Professional Documents
Culture Documents
onthicuoikimain-2
onthicuoikimain-2
Uploaded by
VoMinh Tu AnhCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
onthicuoikimain-2
onthicuoikimain-2
Uploaded by
VoMinh Tu AnhCopyright:
Available Formats
Operating principle of resistance temperature sensor (RTD sensor) Principle of differential pressure sensor
The operating principle of the resistance temperature detector (RTD) sensor is to convert the temperature A differential pressure sensor has two pressure inputs marked as (+) and (–), corresponding to High and
being measured into electrical resistance. When the temperature at the measurement end of the RTD sensor Low, respectively. The higher pressure is connected to the (+) side and the lower pressure to the (–) side.
changes, a resistance will appear at the other end of the sensor. This forms the basis for measuring Inside the differential pressure sensor, there is a membrane layer containing electrodes arranged neatly.
temperature with the RTD sensor. By measuring that resistance value, we can infer the temperature value. When this membrane is deformed, it leads to changes in the voltage across these electrodes. The
Thermocouple sensor deformation of the membrane will shift left or right depending on the magnitude of the pressure applied,
The thermocouple sensor, also known as a thermocouple, is an important and widely used device in the field which corresponds to either a positive or negative differential pressure. This value represents the pressure
of temperature measurement. difference between the high and low pressure inputs. The differential value is then converted into an
The operating principle of the thermocouple sensor is based on the Seebeck effect. When two different electrical current ranging from 4 to 20mA, depending on the settings configured by the user for the
metals are welded together at their junction (measuring junction), it creates a voltage (electromotive force). pressure sensor.
When the temperature at the junction changes, this temperature difference causes the movement of electrons, Piezoresistive Pressure Sensor (cảm biến áp suất sử dụng điện trở)
leading to the creation of voltage across the ends of the thermocouple sensor wires. The working principle of the piezoresistive sensor is based on the deformation of the membrane structure
Operating principle of capacitive pressure sensor: (when pressure is applied) being converted into an electrical signal through piezoresistive elements
The operating principle of a capacitive pressure sensor involves two electrodes separated by a space embedded on it. The pressure to be measured is sensed by the silicon chip through the membrane and
containing air or a dielectric material. When the surrounding pressure changes, this pressure affects the silicone oil. The chip is powered through an insulated glass feedthrough and connecting wires. The output
sensor membrane, altering the distance between the two electrodes. This change in distance alters the pressure signal is measured in millivolts (mV). This pressure signal is then temperature-compensated and
capacitance of the capacitor formed by the two electrodes. amplified into a corresponding voltage (V) or current (mA) output signal. When the membrane layer is
Operating principle of ultrasonic sensor deformed or bent, the piezoresistors change their value. In piezoresistive pressure sensors, the Wheatstone
An ultrasonic sensor is an electronic sensing device used to measure the distance to a target object by bridge based on silicon is used as the measuring element. It expands minimally under pressure, changing
emitting ultrasonic waves, which are then converted into an electrical signal when the reflected sound is resistance in this way, which is typically referred to as the piezoresistive effect.
received. The sensor system continuously emits sound waves at a fast, strong propagation speed. When these Operating principle of the motor
sound waves encounter an obstacle, such as a solid or liquid surface, they produce reflected wave patterns. In an electric motor, a magnetic field is established either by permanent magnets or electromagnets. Inside
The sensor device receives these reflected waves, analyzes them, and accurately determines the distance the magnetic field, there is a loop of which are part of an armature or rotor. When electric current flows
from the sensor to the obstacle. through these conductors, a magnetic force is exerted on them. According to the Lorentz force law, when a
Operating principle of relay current-carrying conductor is placed within a magnetic field, it experiences a force that is perpendicular to
The operating principle of a relay is based on the concept of electromagnetism. This means that when an both the direction of the current and the magnetic field. This force is what causes the rotor to turn in the
electric current passes through the relay's coil, it generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field exerts a motor. The force acts on the sides of the conductive loop, causing it to spin around its axis.
force on a lever, causing it to move and either close or open the electrical contacts. This movement DC Motor.
