Professional Documents
Culture Documents
pp22_1p11
pp22_1p11
Uploaded by
evelCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
pp22_1p11
pp22_1p11
Uploaded by
evelCopyright:
Available Formats
The differences between
natural betaine and
betaine hydrochloride
by A. M. Amerah, Development Control Control Natural Betaine
SEM2
Scientist, Danisco Animal Nutrition. no heat stress heat stress (HS) betaine (HS) HCl (HS)
Bodyweight (BW)
n the 1860s, a German chemist,
I
2982a 2724b 2963a 2896ab 85
gain (g)
Scheibler, isolated a new organic base
from sugar beet and called it betaine. Feed intake (g) 4359a 3851b 4007ab 4087ab 170
Sugar beet and its derivatives (for example FCR 1.59ab 1.58a 1.55b 1.58ab 0.02
molasses and vinasses) are still the main raw
materials from which natural betaine is BW corrected FCR* 1.59ab 1.66a 1.55b 1.61ab 0.04
extracted to be used in animal feed. Breast meat (% of
27.9ab 26.8b 29.0a 27.8ab 0.004
However, it is increasingly the case that carcase weight)
other sources of betaine, produced by Abdominal fat pad
chemical processes have become commer- 1.39b 1.78a 1.29b 1.43b 0.11
(% of BW)
cially available, for example betaine abc
means within a row without a common superscript are significantly different (P<0.05)
hydrochloride (HCl). *3 points correction per 100g bodyweight difference versus the positive control.
1
Each value represents the mean of eight replicates (10 birds per replicate). 2Pooled standard error of mean.
There is limited data in scientific literature
comparing betaine HCl and natural betaine. Table 1. Performance and carcase measurements of 42 day old broiler chickens as
In 2013, Danisco Animal Nutrition commis- influenced by heat stress and betaine source supplementation1. Betaine products
sioned several studies to compare the prod- added to supply 1.2kg betaine per tonne of feed.
ucts in terms of their physical properties and
their consequent relative bio-efficacies. maintenance energy requirements. This arti- However, there is a general lack of informa-
Literature is abundant with research on cle will not focus on the beneficial effects of tion comparing the levels of TMA in betaine
the beneficial effects of natural betaine – the natural betaine or its mode of action, which HCl and natural betaine. Consequently, the
tri-methyl derivative of the amino acid is well documented in the literature, but first study examined the levels of TMA in
glycine – on animal performance. These rather will focus on comparing natural some betaine products available in the
benefits apply particularly during times of betaine and betaine HCl in recently con- market. Based on the analysis of samples of
heat and disease stress, and have been ducted trials both in vitro and in vivo. three betaine HCl products, the results
attributed to betaine's unique molecular (Fig. 1) showed that there is a big variation
structure. The betaine molecule contains (0.2-6.0g/kg, as fed) in TMA content, even
three methyl groups that are labile, allowing In vitro trials within batches of the same product.
it to function as a methyl donor in metabo- This variation between both products and
lism. The other important key point in the Betaine HCl is a chemically synthesised batches can result in unpredictably high lev-
molecular structure of betaine is that it has product which contains trimethylamine els of TMA in the finished feeds. It is inter-
both a positive and negative charge on the (TMA) as a by-product in varying concentra- esting in this context to note that according
molecule. This lends it the characteristics of tions. to the European Food Safety Authority
an osmolyte, aiding water balance in the Trimethylamine is a volatile amine associ- (EFSA Journal 2012;10(5):2679) ‘For
body with resulting benefits on reducing ated with increased egg taint in poultry. Continued on page 13
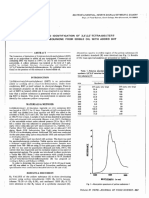
Fig. 1. Betaine HCl contains higher trimethylamine levels than Fig. 2. Betaine HCl reduces the transepithelial electrical
natural betaine. resistance (TEER) of the intestinal epithelial cells (see arrows).
