Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energy, Work & Power Th Qs Worksheet
Energy, Work & Power Th Qs Worksheet
Uploaded by
omaribraheimabdullahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Energy, Work & Power Th Qs Worksheet
Energy, Work & Power Th Qs Worksheet
Uploaded by
omaribraheimabdullahCopyright:
Available Formats
Beaconhouse School System
PHYSICS WORKSHEET
NAME: _______________________________ DATE: _________________
TOPIC: ENERGY, WORK & POWER
1. Electricity is distributed from wind turbines to homes and industry. (0625_s23_qp_31)
(a) Statements A–F describe the main stages in the transfer of energy from the Sun to electrical energy in
a wind turbine generator.
The statements A–F are not in the correct order.
A. Air moves from regions of high pressure to regions of low pressure.
B. The turbine blades turn a generator.
C. Energy from the Sun heats the atmosphere unevenly.
D. Uneven heating of the atmosphere produces regions of different atmospheric pressure.
E. The generator produces electrical energy.
F. Moving air turns the turbine blades.
Complete the flow chart to describe how a wind turbine uses energy from the Sun to generate
electrical energy. Insert the missing letters in the empty boxes.
[3]
(b) State two disadvantages, apart from cost, of using wind turbines to produce electrical energy for
homes and industry.
1 ............................................................................................................................................................
2 .......................................................................................................................................................... [2]
2. A student uses an electric motor to lift a load. Fig. 2.1 shows the arrangement. (0625_s23_qp_31)
Prepared By: M. Kamran, Beaconhouse School System (BMI-B), H-8/4, Islamabad.
(a) (i) The motor exerts a force of 25 N on the load. It lifts the load a vertical distance of 2.0 m.
Calculate the work done by the motor on the load.
work done on the load = ...................................................... J [3]
(ii) State the useful energy output of the electric motor when it lifts the load 2.0 m.
useful energy output = ...................................................... J [1]
(iii) The useful energy output of the motor is less than the energy input to the motor.
Explain why the useful energy output is less than the energy input.
.............................................................................................................................................................
………………………….................................................................................................................... [2]
(b) The student uses the motor to lift a different load. The motor does 80 J of work when it lifts this load. It
takes 5.0 s to lift the load.
Calculate the power output of the electric motor.
power output = ..................................................... W [3]
3. A student has a battery-powered torch. Fig. 3.1 shows the torch. (0625_s23_qp_32)
(a) Fig. 3.2 shows the energy transfers when the torch is switched on. The diagram is incomplete.
Show the energy transfers in the torch by completing the labels on Fig. 3.2. J [3]
(b) The weight of the torch is 8.5 N. The student lifts the torch a vertical distance of 0.80 m to place it on a
shelf.
Calculate the work done on the torch by the student.
work done = ...................................................... J [3]
Prepared By: M. Kamran, Beaconhouse School System (BMI-B), H-8/4, Islamabad.
4. Fig. 2.1 shows an engineer working with wind turbines. (0625_s23_qp_33)
(a) Complete the sentences describing how electrical power is generated by energy in the wind.
(i) The source of the wind energy is ................................................................................................. . [1]
(ii) When the blades turn, electrical power is generated in the ......................................................... . [1]
(b) Describe two advantages, apart from cost, of generating electrical power by using wind turbines
compared with using a coal-fired power station.
1 ...............................................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................................................
2 ................................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................................. [2]
5. A student catches a cricket ball. The speed of the ball immediately before it is caught is 18 m / s. The
mass of the cricket ball is 160 g. (0625_s23_qp_42)
Calculate the kinetic energy stored in the cricket ball immediately before it is caught.
kinetic energy = ......................................................... [3]
6. Fig. 1.1 shows a helicopter which is stationary at a height of 1500 m above the ground.
(0625_s23_qp_42)
The mass of the helicopter is 3200 kg.
Calculate the change in the gravitational potential energy of the helicopter as it rises from the ground to
1500 m.
change in gravitational potential energy = ......................................................... [2]
Prepared By: M. Kamran, Beaconhouse School System (BMI-B), H-8/4, Islamabad.
