Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SCIENCE REVIEWER
SCIENCE REVIEWER
Uploaded by
veraabalossarahmae0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesSCIENCE REVIEWER
SCIENCE REVIEWER
Uploaded by
veraabalossarahmaeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Mitosis is used for almost all of your
body’s cell division needs. It adds new
SCIENCE REVIEWER
cells
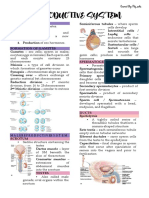
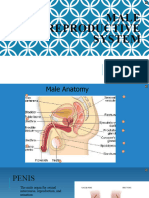
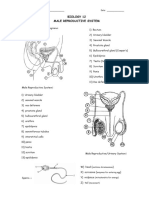
MALE REPRODUCTICE SYS:
Meiosis is used for just one purpose in
the human body: the production of
gametes –sex cells, or sperm and eggs
EPIDIDYMIS - forms a mass over the back and
upper part of each testes. ; Sperm are stored
there for as long as six weeks
Vas Deferens/ductus deferens - described as
the excretory duct of the testes ; two long, thin
tubes that serve as a passageway for sperm and
a place for sperm storage.
EJACULATION - passage of sperm from the
penis, a result of a series of muscular
contractions ; 3.5 milliliters of semen is expelled
during ejaculation ; 300 to 400 million sperm &
5 to 10 million in just one drop.
Urethra - A dual purpose tube that both semen
and urine pass through to leave the body
SEMEN - combination of fluid that is produced
in the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and
bulbourethral gland ; Thickened milky fluid that
Testicles or Testes – The two testes are small
is expelled from the penis during sexual activity.
organs that lie in the scrotum and produce
sperm and the male hormone testosterone. Hypospermia – less than 1.5 ml semen
- The testicles are the male sex gland. Hyperspermia - more than 5.5ml : abnormal
- Each lobe of testis contains 1 to 3 coiled
Average volume of semen produced at
tubes - SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES
ejaculation is 2 to 5 ml
- Four to five billion sperm cells are
produced each month. Seminal Vesicles - Secrete 60% of the total
volume of the semen, which includes fructose,
SCROTUM – A sac-like pouch located behind
the energy source of the sperm ; two small
the penis that holds each testes and helps
glands that secrete a fluid that nourishes and
regulate temperature for sperm production.
enables the sperm to move
SPERM - They are tiny, living cells 100 times
Prostate Gland - released by seminal vesicle
smaller than a pencil dot. ; can survive in a
and prostrate gland into the mix that induce
women’s body for 5-8 days.
contractions ; help sperm reach the egg.
Head – contains nucleus that stores the
Bulbourethral/Cowper’s Gland - two small pea-
male chromosomes and has a
sized glands located beneath the prostate
protective cap called the acrosome
gland ; They secrete a clear, sticky (mucus-rich)
Midpiece – contains mitochondria,
fluid that helps to neutralize the acidity of the
which supply energy to the tail.
urethra.
Tail – helps propel if forward with
snake-like motion. PENIS - male organ for sexual intercourse,
reproduction, and urination ; loosely fitting skin
Semen contains about 100 million
called the prepuce or foreskin.
sperm per millilite
An erection occurs when the sponge-
SPERM CELLS - produced in the linings of the
like chambers in the penis fill with
seminiferous tubules through MEIOSIS.
blood.
Positive feedback - brings more
hormone output
Negative feedback – inhibits/stops the
production of more hormones.
Zona Pellucida (egg wall) is an outer
TIMELINE: membrane that helps the sperm to
enter the egg through its hard outer
Infancy - Erections begin layer
Ages 11-14- Secondary sex characteristics - 1 egg being released per month, only
appear 400-500 eggs in total will be released.
- 1 % of women will experience
Ages 13-16- Sperm produced in adult amounts premature menopause, they will run
(puberty) out of eggs well before the normal age
Late teens- Peak sexual urges for boys of menopause
ATRESIA – process when no. of eggs will
steadily decline over her lifetime and be
absorbed back into the body
Progesterone builds up the lining of the uterus
called the endometrium
Estrogen - Assists in endometrial
regrowth/thickens endometrium
FALLOPIAN TUBES - Two tubes attached on
either side of the uterus.
They are about 4-5 inches long and 0.2-
0.6 inches in diameter (the size of a
cooked spaghetti noodle).
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYS:
carry egg cells toward the uterus and
OVARY - Two solid egg-shaped structures ; They sperm cells toward the egg cell.
are attached to the uterus by ligaments.