7 300 A decrease in resistance by betaine HC1
Trimethylamine level in
6 *** ***
TEER (ohm x cm2)
product (g/kg)
5
200
4
3
2 100
1
0
Betafin S1 Betaine HCI Betaine HCI Betaine HCI 0
natural (Product P) (Product B) (Product I - Control Betafin Betaine Control Betafin Betaine
betaine mean of 3 HCI HCI
samples ± SD) 1 hour 6 hours
*** Significantly different (P<0.001)
International Poultry Production — Volume 22 Number 1 11
Continued from page 11 Un- Challenged Challenged Natural Betaine SEM2
trimethylamine and its salt the proposed challenged control control – betaine HCl
high use level of 5mg/kg complete feeding control reduced (CC) (CC)
stuff is safe for all animal species with a mar- methionine
gin of safety ranging between 3 and 15’. (CC)
For this reason, it is important for nutri-
tionists considering the use of betaine HCl IDE (MJ/kg DM) 13.38a 8.80c 8.91c 12.41ab 11.89b 0.52
to be well aware of the levels of TMA in the Lysine 88 a
70 c
74 c
85 ab
81b
2.2
product, and its typical variation from batch
to batch. Natural betaine was found to con- Methionine 90 a
72 c
66 d
79 b
76b c
1.6
tain no detectable TMA (Fig. 1).
Average AA 81 a
58 c
62 c
76 ab
73b
1.9
For betaine to function as an efficient
abc
osmolyte in vivo, the molecule must first be means within a row without a common superscript are significantly different (P<0.05)
1 2
Each value represents the mean of eight replicates (eight birds per replicate). Pooled standard error of mean.
fully and rapidly solubilised in water. To test
the difference in betaine solubility between Table 2. Ileal digestible energy (IDE), ileal lysine and methionine digestibility (%) and
natural betaine and betaine HCl, a further average amino acid (AA) digestibility (%) of 21 day old broilers as influenced by
study was conducted at DuPont Nutrition coccidia challenge and betaine source supplementation1. Betaine products added to
and Health, Kantvik Active Nutrition, supply 960g betaine per tonne of feed.
Finland.
This showed that Betafin natural betaine formance of broilers exposed to production Betafin natural betaine can offer greater net
was approximately three times more solu- stresses such as coccidial challenge and heat value in use than betaine HCl, particularly
ble, and dissolved in water more than twice stress. for birds under production stress.
as rapidly as betaine HCl. However, most of the early published
In a different type of study, using an in studies on betaine were conducted using
vitro intestinal cell model, betaine HCl was natural betaine and there is lack of data Conclusion
found to negatively influence the gut barrier comparing the natural source of betaine and
compared to natural betaine (Fig. 2). If repli- betaine HCl on performance of broilers in These recent comparative studies between
cated in vivo this would have important challenge situations. This has been natural betaine and betaine HCl clearly
implications for the animal’s digestive physi- addressed in two recent studies carried out illustrate that some of the differences seen
ology. at Massey University, New Zealand. in vitro, for example relative solubility in
Weak cellular tight junctions between gut In the first study broilers under heat stress water, speed of dissolution and relative
epithelial cells (indicated by a reduced TEER showed a significant improvement in carcase effects in in vitro intestinal cell models are
value, see Fig. 2) can lead to movement of breast meat yield, bodyweight gain and feed reflected in the in vivo bio-efficacy compar-
antigens across the gut barrier to provoke a conversion ratio with Betafin natural betaine isons. The differences in residual levels of
damaging and energetically costly inflamma- supplementation compared with the heat TMA in betaine HCl products should also
tory response. stress control group. In contrast, the betaine be considered as part of a routine QC
This effect was supported by significantly HCl product only showed numerical process.
higher in vitro cytokine IL-8 production with improvement compared with the heat stress In animal studies the true relative value of
betaine HCl compared to both control and control. the two products can only be critically
natural betaine. In a second study, using a coccidial chal- assessed in ’challenge’ situations (for exam-
lenge model, both betaine sources were ple heat stress, coccidial challenge) and,
able to improve nutrient digestibility com- under these circumstances and on the basis
Animal trials pared to the challenged control, but only of these recent trials, natural betaine
the birds fed the natural betaine were able showed clear added-value benefits.
