - The human body needs RNA synthesis
template at a promoter site on for making proteins. It is also important
DNA. Initiation of new strand. for DNA replication.
Elongation. Termination and
release.
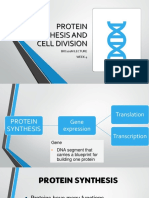
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
- Protein synthesis is process in which - Protein synthesis
polypeptide chains are formed from is one of the most
coded combinations of single amino acids fundamental
inside the cell. The synthesis of new biological
polypeptides requires a coded sequence, processes by which
enzymes, and messenger, ribosomal, and individual cells build
transfer ribonucleic acids (RNAs). their specific
proteins.
- Protein synthesis is
important because the
proteins created during this
process control the
activities of the cells.
Without these proteins,
many of the processes in
the body would fail or not
work properly.
You might also like
- Nucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidDocument60 pagesNucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidWillar Deanson Navarro100% (1)
- CRISPR-Cas Extraordinary Editing PostersDocument1 pageCRISPR-Cas Extraordinary Editing Postersk100% (1)
- Chapter 9 (Protein Synthesis)Document15 pagesChapter 9 (Protein Synthesis)dellavajames192000No ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Nucleic Acid and Synthesis ProteinDocument32 pagesChapter 6. Nucleic Acid and Synthesis ProteinratuadhwaNo ratings yet
- Discussion Questions Exam 4Document3 pagesDiscussion Questions Exam 4Subham BhandariNo ratings yet
- (SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and PhotosynthesisDocument2 pages(SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and Photosynthesisitz.jdv1694No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Genetic CodeDocument2 pagesNucleic Acid: Genetic CodeAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication, Protein Synthesis, and Gene RegulationDocument15 pagesDNA Replication, Protein Synthesis, and Gene RegulationKarl LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Genetic ControlDocument53 pagesChapter 3 Genetic ControlCor GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry FinalsDocument11 pagesBiochemistry FinalsKc CalderonNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument35 pagesProtein SynthesisDaryl GumacalNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Functions and Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument12 pagesNucleic Acid Functions and Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyJennifer MalunaoNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis (1)Document1 pageProtein-Synthesis (1)Juan Carlo SamsonNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument28 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologysannsannNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody DNA Ebook Oct2021Document14 pagesVisibleBody DNA Ebook Oct2021Anjarika TripathyNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid SynthesisDocument9 pagesNucleic Acid SynthesisrosalindaNo ratings yet
- Biochem ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiochem ReviewerKathleenNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTSDocument3 pagesHANDOUTScareeseta bongcawilNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Biotech 2Document3 pagesQuarter 3 Biotech 2Hezekiah GatesNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument35 pagesDNA Replication and Protein Synthesisryangela545No ratings yet
- BIOTECHNOLOGYDocument4 pagesBIOTECHNOLOGYheyyouNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Study MaterialDocument58 pagesMolecular Biology Study MaterialchitraNo ratings yet
- 00a Ch. 8 VocabDocument7 pages00a Ch. 8 VocabaubreymertNo ratings yet
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocument73 pagesDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five GeneticsDocument28 pagesChapter Five GeneticsYahya AbdiwahabNo ratings yet
- Heredity Inheritance and Variations PDFDocument56 pagesHeredity Inheritance and Variations PDFNoean LargoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument33 pagesLesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologySherwin YenogacioNo ratings yet
- BMD-3201 - Trans 2.2 - Cells and Tissue ContinuationDocument15 pagesBMD-3201 - Trans 2.2 - Cells and Tissue ContinuationOwen RoldanNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument5 pagesBio ReviewerFaye Lianne MaderoNo ratings yet
- Part 3Document18 pagesPart 3Ultima PhaseNo ratings yet
- Self Study Assignment On Marker Enzymes, Semiautonomous - PPTX 1740512Document20 pagesSelf Study Assignment On Marker Enzymes, Semiautonomous - PPTX 1740512aswinNo ratings yet
- HEREDITYDocument23 pagesHEREDITYvivas.kznne.9No ratings yet
- Protein Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesProtein Structure and FunctionCindy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules IIDocument20 pagesBiomolecules IIMark Vincent Rei VillacruzNo ratings yet
- Week 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Unit IV and VDocument60 pagesMolecular Biology Unit IV and VchitraNo ratings yet
- The Replication of DNA in ProkaryotesDocument6 pagesThe Replication of DNA in ProkaryotesAditya KukretiNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument41 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular Biologyanmbeltran31No ratings yet
- Assignment # 8 Genes & Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pagesAssignment # 8 Genes & Nucleic Acidskyle james duclanNo ratings yet
- 2021 Protein-Synthesis-And-Genetic-CodeDocument5 pages2021 Protein-Synthesis-And-Genetic-CodeLucila OriveNo ratings yet
- 5.2 - DNA Replication During The S PhaseDocument23 pages5.2 - DNA Replication During The S PhaseAna JuatasNo ratings yet
- Asam Nukleat Dan Protein With SoundDocument18 pagesAsam Nukleat Dan Protein With SoundFika Nurul HafidzohNo ratings yet
