Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes Haemaotology NinjaNerd
Notes Haemaotology NinjaNerd
Uploaded by
NinyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes Haemaotology NinjaNerd
Notes Haemaotology NinjaNerd
Uploaded by
NinyCopyright:
Available Formats
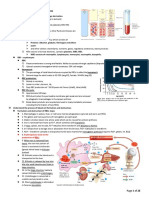
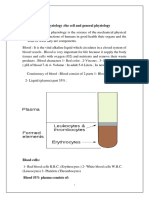
Hematocrit also called PCV (Packed cell volume)
3 levels- RBC, buffy coat (WBC & PLT), plasma (Water/ Solute , Plasma protein, O2, CO2, NO,
Electrolytes, Enzymes, Nutrients, Hormones, Metabolic waste products- lactate, uric acid,
creatinine)
Plasma protein: Albumin (60%), Globulins- alpha and beta + gama
Alpha and beta globulin- transport proteins- transferrin, thyroxin binding globulin (TBG)
Gama globulin- antibodies
Erythropoiesis- Red blood cell formation
Increased erythropoiesis by Hypoxia
Fe3+ Iron absorption in duodenum > Duodenol cytochrome B (DCYTB) Ferrous reductase enzyme
Fe3+ to Fe2+ > Divalent metal transporter 1 (DVMT1) take Fe2+ into intestinal cell > Inside
intestinal cell, Fe2+ bind with ferritin, multiple ferritin bind together called Hemosiderin > Some
ferritin drop the Fe2 at Ferroportin transporter to outside the cell with Hephaesten enzyme covert
Fe2+ to Fe3+ into the blood.
In blood, Fe3+ bind to transferrin protein (transporter protein) to be brought to bone marrow,
spleen, liver for the Fe3+ usage.
In liver, Fe3+ storage, produce Hepcidin protein (regulate/ control Ferroportin). HFE protein at liver
regulate Hepcidin.
*Hemochromatosis disease- absent of HFE protein, no Hepcidin, no Ferroportin regulation, Iron
accumulation.
Vitamin B12, Folic acid (FA) in stomach > duodenum absorption to blood stream. Folic acid
transported via intestinal cell easily. However, VitB12 required protein intrinsic factor in stomach
to bind VitB12 transport to ileum. In ileum receptor bind intrinsic factor+VitB12, then VitB12
released into the blood circulation bind to protein Transcobalamin I and II.
In kidney has EPO gene (erythropoietin hormone), HIF (hypoxia inducible factor, transcription
factor)). If hypoxia detected, HIF bind to EPO gene to produce EPO to form more RBC to transport
O2 to tissues. Thus, in adequate oxygenation, HIF will be coated by enzyme to prevent binding
with EPO gene.
In bone marrow, has stem cells called haemocytoblast (has others name too). Haemocytoblast has
2 different lineage (Myeloid and Lymphoid). Myeloid divides to 3 lineage (PLT, RBC, WBC). EPO will
drive myeloid to produce RBC only (myeloid > proerythroblast > basophilic erythroblast >
polychromatic erythroblast > orthochromatic erythroblast > reticulocytes (after ejected nucleus
and organelles) > pushed out to blood vessels to be matured to > Erythrocytes
*Basophilic erythroblast is blue color cause of ribosome and mRNA.
*Polychromatic erythroblast is blue + red color cause not all ribosome was synthesized by protein
and not all mRNA was translated to protein, red color cause of some red hemoglobin produced.
*Orthochromatic erythroblast enriched by red hemoglobin with some blue due to some mRNA left
Nucleus and organelles will gradually condense and ejected from the erythroblast, and destroyed
by macrophages.
Erythrocytes got no mitochondria, thus, it won’t utilize the O2 and it mainly transport O2, CO2.
*Mitochondria loves to take pyruvate utilize O2 to make ATP
*Bone marrow capillaries are sinusoidal
(3 types of capillaries: sinusoidal, fenestrated, continuous)
DNA > mRNA > Protein > Hemoglobin.