NOTE:
two main functions:
1-store and release the ova or female egg cell. Only 1 sperm can fertilize an egg
Fertilized egg = zygote
2-produce female sex hormones called
ESTROGEN and PROGESTERONE UTERUS - small pear-shaped muscular organ
situated between urinary bladder and rectum ;
1-2 million egg cell at birth Site of Embryonic Development.
- There is a continuous decline in the
number of eggs each month, by the - protect and nourish a fetus
time a girl enters puberty, only about 25
- size of a small watermelon
% of her lifetime total egg pool
- After childbirth the uterus shrinks back
remains, around 300,000.
to the original shape in 6-8 weeks
OVUM OR OVA - main function is to carry the
Cervix - The neck or the narrow opening of
set of chromosomes contributed by the female
the uterus.
and create the right environment to enable
fertilization by the sperm. Accommodates the penis during
intercourse.
- The formation of an egg cell or ovum is
called oogenesis. Channels the blood discharged during
- 2 million immature egg cells are called menstruation
primary oocytes.
Dilate from 6 cm to 10 cm
nucleus or germinal spot it is the heart VAGINA
of the egg cell
- birth canal during child birth
- 3-4 inches long, but will lengthen during
arousal.
Cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that
- has a high acidity level to fight against
holds all the organelles.
bacteria
- Occur 10 days after exposure to an infected
sexual partner.
Ovulation
Chlamydia
• Release of an egg from your ovary, into
your fallopian tube - is caused by a bacteria called Chlamydia
trachomatis
Menstruation
AIDS - Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
• When blood and tissue from uterus
comes out from vagina - Cause by virus known as the HUMAN
IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV),
Menstrual cramps happen because of
which attacks the immune system
contractions in the uterus or womb
NO CURE is available
Labor
Menstrual Abnormalities:
-Uterine contractions begin
• Amenorrhea = absence of menstruation
-Cervix dilates to 10 cm.
; no menstrual flow for at least 3
months
Cesarean Section (c-section) is a surgery that • Dysmenorrhea = pain associated with
cuts through the uterus to deliver the baby if it menstruation
cannot be born vaginally
• Abnormal uterine bleeding = excessive
amount or duration of menstrual
bleeding
Sexually transmitted disease (STD’s)
Prostaglandins control processes such as blood
Syphilis flow, contraction and relaxation of muscles and
Gonorrhea others
Genital Herpes 2 types of abnormal uterine bleeding:
Menorrhagia and Metrorrhagia
Chlamydia
Menorrhagia- Excessive bleeding during the
AIDS regular menstrual flow
Syphilis Metrorrhagia- Uterine bleeding between
- It is a bacterial infection usually spread by regular menstrual periods or after menopause
sexual contact, this disease starts as a painless Infertility- Inability to conceive after 1 year of
sore (CHANCRE) - typically on your genitals, sexual intercourse without birth control
rectum or mouth.
Cervical cancer - type of cancer that occurs in
-caused by a bacterium Treponema pallidum the cells of cervix- the lower part of the uterus
Congenital Syphilis – a baby born with infected Erectile Dysfunction - Inability of an adult man
mother (deafness, tooth deformities, and to achieve penile erection
collapse of the nose bridge.
Ovarian cysts - fluid-filled sacs or pockets in an
Gonorrhea ovary or on its surface
- caused by a bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae,
which invades the epithelial lining of the vagina
and the male urethra that causes discharge
called PUS ; often seen in young adults.
