Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deciduous 1-1rdg
Deciduous 1-1rdg
Uploaded by
harshmakwana0901Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- EPA Clasificacion COSLETDocument6 pagesEPA Clasificacion COSLETSebastián BernalNo ratings yet
- 300 EDIT Dental Facts NBDE - WITH PICTURESDocument39 pages300 EDIT Dental Facts NBDE - WITH PICTURESCamellia ShahmoradiNo ratings yet
- Development of Occlusion 1 PDFDocument5 pagesDevelopment of Occlusion 1 PDFFadiShihabNo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial Prosthetics Theory and PracticeDocument305 pagesMaxillofacial Prosthetics Theory and PracticeMostafa Fayad100% (11)
- Twin Block Case ReportDocument5 pagesTwin Block Case ReportwjeelaniNo ratings yet
- 2.development 2020Document39 pages2.development 2020Mohamed Yosef MoradNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Dentition and OcclusionDocument3 pagesGrowth and Development of Dentition and OcclusionFidz Lianko100% (2)
- Dental Morphology (111 RDS) : Lab ManualDocument34 pagesDental Morphology (111 RDS) : Lab ManualNatalia CojocaruNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Primary and Permanent Teeth 1Document29 pagesDifference Between Primary and Permanent Teeth 1Bharat Kachhawaha100% (2)
- The Mixed Dentition PedodonticsDocument29 pagesThe Mixed Dentition PedodonticsFourthMolar.com100% (2)
- Development of OcclusionDocument75 pagesDevelopment of Occlusionsadaf.cmw1No ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy and Nomenclature For The RadiologistDocument11 pagesDental Anatomy and Nomenclature For The RadiologistKAREN ANAIS URGILES ESPINOZANo ratings yet
- 03 CanineDocument12 pages03 Canine蕭亦No ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy2021Document77 pagesDental Anatomy2021barrahamzawiNo ratings yet
- Miexd Dentiitno NormDocument29 pagesMiexd Dentiitno Norm陳碩璠No ratings yet
- Development of OcclusionDocument39 pagesDevelopment of Occlusiondrdeepikajoash16No ratings yet
- Chronology & MorphologyDocument30 pagesChronology & MorphologyAhsan Ul Kayum BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Chutinan Dental AnatomyDocument103 pagesDr. Chutinan Dental AnatomyAlbisladys Castellanos PujolsNo ratings yet
- Dental AnatomyDocument25 pagesDental AnatomyCésar HelenoNo ratings yet
- MUCLecture_2024_1320989Document8 pagesMUCLecture_2024_13209893adel.sob7aniNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy & Occlusion NOTESDocument7 pagesDental Anatomy & Occlusion NOTESyosman1000100% (1)
- Ortho Lec3Document13 pagesOrtho Lec3dr.h.elseoudiNo ratings yet
- Presented by Minnu.P 4th BDSDocument24 pagesPresented by Minnu.P 4th BDSMinnuNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 P 4Document5 pagesLec 5 P 4brshlwnytwaftkhr956No ratings yet
- Development of Occlusion (Seminar 1)Document47 pagesDevelopment of Occlusion (Seminar 1)Isha GargNo ratings yet
- Maxillary 2nd Premolar: Smaller Less Seldom SeenDocument16 pagesMaxillary 2nd Premolar: Smaller Less Seldom SeenAbdallah Essam Al-ZireeniNo ratings yet
- Contacts and ContoursDocument35 pagesContacts and ContoursGayathriNo ratings yet
- Morphological Difference Between Deciduous and Permanent TeethDocument19 pagesMorphological Difference Between Deciduous and Permanent TeethHaidy Mahmoud El-SanosyNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Impacted TeethDocument14 pagesAssessment of Impacted TeethAnupama Nagraj100% (1)
- Dental Anatomy - Lecture 6 Pt1+Pt2Document9 pagesDental Anatomy - Lecture 6 Pt1+Pt2Mohamed Harun B. SanohNo ratings yet