changes the operational state of the relay, allowing it to control a circuit by turning it on or off. DC motors are also known as 1-way motors that operate with 1-way current, carrying average weight
Operating principle of solenoid valve loads. DC motor has two main parts: Stator and Rotor. The stator of a DC electric motor is usually 1 or
The operating principle of a solenoid valve is based on the use of an electromagnetic field. When electric more pairs of permanent magnets, or electromagnets.The rotor has a coiled wire and is connected to a DC
current is supplied to the coil, it generates a strong magnetic field that pulls the iron core, overcoming the power source. Another important part of the DC motor is the rectifier, its main task is to change the
spring force, thus opening the valve. Conversely, in the closed valve state, the electric current to the coil direction of the current while the rotation of the rotor is continuous. custom. The rotor housing normally
is interrupted. When this happens, the compressed spring forces the valve to close. This system allows for consists of a commutator and a commoner that is in contact with the commutator.
the control of fluid flow electronically, enabling precise and quick opening or closing of the valve in AC motor
response to electrical signals. AC motor is an alternating current electric motor that operates with alternating current, can withstand large
loads and is very suitable for electric treadmills for gyms, meeting all exercise needs on treadmills. . AC
Operating principle of pneumatic valve
motors also include two main parts: Stator and Rotor. The stator consists of coils of three electrical phases
When electric power is supplied, the current flows into the coil. The copper wire inside the coil generates
wound on iron cores arranged on a circular rim to create a rotating magnetic field. The rotor has a
a magnetic field. This magnetic field creates a force that is transmitted through a connecting shaft to the cylindrical shape, it acts like a coil wound on a steel core.
valve body. The magnetic force is strong enough to overcome the spring force and impacts the valve Principle of operation of PWM
core, causing it to move. Depending on whether the valve is normally closed or normally open, the core PWM, which stands for Pulse Width Modulation, is a technique used to adjust the voltage supplied to a
will retract or extend, respectively, changing the state of the valve gate. load by varying the width of square wave pulses. This variation in pulse width changes the voltage across
When the power is cut off, the magnetic field is not generated, allowing the spring force to move the valve the load. PWM operates by periodically turning the power supply to the load on and off. When the switch
core back to its original position, thus closing or opening the valve depending on whether it is normally (often referred to as a gate) is open, the full voltage is applied to the load. When the switch is closed, the
closed or normally open. This mechanism allows for the automatic control of fluid flow in response to load is disconnected from the voltage. Thus, during the cycle of the switch opening and closing, the load
electrical signals. receives the full voltage at times, partial voltage at other times, and no voltage at all at certain intervals.
A transistor is a device that operates based on applying a DC voltage to the junction region, known as the activation Photoresistor working principle:
voltage. The operating principle of the transistor is built according to two modes: forward bias and reverse bias, A photoresistor operates on the principle of photoconductivity, which is based on the photoelectric effect
corresponding to NPN and PNP types. When applying a DC source UCE to the E and C terminals, it is necessary to ensure
that the (+) terminal is connected to the C terminal and the (-) terminal is connected to the E terminal. To activate the
in semiconductors. When stimulated by photons of light, electrons can be ejected from molecules,
transistor, first apply a DC source UBE through a switch, limiting the current flowing through both B and E terminals, becoming free electrons and leaving behind positively charged holes. Therefore, in conditions without
with the (+) terminal connected to the B terminal and the (-) terminal connected to the E terminal. When the switch is stimulation, a photoresistor typically has a very high resistance, up to several megaohms (MΩ).
turned on, both C and E terminals have voltage, but no current flows through CE (IC = 0). When the switch is closed, the Nguyên lý nút nhấn
P-N junction is forward biased, creating a current from the (+) terminal of the UBE source, through the switch, through R, When you press a button, it makes contact with a stationary contact point, changing the state of the
through the BE junction, and back to the (-) terminal, forming the IB current. When the IB current appears, the IC current connection. In some cases, users need to hold the button down or press it repeatedly for the device to
flows through the CE junction, causing the bulb to light up. The IC current is much stronger than the IB current. function. For other types of buttons, a latch mechanism keeps the button in the open position until the user
formular: IC = β.IB presses it again. This allows for different types of control, depending on the design and intended use of the
IC là dòng chạy qua mối CE , IB là dòng chạy qua mối BE, β là hệ số khuếch đại của transistor
button in various electronic devices or systems.