7. (a) State two energy resources for which the Sun is not the main source. (0625_s23_qp_43)
1 ..............................................................................................................................................................
2 .......................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(b) State and explain whether each of the following methods of electrical power generation is renewable.
(i) power generation in a nuclear power station
statement ..........................................................................................................................................
explanation .......................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(ii) power generation from waves in the sea
statement .........................................................................................................................................
explanation .......................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................... [2]
8. Fig. 4.1 shows an electric motor and pulley wheel being used to raise a load M. The electric motor uses a
belt to turn the pulley wheel. (0625_s22_qp_31)
When the electric motor lifts the load, it transfers energy. Fig. 4.2 shows the energy transfers. Write on
Fig. 4.2 to complete the label in each box. The first label is done for you.
[3]
9. (a) Describe how a wind turbine generates electricity from energy in the wind. (0625_s22_qp_31)
...................................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................................. [3]
Prepared By: M. Kamran, Beaconhouse School System (BMI-B), H-8/4, Islamabad.
(b) Apart from cost, state two advantages of generating electricity using wind turbines compared with
using a power station that burns coal.
1. ...............................................................................................................................................................
2. ………............................................................................................................................................... [2]
(c) Apart from cost, state two disadvantages of generating electricity using wind turbines compared with
using a power station that burns coal.
1. ..............................................................................................................................................................
2. ………............................................................................................................................................... [2]
10. Fig. 4.1 shows parts of a coal-fired power station. (0625_s22_qp_32)
(a) (i) State the names of the parts of the power station labelled X and Y.
X .........................................................................................................................................................
Y ..................................................................................................................................................... [2]
(ii) Describe two useful energy transfers in this power station.
1. .........................................................................................................................................................
2. .................................................................................................................................................... [2]
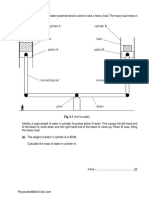
11. Fig. 2.1 shows two identical metal blocks, A and B, being lifted 3.0 m from ground level. Block A is lifted by
a motor. Block B is lifted by a person. (0625_s22_qp_33)
Prepared By: M. Kamran, Beaconhouse School System (BMI-B), H-8/4, Islamabad.
(a) Complete the following sentences.
(i) As the motor starts turning, it usefully transfers ............................................................ energy to
......................................................... energy. [2]
(ii) Both blocks gain ................................................................ energy. [1]
(b) Both blocks are lifted at the same steady speed. The blocks are then held at a height of 3.0 m.
(i) Compare the energy gained by block A with the energy gained by block B.
........................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(ii) Explain why the energy input to the motor is more than the energy gained by block A.
.............................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................................ [2]
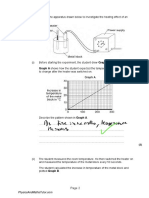
(iii) An engineer determines the power output of the motor.
State the three measurements that the engineer needs to determine the power output of the
motor.
1. ........................................................................................................................................................
2. .........................................................................................................................................................
3. .................................................................................................................................................... [2]
12. Fig. 1.1 shows an electrically powered bicycle. (0625_s22_qp_42)
When fully charged, the battery can deliver a power of 600 W for 60 min.
(a) (i) Calculate the energy, in joules, stored in the battery when fully charged.
energy = ...................................................... J [3]
(ii) State the form of energy stored by the battery. .............................................................................. [1]
(b) The bicycle has a motor with an electrical input power of 250 W.
Calculate the time for which the battery can power the bicycle.
time = ......................................................... [2]
Prepared By: M. Kamran, Beaconhouse School System (BMI-B), H-8/4, Islamabad.
(c) Consider this bicycle compared to a small motorcycle.
State two environmental benefits of the electrically powered bicycle.
1. ...............................................................................................................................................................
2. .......................................................................................................................................................... [2]
13. Water is held behind a dam in a hydroelectric power scheme. (0625_s22_qp_43)
(a) State the main form of energy stored in the water behind the dam.
