Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histology 6
Histology 6
Uploaded by
amirhsheikhi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesHistology 6
Histology 6
Uploaded by
amirhsheikhiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Chapter 6:
Adipocytes specialize in concentrating triglycerides as lipid droplets.
Adipocytes are very active cells metabolically, responding to both, nervous and hormonal
stimuli.
It is recognized as an endocrine tissue (releases hormones)
Thermally insulate the body and helps cushion other cells.
2 major groups of adipose tissue:
o White adipose tissue
o Brown adipose tissue
White adipose tissue:
o Long-term energy storage
o Contains single large droplet of lipid that fills almost the entire cell
o They are called unilocular because triglyceride is stored as 1 droplet.
o Surrounded by external lamina of type 4 collagen
o Chylomicrons are brought to adipocytes first, then stored as triglycerides
o Chylomicrons are transported as VLDL and they are synthesized in intestinal epithelial
cells and transported in blood plasma and lymph.
o Lipoprotein lipase hydrolyzes VLDL and chylomicrons and then free fatty acids enter the
adipocyte by active transport and diffusion.
o The free fatty acids bund to glycerol phosphate in cell to form triglycerides which
become lipid droplet.
o Mitochondria and SER participate actively in the process of lipid uptake and storage.
o Synthesis of adipocytes is accelerated by insulin which stimulates the uptake of glucose
into adipocytes and increases the synthesis of lipoprotein lipase.
o Norepinephrine (released by postganglionic sympathetic nerves in adipose tissues)
activates hormone sensitive lipase
This lipase breaks down triglycerides at the surface of the stored lipid droplets.
Insulin inhibits hormone sensitive lipase
o White adipose tissue functions as important endocrine gland
They produce hormone leptin (satiety factor) with target cells in the
hypothalamus and other organs
Leptin regulates appetite and participates in formation of new adipose
tissues.
o Histogenesis of white adipose tissue:
Differentiate from embryonic mesenchymal cells (like fiber-producing cells)
Starts off as preadipocytes
Appearance of fibroblasts but accumulate lipid droplets in the
cytoplasm
Multilocular: had many small lipid droplets
Unilocular: has one big lipid droplet
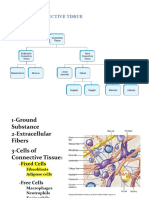
Mesenchymal
cells
Fibroblasts Preadipocyte
Differentiating
Adipocyte
Multilocular Unilocular
adipicyte adipocyte
Excess formation of adipose tissue (obesity) happens when energy intake exceeds energy
expenditure.
Brown adipose tissue:
o Constitutes 2 -5% of the newborn body weight.
o It is brown due to :
Abundant mitochondria (contains cytochrome pigment)
Large number of blood capillaries in this tissue
o They are multilocular: contain many small lipid inclusions.
o Helps in heat production.
o Smaller than white tissues
o Often packed around large capillaries
o Receive direct sympathetic innervation
o Functions of brown adipocytes:
Thermogenesis:
Production of heat without shivering
Activate hormone-sensitive lipase of adipocytes promoting hydrolysis of
triglycerides to fatty acids and glycerol.
Thermogenin or uncoupling protein:
Transmembrane proteins found in the inner membrane of
mitochondria that increase heat production.
Permits of backflow of protons previously transported to the
intermembranous space without passing through the ATP-synthase
complexes
o Histogenesis:
Also develops from embryonic mesenchyme
Same as white adipocyte tissue
o They increase in cold adaptations in adults.