- Classifications of MalocclusionDocument3 pagesClassifications of MalocclusionLolita A. HicksNo ratings yet
- Practical Alignment of Teeth and Occlusion 1Document8 pagesPractical Alignment of Teeth and Occlusion 1Yuyeen FarhanahNo ratings yet
- Wells - OralanaDocument6 pagesWells - OralanaAlej DonesaNo ratings yet
- 5) Maxillary and Mandibular Canine MorphologiesDocument11 pages5) Maxillary and Mandibular Canine MorphologiesZahra BaniameryanNo ratings yet
- Space MaintenanceDocument17 pagesSpace MaintenanceAla StarNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument25 pagesClassificationMustafa AhmedhamdiNo ratings yet
- On ImpactionDocument44 pagesOn Impactionmesssi269No ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument4 pagesMorphologyminimayar99No ratings yet
- Classification of MalocclusionDocument58 pagesClassification of MalocclusionPranshu TomerNo ratings yet
- Development of Normal Occlusion Part 2 Copy 2Document49 pagesDevelopment of Normal Occlusion Part 2 Copy 2MSA universityNo ratings yet
- Dental AnatomyDocument14 pagesDental Anatomyheenagoswami158No ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy & Interactive 3 - D Tooth AtlasDocument16 pagesDental Anatomy & Interactive 3 - D Tooth AtlasbemaegamalielNo ratings yet
- Development of OcclusionDocument9 pagesDevelopment of OcclusionЕленаNo ratings yet
- 4 CaninesDocument9 pages4 CaninesFLORENCE GERENTENo ratings yet
- Lec 2 C Anatomical LandmarksDocument6 pagesLec 2 C Anatomical LandmarksRohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- 11 The Permanent Maxillary Molars Pocket DentistryDocument1 page11 The Permanent Maxillary Molars Pocket DentistryariipratiwiiNo ratings yet
- 300 Dental Anatomy Facts To Ace The Boards PDFDocument19 pages300 Dental Anatomy Facts To Ace The Boards PDFMihika MahandwanNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy 1Document33 pagesDental Anatomy 1dehaa100% (1)
- Dental AnatomyDocument18 pagesDental AnatomyAlbisladys Castellanos PujolsNo ratings yet
- 300 Dental Anatomy Facts - NBDEDocument13 pages300 Dental Anatomy Facts - NBDEmilagros falconNo ratings yet
- Tyson's Dental AnatomyDocument21 pagesTyson's Dental AnatomyTcdm NotesNo ratings yet
- Permanent Maxillary CanineDocument4 pagesPermanent Maxillary CanineSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Third Molar Impactions NotesDocument18 pagesMandibular Third Molar Impactions NotesJoseph John K Pothanikat100% (1)
- Dental Radiograph InterpretationDocument13 pagesDental Radiograph InterpretationGenevieve Marie MacabudbudNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Dental Anatomy: Learning Objec TivesDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Dental Anatomy: Learning Objec Tivesbalkiz mahamedNo ratings yet
- A. Definition: Literature ReviewDocument14 pagesA. Definition: Literature ReviewBramantio DiningratNo ratings yet
- 1. Dentin and its clinical significanceDocument110 pages1. Dentin and its clinical significanceRoopa BabannavarNo ratings yet
- 2017 2018 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion 1Document435 pages2017 2018 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion 1Aura UrbayoNo ratings yet
- Ortho Lec4Document9 pagesOrtho Lec4dr.h.elseoudiNo ratings yet
- 0090 Vol 27 No 1 May 2011 - 2Document92 pages0090 Vol 27 No 1 May 2011 - 2Isna Nur Inayatur RNo ratings yet
- Damon System Mechanics Four Bicuspid Extraction Deep Bite PDFDocument2 pagesDamon System Mechanics Four Bicuspid Extraction Deep Bite PDFGokul SivaNo ratings yet