You might also like
- 8 Series Electrical Wiring Diagram (Toyota Forklift)Document234 pages8 Series Electrical Wiring Diagram (Toyota Forklift)Christopher M Hightower92% (51)
- 220v Ac To 12vdc Rectifier CircuitDocument10 pages220v Ac To 12vdc Rectifier CircuitSandeep Guha NiyogiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument21 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsHassaan ShahNo ratings yet
- Vs Controller Gs Driver p100 Operating ManualDocument124 pagesVs Controller Gs Driver p100 Operating ManualSimon Ngigi100% (2)
- Temperature Measurement Lab Report PDFDocument13 pagesTemperature Measurement Lab Report PDFjackjbandara1100% (1)
- Khushi Report3Document4 pagesKhushi Report3Khushi YadavNo ratings yet
- INDUCCIONDocument11 pagesINDUCCIONDiego JimenezNo ratings yet
- Ee 101 Lexp 3 ConclusionDocument3 pagesEe 101 Lexp 3 Conclusionystine95No ratings yet
- Power System Protection (Control System) : Protective RelaysDocument29 pagesPower System Protection (Control System) : Protective RelaysBagirath SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Symbols Industrial MotorDocument6 pagesSymbols Industrial MotorRODLAN DIPONNo ratings yet
- Plate 3Document15 pagesPlate 3Jikni NobleNo ratings yet
- Text in EnglishDocument15 pagesText in EnglishMartin GeorgievNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ControlDocument55 pagesMeasurement and ControlNamrajit DeyNo ratings yet
- ECE-526-Instrumental &controlDocument2 pagesECE-526-Instrumental &controlKirck John PacañaNo ratings yet
- Linear Solenoid Actuator Theory and TutorialDocument7 pagesLinear Solenoid Actuator Theory and TutorialKhairiBudayawanNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Relays and Their Working Principles: A Relay Is A Switching DeviceDocument17 pagesDifferent Types of Relays and Their Working Principles: A Relay Is A Switching DeviceVIPIN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Relay1Document39 pagesElectromagnetic Relay1Allen Kyle PrielaNo ratings yet
- Transducer PracticalDocument6 pagesTransducer PracticalBhumit TrivediNo ratings yet
- Position, Displacement, and Proximity SensorsDocument27 pagesPosition, Displacement, and Proximity SensorsNyandaMadili MalashiNo ratings yet
- MAINTOPIC Displacement MeasurementDocument43 pagesMAINTOPIC Displacement MeasurementLoreto CorderoNo ratings yet
- AC GeneratorDocument7 pagesAC Generatoraswardi8756No ratings yet
- Bio Instrumentation: ECG, EEG, EMG, Cardiovascular Measurements & Venous PressureDocument11 pagesBio Instrumentation: ECG, EEG, EMG, Cardiovascular Measurements & Venous PressureSaeed Ali ShahaniNo ratings yet
- CSPDCL, BHILAI (2012-2013) : MemorandumDocument14 pagesCSPDCL, BHILAI (2012-2013) : MemorandumAshish MauryaNo ratings yet
- EE312L Research WorkDocument20 pagesEE312L Research WorkJohn Carl TiburcioNo ratings yet
- ELECTRODYNAMOMETERDocument14 pagesELECTRODYNAMOMETERaisyahNo ratings yet
- Pressure Voltage: Chapter Review QuestionsDocument16 pagesPressure Voltage: Chapter Review QuestionsPrakash Chandran CNo ratings yet
- 1004 Controlling Electrical AppliancesDocument33 pages1004 Controlling Electrical AppliancesGowtham ReddyNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of TransformerDocument16 pagesWorking Principle of TransformerSunil100% (1)
- Piezoelectric AccelerometerDocument9 pagesPiezoelectric AccelerometerSARDAR PATELNo ratings yet