Both coccidia and high ambient temperature to fully recover the reduction in nutrient The factors mentioned in this article
can cause damage to gut tissues, increase digestibility caused by the coccidial chal- should be seriously considered before mak-
gut permeability, reduce nutrient digestion lenge. This trial showed Betafin natural ing a purchasing decision based purely on
and absorption, and consequently reduce betaine delivered >€11 per tonne of feed cost per tonne treated to provide equivalent
animal performance. more value than betaine HCl based on rela- betaine levels. n
Betaine is known to be a highly effective tive energy and amino acid digestibility in
organic osmoprotectant and several studies coccidia challenged birds. References are available on request
have shown its positive effects on the per- These two studies clearly illustrated that from monica.hart@dupont.com
International Poultry Production — Volume 22 Number 1 13
You might also like
- BreedTown 2 GuideDocument53 pagesBreedTown 2 GuideXephy100% (2)
- John Ruganda THE BURDENSDocument177 pagesJohn Ruganda THE BURDENSjalody cherono80% (10)
- Vasilisa The BraveDocument6 pagesVasilisa The BraveMorick MwasagaNo ratings yet
- Amelia BedeliaDocument36 pagesAmelia BedeliaSheila Leticia López Garcia100% (1)
- Leaflet Beta KeyDocument4 pagesLeaflet Beta KeysakthivelpcNo ratings yet
- Effective in Broiler DietsDocument1 pageEffective in Broiler DietssakthivelpcNo ratings yet
- Potential Nutritional and Physiological Functions of Betaine in LivestockDocument18 pagesPotential Nutritional and Physiological Functions of Betaine in Livestock119 - Muhammad Arazy FakhrianNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Betaine in Laying Hen DietsDocument3 pagesBenefits of Betaine in Laying Hen Dietswl cNo ratings yet
- Choline Vs Betaine White Paper 09Document10 pagesCholine Vs Betaine White Paper 09mustabshirah.nayerNo ratings yet
- 2022 Article 740Document12 pages2022 Article 740mospina221No ratings yet
- Agilent Milk Protein AnalysisDocument8 pagesAgilent Milk Protein AnalysisDavidNo ratings yet
- BBi3ds Am J Clin Nutr 2004 Craig 539 49Document11 pagesBBi3ds Am J Clin Nutr 2004 Craig 539 49leuthenjournalNo ratings yet
- Betain in Energy Metabolism in PigsDocument10 pagesBetain in Energy Metabolism in PigsleuthenjournalNo ratings yet
- INRA - My TemplateDocument1 pageINRA - My TemplatethulileNo ratings yet
- Abecia Et Al., 2012. Bromoclorometano y Su Efecto Sobre El Metano, Patron de Fermentación, Producción de Leche y Perfil de AG en CabrasDocument10 pagesAbecia Et Al., 2012. Bromoclorometano y Su Efecto Sobre El Metano, Patron de Fermentación, Producción de Leche y Perfil de AG en CabrasLuis Alberto Canul KuNo ratings yet
- Araya-Cloutier - FHM30806 Food Ingredients by Fermentation I - 2023-2024 - v2Document36 pagesAraya-Cloutier - FHM30806 Food Ingredients by Fermentation I - 2023-2024 - v2matthewlowton2255No ratings yet
- TSButamer ProcessDocument2 pagesTSButamer ProcessInsenior FirdausNo ratings yet
- Metabolic EngineeringDocument10 pagesMetabolic EngineeringArshia NazirNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A and Carotene Stability in Feed Containing Antioxidants Treated Animal FatsDocument7 pagesVitamin A and Carotene Stability in Feed Containing Antioxidants Treated Animal FatsSumankeerthiNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Engineering JournalDocument5 pagesBiochemical Engineering JournalThúy NgânNo ratings yet
- StalibenzoqunoneDocument2 pagesStalibenzoqunoneumegeeNo ratings yet
- 8C5AFC914001Document4 pages8C5AFC914001Puneet singhNo ratings yet
- Subclinical Ketosis in Dairy Cattle - The Silent Profit RobberDocument2 pagesSubclinical Ketosis in Dairy Cattle - The Silent Profit RobberAndres Alejandro CoralNo ratings yet