- Dental Radiology An Adjunctive Aid in Age EstimationDocument5 pagesDental Radiology An Adjunctive Aid in Age EstimationalyaNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement of A Mandibular CD Wid Metal FrameworkDocument4 pagesReinforcement of A Mandibular CD Wid Metal FrameworkNajeeb UllahNo ratings yet
- Esthetic and Functional Rehabilitation of Maxillary Anterior Teeth by Richmond Crown: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesEsthetic and Functional Rehabilitation of Maxillary Anterior Teeth by Richmond Crown: A Case ReportRaghav PratapNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Oral DiseasesDocument38 pagesEpidemiology of Oral DiseasesZainab MohammadNo ratings yet
- Overcoming Compact Bone Resistance To Tooth Movement: Special ArticleDocument6 pagesOvercoming Compact Bone Resistance To Tooth Movement: Special ArticlenomanNo ratings yet
- EnamelDocument89 pagesEnamelPavanNo ratings yet
- Desensitasi 2Document7 pagesDesensitasi 2fennilubisNo ratings yet
- Dental Health Record: Department of EducationDocument1 pageDental Health Record: Department of EducationSerLem WellNo ratings yet
- Dental MaterialsDocument33 pagesDental Materialskevin1678No ratings yet
- RUHS Pre PG 2014 BDS Section II Question Paper and Answer KeyDocument18 pagesRUHS Pre PG 2014 BDS Section II Question Paper and Answer KeyAnweshaBose100% (1)
- Surgical Guide For Dental Implant Placement: PresentedDocument4 pagesSurgical Guide For Dental Implant Placement: PresentedAmy CuadraNo ratings yet
- Pt. Berito Jaya Medika - Dentsply Price List 2021: Access InstrumentDocument11 pagesPt. Berito Jaya Medika - Dentsply Price List 2021: Access InstrumentBerito Jaya MedikaNo ratings yet
- Esthetics in The Composite Resin Veneer Technique PDFDocument10 pagesEsthetics in The Composite Resin Veneer Technique PDFsolodont1No ratings yet
- Oral Histology IDEDocument765 pagesOral Histology IDEArwa Chekrouni100% (1)
- ClinicalDocument197 pagesClinicalAlondra BocanegraNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Introduction To EndodonticsDocument20 pagesLec 1 Introduction To Endodonticsبراءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- Retention and Relapse 2Document13 pagesRetention and Relapse 2Tara TeraNo ratings yet
- How To Reduce The Size of My Buccinator Muscles With Mewing - QuoraDocument1 pageHow To Reduce The Size of My Buccinator Muscles With Mewing - QuoraJan DušekNo ratings yet
- RCOS Vs ABTDocument18 pagesRCOS Vs ABTDeborah AnneNo ratings yet
- Fixed ApplainceDocument2 pagesFixed ApplainceSaravanan KanagavelNo ratings yet
- Multilink Automix BrochureDocument4 pagesMultilink Automix BrochureIvoclar Vivadent100% (2)
- Numbers DocxfinalDocument12 pagesNumbers DocxfinalSubhajit SahaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Problem Solving in Periodontology and Implantology-01Document195 pagesClinical Problem Solving in Periodontology and Implantology-01Reman DhakalNo ratings yet
- Third Molars: A Dilemma! or Is It?: Clinicians' CornerDocument6 pagesThird Molars: A Dilemma! or Is It?: Clinicians' CornerElizabeth CortésNo ratings yet
- Wave OneDocument6 pagesWave OnePudji HandayaniNo ratings yet
Deciduous 1-1rdg
Deciduous 1-1rdg
Uploaded by
harshmakwana0901Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Deciduous 1-1rdg
Deciduous 1-1rdg
Uploaded by
harshmakwana0901Copyright:
Available Formats
. 3mmar’s oral Morphology 0106 39 700 30 mahmoud_3mmar@yahoo.com !"#$/!"!
"
Deciduous teeth
F.B: Morphology-Book #42
Secretary: 0106 39 700 30 , Dr. 3mmar
chapter 4 Deciduous teeth ( 1 lecture . )
. 3mmar’s oral Morphology 0106 39 700 30 mahmoud_3mmar@yahoo.com !"#$/!"!"