DNA > mRNA called transcription
mRNA > Protein called translation
Hemoglobin- Heme + Globin
Heme made from carbohydrates, fats, amino acids
*RBC recipe: Iron, VitB12, FA, Carbs, Fats, Amino acids
*VitB12, FA is essential for DNA maturation and nucleus condensation. If deficiency, nucleus will
not be condensed, the RBC will be huge (macrocytic/ megaloblastic). Needed during translation
from basophilic > polychromatic and polychromatic > orthochromatic
*Iron essential for haemoglobin production, if no iron, no heme, RBC become small (microcytic)
You might also like
- Maturana Varela Tree of KnowledgeDocument231 pagesMaturana Varela Tree of KnowledgeFedor Volyanskiy100% (17)
- Chapter 30 Nursing Assessment Hematologic SystemDocument14 pagesChapter 30 Nursing Assessment Hematologic Systemmedic-24100% (1)
- Strawberry DNA Extraction Lab HonorsDocument3 pagesStrawberry DNA Extraction Lab HonorsAakash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Nucleolus Nucleus Organ Tissue Vacuole Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chlorophyll Chloroplast ChromosomeDocument17 pagesCytoplasm Mitochondrion Nucleolus Nucleus Organ Tissue Vacuole Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chlorophyll Chloroplast Chromosomeardusias100% (1)
- Formative Assessment BiologyDocument2 pagesFormative Assessment Biologyroosita damayantiNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Chart Key 2011Document3 pagesCell Organelle Chart Key 2011Angel Silva Vicente50% (2)
- APP2 E1 NoteDocument28 pagesAPP2 E1 NotelifecostNo ratings yet
- Physiology of BloodDocument73 pagesPhysiology of BloodAggamemnon populosNo ratings yet
- Dr. Eman Blood Part 1Document20 pagesDr. Eman Blood Part 1atfbdalmsyh672No ratings yet
- Hematopoeitic System: Nsoh Fofang Mia Bios 2021 Edited by Laouna Fru Supervised by DR DimitriDocument66 pagesHematopoeitic System: Nsoh Fofang Mia Bios 2021 Edited by Laouna Fru Supervised by DR DimitriVerla MfeerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument10 pagesChapter 17 Anatomy and Physiology NotesZachary WatsonNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cells, Anemia, and PolycythemiaDocument7 pagesRed Blood Cells, Anemia, and PolycythemiaShi no Me100% (1)
- Blood BiochemistryDocument124 pagesBlood BiochemistrySohail AhamdNo ratings yet
- RBC Production and DestructionDocument44 pagesRBC Production and DestructionNehemiah FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 11 Blood BiochemistryDocument98 pages11 Blood Biochemistryfeby ary annasNo ratings yet
- Blood Cells and The Hematopoetic SystemDocument53 pagesBlood Cells and The Hematopoetic SystemMeet RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Haemopoiesis: Composition of Whole Blood & Its ComponentsDocument8 pagesHaemopoiesis: Composition of Whole Blood & Its ComponentsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - BloodDocument5 pagesChapter 19 - Bloodtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Physiology of BloodDocument97 pagesPhysiology of Bloodbelete psychiatry100% (6)
- Fisiologi DARAHDocument31 pagesFisiologi DARAHTririn RinantiNo ratings yet
- BLOOD Physiology Guyton 14th Edition Chapter 33Document57 pagesBLOOD Physiology Guyton 14th Edition Chapter 33Dr Alamzeb Jadoon100% (1)
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument79 pagesThe Cardiovascular Systemhed-ikaquinoNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cell BiochemistryDocument19 pagesRed Blood Cell BiochemistryPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Blood: Ratna Kusumawati Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Sebelas Maret SurakartaDocument60 pagesPhysiology of Blood: Ratna Kusumawati Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Sebelas Maret SurakartaZidaneNo ratings yet
- Anaphysio Module 10 Hematologic SystemDocument39 pagesAnaphysio Module 10 Hematologic SystemJoshua UveroNo ratings yet