You might also like
- Anatomy & Physiology SlidesDocument372 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Slidesnursereview100% (184)
- Hematology Review NotesDocument28 pagesHematology Review NoteszachNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5From EverandIntegumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Biology Lesson 9.1 WorksheetDocument3 pagesBiology Lesson 9.1 WorksheetAbhay MonNo ratings yet
- Adipose Tissue: Dr. Bernal September 2018Document3 pagesAdipose Tissue: Dr. Bernal September 2018A18- Jessa Mae DayagNo ratings yet
- Adipose TissueDocument5 pagesAdipose TissueMike GNo ratings yet
- Adipose TissueDocument1 pageAdipose TissuevallecerajamaicaNo ratings yet
- Adipose TissueDocument14 pagesAdipose TissueEKE CNo ratings yet
- Adipose TissueDocument3 pagesAdipose TissueJohn andersonNo ratings yet
- Adipose TissueDocument7 pagesAdipose Tissueİpek DemiryurekNo ratings yet
- Adipose TissueDocument19 pagesAdipose TissueMemeowwNo ratings yet
- Adipose Tissue: Differentiation of AdipocytesDocument4 pagesAdipose Tissue: Differentiation of AdipocytesErika VerastigueNo ratings yet
- Location: Transcription Factors in DifferentiationDocument4 pagesLocation: Transcription Factors in DifferentiationZyrea HarwoleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Histology ReviewerDocument3 pagesChapter 6 Histology ReviewerIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- Histoligy Homework Assignment سعيد تيسير عبد الجوادDocument15 pagesHistoligy Homework Assignment سعيد تيسير عبد الجوادSaid Taysir AbdlJawadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Adipose Tissue: Two Major Types of AdiposeDocument3 pagesChapter 6: Adipose Tissue: Two Major Types of AdiposeAALIYAH REIGN MAPUSAONo ratings yet
- Adiadipose Tissue NotesDocument5 pagesAdiadipose Tissue NotesClyde BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Adipose TissueDocument10 pagesAdipose TissueBenish jabeenNo ratings yet
- Title: Adipose Tissues.: ContentsDocument13 pagesTitle: Adipose Tissues.: ContentsGul Rehman GulNo ratings yet
- Adipose TissueDocument22 pagesAdipose TissueScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- AdiposeDocument31 pagesAdiposeCzarina David100% (1)
- How Fat Cells WorkDocument7 pagesHow Fat Cells Workapi-3709951100% (2)
- Connective TissueDocument63 pagesConnective TissueJeniNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of LipidDocument30 pagesMetabolism of Lipidnmadni827No ratings yet
- Adipose Tissue LecDocument2 pagesAdipose Tissue Lecrhona esteibarNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue EdDocument95 pagesConnective Tissue EdGirmay GebrehiwotNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue CellsDocument8 pagesConnective Tissue Cellsاسماء زياد عبدالجبارNo ratings yet
- Hist Adipose Tissue QestDocument4 pagesHist Adipose Tissue QestAnonymous t5TDwdNo ratings yet
- Adiposetissue Mahahammady 200306103322Document18 pagesAdiposetissue Mahahammady 200306103322ravikop43No ratings yet
- Written Report in Biochemistry (Lipids) : Submitted byDocument9 pagesWritten Report in Biochemistry (Lipids) : Submitted byWayne David C. PadullonNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria: Dr. Raheela Jabeen Assistant Professor Department of Biochemistry & Biotechnology, WUMDocument30 pagesMitochondria: Dr. Raheela Jabeen Assistant Professor Department of Biochemistry & Biotechnology, WUMMah Noor100% (1)
- Connective Tissue.Document31 pagesConnective Tissue.Abdo KhalafNo ratings yet
- Connective TissuesDocument45 pagesConnective TissuesAbrar osmanNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-6 - Non-Living InclusionsDocument30 pagesHDTD-B-6 - Non-Living InclusionsMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument20 pagesCell Membranejohn maphil labastillaNo ratings yet
- All of Biology Paper 1 IGCSE EdexcelDocument30 pagesAll of Biology Paper 1 IGCSE EdexcelzakariyahmurshedNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument6 pagesAnimal TissuenagasreekazaNo ratings yet
- Adipose TissueDocument16 pagesAdipose Tissueanas cabdisalaam NuurNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument25 pagesConnective TissueSumayya KabeerNo ratings yet
- Histology 5Document4 pagesHistology 5amirhsheikhiNo ratings yet
- Presented By-Mohammad Zainul PG First YearDocument56 pagesPresented By-Mohammad Zainul PG First YearLAVKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- 15.endocrine II - StudentDocument9 pages15.endocrine II - StudentLeslie CuevasNo ratings yet
- Fat and Protein MetabolismDocument2 pagesFat and Protein MetabolismMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Adipose TissuesDocument34 pagesAdipose TissuesMilcah Alia LagajetNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument58 pagesConnective TissueClive NyabutiNo ratings yet
- How Animals SurviveDocument66 pagesHow Animals SurviveDionne MagnoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE BiologyDocument47 pagesIGCSE BiologyShaguNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four NUTD231Document20 pagesChapter Four NUTD231saraqasm197No ratings yet