- Deciduous teeth -
à Differences between permanent , Deciduous teeth :-
1- General difference : deciduous teeth differ from the permanent in the following
1. Dental formula :
2. 20 in number .
3. no premolars.
4. they are smaller in size & more consistent in shape & whitish-whiter or bluish-white ( less transparent )
than permanent teeth which is
yellowish-white to grayish white .
5. Enamel of deciduous teeth is less mineralized , more permeable so its easily worn down .
6. Enamel , dentin of deciduous are thin
7. Pulp of deciduous is proportionally larger , the pulp horns are longer .
8. they have marked constriction at the cervix so the enamel seem to bulge
rather than gradually tapering so the crown appear bulbous ( onion ) .
8. Cervical ridge is more prominent .
9. crown is shorter inciso-cervical relative to to root ( crown root ratio is 1 : 2 ).
10. crown is wider M-D relative to I-C length , even MD > IC in upper A , upper D .
ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
2- difference in anterior teeth :
1. No mamelons .
.
2. No depressions on the labial surface of the crown .
.
3. No imbrication lines ( perikymata ) at cervical third .
.
4. C.R , cinglum is more prominent( due to neck constriction )
.
5. Root is narrow M-D .
.
6. In upper central : M-D width of crown is greater than C-I length.
.
7. in lower incisors ; incisal edge lying in line with long axis (no ling inclination) ,
they are wider lab-ling than their permanent incisors
.
8. in upper canine ; cusp tip is shifted distally so M-slope > D-slope
while D-slope is longer in lower canine .
9. on lingual surface of upper canine ; Tubercle : located at center of ling ridge where cinglum merge with ling ridge
ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
chapter 4 Deciduous teeth ( lecture 1 from 2 lectures )
2
. 3mmar’s oral Morphology 0106 39 700 30 mahmoud_3mmar@yahoo.com !"#$/!"!"
3- difference in Posterior teeth :
1. Molars occlusal surfaces are shallow ( cusps are not pointed , their slopes meet at very wide obtuse angle
so the cusps are short & ridges are not prominent & depressions are not deep ) ..
2. rarely have buccal or lingual Dev. Groove however there is just depression between cusps
3. Molars crowa are shorter Cervico-occlusal , even in upper D the mesio-distal width > cervico-occlusal high .
4. Furcation area is near the cervical line so there is no easily defined root trunk .
5. Roots are thinner , selender , appear longer ( so they easier to fracture during extraction ) .
6. Roots are widely separated (diverge or flared ) to provide space for the developing premolars .
.
ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
à Chronology , sequence of eruption
Lower order Upper order
A 6m 1 7.5 m 1
B 7m 2 9m 2
C 16 m 4 19 m 4
D 12 m 3 14 m 3
E 20 m 5 24 m 5
ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
à occlusal relation between upper , lower 2nd deciduous molars ( E ) ,
their effect on occlusal relation bt upper , lower 1st permanent molars ( 6 ) .
1. Flush-terminal plane( 30% ) : the distal surfaces of upper , lower E are in the same vertical line .
6 erupt in end-to end , will shift into class 1
2. Mesial-Step terminal plane( 60%) : the distal surface of lower E is mesial to distal surface of upper E .
6 erupt directly into class 1 but its may lead to class 3
3. Distal-Step terminal plane( 10% ) : the distal surface of lower E is distal to distal surface of upper E .
6 erupt directly into class 2
ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
chapter 4 Deciduous teeth ( lecture 1 from 2 lectures )
3
. 3mmar’s oral Morphology 0106 39 700 30 mahmoud_3mmar@yahoo.com !"#$/!"!"
à Spaces between Deciduous teeth :-
1- Primate space
Def. It’s a space space located mesial to upper C , distal to lower C
Import. - utilized in reliving the crowding in the permanent teeth ,
absence of primate space may cause crowding
2- Leeway space
its the space result from difference bt combined
Def. M-D width of deciduous canines , molars
& their successors .
cause M-D width of deciduous molars > MD width of premolars .
- in Maxilla its 0.9mm for each side = 1.8mm for total arch .
Value
- in Mandible its 1.7 for each segment = 3.4mm for total arch .