- BLOODDocument11 pagesBLOODshapan biswaNo ratings yet
- Blood HBDocument31 pagesBlood HBBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Blood Continuation - 105835Document6 pagesCardiovascular System Blood Continuation - 105835KIM KALIBAYNo ratings yet
- Aspek Biokimiawi HematologiDocument72 pagesAspek Biokimiawi HematologiExcelsis Deo SombolinggiNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Test 2Document26 pagesStudy Guide Test 2meaghan2215No ratings yet
- MD-5 Plasma Cont. Blood CellssDocument20 pagesMD-5 Plasma Cont. Blood CellssvincenzoNo ratings yet
- BLOODDocument9 pagesBLOODArianne Jen GenotivaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Blood and Body Fluids Mbbsii Bdsii Lecture Note 2019-2020Document39 pagesPhysiology of Blood and Body Fluids Mbbsii Bdsii Lecture Note 2019-2020MUHAMMAD AHMAD HAMMANo ratings yet
- BCH102 Unit - III: Physiology Topic: BloodDocument18 pagesBCH102 Unit - III: Physiology Topic: Blooddivya vajpayeeNo ratings yet
- Blood: (WBCS), Platelets, and A Fluid Matrix Called PlasmaDocument10 pagesBlood: (WBCS), Platelets, and A Fluid Matrix Called PlasmaShiela Mae SagayoNo ratings yet
- Blood Functions PDFDocument12 pagesBlood Functions PDFRobins DhakalNo ratings yet
- Nurs 107 Blood Physiology Lecture 4Document46 pagesNurs 107 Blood Physiology Lecture 4Ann AgyeiwaaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Dan Patofisiologi KardiovaskulerDocument18 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Dan Patofisiologi KardiovaskulerWd. Isti RamadaniNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument45 pagesBloodmaryumaziz388No ratings yet
- General Function of The BloodDocument25 pagesGeneral Function of The BloodMsKizzyNo ratings yet
- Blood Part 1Document29 pagesBlood Part 1raneem fakhouriNo ratings yet
- Physiology Lec 1Document6 pagesPhysiology Lec 1Hussein AlaNo ratings yet
- Blood PhysiologyDocument39 pagesBlood PhysiologySarmad Laith MortadaNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument5 pagesBloodAkachukwu ObunikeNo ratings yet
- 1 Red Blood Cells Anemia and PolycythemiaDocument43 pages1 Red Blood Cells Anemia and PolycythemiaGeevee Naganag VentulaNo ratings yet
- Composition and Functions: BloodDocument86 pagesComposition and Functions: BloodYeyeh SantosNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Blood: Ratna Kusumawati Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Sebelas Maret SurakartaDocument65 pagesPhysiology of Blood: Ratna Kusumawati Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Sebelas Maret SurakartaRizal AbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter17 Blood MariebDocument30 pagesChapter17 Blood MariebMario AndersonNo ratings yet
- FBC Interpretation and Function of Blood ComponentsDocument7 pagesFBC Interpretation and Function of Blood ComponentsFrancesca LiNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and Blood - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGYDocument29 pagesBody Fluids and Blood - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGYSodeinde SimeonNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Manusia: HematologiDocument54 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Manusia: HematologiARUMNo ratings yet
- Haemopoetic SystemDocument73 pagesHaemopoetic SystemManjunathNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - BloodDocument51 pagesUnit 3 - BloodzulieyanaNo ratings yet
- Blood Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesBlood Lecture NotesSimonNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Part I - BloodDocument123 pagesCirculatory System Part I - BloodAngelyn DomingoNo ratings yet
- Cardio WhatsoeverDocument12 pagesCardio WhatsoeverFernando DisuNo ratings yet
- Ap2 Chapter18 Powerpoint Blood SU21Document37 pagesAp2 Chapter18 Powerpoint Blood SU21btheresakNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument49 pagesBloodkaursukhmanvir0921No ratings yet