Genital Herpes
- common sexually transmitted infection caused
by the herpes simplex virus-2 (HSV)-2
(Incurable) ; Blisters appear a few days or
weeks after infection
You might also like
- Herbs Magickal and OtherwiseDocument278 pagesHerbs Magickal and OtherwiseShakala91% (11)
- Reproductive Systems ReviewerDocument4 pagesReproductive Systems ReviewerAustin LaurenNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 3RD QUARTER - Repoductive SystemDocument2 pagesSCIENCE 3RD QUARTER - Repoductive SystemAiana Laurice ImperialNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesReproductive SystemkhakimagdalenaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesReproductive SystemJanelle LasalaNo ratings yet
- S10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREDocument35 pagesS10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREREGLOS, Marie Nhelle K.No ratings yet
- 19 Reproductive SystemDocument6 pages19 Reproductive SystemEugene HerreraNo ratings yet
- Chap 15&16Document27 pagesChap 15&16Janine AlintanaNo ratings yet
- Ob Notes NormalDocument41 pagesOb Notes NormalLyra Penelope OliquinoNo ratings yet
- 3RD Quarter - Science ReviewerDocument9 pages3RD Quarter - Science Reviewertaspata146No ratings yet
- Ob Notes Normal 1Document41 pagesOb Notes Normal 1pinpindalgoNo ratings yet
- Reproducrive SystemDocument15 pagesReproducrive SystemEfren GuinumtadNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesReproductive SystemshaniaericaNo ratings yet
- Human Male and Female Reproductive System (Reviewer)Document8 pagesHuman Male and Female Reproductive System (Reviewer)Justine Yuan DoradoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburDocument24 pagesReproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburOKTAVIANI HAPSARINo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 - The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesSCIENCE 10 - The Reproductive SystemJyña Khura TanoNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience ReviewerGilvert PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Reviewer 3RDDocument12 pagesScience 10 Reviewer 3RDaltheaburgas9No ratings yet
- The Organs of The Male Reproductive System Are Specialized For The Following FunctionsDocument3 pagesThe Organs of The Male Reproductive System Are Specialized For The Following FunctionsGabrielaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction: Male Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesSexual Reproduction: Male Reproductive SystemcyprianNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIVESYSTEMDocument2 pagesREPRODUCTIVESYSTEMMartin, Espencer WinsletNo ratings yet
- Reviewers 3rd Qrtr.Document33 pagesReviewers 3rd Qrtr.Kim Jay Ann HalongongNo ratings yet
- 08 Reproductive SystemDocument87 pages08 Reproductive SystemcelynjasminegNo ratings yet
- 18 - Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pages18 - Male Reproductive SystemGrace FloresNo ratings yet
- Science 5 ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 5 ReviewerAlexandra Pauline DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Third Term s2 BiologyDocument34 pagesThird Term s2 BiologyADEYI KAYODE SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesReproductive Systemmuli.michaelNo ratings yet
- (Week 17) Reproductive SystemDocument3 pages(Week 17) Reproductive SystemDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Notes in ScienceDocument4 pagesNotes in ScienceKate NicoleNo ratings yet
- Science 5 DLP 1 Human Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesScience 5 DLP 1 Human Reproductive SystemDyaan TrajicoNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesMale Reproductive Systemencouragemthethwa3No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesMale Reproductive SystemCurex QANo ratings yet
- Science 10 NOTESDocument23 pagesScience 10 NOTESnamoramica1No ratings yet
- G.R. Pitts, J.R. Schiller, and James F. Thompson, PH.DDocument91 pagesG.R. Pitts, J.R. Schiller, and James F. Thompson, PH.DrerenNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive Systemmoramabel950No ratings yet
- The Reproductive Systems: Presented in Class 2020/2021Document49 pagesThe Reproductive Systems: Presented in Class 2020/202120 087Arsyilla Khairun NissaNo ratings yet
- Biology Lectures Finals-2Document12 pagesBiology Lectures Finals-2Jaina Alexandra MendozaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproduction AudioDocument17 pagesMale Reproduction AudiomahomedshahirNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document3 pagesScience 10Andrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- A. Internal Male Reproductive OrgansDocument2 pagesA. Internal Male Reproductive OrgansDel Enriquez RiboNo ratings yet
- G10 3RD Quarter ScienceDocument15 pagesG10 3RD Quarter ScienceRaven MayoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Sci Ed 204 p2Document29 pagesLesson 7 Sci Ed 204 p2Allysa Marie SilbolNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 Worksheet Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesBiology 12 Worksheet Male Reproductive SystemMJ VergaraNo ratings yet
- 2.animal Reprodcation and Developmental BiologyDocument88 pages2.animal Reprodcation and Developmental BiologyAnkit JyaniNo ratings yet
- Simple Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesSimple Anatomy and PhysiologyPatrick ValerioNo ratings yet