1- in Maxilla : its utilized for relieve the crowding of permanent upper incisors .
Importance
2- in mandible : part of this space is utilized for relieve the crowding of permanent lower incisors and
the remaining part will be utilized by the forward movment of mandibular molars .
( may correct end-to-end relationship ‘’normal in mixed dentition’’
into a normal molar relationship `class 1` in permanent dentition *discussed latter* ) .
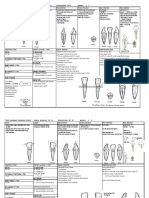
Difference in MD width between primary teeth (A) and permanent teeth (B).
Arrows indicate the mesial movement of permanent molars after loss of primary molars ,
eruption of the second permanent premolar
chapter 4 Deciduous teeth ( lecture 1 from 2 lectures )
4
. 3mmar’s oral Morphology 0106 39 700 30 mahmoud_3mmar@yahoo.com !"#$/!"!"
Upper A Upper B Lower A Lower B Upper C Lower C
is wide MD but still is wide MD but still slightly
Dimensions MD is wider than C.I high slightly less than CI less than CI
4. D-slope is longer than M-slope ( cusp tip shifted M ) .
max canine both C-I , M-D are much closer to each other .
3. the crown is : high C-I relative to M-D however in
more convex evenly convex
1- the crown is : slightly larger in all dimensions
M,D than than convex
1- the crown is : smaller in all dimensions
permanent central permanent central
3- DIA , MIA are more rounded hwoever
Outlines
Cervical Convex root-wise Convex root-wise Convex root-wise
D-outline is shorter than M-outline .
2- the crown is : Wider CI than MD . .
( the most difference bt the two teeth ) .
2- incisal edge : has distal sloping so
1. the crown is : narrower Lab-lingual
( narrower MD & shorter CI ) .
flat , sloped toward the distal formed of
Labial S.
Incisal flat
after wear 1. M-slope: longer
( longer CI & wider MD ) .
2. the crown is : narrower M-D .
DIA is more rounded DIA , MIA are sharp 2. D-slope :
than MIA 3. cusp tip : shifted distally
DIA is more rounded
smooth , flatter than
Shape is smooth , convex
permanent incisors
4- DIA is rounded
S. anatomy
- Prominent C.R - Prominent C.R - Prominent C.R
Shape.
- No mamelons - No mamelons
Depr. No dev. depressions No dev. depressions
Upper A Upper B Lower A Lower B Upper C Lower C
Dimensions the same as labial but the same as labial but the same as labial but
5- all elevations , depressions
& Outlines reverse , narrower ? reverse , narrower ? reverse , narrower ?
6- lingual fossa is little deeper
4- MRs are more prominent.
Shape smooth & smooth & smooth &
are less prominent
shifted distally .
has convexity , concavity has convexity , concavity has convexity , concavity
5- cinglum is little larger ,
5- lingual fossa is deeper
Lingual S.
Elev. 1- Prominent cinglum: 1- well defined cinglum , 1- Prominent cinglum .
S. anatomy
extend more incisal than its centeralized . 2. Prominent MMR , DMR
permanent central. 2. Less defined MMR , DMR 3. Prominent lingual ridge .
2. Prominent MMR , DMR
4. Tubercle : located at center
of ling ridge where cinglum
merge with ling ridge
Depr. lingual fossae is deeper lingual fossae is shallow ML , DL fossae
chapter 4 Deciduous teeth ( 1 lecture . )
. 3mmar’s oral Morphology 0106 39 700 30 mahmoud_3mmar@yahoo.com !"#$/!"!"
Upper A Upper B Lower A Lower B Upper C Lower C
à similar permanent central but differ in: à the most outstanding features are: à Lab.Ling : thicker than max incisors.
