Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Information Report Assessment Rubric_Guide to Making Judgement
Information Report Assessment Rubric_Guide to Making Judgement
Uploaded by
sara ibrahimCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Information Report Assessment Rubric_Guide to Making Judgement
Information Report Assessment Rubric_Guide to Making Judgement
Uploaded by
sara ibrahimCopyright:
Available Formats
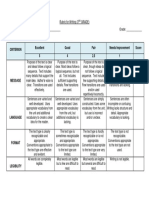
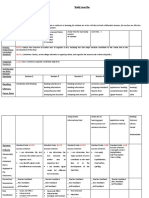
Student Name: Date:
Very High High Sound Developing Emerging
Year 1
Rubric/Guide to Making A clear understanding and uses
A thorough understanding and Understands aspects of and A basic understanding and
Judgement a high level of skill in familiar Has an understanding and uses
uses a high level of skill in both uses varying levels of skill in is beginning to use skills in
Information Report situations. Is beginning to use skills in familiar situations.
familiar and new situations. familiar situations. familiar situations.
skills in new situations.
Text Structure ‣ Text organised with the correct use ‣ Uses paragraphs to structure their ‣ The text is generally organised ‣ Requires some support to recognise ‣ Requires support to produce a
The organisation of the of paragraphs. report. and follows an information report the structural elements of an written text.
structural components of ‣ Information is organised correctly ‣ Paragraphs are generally used structure: information report. ‣ Has difficulty recognising
into related paragraphs. correctly and consistently. ‣ title ‣ Needs assistance/prompts from the structural elements of an
a text.
‣ Effectively follows the information ‣ Follows the correct structure of an ‣ introduction/opening statement modelled texts. information report.
report structure: information report: ‣ basic information with some ‣ Some of the structural elements ‣ Text may have some structure, but
‣ title ‣ title detail added may be included without assistance. it may not be relevant.
‣ introduction/opening statement ‣ introduction/opening statement ‣ the ending which concludes the ‣ Text structure is difficult to
‣ contains a variety of information ‣ contains more than one piece of text recognise.
with relevant details and information with some detail ‣ Heavily relies on drawings and
examples ‣ the ending which concludes the examples of information reports.
‣ the ending which concludes the text
text
Sentence Structure and • Consistent in sentence structure • Applies their knowledge into their • Identifies the parts of a simple ‣ Requires some support to identify ‣ Requires significant support to
Vocabulary when writing. Goes beyond that writing. sentence that represent: the parts of a simple sentence. identify the parts of a simple
The production of expected for Year 1, for example: • Effectively uses adjectives, adverbs, • what’s happening? (verb) ‣ Uses limited vocabulary and may be sentence.
• simple connections are made and unusual verbs to make a • what state is being described? repetitive. ‣ Often omits correct spacing
grammatically correct,
between ideas by using sentence more vivid. (verb) ‣ Needs reminding to use correct between words.
structurally sound and
compound sentences with two • Beginning use of a limited bank of • who or what is involved? (noun spacing between words. ‣ Struggles to read back own writing
meaningful sentences.
or more clauses conjunctions group/phrase) and relies on memory for an oral
Use of appropriate language • sometimes expands noun • the surrounding circumstances retell.
choices. groups/phrases using articles (adverb group/phrase)
(the, a and an) and adjectives • Understands a simple sentence
• Understands there are three types expresses a single idea.
of nouns. • Experiments using different words
that represent nouns, verbs,
adjectives and adverbs.
Punctuation • Consistent in application. • Uses full stops correctly. • Recognises that full stops, question • Understands the use of full stops. • Does not recognise the difference
The use of correct and • The punctuation usage goes • Predominately uses question marks marks and exclamation marks, signal • Requires some support to: between the various sentence
appropriate punctuation beyond that expected for Year 1, and exclamation marks correctly. sentences that make statements, • recognise the difference types.
for example: ask questions, express emotion or between the various sentence • Uses punctuation randomly in their
that aids reading of a piece
• recognises that capital letters give commands. types writing.
of text.
signal proper nouns • Attempts to apply this knowledge in • apply this in their writing
• commas are used to separate their writing.
items in lists • Punctuation may have been
overused.