- 3 - Electrics & ElectronicsDocument27 pages3 - Electrics & ElectronicsJoe ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Instrument and Measurment Technology Mid AssignDocument8 pagesInstrument and Measurment Technology Mid AssignZeeshan Naeem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction: Fleming's Right Hand RuleDocument16 pagesFaraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction: Fleming's Right Hand RuleMahesh Kumar SahNo ratings yet
- Relay Circuit GlobeDocument33 pagesRelay Circuit Globevikas mauryaNo ratings yet
- Day-28 Notes (EEE)Document2 pagesDay-28 Notes (EEE)Aayush KartikNo ratings yet
- Edi Meow Exp 1Document6 pagesEdi Meow Exp 1Jay Romar PabianiaNo ratings yet
- U1A1 Relays.Document10 pagesU1A1 Relays.JESUS ALBERTO SANCHEZ GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment 2 SensorDocument4 pagesDigital Assignment 2 SensorSoumyajyoti MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1Document8 pagesExperiment No 1mahamchudry2No ratings yet
- Relay ESDDocument5 pagesRelay ESDAditi JadhavNo ratings yet
- Senzori Miscare EnglDocument16 pagesSenzori Miscare EnglCristian GodeanuNo ratings yet
- An Ammeter Is A Measuring Instrument Used To Measure The Current in A CircuitDocument3 pagesAn Ammeter Is A Measuring Instrument Used To Measure The Current in A CircuitLeigh Andrei SiguaNo ratings yet
- MotorDocument19 pagesMotoreshet chafNo ratings yet
- Hindalco School of Excellence: Trainer: - Abhisek PagadDocument15 pagesHindalco School of Excellence: Trainer: - Abhisek PagadAbhisek PagadNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Generation and Excitation SystemDocument20 pagesElectric Power Generation and Excitation SystemMansen NsubugaNo ratings yet
- KMT#4Document5 pagesKMT#4RomanHerreraNo ratings yet
- Transducer: TypesDocument39 pagesTransducer: Typestujuh belasNo ratings yet
- Protective Relay - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesProtective Relay - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediakishoreneveNo ratings yet
- EEM Chap-5Document67 pagesEEM Chap-5patilrudreshNo ratings yet
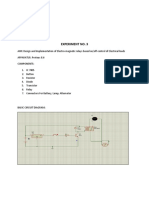
- Mechanical Engineering Department Thapar University: Experiment No. 3: Electrical ComparatorDocument4 pagesMechanical Engineering Department Thapar University: Experiment No. 3: Electrical ComparatorMitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Six Units of MDocument21 pagesSix Units of MMayank Singh KushwahNo ratings yet
- Relay: Relay Is Basically A Magnetism Based Switch. It Consists of A Coil Through Which Current Passes and OnDocument9 pagesRelay: Relay Is Basically A Magnetism Based Switch. It Consists of A Coil Through Which Current Passes and OnAnonymous v5QjDW2eHxNo ratings yet
- What Is RelayDocument8 pagesWhat Is RelayLorenz BanadaNo ratings yet
- Potentiometer (POT)Document11 pagesPotentiometer (POT)muru543210% (1)
- Electrodynamic: Pachuca Mexico Electrodynamic Coils Series Parallel Analog Electromagnetic Field ResistorDocument3 pagesElectrodynamic: Pachuca Mexico Electrodynamic Coils Series Parallel Analog Electromagnetic Field ResistorJeeva JosyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Transducers & Measuring InstrumentsDocument85 pagesChapter 3 - Transducers & Measuring InstrumentsYab TadNo ratings yet
- Hall Effect Transducers and Its ApplicationsDocument16 pagesHall Effect Transducers and Its ApplicationsMynam MeghanaNo ratings yet