Mesial
1- Lab.Ling : is relatively wider . 1- incisal edge : is in line with center à Cervical line : lesscurved than
narrower ,
Crown is
smaller
smaller
longer
2- Cervical line : is less curved . of the root max incisors
2- greater lab-lingual width
Distal
à similar to mesial aspect but differ in: à similar to mesial aspect but differ in: à similar to mesial aspect but differ in:
Cervical line is less curved Cervical line is less curved Cervical line is less curved
à most noticeabl feature is : à MD , Lab-Ling is nearly equal . à Geometry is rhomboid
Incisal S.
------------
------------
------------
crown MD is wider tha Lab-Ling. but more rounded than
à incisal edge is straight , divide permanent canine .
à incisal edge is straight , divide the crown into 2 equal lab , ling half
crown into 2 equal lab , ling half .
à Single conical root with à Single conical roots &
longer &
pointed
shorter
distally
curved
apex is
Root
more
rounded apex which is its convex from lab , lingual &
long relative to the crown its somehat flat from proximals
than in permanent central
chapter 4 Deciduous teeth ( lecture 1 from 2 lectures )
6
You might also like
- EPA Clasificacion COSLETDocument6 pagesEPA Clasificacion COSLETSebastián BernalNo ratings yet
- 300 EDIT Dental Facts NBDE - WITH PICTURESDocument39 pages300 EDIT Dental Facts NBDE - WITH PICTURESCamellia ShahmoradiNo ratings yet
- Development of Occlusion 1 PDFDocument5 pagesDevelopment of Occlusion 1 PDFFadiShihabNo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial Prosthetics Theory and PracticeDocument305 pagesMaxillofacial Prosthetics Theory and PracticeMostafa Fayad100% (11)
- Twin Block Case ReportDocument5 pagesTwin Block Case ReportwjeelaniNo ratings yet
- 2.development 2020Document39 pages2.development 2020Mohamed Yosef MoradNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Dentition and OcclusionDocument3 pagesGrowth and Development of Dentition and OcclusionFidz Lianko100% (2)
- Dental Morphology (111 RDS) : Lab ManualDocument34 pagesDental Morphology (111 RDS) : Lab ManualNatalia CojocaruNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Primary and Permanent Teeth 1Document29 pagesDifference Between Primary and Permanent Teeth 1Bharat Kachhawaha100% (2)
- The Mixed Dentition PedodonticsDocument29 pagesThe Mixed Dentition PedodonticsFourthMolar.com100% (2)
- Development of OcclusionDocument75 pagesDevelopment of Occlusionsadaf.cmw1No ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy and Nomenclature For The RadiologistDocument11 pagesDental Anatomy and Nomenclature For The RadiologistKAREN ANAIS URGILES ESPINOZANo ratings yet
- 03 CanineDocument12 pages03 Canine蕭亦No ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy2021Document77 pagesDental Anatomy2021barrahamzawiNo ratings yet
- Miexd Dentiitno NormDocument29 pagesMiexd Dentiitno Norm陳碩璠No ratings yet
- Development of OcclusionDocument39 pagesDevelopment of Occlusiondrdeepikajoash16No ratings yet
- Chronology & MorphologyDocument30 pagesChronology & MorphologyAhsan Ul Kayum BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Chutinan Dental AnatomyDocument103 pagesDr. Chutinan Dental AnatomyAlbisladys Castellanos PujolsNo ratings yet
- Dental AnatomyDocument25 pagesDental AnatomyCésar HelenoNo ratings yet
- MUCLecture_2024_1320989Document8 pagesMUCLecture_2024_13209893adel.sob7aniNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy & Occlusion NOTESDocument7 pagesDental Anatomy & Occlusion NOTESyosman1000100% (1)
- Ortho Lec3Document13 pagesOrtho Lec3dr.h.elseoudiNo ratings yet
- Presented by Minnu.P 4th BDSDocument24 pagesPresented by Minnu.P 4th BDSMinnuNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 P 4Document5 pagesLec 5 P 4brshlwnytwaftkhr956No ratings yet