- Heredity Protein SynthesisDocument23 pagesHeredity Protein SynthesispaulangelomicoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Genetic Control of Protein Synthesis, Cell Function, and Cell ReproductionDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 3: Genetic Control of Protein Synthesis, Cell Function, and Cell ReproductionMan DejeloNo ratings yet
- Biotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 5 Role of DNA RNA and Protein in The Transmission of Hereditary Traits 3Document14 pagesBiotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 5 Role of DNA RNA and Protein in The Transmission of Hereditary Traits 3Aileen Ocampo100% (1)
- 2.3. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pages2.3. Nucleotides and Nucleic Acidsstu.suman-iftikharNo ratings yet
- Activity 09Document2 pagesActivity 09Shella Mie JamisonNo ratings yet
- Week 4 NotesDocument13 pagesWeek 4 NotesGHEIST INC.No ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument88 pagesNucleic AcidJoyce Jimenez100% (1)
- Bnbi Oral PresentationDocument17 pagesBnbi Oral PresentationAshria Sonali PrakashNo ratings yet
- Nuceic Acid ProjectDocument2 pagesNuceic Acid ProjectCaryl Alvarado SilangNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNucleic AcidsAntonette SolaresNo ratings yet
- Chapt 7 DNA Replication NotesDocument8 pagesChapt 7 DNA Replication Notesmalenya1100% (1)
- Ensayo-Ácidos Nucléiocs.Document18 pagesEnsayo-Ácidos Nucléiocs.Jampier BritoNo ratings yet
- Codon ChartDocument3 pagesCodon ChartMymy SalgadoNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDocument12 pagesDNA Replication in ProkaryotesSumit MandalNo ratings yet
- THE Geneticists: Grade 11 St. John BoscoDocument24 pagesTHE Geneticists: Grade 11 St. John Boscojason balmasNo ratings yet
- 1.central DogmaDocument2 pages1.central DogmaShantel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- U5 Study GuideDocument6 pagesU5 Study GuideJuan CastellanosNo ratings yet
- 13.5 DNA Structure and Protein Synthesis (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsDocument55 pages13.5 DNA Structure and Protein Synthesis (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 6 Common Factors Contributed To Pathogenic Mechanism of Repeat Expansion DiseasesDocument3 pages6 Common Factors Contributed To Pathogenic Mechanism of Repeat Expansion DiseasesGia HoàngNo ratings yet
- Aeromonas Salmonicida Aeromonas Bestiarum: Phenotypic, Genotypic, and Phylogenetic Discrepancies To Differentiate FromDocument11 pagesAeromonas Salmonicida Aeromonas Bestiarum: Phenotypic, Genotypic, and Phylogenetic Discrepancies To Differentiate FromIon MacreaNo ratings yet
- DNA RepilicationDocument57 pagesDNA RepilicationJeevikaGoyalNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Genetic EngineeringDocument11 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Genetic EngineeringHazel AbitriaNo ratings yet
- Hi Scribe T7 ARCAm RNAmanual E2060Document11 pagesHi Scribe T7 ARCAm RNAmanual E2060starkonly7No ratings yet
- tRNA-derived Small RNAs Target Transposable Element TranscriptsDocument11 pagestRNA-derived Small RNAs Target Transposable Element TranscriptsMan Ba SotzNo ratings yet
- Purines, Pyrimidine MetabolismDocument22 pagesPurines, Pyrimidine Metabolism202210034No ratings yet
- BasicsDocument18 pagesBasicsBiraj KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Replication, Transcription, Translation, Mutation HWDocument20 pagesReplication, Transcription, Translation, Mutation HWtahamidNo ratings yet
- Linkers and AdaptersDocument11 pagesLinkers and AdaptersYogesh Pawar0% (1)
- Midi-And Mini-Primer Sets For Mtdna Control Region Sequence Analysis From Highly Degraded Forensic SamplesDocument1 pageMidi-And Mini-Primer Sets For Mtdna Control Region Sequence Analysis From Highly Degraded Forensic Samplesoday_ada76No ratings yet
- Metabolizam SeceraDocument52 pagesMetabolizam SeceraAnel RedzepiNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument35 pagesDNA and RNAalchristian tomatomNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDocument24 pagesDNA Replication in ProkaryotesAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- RNAProtein Synthesis SEDocument7 pagesRNAProtein Synthesis SEAmbrielle WhiteNo ratings yet
- Genetic Information and Protein SynthesisDocument22 pagesGenetic Information and Protein Synthesisjason balmasNo ratings yet
- Dna Transcription NotesDocument3 pagesDna Transcription NotesviennaNo ratings yet
- Hair PresentationDocument7 pagesHair PresentationxMiracleNo ratings yet
- 12 Fire Letters - 1 DNA Strand Template (1 Fire Letter Sequence 144 Vector Codes)Document1 page12 Fire Letters - 1 DNA Strand Template (1 Fire Letter Sequence 144 Vector Codes)RobertNo ratings yet
- Equipe1 - A Tale of Three Next Generation Sequencing Platforms - Comparison of Ion Torrent, Pacific Biosciences and Illumina MiSeq SequencersDocument13 pagesEquipe1 - A Tale of Three Next Generation Sequencing Platforms - Comparison of Ion Torrent, Pacific Biosciences and Illumina MiSeq SequencersFagnerOliveiraNo ratings yet
- En QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR HandbookDocument32 pagesEn QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR Handbooknaini21No ratings yet
- Real Time PCR Handbook PDFDocument73 pagesReal Time PCR Handbook PDFRodney SalazarNo ratings yet
- Cloning MethodsDocument24 pagesCloning MethodsRam Nivas Ahirwar100% (7)
- BioCentralDogmaWorksheet 1Document3 pagesBioCentralDogmaWorksheet 1jaelajeanine326No ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance PDFDocument19 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance PDFBiju Mylachal94% (16)
- MA 7.2 DNA Replication Lab Answer KeyDocument5 pagesMA 7.2 DNA Replication Lab Answer KeyddNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - MBDocument31 pagesChapter 3 - MBMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- CORONA-SARS Detection BASED ON SPOT-CHECK PCR - PSA-PASTEUR TEST - V.0120Document22 pagesCORONA-SARS Detection BASED ON SPOT-CHECK PCR - PSA-PASTEUR TEST - V.0120Thanh DoNo ratings yet