- Tugasan E4100Document11 pagesTugasan E4100khairulfathurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Slip Ring: Ring Can Be Used in Any Electromechanical System That Requires RotationDocument8 pagesSlip Ring: Ring Can Be Used in Any Electromechanical System That Requires RotationMian UsmanNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii: Transducers: Lecture NotesDocument28 pagesUnit-Ii: Transducers: Lecture NotesVikram VermaNo ratings yet
- Hardware CircuitryDocument22 pagesHardware CircuitryMahesh NeelarapuNo ratings yet
- TRANSDUCERDocument11 pagesTRANSDUCERLucks GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Module 1 IntroductionDocument22 pagesModule 1 IntroductionaliyumaidamisaNo ratings yet
- Alpine MRVDocument26 pagesAlpine MRVLorenzo TorresNo ratings yet
- Main Panel StandardDocument56 pagesMain Panel StandardWHYSHYNo ratings yet
- Sensor - Tacometro E17x - BDocument64 pagesSensor - Tacometro E17x - BDavidazcNo ratings yet
- LNK605 DatasheetDocument18 pagesLNK605 DatasheetdgujarathiNo ratings yet
- Shindengen: Stepping Motor Driver IcsDocument2 pagesShindengen: Stepping Motor Driver IcsEngin UzunNo ratings yet
- 1PR X 0.7mm Cables - Test Report PDFDocument4 pages1PR X 0.7mm Cables - Test Report PDFSiriepathi SeetharamanNo ratings yet
- Product Manual 02035 (Revision B) : Load Sharing ModuleDocument36 pagesProduct Manual 02035 (Revision B) : Load Sharing Moduleincore1976No ratings yet
- High Precision Volt DetectorDocument40 pagesHigh Precision Volt DetectorvaskribNo ratings yet
- Exercicios 8Document3 pagesExercicios 8douglas.julianiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Photo DiodeDocument11 pagesPHYSICS Photo DiodeArshat ParvaesNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet: Manual Source Changeover Switch INS400 - 4 Poles - 400 ADocument2 pagesProduct Data Sheet: Manual Source Changeover Switch INS400 - 4 Poles - 400 AArpithaNo ratings yet
- Part-Number DescriptionDocument6 pagesPart-Number Descriptionalexandre donizetiNo ratings yet
- Microphone Peiker TM110 2109-002-000-02 ENDocument1 pageMicrophone Peiker TM110 2109-002-000-02 ENRiamel EscoridoNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument23 pagesDC MachinesSona maharanaNo ratings yet
- HK 2014 EN - T12 Current Ratings Basic Table PDFDocument7 pagesHK 2014 EN - T12 Current Ratings Basic Table PDFZoran FabekovicNo ratings yet
- Em IIIDocument64 pagesEm IIIGopinath B L NaiduNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction Motor ReportDocument24 pagesThree Phase Induction Motor ReportSiddharth NandhanNo ratings yet
- SDC 631RF Instruction ManualDocument2 pagesSDC 631RF Instruction ManualJMAC SupplyNo ratings yet
- Circuit Construction Kit DC Virtual Lab HTML Guide - enDocument3 pagesCircuit Construction Kit DC Virtual Lab HTML Guide - enDannisa aaNo ratings yet
- Tanzy ProjectDocument24 pagesTanzy Projecttanzeem10No ratings yet
- Lab 1 PCBDesignDocument38 pagesLab 1 PCBDesignrainceder100No ratings yet
- Ceriatone JM 100w ManualDocument16 pagesCeriatone JM 100w ManualJacimário SanfimNo ratings yet
- 7MH5106 Siemens Siwarex WL230 Bending Beam Load CellDocument1 page7MH5106 Siemens Siwarex WL230 Bending Beam Load CellEong Huat Corporation Sdn BhdNo ratings yet
- Ignition SystemDocument10 pagesIgnition SystemParag100% (1)
- Meier Electric, Inc: 904 North Riverview Bellevue, IA 52031Document1 pageMeier Electric, Inc: 904 North Riverview Bellevue, IA 52031Ty GarzaNo ratings yet
- Cannot Cannot: Allison 4 Generation TCMDocument1 pageCannot Cannot: Allison 4 Generation TCMamineNo ratings yet
- Electrical Plan SegoviaDocument1 pageElectrical Plan SegoviaVee KeeNo ratings yet