- Betaine in Food (HPLC)Document9 pagesBetaine in Food (HPLC)Yap Poh SiewNo ratings yet
- Butanol Production Using Clostridium Beijerinckii BA101 Hyper-Butanol Producing Mutant Strain and Recovery by PervaporationDocument12 pagesButanol Production Using Clostridium Beijerinckii BA101 Hyper-Butanol Producing Mutant Strain and Recovery by PervaporationnicoNo ratings yet
- Shi-Bin and Hong - 3Document6 pagesShi-Bin and Hong - 3Rio Arizona WinarthaNo ratings yet
- Original Article Betalains: Properties, Sources, Applications, and Stability - A ReviewDocument12 pagesOriginal Article Betalains: Properties, Sources, Applications, and Stability - A ReviewTrương Thị Kim LyNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Antibiotic Zinc Bacitracin in Animal Food by HPLC UVDocument6 pagesDetermination of The Antibiotic Zinc Bacitracin in Animal Food by HPLC UVngobaochanNo ratings yet
- 1998v46no1p206 210Document5 pages1998v46no1p206 210Glédyson FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Isolation, Purification and Characterization of The AntibacterialDocument9 pagesIsolation, Purification and Characterization of The AntibacterialNasfati IktarastiwiNo ratings yet
- Animals 10 01840 v2Document11 pagesAnimals 10 01840 v2Ging OcayNo ratings yet
- Betalains - Properties, Sources, Applications, and Stability - A Review PDFDocument12 pagesBetalains - Properties, Sources, Applications, and Stability - A Review PDFBiyaya San PedroNo ratings yet
- Selective Extraction of Carotenoids From The Microalga Dunaliella Salina With Retention of ViabilityDocument8 pagesSelective Extraction of Carotenoids From The Microalga Dunaliella Salina With Retention of ViabilityYellow MarmotNo ratings yet
- Supplementation of Vitamin E and CDocument6 pagesSupplementation of Vitamin E and COliver TalipNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0308814622019501 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0308814622019501 MainJoaquín Ignacio Oses GámezNo ratings yet
- Vitamin C LcmsDocument1 pageVitamin C LcmsdewiNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 3Document2 pagesKelompok 3DesyNo ratings yet
- Butanol Production by Clostridium Acetobutylicum in A Series of Packed Bed Biofilm ReactorsDocument11 pagesButanol Production by Clostridium Acetobutylicum in A Series of Packed Bed Biofilm ReactorsDiah MuslimawatiNo ratings yet
- Characterization and Digestibility of Detoxified Castor Oil Meal For Japanese QuailsDocument8 pagesCharacterization and Digestibility of Detoxified Castor Oil Meal For Japanese QuailssumitNo ratings yet
- Original Article Study On Efficiency of Betacyanin Extraction From Red BeetrootsDocument6 pagesOriginal Article Study On Efficiency of Betacyanin Extraction From Red BeetrootsDehison Guerrero PurisNo ratings yet
- Basic Methylation and Betaine - Janet Remus - Danisco DataBaseDocument12 pagesBasic Methylation and Betaine - Janet Remus - Danisco DataBaseAnastácia CamposNo ratings yet
- Method For The Determination of Beta Carotene in Supplements and Raw Materials by Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography Single Laboratory ValidationDocument13 pagesMethod For The Determination of Beta Carotene in Supplements and Raw Materials by Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography Single Laboratory ValidationChris JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Cobb 500-2Document6 pagesCobb 500-2Kasmi AgronomieNo ratings yet
- Poster Icpeb Yudith A0Document1 pagePoster Icpeb Yudith A0Monica DrestiaNo ratings yet
- Choline and Betaine Defined Diets For Use in Clinical Research and For The Management of TrimethylaminuriaDocument10 pagesCholine and Betaine Defined Diets For Use in Clinical Research and For The Management of TrimethylaminuriairidntNo ratings yet