.............................................................................................................................................................. [1]
(b) The water is released from the dam and falls a vertical height of 410 m at a rate of 480 kg / s.
Calculate the rate at which energy is transferred by the falling water.
rate of energy transfer = ......................................................... [3]
(c) Hydroelectric energy is a renewable form of energy.
(i) State one disadvantage of hydroelectric power schemes.
........................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(ii) State one other renewable source of energy.
........................................................................................................................................................ [1]
Prepared By: M. Kamran, Beaconhouse School System (BMI-B), H-8/4, Islamabad.
3
Prepared By: M. Kamran, Beaconhouse School System (BMI-B), H-8/4, Islamabad.
10
11
12
13
Prepared By: M. Kamran, Beaconhouse School System (BMI-B), H-8/4, Islamabad.
You might also like
- Poly Hub - 1 MWP Ground Mounted Solar Project QuotationDocument22 pagesPoly Hub - 1 MWP Ground Mounted Solar Project Quotationchander100% (1)
- Energy Work Power ProblemsDocument4 pagesEnergy Work Power ProblemsNudratNo ratings yet
- Past PaperDocument45 pagesPast PaperFATIMA ABDULHUSAIN ISA ABDULLANo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - TestDocument7 pagesUnit 4 - Testevioktavianti260619No ratings yet
- energy_resources_-_slm_240521_143156Document11 pagesenergy_resources_-_slm_240521_143156dearmissporterNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgCoIny7DX7dmZo0RMK OCe IbSU80H19mtVrNVrCHGYHpJrYXILm3ceenGzNf5INzwoVjfp5 F4Iunspp6c70hNyk12xHxRtCVznXFhluCkOF3 p25skFY9P1Fgm1KSIjrYI WbjADpgWaqiMJ0V9hVQdUDdrwUs L3jADocument8 pagesACFrOgCoIny7DX7dmZo0RMK OCe IbSU80H19mtVrNVrCHGYHpJrYXILm3ceenGzNf5INzwoVjfp5 F4Iunspp6c70hNyk12xHxRtCVznXFhluCkOF3 p25skFY9P1Fgm1KSIjrYI WbjADpgWaqiMJ0V9hVQdUDdrwUs L3jArakibhossain.official1992No ratings yet
- Assessment April 18Document7 pagesAssessment April 18wajeehmohsin96No ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Energy) PDFDocument7 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Energy) PDFMuhammad ObaidullahNo ratings yet
- 1.7 WK 5 TheoryDocument10 pages1.7 WK 5 TheoryMaira setiaNo ratings yet
- Y10 Worksheet For Revision (Energy)Document7 pagesY10 Worksheet For Revision (Energy)Nisha zehraNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 03 QP PDFDocument11 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 03 QP PDFWai HponeNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 04 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 04 QPTran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument19 pagesPhysicsArsham AfzalNo ratings yet
- National & Global Energy Resources 2 QPDocument15 pagesNational & Global Energy Resources 2 QPEman RizwanNo ratings yet
- p1 Conservation of Energy - Exam QsDocument29 pagesp1 Conservation of Energy - Exam QsKimberly OburuNo ratings yet
- Igcse C Energy Resources and Enenrgy TransfersDocument13 pagesIgcse C Energy Resources and Enenrgy TransfersaliNo ratings yet
- Energy and Thermal Extra Questions PDFDocument29 pagesEnergy and Thermal Extra Questions PDFsib menoNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 05 QPDocument9 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 05 QPRahat RizwanNo ratings yet
- Physics Assessment Grade 10Document7 pagesPhysics Assessment Grade 10Steven ShemdoeNo ratings yet
- 1.7 WK 3 TheoryDocument12 pages1.7 WK 3 TheoryMaira setiaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Quantities WorksheetDocument10 pagesElectrical Quantities WorksheetMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- National - Global Energy Resources 2 QPDocument15 pagesNational - Global Energy Resources 2 QPGbenga AjibikeNo ratings yet