Page 1 of 2 visit twinkl.com.au
Year 1 Rubric/Guided to Making Judgement Information Report
Spelling ‣ Consistent in the application and • Correctly spells one and two • Correctly spells some one and two • Requires some support to: • Has difficulty recognising one and
The accuracy of spelling and goes beyond that expected for Year syllable words with common letter syllable words with common letter • recognise one and two syllable two syllable words.
the difficulty of words used. 1, for example: patterns e.g. known blends ‘bl’, ‘st.’ patterns e.g. known blends ‘bl’, ‘st’. words • Unable to build word families from
‣ shows a knowledge of • Understands that a letter can • Builds word families from common • build word families from common common morphemes.
morphemic word families by represent more than one sound and morphemes e.g. play, plays, playing. morphemes • Applies basic knowledge of letters
attempting to use prefixes and applies this correctly when spelling • Uses visual memory to write high- • recognise the letters that and sounds to spell words.
suffixes words. frequency words. represent more than one sound • Relies heavily on environmental
‣ uses knowledge of letter • Correctly spells an increasing • Understands that a letter can • Relies on the environmental print print.
patterns and morphemes to number of high-frequency words. represent more than one sound. for some high-frequency words
attempt spelling not predictable (limited visual memory).
from their sounds
‣ uses most letter-sound matches
when writing words of one or
more syllables
Editing • Consistent in approach and goes • Actively re-reads own work. ‣ When prompted: • Requires support to read own work. • Minimal or no evidence of appropriate
Ability to re-read and beyond that expected for Year 1, • Attempts to edit own work to ‣ Re-reads own work • Requires encouragement to discuss editing skills.
edit own work to check for example: improve meaning, spelling, and ‣ Discusses possible changes to changes to improve own work.
for meaning, spelling, • edits text for spelling, sentence- punctuation. improve meaning, spelling, and
punctuation, and grammar. boundary, punctuation and text punctuation
structure
Teacher Name:
Page 2 of 2 visit twinkl.com.au
You might also like
- Restart 2 Grammar BookDocument23 pagesRestart 2 Grammar BookDina FatourouNo ratings yet
- Nouns Verbs and Adjectives Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesNouns Verbs and Adjectives Lesson Planapi-383717086100% (2)
- Narration Notes (Class 11-12)Document12 pagesNarration Notes (Class 11-12)Anugrah Stanley80% (5)
- Bishkek State University Named After K.Karasaev The Faculty of European Civilizations The Theory and Practice of Translations DepartmentDocument44 pagesBishkek State University Named After K.Karasaev The Faculty of European Civilizations The Theory and Practice of Translations DepartmentGulandaNo ratings yet
- Recount Assessment Rubric_Guide to Making JudgementDocument2 pagesRecount Assessment Rubric_Guide to Making Judgementsara ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing Assessment Rubric - Guide To Making JudgementDocument2 pagesCreative Writing Assessment Rubric - Guide To Making JudgementSonia KamalNo ratings yet
- Recount Assessment RubricDocument3 pagesRecount Assessment RubricJasmine TranNo ratings yet
- Information Report Assessment RubricDocument3 pagesInformation Report Assessment RubricJasmine TranNo ratings yet
- Narrative Assessment RubricDocument3 pagesNarrative Assessment RubricJasmine TranNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing Assessment RubricDocument3 pagesCreative Writing Assessment RubricJasmine TranNo ratings yet
- Gatbsy Essay - Prompt and RubricDocument2 pagesGatbsy Essay - Prompt and Rubricapi-459542710No ratings yet
- Problem-Solution Essay RubricDocument2 pagesProblem-Solution Essay Rubric白卡持有人No ratings yet
- English RubricsDocument2 pagesEnglish Rubricsapi-662977389No ratings yet
- Grasps 3Document13 pagesGrasps 3ÄllypÖt DiÖnisioNo ratings yet
- Gaffney 9 Point Cer RubricDocument2 pagesGaffney 9 Point Cer Rubricapi-292471186No ratings yet