- Effect-of-pelleting-and-different-feeding-programs-on-growth-per_2019_PoultrDocument7 pagesEffect-of-pelleting-and-different-feeding-programs-on-growth-per_2019_PoultrAleneNo ratings yet
- Qureshi Butanol Production Using Clostridium Beijerinckii BA101 Hyper-Butanol Producing Mutant Strain and Recovery by PervaporationButanolprodDocument12 pagesQureshi Butanol Production Using Clostridium Beijerinckii BA101 Hyper-Butanol Producing Mutant Strain and Recovery by PervaporationButanolprodschall0No ratings yet
- G. Tonon B. Magnus R. A. Mohedano W. R. M. Leite R. H. R. Costa P. Belli FilhoDocument1 pageG. Tonon B. Magnus R. A. Mohedano W. R. M. Leite R. H. R. Costa P. Belli Filhotonon1111No ratings yet
- Biological Activities of Bovine Glycomacropeptide: Ernest P. BrodyDocument8 pagesBiological Activities of Bovine Glycomacropeptide: Ernest P. BrodyPetya PavlovaNo ratings yet
- García, A., Umaña, K. - Post Laboratorio #2Document12 pagesGarcía, A., Umaña, K. - Post Laboratorio #2Alisson GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Johan Osorio Formuleite 2018Document57 pagesJohan Osorio Formuleite 2018José Marcílio Oggioni BorgesNo ratings yet
- Ratelisthiqpdf AspxDocument37 pagesRatelisthiqpdf AspxSumit MalikNo ratings yet
- L+ Choline Bitartrate: ApplicationsDocument2 pagesL+ Choline Bitartrate: ApplicationsJosé PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Syn TheseDocument6 pagesSyn Thesekadi radiaNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry: Sujung Hu, Byung-Yong Kim, Moo-Yeol BaikDocument6 pagesFood Chemistry: Sujung Hu, Byung-Yong Kim, Moo-Yeol Baikaledrop1No ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Mannitol Production by Two Lactic Acid BacteriaDocument6 pagesA Comparative Study of Mannitol Production by Two Lactic Acid BacteriaCarlos Andres EstacioNo ratings yet
- Effectof Conditioning Temperatureon PelletDocument12 pagesEffectof Conditioning Temperatureon Pelletghazal zainNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Analysis 2001, 12 (6), 374-376.Document3 pagesPhytochemical Analysis 2001, 12 (6), 374-376.srinivasarao meneniNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Engineering: Mingrui Yu, Yali Zhang, I-Ching Tang, Shang-Tian YangDocument10 pagesMetabolic Engineering: Mingrui Yu, Yali Zhang, I-Ching Tang, Shang-Tian YangYork De Moya LlanosNo ratings yet
- Formulating Feed in Challenging Times: June 2007Document4 pagesFormulating Feed in Challenging Times: June 2007amamùra maamarNo ratings yet
- Composição em Ácidos Graxos No Leite de Vacas e Ovelhas Suplementadas Com Extrato Tanífero de Acácia NegraDocument10 pagesComposição em Ácidos Graxos No Leite de Vacas e Ovelhas Suplementadas Com Extrato Tanífero de Acácia NegraAulas gravadasNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0032579119412856 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0032579119412856 MainWendi RahmatsyahNo ratings yet
- Bioactive Peptides and Proteins: Anne Pihlanto and Hannu KorhonenDocument102 pagesBioactive Peptides and Proteins: Anne Pihlanto and Hannu KorhonenMaritsa PerHerNo ratings yet
- Coa 07-04Document1 pageCoa 07-04evelNo ratings yet
- DIATOMITEDocument2 pagesDIATOMITEevelNo ratings yet
- Animals 10 01863 v2Document18 pagesAnimals 10 01863 v2evelNo ratings yet
- Booklet, Vol 10, No 3, September 2020Document154 pagesBooklet, Vol 10, No 3, September 2020evelNo ratings yet
- Microalgae For Immunomodulation and Gut Health Improvement in Poultry IndustryDocument6 pagesMicroalgae For Immunomodulation and Gut Health Improvement in Poultry IndustryevelNo ratings yet
- Beneficial Effects of Spore-Forming Bacillus ProbiDocument12 pagesBeneficial Effects of Spore-Forming Bacillus ProbievelNo ratings yet
- 03 Swine Diarrhea A Worldwide ProblemDocument3 pages03 Swine Diarrhea A Worldwide ProblemevelNo ratings yet