- Cell DR Fasiha Hussain Biochemistry DemonstratorDocument37 pagesCell DR Fasiha Hussain Biochemistry DemonstratorAqsa ArifNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument49 pagesConnective TissueMajd HusseinNo ratings yet
- Adipose - Tissues - and - Blood - PPTX Filename UTF-8''Adipose Tissues and BloodDocument63 pagesAdipose - Tissues - and - Blood - PPTX Filename UTF-8''Adipose Tissues and BloodJude AllenNo ratings yet
- Digestion Absorption and Utilization Digestion: Jun Akizaki The Power of PowerpointDocument76 pagesDigestion Absorption and Utilization Digestion: Jun Akizaki The Power of PowerpointNovitaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument32 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistryArbaan HashmiNo ratings yet
- Adipose Tissue-SsDocument13 pagesAdipose Tissue-SsAndika Yusuf RamadhanNo ratings yet
- 6 - Connective TissuesDocument65 pages6 - Connective TissuesVasty AbdulNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue Slide #1Document19 pagesConnective Tissue Slide #1Faisal AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Vi LipidsDocument5 pagesChapter Vi LipidsJohn TacordaNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Rational Drug DesignDocument25 pagesRational Drug DesignWaseem KhanNo ratings yet
- ARS - NET Previous Questions - Agricultural Biotechnology Biology Exams 4 UDocument5 pagesARS - NET Previous Questions - Agricultural Biotechnology Biology Exams 4 UvalmikisatishNo ratings yet
- Unit 2B Guided Notes 2022Document6 pagesUnit 2B Guided Notes 2022Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Neuroprotective Effects of Ginkgo Biloba ExtractDocument14 pagesNeuroprotective Effects of Ginkgo Biloba Extractcpt-n3moNo ratings yet
- Identification of Sex-Specific Molecular Markers Using Restriction Site-Associated DNA SequencingDocument12 pagesIdentification of Sex-Specific Molecular Markers Using Restriction Site-Associated DNA SequencingFernando Castro EchavezNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Dna Replication PDFDocument2 pagesEukaryotic Dna Replication PDFHughNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA (Part 1)Document36 pagesRecombinant DNA (Part 1)Peter JofilisiNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument27 pagesFinal Reportapi-340511124No ratings yet
- New Lab 3 Manual Fall 2017Document11 pagesNew Lab 3 Manual Fall 2017Kim Jae WonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 BioDocument2 pagesChapter 10 BioPaul Meyer75% (8)
- The Role of Dimethylaminoethanol in Cosmetic Dermatology: Rachel GrossmanDocument26 pagesThe Role of Dimethylaminoethanol in Cosmetic Dermatology: Rachel GrossmanLibe Palomino RivasNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Toxicology - 4th EdDocument41 pagesPharmacology Toxicology - 4th EdYorlenie Juárez100% (1)
- Embryo QuizDocument2 pagesEmbryo QuizAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Ch. 14Document153 pagesCh. 14sgarcia2156No ratings yet
- Micropara: Chapter 4 NotesDocument5 pagesMicropara: Chapter 4 NotesPatrick JuacallaNo ratings yet
- Wanger A, Chavez V, Huang R, Wahed A, Dasgupta A, Actor J. 2017. Microbiology and Molecular Diagnosis in Pathology. Camridge (US) Academic Press.Document12 pagesWanger A, Chavez V, Huang R, Wahed A, Dasgupta A, Actor J. 2017. Microbiology and Molecular Diagnosis in Pathology. Camridge (US) Academic Press.Annisa YohanesNo ratings yet
- Determinación de Proteínas Con Púrpura de Bromocresol PDFDocument7 pagesDeterminación de Proteínas Con Púrpura de Bromocresol PDFAurora ZapoteNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle DiagramsDocument2 pagesCarbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle DiagramsEdward OllingerNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Nutritional Compositions of Flame of Forest (Delonix Regia) Seeds and Seed OilDocument5 pagesChemical and Nutritional Compositions of Flame of Forest (Delonix Regia) Seeds and Seed OilAbdulrasaq OyedejiNo ratings yet
- CRISPR Screens in Colon CancerDocument7 pagesCRISPR Screens in Colon CancerInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of Life Organic Compounds: By: Ej R. Agsalda Bsbio-1Document15 pagesChemical Basis of Life Organic Compounds: By: Ej R. Agsalda Bsbio-1Ej AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Medical Genetics ItemsDocument1 pageMedical Genetics ItemsМөнхгэрэл ГанбатNo ratings yet
- RNA InterferenceDocument26 pagesRNA InterferenceAjayChandrakarNo ratings yet
- Various Expression SystemDocument15 pagesVarious Expression SystemVamsi K KuchibhotlaNo ratings yet
- WHLP StemDocument8 pagesWHLP Stemcristina maquintoNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 WW 4Document4 pagesGrade 9 WW 4JOEL MONTERDENo ratings yet
- Journal of Microbiological Methods: SciencedirectDocument7 pagesJournal of Microbiological Methods: Sciencedirectfrancis3ndourNo ratings yet
- Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews Volume 64 IssueDocument10 pagesAdvanced Drug Delivery Reviews Volume 64 IssueNirvani HarisNo ratings yet
- Yohannes BirukDocument6 pagesYohannes BirukYohannes BirukNo ratings yet