Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ejercicios prácticos - Cimentaciones superficiales P1
Ejercicios prácticos - Cimentaciones superficiales P1
Uploaded by
ANA ROMERO ZARZACopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ejercicios prácticos - Cimentaciones superficiales P1
Ejercicios prácticos - Cimentaciones superficiales P1
Uploaded by
ANA ROMERO ZARZACopyright:
Available Formats
Ejercicios prácticos / Cimentaciones superficiales
Curso: ESTRUCTURAS GEOTÉCNICAS
Prof.: Rafael Méndez, I.C., M.Eng.
1. A circular foundation of diameter 8 m supports a tank. The base of the foundation is at 1
m from the ground surface. The vertical load is 20 MN. The tank foundation was designed
for short-term loading conditions (cu=80 kPa y γsat=19 kN/m3). The groundwater level
when the tank was initially designed was at 4 m below the ground surface. It was assumed
that the groundwater level was stable. Fourteen months after the tank was constructed,
during a week of intense rainfall, the tank foundation failed. It was speculated that failure
occurred by bearing capacity failure. Establish whether this is so or not. The friction angle
is 25° from direct shear tests.
2. A mat foundation 10 x 30 m is to be placed at a depth of 3.5 m in a deep stratum of soft,
saturated clay of γ=17.5 kN/m. The water table is at 2.5 m below the ground surface. The
strength parameters of the soil, obtained from unconsolidated, undrained test are cu= 28
kPa, whereas consolidated, drained tests give c’=5 kPa and ϕ’=22°. Find the allowable
bearing capacity.
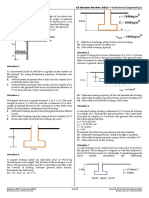
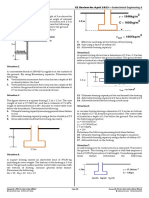
3. A square footing is shown in the following figure. The footing is subjected to an eccentric
load. Determine the gross allowable load that the footing could carry if γ=19.5 kN/m3,
c’=0, ϕ’=40°, B=3 m, Df=1.4 m and e=0.3 m.
4. Determine the factor of safety against bearing capacity failure of the cantilever gravity
retaining wall shown in the following figure. The existing soil is a clay (γ=20.5 kN/m3,
cu= 48 kPa, c’=9 kPa, ϕ’=23°) and the backfill is a coarse-grained soil. The base of the
wall will rest on a 50 -mm-thick, compacted layer of the backfill. The interface friction
between the base and the compacted layer of backfill is 28°. Groundwater level is 8 m
below the base.
You might also like
- Selective Numerical - Lateral Earth Pressure 075Document4 pagesSelective Numerical - Lateral Earth Pressure 075Rajesh Khadka100% (1)
- Foundation Engineering Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesFoundation Engineering Exam QuestionsRamiz Keyra0% (1)
- Taller de Cimentaciones SuperficialesDocument11 pagesTaller de Cimentaciones SuperficialesVerónica CastroNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering Tutorial Questions 1Document2 pagesFoundation Engineering Tutorial Questions 1emmanuel alimaNo ratings yet
- Ceu313 CT2Document3 pagesCeu313 CT2Krishna Prasad ENo ratings yet
- Cimentacion Actividad DDocument9 pagesCimentacion Actividad DĐaniela J PabaNo ratings yet
- Assignments and Project 2014aDocument32 pagesAssignments and Project 2014aMin Khine KyawNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Foundation EngineeringDocument5 pagesProblem Set Foundation EngineeringJohn Mathew BrionesNo ratings yet
- Ce422 Foundation Engineering Laboratory 01Document1 pageCe422 Foundation Engineering Laboratory 01Ray RabaraNo ratings yet
- Examination Papers On Introductory GeotechnicsDocument53 pagesExamination Papers On Introductory GeotechnicsTakchandra JaikeshanNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3Document2 pagesAssignment # 3SUNDARAVELNo ratings yet
- M. H. S. S. College of Engineering Department of Civil EngineeringDocument3 pagesM. H. S. S. College of Engineering Department of Civil Engineeringjay shankar prabhatNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Tu Tu DarNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Prácticos - Cimentaciones Superficiales (Parte 1)Document1 pageEjercicios Prácticos - Cimentaciones Superficiales (Parte 1)runningoisaithNo ratings yet
- Assignment On BC of Shallow FoundationsDocument2 pagesAssignment On BC of Shallow FoundationsTasneem ZargarNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument4 pagesProblemsbalaNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of Shalllow FoundationDocument2 pagesBearing Capacity of Shalllow Foundationrx135boyNo ratings yet
- Ce 342 Tutorial 2Document5 pagesCe 342 Tutorial 2Deus IrechoNo ratings yet