- English SLO G VDocument27 pagesEnglish SLO G VRehanKakarNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Collaborative EssayDocument4 pagesModule 2 Collaborative EssayDinu ElenaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem 1st Quarter ENGLAPP ReviewerDocument4 pages2nd Sem 1st Quarter ENGLAPP ReviewerGummy Min0903No ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay Drafting AssignmentDocument7 pagesArgumentative Essay Drafting Assignmentalysanajla04No ratings yet
- Criterion Excellent Good Fair Needs Improvement Score 5 4 2.5 1Document1 pageCriterion Excellent Good Fair Needs Improvement Score 5 4 2.5 1Iván CamposNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 - GEC 3Document4 pagesQuiz 2 - GEC 3Cabahug, Kobe RyanNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Perf Feedback PDFDocument9 pagesTOEFL Perf Feedback PDFwleaNo ratings yet
- Rubric To Assess An Oral Presentation PDFDocument2 pagesRubric To Assess An Oral Presentation PDFmaria herrera riveraNo ratings yet
- Learner'S Copy: Wbls-Obe MELC-Aligned Summative Assessment English 10Document4 pagesLearner'S Copy: Wbls-Obe MELC-Aligned Summative Assessment English 10Rachel Yam 3nidadNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Writing Assessment Rubric - Guide To Making A JudgementDocument2 pagesPersuasive Writing Assessment Rubric - Guide To Making A JudgementSonia KamalNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary Professional Ethics (NURS 523)Document2 pagesInterdisciplinary Professional Ethics (NURS 523)prakash kumarNo ratings yet
- WGSD - Narrative - Based Rubric, Grade 4: Trait/CCSS 4 3 2 1Document2 pagesWGSD - Narrative - Based Rubric, Grade 4: Trait/CCSS 4 3 2 1api-309067146No ratings yet
- Master IELTS Visuals OfficialDocument80 pagesMaster IELTS Visuals OfficialDiễm Bùi Thị ThúyNo ratings yet
- The Formal Email RubricDocument1 pageThe Formal Email RubricAzaliaNo ratings yet
- OkBM BS ENT 4th QA Output BasedDocument9 pagesOkBM BS ENT 4th QA Output Basedaldrin.madambaNo ratings yet
- 9th-10th Info-Explan RubricDocument2 pages9th-10th Info-Explan Rubricapi-362261785No ratings yet
- Writing Prompt: D C B A Generic Structure: LayoutDocument1 pageWriting Prompt: D C B A Generic Structure: LayoutWendy Herrera FernandezNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Writing One Point RubricDocument2 pagesArgumentative Writing One Point Rubricapi-614253116No ratings yet
- Performance Task-Position PaperDocument4 pagesPerformance Task-Position PaperNathan Russel PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Speechcom Mid TermDocument6 pagesSpeechcom Mid Termsamin aliNo ratings yet
- English Gr.7 LP Wk16.JanDocument9 pagesEnglish Gr.7 LP Wk16.JanOgechi ElekwaNo ratings yet
- 9 ENG Short Story R&J Unit Assignment 2024Document3 pages9 ENG Short Story R&J Unit Assignment 2024mahi4740.patelNo ratings yet
- Critical Synthesis Paper Rubric 08-13-23Document2 pagesCritical Synthesis Paper Rubric 08-13-23Ayush JaggiNo ratings yet
- Communication Letter and Activity Design ActivityDocument4 pagesCommunication Letter and Activity Design ActivityJahn Rey BautistaNo ratings yet
- BUSM4409 - A1 Management Brief 1 16S1 v1Document2 pagesBUSM4409 - A1 Management Brief 1 16S1 v1Sindhura ValluriNo ratings yet
- Carl Labininay - Assessment - Module 7 - DCIT65Document3 pagesCarl Labininay - Assessment - Module 7 - DCIT65gelaNo ratings yet
- ELC3531 2021-22 Sem1 Assessment RubricsDocument5 pagesELC3531 2021-22 Sem1 Assessment RubricsAlumni WONG WING HUNGNo ratings yet
- Rhetorical Analysis Final DraftDocument12 pagesRhetorical Analysis Final Draftapi-440153923No ratings yet
- Writingrubric6 8Document2 pagesWritingrubric6 8Made CangguNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentapi-393180311No ratings yet
- Jfkhs Writing Rubric 1 6 12Document1 pageJfkhs Writing Rubric 1 6 12api-281117976No ratings yet
- Ap22 Apc Chinese Language Task 1Document7 pagesAp22 Apc Chinese Language Task 1fuliuqing1133No ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Band DescriptorsDocument39 pagesIELTS Writing Band DescriptorsArifur RahmanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 8 Individual Activity 1Document2 pagesUNIT 8 Individual Activity 1babyboyNo ratings yet
- ENG 3CMaus Chapter Five - The Second HoneymoonDocument4 pagesENG 3CMaus Chapter Five - The Second Honeymoonharry nguyenNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Band Descriptors (Public Version) : Task 2Document4 pagesIELTS Writing Band Descriptors (Public Version) : Task 2Jessica HB ZhangNo ratings yet