- 8.2 PowerDocument14 pages8.2 PowerVictor WuNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Energy HDocument15 pagesTopic 1 Energy HJosephineNo ratings yet
- Efficiency 1 QP (1) 222222222222Document12 pagesEfficiency 1 QP (1) 222222222222DumpsterFireGamingNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Question Paper (Chapter 4 - Force and Energy)Document6 pagesIGCSE Physics Question Paper (Chapter 4 - Force and Energy)Yan Naing SoeNo ratings yet
- Draft 11 12 1 Lum Test 2Document12 pagesDraft 11 12 1 Lum Test 2SpidocadoNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power ERDocument6 pagesEnergy, Work & Power EREman Gurmani100% (2)
- Work Power and Energy FinalDocument10 pagesWork Power and Energy FinalAnki AccountNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument29 pagesMomentumemaantejani10No ratings yet
- Physics Assessment Grade 10Document7 pagesPhysics Assessment Grade 10Steven ShemdoeNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism 6 - 5 MarkerDocument35 pagesElectricity and Magnetism 6 - 5 MarkerLalit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 1 1-QPDocument8 pages1 1-QPQasim BilalNo ratings yet
- Assesssment TheoryDocument3 pagesAssesssment TheoryZubairHassanNo ratings yet
- P3.1 GPE and KE QuestionsDocument8 pagesP3.1 GPE and KE QuestionsAndreas LambriasNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument14 pagesPhysicsKrishan BalajiNo ratings yet
- P3.2 Energy Resources QuestionsDocument14 pagesP3.2 Energy Resources QuestionsAndreas LambriasNo ratings yet
- Set 61 - Chapter 1Document25 pagesSet 61 - Chapter 1lelon81No ratings yet
- Energy Conversion WS-1Document8 pagesEnergy Conversion WS-1ekagra.fuloriaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticeDocument27 pagesIGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticealfaazmcsNo ratings yet
- G481 Module 3 Work and Energy QuestionsDocument14 pagesG481 Module 3 Work and Energy QuestionsAmberNo ratings yet
- 1.7 WK 4 TheoryDocument11 pages1.7 WK 4 TheoryMaira setiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - TestDocument5 pagesUnit 2 - Testevioktavianti260619No ratings yet
- P1 3 The Usefulness of Electrical Appliances StandDocument59 pagesP1 3 The Usefulness of Electrical Appliances StandjesudassajNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power Questions: Physics AS (Unit1) Work Sheet-4 TopicDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power Questions: Physics AS (Unit1) Work Sheet-4 Topicmomentum bdNo ratings yet
- Phy Worksheet IG 3 Phase 2Document6 pagesPhy Worksheet IG 3 Phase 2Umair RazaNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power PDFDocument11 pagesEnergy, Work & Power PDFyolanda gaoliNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Energy F PDFDocument16 pagesTopic 1 Energy F PDFvliaseNo ratings yet
- Safari PDFDocument13 pagesSafari PDFHussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Igcse Physics c9 Prac Questions MSDocument6 pagesIgcse Physics c9 Prac Questions MShuxxiNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and Power - Practice WorksheetDocument6 pagesWork Energy and Power - Practice WorksheetjollykeiyonaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-03 at 9.41.01 PMDocument100 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-03 at 9.41.01 PM8f7cbjgh6vNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/43Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/43Krisha ElangovanNo ratings yet
- 2023 Specimen Paper 4Document16 pages2023 Specimen Paper 4Olanibi GratitudeNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - TestDocument8 pagesUnit 5 - Testevioktavianti260619No ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 09 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 09 QPRahat RizwanNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 09 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 09 QP-Samra-No ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 09 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 09 QPmexicohunt6No ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 09 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 09 QPItz MeNo ratings yet