- Development of Occlusion (Seminar 1)Document47 pagesDevelopment of Occlusion (Seminar 1)Isha GargNo ratings yet
- Maxillary 2nd Premolar: Smaller Less Seldom SeenDocument16 pagesMaxillary 2nd Premolar: Smaller Less Seldom SeenAbdallah Essam Al-ZireeniNo ratings yet
- Contacts and ContoursDocument35 pagesContacts and ContoursGayathriNo ratings yet
- Morphological Difference Between Deciduous and Permanent TeethDocument19 pagesMorphological Difference Between Deciduous and Permanent TeethHaidy Mahmoud El-SanosyNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Impacted TeethDocument14 pagesAssessment of Impacted TeethAnupama Nagraj100% (1)
- Dental Anatomy - Lecture 6 Pt1+Pt2Document9 pagesDental Anatomy - Lecture 6 Pt1+Pt2Mohamed Harun B. SanohNo ratings yet
- Classifications of MalocclusionDocument3 pagesClassifications of MalocclusionLolita A. HicksNo ratings yet
- Practical Alignment of Teeth and Occlusion 1Document8 pagesPractical Alignment of Teeth and Occlusion 1Yuyeen FarhanahNo ratings yet
- Wells - OralanaDocument6 pagesWells - OralanaAlej DonesaNo ratings yet
- 5) Maxillary and Mandibular Canine MorphologiesDocument11 pages5) Maxillary and Mandibular Canine MorphologiesZahra BaniameryanNo ratings yet
- Space MaintenanceDocument17 pagesSpace MaintenanceAla StarNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument25 pagesClassificationMustafa AhmedhamdiNo ratings yet
- On ImpactionDocument44 pagesOn Impactionmesssi269No ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument4 pagesMorphologyminimayar99No ratings yet
- Classification of MalocclusionDocument58 pagesClassification of MalocclusionPranshu TomerNo ratings yet
- Development of Normal Occlusion Part 2 Copy 2Document49 pagesDevelopment of Normal Occlusion Part 2 Copy 2MSA universityNo ratings yet
- Dental AnatomyDocument14 pagesDental Anatomyheenagoswami158No ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy & Interactive 3 - D Tooth AtlasDocument16 pagesDental Anatomy & Interactive 3 - D Tooth AtlasbemaegamalielNo ratings yet
- Development of OcclusionDocument9 pagesDevelopment of OcclusionЕленаNo ratings yet
- 4 CaninesDocument9 pages4 CaninesFLORENCE GERENTENo ratings yet
- Lec 2 C Anatomical LandmarksDocument6 pagesLec 2 C Anatomical LandmarksRohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- 11 The Permanent Maxillary Molars Pocket DentistryDocument1 page11 The Permanent Maxillary Molars Pocket DentistryariipratiwiiNo ratings yet
- 300 Dental Anatomy Facts To Ace The Boards PDFDocument19 pages300 Dental Anatomy Facts To Ace The Boards PDFMihika MahandwanNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy 1Document33 pagesDental Anatomy 1dehaa100% (1)
- Dental AnatomyDocument18 pagesDental AnatomyAlbisladys Castellanos PujolsNo ratings yet
- 300 Dental Anatomy Facts - NBDEDocument13 pages300 Dental Anatomy Facts - NBDEmilagros falconNo ratings yet
- Tyson's Dental AnatomyDocument21 pagesTyson's Dental AnatomyTcdm NotesNo ratings yet
- Permanent Maxillary CanineDocument4 pagesPermanent Maxillary CanineSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Third Molar Impactions NotesDocument18 pagesMandibular Third Molar Impactions NotesJoseph John K Pothanikat100% (1)
- Dental Radiograph InterpretationDocument13 pagesDental Radiograph InterpretationGenevieve Marie MacabudbudNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Dental Anatomy: Learning Objec TivesDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Dental Anatomy: Learning Objec Tivesbalkiz mahamedNo ratings yet
- A. Definition: Literature ReviewDocument14 pagesA. Definition: Literature ReviewBramantio DiningratNo ratings yet
- 1. Dentin and its clinical significanceDocument110 pages1. Dentin and its clinical significanceRoopa BabannavarNo ratings yet