- 3 1965kg/m sat γ: CE Review for Nov 2022 - Geotechnical Engineering 8Document2 pages3 1965kg/m sat γ: CE Review for Nov 2022 - Geotechnical Engineering 8JuDeNo ratings yet
- SJBIT - Geotech - II Assignment 2Document1 pageSJBIT - Geotech - II Assignment 2sagar_srNo ratings yet
- TR 334 Tutorial-1Document5 pagesTR 334 Tutorial-1Adaminovic MrishoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8: Soil Bearing Capacity For Shallow FoundationsDocument30 pagesLesson 8: Soil Bearing Capacity For Shallow FoundationsgailNo ratings yet
- 3 1965kg/m sat γ: CE Review for April 2023 - Geotechnical Engineering 8Document2 pages3 1965kg/m sat γ: CE Review for April 2023 - Geotechnical Engineering 8Nica SudamaNo ratings yet
- CV3013 - Tutorials 1 To 3 (2015) PDFDocument3 pagesCV3013 - Tutorials 1 To 3 (2015) PDFlevanviet0410100% (1)
- FE - Foundation EnggDocument2 pagesFE - Foundation EnggmontibonjoshuaeugeneNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering: Indian Institute of Technology Madras, ChennaiDocument2 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering: Indian Institute of Technology Madras, ChennaiAnonymous Vx9KTkM8nNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentsajjadsiyal144No ratings yet
- 5 6149912092880142413Document10 pages5 6149912092880142413Rushikesh patilNo ratings yet
- QuestionBank SoilMEchanics-IIDocument4 pagesQuestionBank SoilMEchanics-IIrx135boyNo ratings yet
- Geotech Engg QuestionsDocument2 pagesGeotech Engg QuestionsYashasviNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document4 pagesHomework 2Ali AratNo ratings yet
- Bearing CapacityDocument14 pagesBearing CapacityMohamed KadryNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Suman RoyNo ratings yet
- Finals Exam GeotechDocument1 pageFinals Exam GeotechAnfrett E. BanggollayNo ratings yet
- Questions FinalDocument9 pagesQuestions FinalRavindra JagadaleNo ratings yet
- FE Imp QuestionsDocument8 pagesFE Imp QuestionsYeswanth PaluriNo ratings yet
- TR 335 Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTR 335 Tutorial 1Deus IrechoNo ratings yet
- Shallow Foundations 2019 - Assignment - MAKDocument7 pagesShallow Foundations 2019 - Assignment - MAKOdiit StephenNo ratings yet
- Nse-1491259045342336576-Examples - CH 8 Shallow Foundations-1 - 221020 - 010533 PDFDocument16 pagesNse-1491259045342336576-Examples - CH 8 Shallow Foundations-1 - 221020 - 010533 PDFTiago PhillipeNo ratings yet
- CE407 - Updated Midsem SolutionsDocument31 pagesCE407 - Updated Midsem SolutionsManan GoyalNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 Dec2011Document1 pageAssignment2 Dec2011Khaliq Mohd SalehNo ratings yet
- Tutorial A7 & A8 Earth Pressure & Retaining WallsDocument3 pagesTutorial A7 & A8 Earth Pressure & Retaining WallsSaiful Azhar Ahmad TajudinNo ratings yet
- 620PT4032007 2008 2009 2010Document4 pages620PT4032007 2008 2009 2010Mona fabrigarNo ratings yet
- 11 - Tutorial - Earth Pressures & Retaining WallsDocument2 pages11 - Tutorial - Earth Pressures & Retaining Wallsmannie edetNo ratings yet
- CIVE09016 Geotechical Engineering 3 - December 2016Document9 pagesCIVE09016 Geotechical Engineering 3 - December 2016Praise Okoro ResLifeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Monika AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsNametso MoatsheNo ratings yet
- Project On GED IIDocument4 pagesProject On GED IIakhjazrNo ratings yet
- GT 2 QBDocument6 pagesGT 2 QBPrajakta ShindeNo ratings yet
- FE - Foundation EnggDocument1 pageFE - Foundation EnggAram ClamorNo ratings yet
- Assignment-7question and SolutionDocument3 pagesAssignment-7question and SolutionTusharNo ratings yet
- GTE-2 (CE355) - Problems - EPRWDocument4 pagesGTE-2 (CE355) - Problems - EPRWShaswath SasiNo ratings yet
- TD2 Shallow FoundationDocument3 pagesTD2 Shallow FoundationSan SakdaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 2 Bearing CapacityDocument2 pagesProblem Set No. 2 Bearing CapacityYves VillagraciaNo ratings yet
- Bearing CapacityDocument59 pagesBearing CapacityAryan Arora67% (3)
- Tech 1 Exam SemisDocument1 pageTech 1 Exam SemisSn CarbonelNo ratings yet
- Afe QuesDocument8 pagesAfe Questkumar111No ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Geotechnical Engineering Nov 2022Document24 pagesHydraulics and Geotechnical Engineering Nov 2022Cat Kuting100% (1)
- Pressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910From EverandPressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910No ratings yet
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Reinforced Concrete Pier ConstructionFrom EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Reinforced Concrete Pier ConstructionNo ratings yet