- GertDocument20 pagesGertSuvdaa SanjaanyamNo ratings yet
- Alternator Clutch Pulley Designs: ISSUE 03.2010 ISSUE 02.2011Document4 pagesAlternator Clutch Pulley Designs: ISSUE 03.2010 ISSUE 02.2011venothNo ratings yet
- G For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of TheDocument6 pagesG For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of Theክበር ተመስጌንNo ratings yet
- 00 Ytc MR - Tre 001 EngDocument81 pages00 Ytc MR - Tre 001 EngJessica RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Blowby AcertDocument14 pagesBlowby AcertWilbort Encomenderos RuizNo ratings yet
- Top Gun I-ARC 180Document9 pagesTop Gun I-ARC 180Tom PleysierNo ratings yet
- Ecrotek Queen Cell Incubator User ManualDocument3 pagesEcrotek Queen Cell Incubator User ManualMirelaMilan100% (1)
- Newest Catalog of Solar System From AnernDocument28 pagesNewest Catalog of Solar System From AnernTomás SastreNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Minimum Ignition Energy On DiDocument8 pagesDetermination of The Minimum Ignition Energy On Dieky susilowatiNo ratings yet
- DG PresentationDocument19 pagesDG Presentationalbert rajNo ratings yet
- 01 FLP-1 by Doctor Biology 03333354576Document14 pages01 FLP-1 by Doctor Biology 03333354576Aashir Ali AyubNo ratings yet
- Sparks 19965Document49 pagesSparks 19965Marciel Souza CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- 40K-PRV GDDocument2 pages40K-PRV GDtojetechNo ratings yet
- Name of The Work:-Providing MPWS Scheme To Acharya N. G. Ranga Agricultural University in LAM, Village in Tadikonda MandalDocument3 pagesName of The Work:-Providing MPWS Scheme To Acharya N. G. Ranga Agricultural University in LAM, Village in Tadikonda MandalPamula RaviNo ratings yet
- Honeywell Valve Selection GuideDocument58 pagesHoneywell Valve Selection GuideYaz100% (2)
- Holophane Outdoor Substation 04252 Series Brochure 1971Document2 pagesHolophane Outdoor Substation 04252 Series Brochure 1971Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Bunker CalculationDocument10 pagesBunker CalculationNimesh PereraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document25 pagesChapter 5batraz79No ratings yet
- 02 SEP671 REL670 Exercise 1 Distance Protection CharacteristicsDocument26 pages02 SEP671 REL670 Exercise 1 Distance Protection CharacteristicsMarcos Casanova LopezNo ratings yet
- AbcdDocument5 pagesAbcdkumarchaturvedulaNo ratings yet
- Jest QuestionDocument16 pagesJest QuestionThirumugam SNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument3 pagesProblem SetSrikara SNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Wire EdmDocument33 pagesPresentation On Wire EdmArpit HalaniNo ratings yet
- Schneider Recloser, Load Break Switch, Sectionaliser 2902134 PDFDocument10 pagesSchneider Recloser, Load Break Switch, Sectionaliser 2902134 PDFSanjay BhattNo ratings yet
- Load Line MeasurementDocument1 pageLoad Line Measurementfalcon_developmentNo ratings yet
- Plot No. 1907, Phase-II, G.I.D.C., Industrial Estate, Chhatral, Dist: Gandhinagar, Gujarat (INDIA) Pin: 382729Document2 pagesPlot No. 1907, Phase-II, G.I.D.C., Industrial Estate, Chhatral, Dist: Gandhinagar, Gujarat (INDIA) Pin: 382729andres gomezNo ratings yet
- CHEM-E-CAR - PEM FUEL CELL 250 WATT - UnlockedDocument133 pagesCHEM-E-CAR - PEM FUEL CELL 250 WATT - UnlockedAdilanuruldmkNo ratings yet
- Cel Approach Abaqus Explicit Bird Strike Analysis 2010 FDocument14 pagesCel Approach Abaqus Explicit Bird Strike Analysis 2010 FmastarekNo ratings yet
- 1 6 Guided Notes TE Electron ConfigurationDocument10 pages1 6 Guided Notes TE Electron ConfigurationNor IzaNo ratings yet
- Study of Coal Based Thermal Power PlantDocument20 pagesStudy of Coal Based Thermal Power PlantNikita JakhodiaNo ratings yet