- 2017 2018 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion 1Document435 pages2017 2018 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion 1Aura UrbayoNo ratings yet
- Ortho Lec4Document9 pagesOrtho Lec4dr.h.elseoudiNo ratings yet
- 0090 Vol 27 No 1 May 2011 - 2Document92 pages0090 Vol 27 No 1 May 2011 - 2Isna Nur Inayatur RNo ratings yet
- Damon System Mechanics Four Bicuspid Extraction Deep Bite PDFDocument2 pagesDamon System Mechanics Four Bicuspid Extraction Deep Bite PDFGokul SivaNo ratings yet
- Dental Radiology An Adjunctive Aid in Age EstimationDocument5 pagesDental Radiology An Adjunctive Aid in Age EstimationalyaNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement of A Mandibular CD Wid Metal FrameworkDocument4 pagesReinforcement of A Mandibular CD Wid Metal FrameworkNajeeb UllahNo ratings yet
- Esthetic and Functional Rehabilitation of Maxillary Anterior Teeth by Richmond Crown: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesEsthetic and Functional Rehabilitation of Maxillary Anterior Teeth by Richmond Crown: A Case ReportRaghav PratapNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Oral DiseasesDocument38 pagesEpidemiology of Oral DiseasesZainab MohammadNo ratings yet
- Overcoming Compact Bone Resistance To Tooth Movement: Special ArticleDocument6 pagesOvercoming Compact Bone Resistance To Tooth Movement: Special ArticlenomanNo ratings yet
- EnamelDocument89 pagesEnamelPavanNo ratings yet
- Desensitasi 2Document7 pagesDesensitasi 2fennilubisNo ratings yet
- Dental Health Record: Department of EducationDocument1 pageDental Health Record: Department of EducationSerLem WellNo ratings yet
- Dental MaterialsDocument33 pagesDental Materialskevin1678No ratings yet
- RUHS Pre PG 2014 BDS Section II Question Paper and Answer KeyDocument18 pagesRUHS Pre PG 2014 BDS Section II Question Paper and Answer KeyAnweshaBose100% (1)
- Surgical Guide For Dental Implant Placement: PresentedDocument4 pagesSurgical Guide For Dental Implant Placement: PresentedAmy CuadraNo ratings yet
- Pt. Berito Jaya Medika - Dentsply Price List 2021: Access InstrumentDocument11 pagesPt. Berito Jaya Medika - Dentsply Price List 2021: Access InstrumentBerito Jaya MedikaNo ratings yet
- Esthetics in The Composite Resin Veneer Technique PDFDocument10 pagesEsthetics in The Composite Resin Veneer Technique PDFsolodont1No ratings yet
- Oral Histology IDEDocument765 pagesOral Histology IDEArwa Chekrouni100% (1)
- ClinicalDocument197 pagesClinicalAlondra BocanegraNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Introduction To EndodonticsDocument20 pagesLec 1 Introduction To Endodonticsبراءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- Retention and Relapse 2Document13 pagesRetention and Relapse 2Tara TeraNo ratings yet
- How To Reduce The Size of My Buccinator Muscles With Mewing - QuoraDocument1 pageHow To Reduce The Size of My Buccinator Muscles With Mewing - QuoraJan DušekNo ratings yet
- RCOS Vs ABTDocument18 pagesRCOS Vs ABTDeborah AnneNo ratings yet
- Fixed ApplainceDocument2 pagesFixed ApplainceSaravanan KanagavelNo ratings yet
- Multilink Automix BrochureDocument4 pagesMultilink Automix BrochureIvoclar Vivadent100% (2)
- Numbers DocxfinalDocument12 pagesNumbers DocxfinalSubhajit SahaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Problem Solving in Periodontology and Implantology-01Document195 pagesClinical Problem Solving in Periodontology and Implantology-01Reman DhakalNo ratings yet
- Third Molars: A Dilemma! or Is It?: Clinicians' CornerDocument6 pagesThird Molars: A Dilemma! or Is It?: Clinicians' CornerElizabeth CortésNo ratings yet
- Wave OneDocument6 pagesWave OnePudji HandayaniNo ratings yet