- Ap22 Apc Spanish Language Task 2Document12 pagesAp22 Apc Spanish Language Task 2paty4155No ratings yet
- Eng103essayrubric KellithomasDocument1 pageEng103essayrubric Kellithomasapi-300255940No ratings yet
- Rubrics: Rubric For Concept Paper Criteria 4-Excellent 3 - Good 2 - Fair 1 - PoorDocument7 pagesRubrics: Rubric For Concept Paper Criteria 4-Excellent 3 - Good 2 - Fair 1 - PoorIvy Mie SagangNo ratings yet
- Information Report RubricDocument1 pageInformation Report Rubricapi-361854774No ratings yet
- Ielts Writing Task 1 Academic TrainingDocument77 pagesIelts Writing Task 1 Academic Trainingdream bookNo ratings yet
- Task 1 - Part D - AssessmentDocument1 pageTask 1 - Part D - Assessmentapi-357977200No ratings yet
- Guidelines To Power of DiversityDocument3 pagesGuidelines To Power of Diversityanhlenguyenhai78No ratings yet
- Pink Wachirapaet - g8 Unit 2 Formative Presentation 1 CultureDocument3 pagesPink Wachirapaet - g8 Unit 2 Formative Presentation 1 Cultureapi-480730245No ratings yet
- Rubric Draft 1 and Final Version Unit 3Document2 pagesRubric Draft 1 and Final Version Unit 3MILAGROSNo ratings yet
- Magazine Article WritingDocument2 pagesMagazine Article WritingMohammed ZohairNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Presentation 1Document3 pagesYear 2 Presentation 1Meggie MNo ratings yet
- Speaking and Listening Assessment RubricDocument3 pagesSpeaking and Listening Assessment RubricJasmine TranNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document11 pagesAssignment 2Ian KopelowitzNo ratings yet
- Sarf Lesson 05Document24 pagesSarf Lesson 05zakloochNo ratings yet
- Semantic RoleDocument8 pagesSemantic Rolemaryatul kipyaNo ratings yet
- InterjectionDocument21 pagesInterjectionDinda PuspitaNo ratings yet
- GERUNDSDocument3 pagesGERUNDSJeanifer ArapocNo ratings yet
- DEPED K To 12 - EnGLISH Curriculum Guide - Grades 1-3Document14 pagesDEPED K To 12 - EnGLISH Curriculum Guide - Grades 1-3yachiru12192% (60)
- German SynonymsDocument347 pagesGerman Synonymsinhumane78No ratings yet
- Usage - Pronoun-Antecedent AgreementDocument9 pagesUsage - Pronoun-Antecedent AgreementRhen PaguiganNo ratings yet
- An Elementary Grammar of KannadaDocument145 pagesAn Elementary Grammar of KannadaananthakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Iru / - Eru Verbs: Verb Kanji And/or Hiragana EnglishDocument6 pagesIru / - Eru Verbs: Verb Kanji And/or Hiragana EnglishCarlos Moreno100% (1)
- English For Everyone. Level 1 Beginner. Practice Book.Document175 pagesEnglish For Everyone. Level 1 Beginner. Practice Book.MeggiJorbenadzeNo ratings yet
- Participle PDFDocument3 pagesParticiple PDFNineveh Tabligan TagardaNo ratings yet
- Nouns: What Is A Noun?Document15 pagesNouns: What Is A Noun?navanitamganesonNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs PDFDocument4 pagesModal Verbs PDFJésica Anahí FogelNo ratings yet
- Ef4e Int Plus Wordlist PLDocument11 pagesEf4e Int Plus Wordlist PLMaria Radew-KornackaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar All Lectures NotesDocument75 pagesEnglish Grammar All Lectures Notesjanbaaz ghaziNo ratings yet
- In Language, The Ignorant Have Prescribed Laws To The LearnedDocument38 pagesIn Language, The Ignorant Have Prescribed Laws To The LearnedTanwir ShahNo ratings yet
- Pang AbayDocument3 pagesPang AbayJEZZINE F. SALARNo ratings yet
- Grammar 11 PDFDocument31 pagesGrammar 11 PDFJose Luis LanchipaNo ratings yet
- Trigedasleng LanguageDocument11 pagesTrigedasleng LanguageGuilhermeNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be (Am, Is Are)Document36 pagesVerb To Be (Am, Is Are)Julio TiradoNo ratings yet
- 100 Questions On Communicative English - (For Students)Document5 pages100 Questions On Communicative English - (For Students)sunitasunita100% (3)
- Year 3 Summer Term 2 SPaG Activity Mat 2Document6 pagesYear 3 Summer Term 2 SPaG Activity Mat 2Andreea MileaNo ratings yet
- Four Corners 3, Unit 2 QuizDocument9 pagesFour Corners 3, Unit 2 QuizVEIKI JOHELYS BONE VALDERRAMANo ratings yet
- Sílabo 2021-II - Inglés Anual San MarcosDocument5 pagesSílabo 2021-II - Inglés Anual San MarcosSusana Yarleque MejiaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Passive and Active VoiceDocument11 pagesWeek 3 - Passive and Active VoiceTeacher Dee TVNo ratings yet