- Animals: Gut Microbiota-Polyphenol Interactions in Chicken: A ReviewDocument18 pagesAnimals: Gut Microbiota-Polyphenol Interactions in Chicken: A ReviewevelNo ratings yet
- Oral Group Medication in Pig Production: Characterising Medicated Feed and Drinking Water SystemsDocument9 pagesOral Group Medication in Pig Production: Characterising Medicated Feed and Drinking Water SystemsevelNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Poultry Gut Health in Achieving Optimum Value Through The Production Chain 4thInternationalPoultryForumChina PDFDocument25 pagesThe Importance of Poultry Gut Health in Achieving Optimum Value Through The Production Chain 4thInternationalPoultryForumChina PDFevelNo ratings yet
- Answerspercentages Limoneninfruitpeel 635399Document2 pagesAnswerspercentages Limoneninfruitpeel 635399obsotamNo ratings yet
- MALATHION 5% RFU Adulticide USING GUIDELINEDocument3 pagesMALATHION 5% RFU Adulticide USING GUIDELINEZERO PEST BDNo ratings yet
- Procedure Text: Dhea Amalia Putri Xiiap1Document15 pagesProcedure Text: Dhea Amalia Putri Xiiap1Dhea AmaliaNo ratings yet
- How To Start A Vegetable Garden - Edible Gardening IdeasDocument5 pagesHow To Start A Vegetable Garden - Edible Gardening IdeasMichelle BucknerNo ratings yet
- Unit - FinalDocument8 pagesUnit - FinalabdelrhmanNo ratings yet
- WAH5 - Extension WorksheetsDocument6 pagesWAH5 - Extension WorksheetsMilagros ConcinaNo ratings yet
- Cell Analogy As One PieceDocument34 pagesCell Analogy As One PieceJohn LoydNo ratings yet
- h24 Dstrainingguide Usen Rev03Document5 pagesh24 Dstrainingguide Usen Rev03Elisan BrasilNo ratings yet
- Old Fashioned Pie Crust With Vinegar and EggDocument12 pagesOld Fashioned Pie Crust With Vinegar and Eggmarius1971No ratings yet
- @ + + Data FactSheet BanswaraDocument32 pages@ + + Data FactSheet BanswaraAjay Pandey Leo CollegeNo ratings yet
- Electrolux AOS061EBA2 268200Document4 pagesElectrolux AOS061EBA2 268200Ernesto HastieNo ratings yet
- Science P4 Revision Unit 1Document5 pagesScience P4 Revision Unit 1starsschooljktNo ratings yet
- English Travel GuideDocument5 pagesEnglish Travel GuideCecilia PerezNo ratings yet
- Year 5 English Plus 1unit 5 WritingDocument16 pagesYear 5 English Plus 1unit 5 WritingWONG SWEE LIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Mo. 5Document13 pagesMo. 5Mae-maeGarmaNo ratings yet
- Sodium Acetate Lab ReportDocument2 pagesSodium Acetate Lab ReportAaron LiNo ratings yet
- PATHFIT-1 - Week-1-4 - Learning Module - 033105Document35 pagesPATHFIT-1 - Week-1-4 - Learning Module - 033105knightruzelNo ratings yet
- Business Plan MARCH 9, 2021: Executive SummaryDocument10 pagesBusiness Plan MARCH 9, 2021: Executive SummaryRegla SuffladaNo ratings yet
- PepsiCo Inc ReportDocument8 pagesPepsiCo Inc ReportSchwalbe TRNo ratings yet
- 21st CENTURY LITERATURE ILOKANODocument2 pages21st CENTURY LITERATURE ILOKANODianne angel HababNo ratings yet
- Womens Fitness Guide 4 Week Bikini Body PlanDocument68 pagesWomens Fitness Guide 4 Week Bikini Body PlanLaura SeviNo ratings yet
- Thanksgiving b2 c1 StudentDocument3 pagesThanksgiving b2 c1 StudentNerea González SoutoNo ratings yet
- Mastermind 2 Unit 1 Grammar and Vocabulary Test ADocument4 pagesMastermind 2 Unit 1 Grammar and Vocabulary Test ARolando Guzman MartinezNo ratings yet
- Year in Review: Company Trade Name Active Ingredient (S) Use StatusDocument1 pageYear in Review: Company Trade Name Active Ingredient (S) Use StatusCatherine TangNo ratings yet
- The Bodybuilder S Nutrition Book by Franco Columbu (01 07)Document8 pagesThe Bodybuilder S Nutrition Book by Franco Columbu (01 07)CLABERT VALENTIN AGUILAR ALEJONo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrates: 1) Molisch TestDocument20 pagesQualitative Tests For Carbohydrates: 1) Molisch TestFRANCEEN LEANNA KATIGBAKNo ratings yet