- Physiology of Blood 1Document66 pagesPhysiology of Blood 1Hiruni FernandoNo ratings yet
- ErytHroCyte ProduCtionDocument8 pagesErytHroCyte ProduCtionMichelle CaamicNo ratings yet
- Blood ComponentsDocument17 pagesBlood ComponentsJohnSmithNo ratings yet
- Selflearning Kit Blood and Its Components2019Document18 pagesSelflearning Kit Blood and Its Components2019Jeff Bryan Arellano HimorNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - FCIA - Composition & Function of Blood - 2022Document5 pagesClass 12 - FCIA - Composition & Function of Blood - 2022Rebeca MedinaNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Leukemia: From initial gene mutation to survivorship supportFrom EverandFast Facts: Leukemia: From initial gene mutation to survivorship supportNo ratings yet
- Cell - Unit of Life BiohackDocument14 pagesCell - Unit of Life BiohackArghya PaulNo ratings yet
- Appendix B: Karyotyping and Genetic DisorderDocument14 pagesAppendix B: Karyotyping and Genetic DisorderMedina ZahicNo ratings yet
- Cells - Basic Unit of LifeDocument45 pagesCells - Basic Unit of Lifeapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Cellcity AnswerkeyDocument7 pagesCellcity Answerkeyteenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Hematology NotesDocument24 pagesHematology Notesddrei13No ratings yet
- Nucleotides Nucleic Acids, and HeredityDocument15 pagesNucleotides Nucleic Acids, and Hereditycjolou100% (3)
- Low Rates of Pregnancy Termination For Prenatally Diagnosed Klinefelter Syndrome and Other Sex Chromosome PolysomiesDocument5 pagesLow Rates of Pregnancy Termination For Prenatally Diagnosed Klinefelter Syndrome and Other Sex Chromosome PolysomiesAltaicaNo ratings yet
- gr11 Mitosis Meiosis QuizDocument3 pagesgr11 Mitosis Meiosis Quizapi-250802146No ratings yet
- Vikash Residential School: Laboratory Manual Biology Cbse Class-Xii TERM-1Document24 pagesVikash Residential School: Laboratory Manual Biology Cbse Class-Xii TERM-1bhakta_babiNo ratings yet
- Biology 5 Biology 5 Cell Biology and Gen PDFDocument144 pagesBiology 5 Biology 5 Cell Biology and Gen PDFJazmin AVNo ratings yet
- ProeukaryoticADMModule - Grade12 - Quarter1STEM - BIO12-Ia-c-3 (1) Lyka Mae B. BenitoDocument27 pagesProeukaryoticADMModule - Grade12 - Quarter1STEM - BIO12-Ia-c-3 (1) Lyka Mae B. BenitoLyka Mae Benito75% (4)
- Jurnal: Identifikasi Kromosom Homolog Melalui Deteksi Pada Tanaman Bawang MerahDocument9 pagesJurnal: Identifikasi Kromosom Homolog Melalui Deteksi Pada Tanaman Bawang MerahImaniar FitriatasyaVWNo ratings yet
- Click: Cambridge IGCSE Biology Extended LevelDocument20 pagesClick: Cambridge IGCSE Biology Extended Levelkaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- 9th Unit 1Document17 pages9th Unit 1[36] IX-B P.Vishnu Vardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Mitosis PresentationDocument24 pagesMitosis Presentationapi-267309851No ratings yet
- Avian HematologyDocument22 pagesAvian HematologyjudithNo ratings yet
- 1 PB PDFDocument15 pages1 PB PDFmimit sasmitaNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document12 pagesDay 2Maygel pasaforteNo ratings yet
- Science PPT RiDocument187 pagesScience PPT RiLara Myel BelanoNo ratings yet
- Sample Detailed Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesSample Detailed Lesson PlanImee-leen Eusebio-MateoNo ratings yet
- Biology 2010-2018: Lasu-InfoDocument53 pagesBiology 2010-2018: Lasu-InfoAhmad ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles DefinitionDocument40 pagesCell Organelles Definitionmuhammad aslam0% (1)
- Cellular Aberration Lecture 1Document93 pagesCellular Aberration Lecture 1David Dwane Art SilorioNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Biol 1700 Stephanie de La CruzDocument18 pagesAssignment 1 Biol 1700 Stephanie de La Cruzapi-439709228No ratings yet
- 9.4. CellDocument88 pages9.4. CellTUĞRUL ERGÜLNo ratings yet