- G.R. Pitts, J.R. Schiller, and James F. Thompson, PH.DDocument92 pagesG.R. Pitts, J.R. Schiller, and James F. Thompson, PH.DJonalynCollodChewacheoNo ratings yet
- TH THDocument12 pagesTH THchn pastranaNo ratings yet
- MCN Module 2.3Document16 pagesMCN Module 2.3Ma. Ydela MeradoresNo ratings yet
- Strong Sejarah TuhanDocument53 pagesStrong Sejarah TuhanteguhxletNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesReproductive Systemsairakhan215asNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System MALEDocument50 pagesReproductive System MALELance Andre V. RosalNo ratings yet
- A. Internal Male Reproductive OrgansDocument2 pagesA. Internal Male Reproductive OrgansMacchi MagsNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Lecture b516Document2 pagesSCIENCE Lecture b516Justine Mae FeranilNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesReproductive SystemaynNo ratings yet
- Pnle Obstetric NursingDocument15 pagesPnle Obstetric Nursingcanetem1234No ratings yet
- Reproductive System ReproductionDocument9 pagesReproductive System ReproductionDaBestMusicNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System Reproductive Overview: Peristaltic Movement of SpermDocument2 pagesMale Reproductive System Reproductive Overview: Peristaltic Movement of SpermRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument26 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemAlmario DacalcapNo ratings yet
- MATERNAL-AND-CHILD-NURSING Notes For BoardsDocument10 pagesMATERNAL-AND-CHILD-NURSING Notes For BoardsJill Margarett BongatoNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NO 3 - Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesLECTURE NO 3 - Reproductive SystemRebell AeonNo ratings yet
- SuganyaDocument102 pagesSuganyaAlok BhartiNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cysts: Presented by Neha Barari Assistant Professor SNSRDocument52 pagesOvarian Cysts: Presented by Neha Barari Assistant Professor SNSRBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Histology Solution AvnDocument11 pagesHistology Solution AvnDrdo rawNo ratings yet
- OBGYN NotesDocument29 pagesOBGYN NotesavavNo ratings yet
- ISUOG Basic Training: Examining The Uterus, Cervix, Ovaries & Adnexae: Normal FindingsDocument51 pagesISUOG Basic Training: Examining The Uterus, Cervix, Ovaries & Adnexae: Normal FindingsDian Putri NingsihNo ratings yet
- Supporting Women's Fertility With Chinese HerbsDocument2 pagesSupporting Women's Fertility With Chinese HerbsJoana ValenteNo ratings yet
- Antepartal Care: Prepared By: Shalini Santiago-Barroso, RN MANDocument11 pagesAntepartal Care: Prepared By: Shalini Santiago-Barroso, RN MANJabelle Mae DoteNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Cycles: Presented By: Miss. M.K.Kaku Nursing TutorDocument23 pagesHormonal Cycles: Presented By: Miss. M.K.Kaku Nursing TutorKaku ManishaNo ratings yet
- FISIOLOGI HAID-tgs DR NasDocument24 pagesFISIOLOGI HAID-tgs DR NasShandy Suwanto PutraNo ratings yet
- Cupping PointsDocument9 pagesCupping PointsAna Jacinta100% (1)
- Chapter 14 - Reproduction in HumansDocument44 pagesChapter 14 - Reproduction in HumansJnr DogheadNo ratings yet
- Infertility and Climacteric CrisisDocument4 pagesInfertility and Climacteric Crisisgeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Fisiologi Siklus Haid (DR - Kanadi SumaprajaDocument70 pagesFisiologi Siklus Haid (DR - Kanadi SumaprajaIntan DhyaksariNo ratings yet
- Pathoma Female Genital TractDocument7 pagesPathoma Female Genital TractVinNo ratings yet
- Naskah PublikasiDocument11 pagesNaskah PublikasinurfaizahNo ratings yet
- Workbook On Science Science: (Grade 5)Document163 pagesWorkbook On Science Science: (Grade 5)Agnes AvilesNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Disorders 2Document39 pagesMenstrual Disorders 2Nanang HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Fertility HerbsDocument17 pagesFertility HerbsKyle J. Norton100% (1)
- Menopause Semester 6 (IMTU)Document37 pagesMenopause Semester 6 (IMTU)nyangaraNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Neet Special BioDocument75 pagesHuman Reproduction Neet Special BioAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- 3-Ammar Notes (Ob - Gyn)Document6 pages3-Ammar Notes (Ob - Gyn)Dr-Hashem Al-ShareefNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living Organisms Notes For Class 10 Download in PDFDocument3 pagesDiversity in Living Organisms Notes For Class 10 Download in PDFgooodeNo ratings yet
- (Cambridge Medicine) The Fallopian Tube in Infertility and IVF Practice-Cambridge University Press (2010)Document141 pages(Cambridge Medicine) The Fallopian Tube in Infertility and IVF Practice-Cambridge University Press (2010)Natashiwa Chee HongNo ratings yet
- Ellenbogen 2020Document17 pagesEllenbogen 2020MD LarasatiNo ratings yet
- Malformation of Female Reproductive SystemDocument170 pagesMalformation of Female Reproductive SystemKriti BanstolaNo ratings yet
- Ge Elec 2 - Gender and Society Reviewer - 015506Document6 pagesGe Elec 2 - Gender and Society Reviewer - 015506Nonito ValeNo ratings yet
- The Role of Hormones in The Male and Female ReproductiveDocument25 pagesThe Role of Hormones in The Male and Female ReproductiveMa. Jamila JandusayNo ratings yet
- Biology Human Reproduction PDFDocument15 pagesBiology Human Reproduction PDFmbsureshNo ratings yet
- Gyne S1 L10 EndometriosisDocument10 pagesGyne S1 L10 EndometriosisJasper PanosoNo ratings yet